17 April 2025
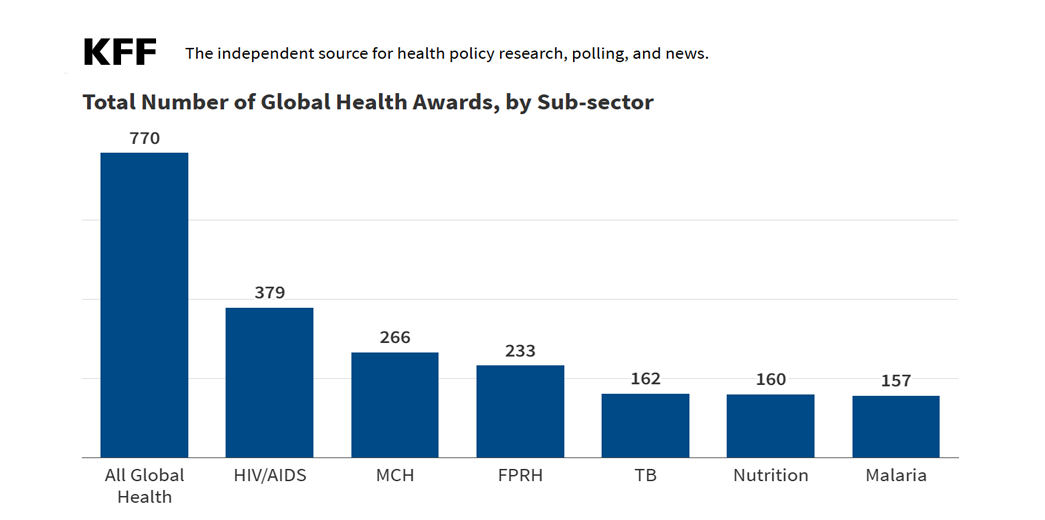
KFF: Analysis of USAID’s Active and Terminated Awards List: How Many Are Global Health?

8 April 2025
Impact of US funding cuts on the global AIDS response — Weekly update 8 April 2025


In January, the US Government paused all foreign assistance. The sudden pause had an immediate impact on the delivery of life-saving HIV medicines and the provision of HIV prevention services to millions of people whose lives depend on them.
UNAIDS has been monitoring the impact in countries, mobilizing partners, governments, and communities to assess and mitigate the impact of the pause on the continuity of essential HIV services.
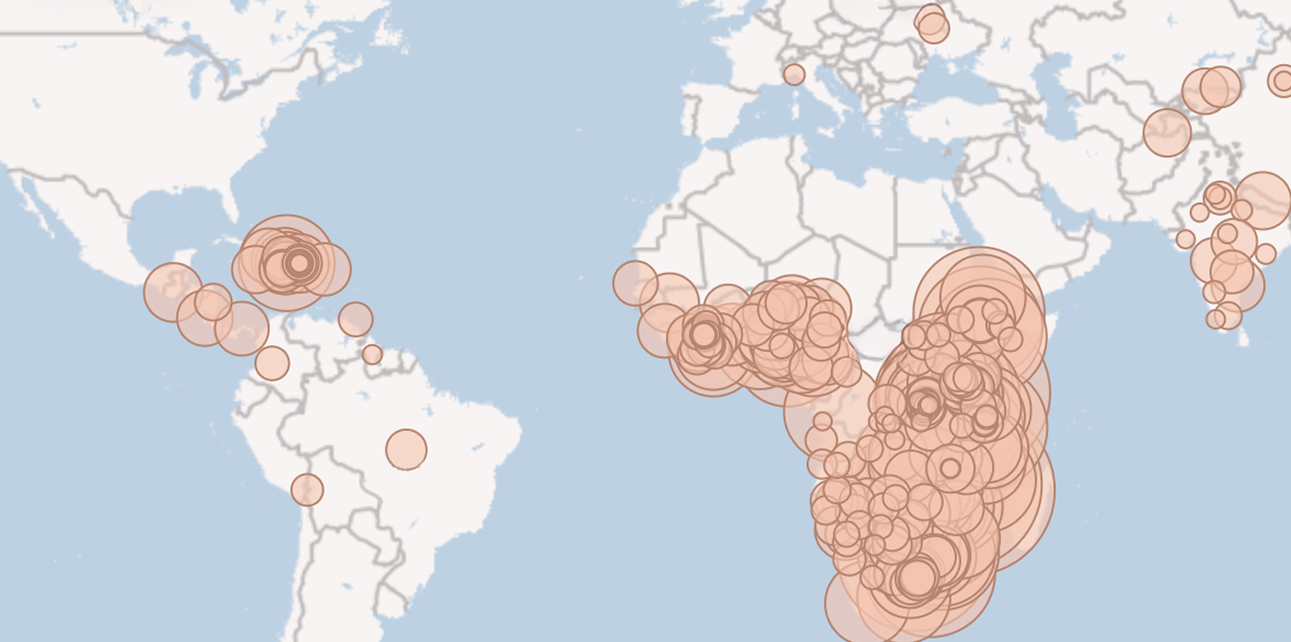
This portal exists to provide real-time, ongoing country updates to share the latest global and country information, data, guidance, and other resources related to the impact of these developments across 55 countries and on the global HIV response.
Read more
Read more
Country updates
Filter
Read more
Resources
Filter
UNAIDS
Partners
Cosponsors
US Government
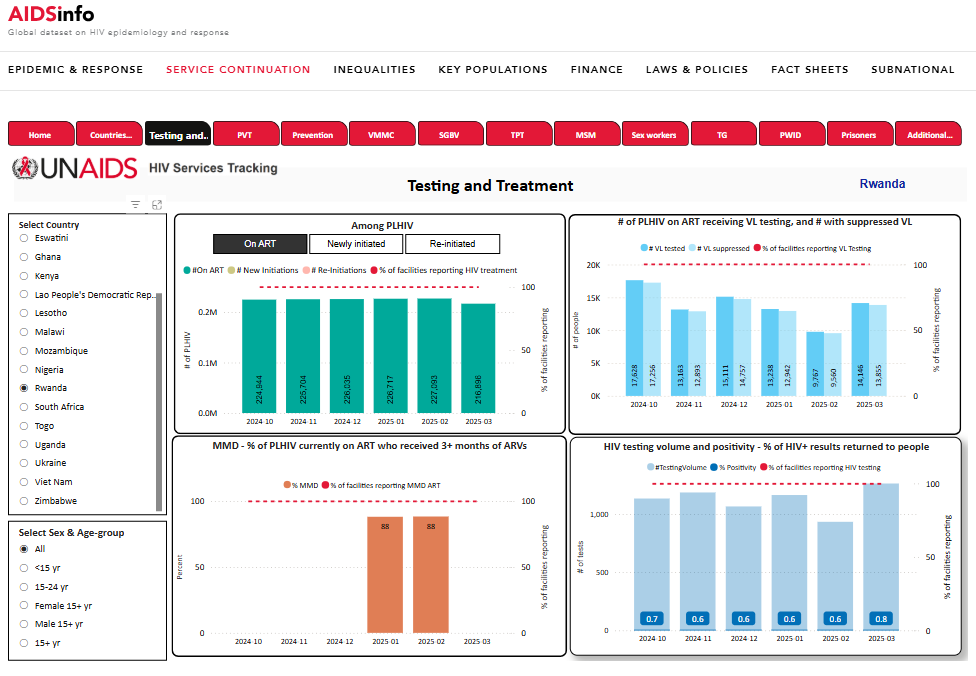
Impact data
Service disruption
Read more
Procurement / HRH data
Read more
Programme coverage
Read more