

Press Release
Germany ramps up its contribution to the HIV response with an extra €20 million to UNAIDS
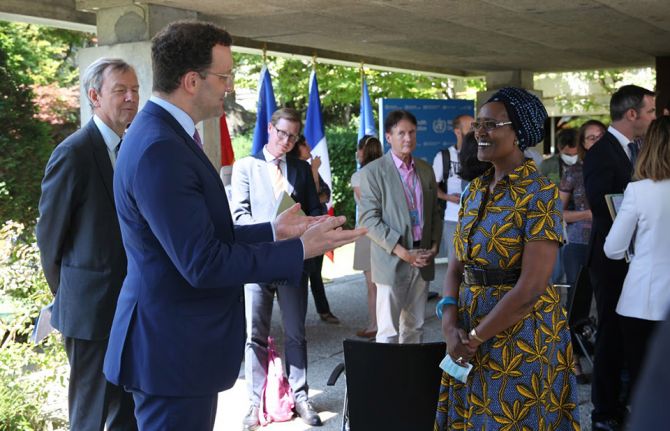
25 June 2020 25 June 2020GENEVA, 25 June 2020—The Government of Germany has announced that, in addition to its annual core contribution of €5 million, it will contribute a further €20 million to UNAIDS in 2020 to strengthen the response to HIV during the COVID-19 pandemic. The Federal Minister of Health, Jens Spahn, made the announcement during a meeting with Winnie Byanyima, the UNAIDS Executive Director, in Geneva, Switzerland, during the 46th meeting of the UNAIDS Programme Coordinating Board.
“We commend UNAIDS’ work in the fight against COVID-19, which focuses on engaging communities, ensuring that vulnerable and key populations are reached with essential health services, including HIV services, protecting basic rights and mitigating the socioeconomic impacts of the epidemic,” said Mr Spahn. “With the additional funds, we encourage UNAIDS to continue this important work alongside the World Health Organization and other global health partners.”
The Government of Germany and parliamentarians, civil society and other partners in Germany have long shown commitment to the global HIV response and to global health and health security, with Germany pledging US$ 1 billion to the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria at its last replenishment. A valued partner of UNAIDS, the Government of Germany is firmly committed to ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030 and has invested significant resources to ensure that no one is left behind.
“UNAIDS welcomes this show of support by Germany. It is an encouraging recognition of the work undertaken by UNAIDS with countries and partners to respond to HIV during the COVID-19 pandemic. It is also a crucial recognition of the lessons and experiences gained over the past decades in the HIV response, which are now being used in the fight against COVID-19,” said Ms Byanyima. “I call upon others to follow Germany’s lead and continue to invest in the global HIV response.”
German’s increased support is a critical investment in saving lives and protecting the dignity of people living with or at risk of HIV. At a time when the world faces the colliding pandemics of HIV and COVID-19, Germany is continuing to demonstrate the need for shared responsibility and global solidarity. Modelling suggests that an unmitigated six-month interruption of HIV services due to COVID-19 could double AIDS-related deaths in sub-Saharan Africa, setting the clock on AIDS-related deaths in the region back to 2008, and could increase new paediatric HIV infections by up to 162%.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton-Knott
tel. +41 79 514 68 96
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS Media
tel. +41 22 791 4237
communications@unaids.org
Our work
Press centre
Download the printable version (PDF)

Press Release
COVID-19 could affect the availability and cost of antiretroviral medicines, but the risks can be mitigated
22 June 2020 22 June 2020UNAIDS study shows that the impact on production and logistics caused by COVID-19 could have a significant effect on antiretroviral therapy supply worldwide, but steps taken now could lessen the damage done
GENEVA, 22 June 2020— A new analysis by UNAIDS has revealed the potential impacts that the COVID-19 pandemic could have in low- and middle-income countries around the world on supplies of the generic antiretroviral medicines used to treat HIV.
The UNAIDS survey discovered that the lockdowns and border closures imposed to stop COVID-19 are impacting both the production of medicines and their distribution, potentially leading to increases in their cost and to supply issues, including stock-outs over the next two months.
“It is vital that countries urgently make plans now to mitigate the possibility and impacts of higher costs and reduced availability of antiretroviral medicines,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “I call on countries and buyers of HIV medicines to act swiftly in order to ensure that everyone who is currently on treatment continues to be on it, saving lives and stopping new HIV infections.”
Since 24.5 million people were on antiretroviral therapy at the end of June 2019, millions of people could be at risk of harm—both to themselves and others owing to an increased risk of HIV transmission—if they cannot continue to access their treatment. A recent modelling exercise estimated that a six-month disruption of antiretroviral therapy in sub-Saharan Africa alone could lead to 500 000 additional AIDS-related deaths.
The production of antiretroviral medicines has been affected by several factors. Air and sea transport is being severely curtailed, hampering the distribution of the raw materials and other products, such as packaging material, that pharmaceutical companies need to manufacture the medicines. Physical distancing and lockdowns are also restricting the levels of human resources available in manufacturing facilities. The combined result of shortages of materials and workforces could lead to supply issues and pressure on prices in the coming months, with some of the regimens for first-line treatment and those for children projected to be the severest hit.
An array of circumstances are conspiring to add pressure on the overall cost of finished antiretroviral medicines. Increased overhead and transport costs, the need for alternative sourcing of key starting materials and active pharmaceutical ingredients and currency fluctuations caused by the forecasted economic shock are combining to push up the cost of some antiretroviral regimens. It has been estimated that a 10–25% increase in these could result in an annual increase in the final cost of exported antiretroviral medicines from India alone of between US$ 100 million and US$ 225 million. Considering that in 2018 there was an HIV financing shortfall of more than US$ 7 billion, the world cannot afford an added burden on investments in the AIDS response.
UNAIDS and partners are working to mitigate the impact. The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria (Global Fund) is providing immediate funding of up to US$ 1 billion to help countries to respond to COVID-19 and is expanding the use of its procurement platform to non-Global Fund recipients. The United States President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief is promoting continuity of HIV care, implementing new strategies, such as telemedicine, and allowing some programme flexibility in reporting requirements, staffing and funding re-allocation. The World Health Organization is compiling, exchanging and analysing information on HIV services that have been impacted and is liaising with manufacturers of antiretroviral medicines for emergency supply and with countries to switch to available quality alternative products and on possible mitigation measures. UNAIDS has been coordinating efforts to address the procurement and supply management challenges of antiretroviral therapy caused by the COVID-19 response.
However, a series of policy recommendations on the coordinated action that should be taken by governments and suppliers in order to resolve these issues map out how to minimize the impacts on supply chains and prices. By managing effectively current and future stocks of antiretroviral medicines, supply can be continued for all who need treatment.
The UNAIDS analysis collected information from the eight generic manufacturers of antiretroviral medicines in India that together account for more than 80% of generic antiretroviral medicine production worldwide. Government departments in seven other countries that produce generic antiretroviral medicines and that account for most of the production of generic antiretroviral medicines in low- and middle-income countries domestically were also surveyed.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton-Knott
tel. +41 79 514 68 96
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS Media
tel. +41 22 791 4237
communications@unaids.org
Our work


Press Release
World leaders unite in call for a people’s vaccine against COVID-19
19 May 2020 19 May 2020More than 140 world leaders, experts and elders have made an unprecedented call for guarantees that COVID-19 vaccines, diagnostics, tests and treatments will be provided free of charge to everyone, everywhere
GENEVA, 14 MAY 2020—More than 140 world leaders and experts, including the President of South Africa and Chair of the African Union, Cyril Ramaphosa, the Prime Minister of Pakistan, Imran Khan, the President of the Republic of Senegal, Macky Sall and the President of the Republic of Ghana, Nana Addo Dankwa Akufo-Addo have signed an open letter calling on all governments to unite behind a people’s vaccine against COVID-19. The call was made just days before health ministers meet virtually for the World Health Assembly on 18 May.
The letter, which marks the most ambitious position yet set out by world leaders on a COVID-19 vaccine, demands that all vaccines, treatments and tests be patent-free, mass produced, distributed fairly and made available to all people, in all countries, free of charge.
Other signatories include the former President of Liberia, Ellen Johnson Sirleaf, the former Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Gordon Brown, the former President of Mexico, Ernesto Zedillo, the former United Nations Development Programme Administrator and former Prime Minister of New Zealand, Helen Clark.
They join notable economists, health advocates and others, from the Chair of the Elders and the former President of Ireland, Mary Robinson, Nobel Laureate, Joseph Stiglitz, to Moussa Faki, Chairperson of the African Union Commission, Dr John Nkengasong, Director of African Centres for Disease Control and Prevention, and Dainius Puras, the Special Rapporteur on the right of everyone to the enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health.
“Billions of people today await a vaccine that is our best hope of ending this pandemic,” said Cyril Ramaphosa, President of South Africa. “As the countries of Africa, we are resolute that the COVID-19 vaccine must be patent-free, rapidly made and distributed, and free for all. All the science must be shared between governments. Nobody should be pushed to the back of the vaccine queue because of where they live or what they earn.”
“We must work together to beat this virus. We must pool all the knowledge, experience and resources at our disposal for the good of all humanity,” said Imran Khan, Prime Minister of Pakistan. “No leader can rest easy until every individual in every nation is able to rapidly access a vaccine free of charge.”
The letter, coordinated by UNAIDS and Oxfam, warns that the world cannot afford monopolies and competition to stand in the way of the universal need to save lives.
“This is an unprecedented crisis and it requires an unprecedented response,” said former President of Liberia, Ellen Johnson Sirleaf. “Learning the lessons from the fight against Ebola, governments must remove all the barriers to the development and rapid roll out of vaccines and treatments. No interest is more important than the universal need to save lives"
The leaders recognize that progress is being made and that many countries and international organizations are cooperating multilaterally on research and development, funding and access, including the welcome US$ 8 billion pledged on 4 May at the European Union’s international pledging marathon.
However, as many countries and companies are proceeding with unprecedented speed to develop an effective vaccine, the leaders are calling for concrete commitments to ensure that it is made affordable and available to all in the quickest possible time. These include:
- A mandatory worldwide pooling of patents and sharing of all COVID-19-related knowledge, data and technologies in order to ensure that any nation can produce or buy affordable doses of vaccines, treatments and tests.
- The rapid establishment of an equitable global manufacturing and distribution plan for all vaccines, treatments and tests that is fully funded by rich nations and which guarantees transparent “at true cost prices” and supplies in accordance with need rather than the ability to pay.
- This would include urgent action to massively increase manufacturing capacity to produce the vaccines in sufficient quantities and train and recruit millions of health workers to distribute them.
- A guarantee that COVID-19 vaccines, treatments and tests are provided free of charge to everyone, everywhere, with priority given to frontline workers, vulnerable people and poor countries with the least capacity to save lives.
“Faced with this crisis, we cannot carry on business as usual. The health of each of us depends on the health of all of us,” said Helen Clark, former Prime Minister of New Zealand. “The COVID-19 vaccine must not belong to anyone and must be free for everyone. Diplomatic platitudes are not enough—we need legal guarantees, and we need them now.”
“Market solutions are not optimal to fight a pandemic,” said Nelson Barbosa, former Finance Minister of Brazil. “A public health care system, including free vaccination and treatment when that becomes available, is essential to deal with the problem, as shown by the Brazilian experience with compulsory licensing of antiretroviral drugs in the case of HIV.”
Uniting behind a people’s vaccine against COVID-19—open letter and full list of signatories
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton-Knott
tel. +41 79 514 68 96
bartonknotts@unaids.org
Oxfam
Anna Ratcliff
tel. +44 7796 993288
anna.ratcliff@oxfam.org
Oxfam
Annie Theriault
tel. +51 936 307 990
annie.theriault@oxfam.org
The People's Vaccine website
A COVID-19 vaccine for all

Press Release
The cost of inaction: COVID-19-related service disruptions could cause hundreds of thousands of extra deaths from HIV
11 May 2020 11 May 2020Gains made in preventing mother-to-child transmission of HIV could be reversed, with new HIV infections among children up by as much as 162%
GENEVA, 11 May 2020—A modelling group convened by the World Health Organization and UNAIDS has estimated that if efforts are not made to mitigate and overcome interruptions in health services and supplies during the COVID-19 pandemic, a six-month disruption of antiretroviral therapy could lead to more than 500 000 extra deaths from AIDS-related illnesses, including from tuberculosis, in sub-Saharan Africa in 2020–2021. In 2018, an estimated 470 000 people died of AIDS-related deaths in the region.
There are many different reasons that could cause services to be interrupted—this modelling exercise makes it clear that communities and partners need to take action now as the impact of a six-month disruption of antiretroviral therapy could effectively set the clock on AIDS-related deaths back to 2008, when more than 950 000 AIDS-related deaths were observed in the region. And people would continue to die from the disruption in large numbers for at least another five years, with an annual average excess in deaths of 40% over the next half a decade. In addition, HIV service disruptions could also have some impact on HIV incidence in the next year.
“The terrible prospect of half a million more people in Africa dying of AIDS-related illnesses is like stepping back into history,” said Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, Director-General of the World Health Organization.
“We must read this as a wake-up call to countries to identify ways to sustain all vital health services. For HIV, some countries are already taking important steps, for example ensuring that people can collect bulk packs of treatment, and other essential commodities, including self-testing kits, from drop-off points, which relieves pressure on health services and the health workforce. We must also ensure that global supplies of tests and treatments continue to flow to the countries that need them,” added Dr Tedros.
In sub-Saharan Africa, an estimated 25.7 million people were living with HIV and 16.4 million (64%) were taking antiretroviral therapy in 2018. Those people now risk having their treatment interrupted because HIV services are closed or are unable to supply antiretroviral therapy because of disruptions to the supply chain or because services simply become overwhelmed due to competing needs to support the COVID-19 response.
“The COVID-19 pandemic must not be an excuse to divert investment from HIV,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “There is a risk that the hard-earned gains of the AIDS response will be sacrificed to the fight against COVID-19, but the right to health means that no one disease should be fought at the expense of the other.”
When treatment is adhered to, a person’s HIV viral load drops to an undetectable level, keeping that person healthy and preventing onward transmission of the virus. When a person is unable to take antiretroviral therapy regularly, the viral load increases, impacting the person’s health, which can ultimately lead to death. Even relatively short-term interruptions to treatment can have a significant negative impact on a person’s health and potential to transmit HIV.
This research brought together five teams of modellers using different mathematical models to analyse the effects of various possible disruptions to HIV testing, prevention and treatment services caused by COVID-19.
Each model looked at the potential impact of treatment disruptions of three months or six months on AIDS mortality and HIV incidence in sub-Saharan Africa. In the six-month disruption scenario, estimates of excess AIDS-related deaths in one year ranged from 471 000 to 673 000, making it inevitable that the world will miss the global 2020 target of fewer than 500 000 AIDS-related deaths worldwide.
Shorter disruptions of three months would see a reduced but still significant impact on HIV deaths. More sporadic interruptions of antiretroviral therapy supply would lead to sporadic adherence to treatment, leading to the spread of HIV drug resistance, with long-term consequences for future treatment success in the region.
Disrupted services could also reverse gains made in preventing mother-to-child transmission of HIV. Since 2010, new HIV infections among children in sub-Saharan Africa have declined by 43%, from 250 000 in 2010 to 140 000 in 2018, owing to the high coverage of HIV services for mothers and their children in the region. Curtailment of these services by COVID-19 for six months could see new child HIV infections rise drastically, by as much as 83% in Mozambique, 106% in Zimbabwe, 139% in Uganda and 162% in Malawi.
Other significant effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the AIDS response in sub-Saharan Africa that could lead to additional mortality include reduced quality clinical care owing to health facilities becoming overstretched and a suspension of viral load testing, reduced adherence counselling and drug regimen switches. Each model also considered the extent to which a disruption to prevention services, including suspension of voluntary medical male circumcision, interruption of condom availability and suspension of HIV testing, would impact HIV incidence in the region.
The research highlights the need for urgent efforts to ensure the continuity of HIV prevention and treatment services in order to avert excess HIV-related deaths and to prevent increases in HIV incidence during the COVID-19 pandemic. It will be important for countries to prioritize shoring up supply chains and ensuring that people already on treatment are able to stay on treatment, including by adopting or reinforcing policies such as multimonth dispensing of antiretroviral therapy in order to reduce requirements to access health-care facilities for routine maintenance, reducing the burden on overwhelmed health-care systems.
“Every death is a tragedy,” added Ms Byanyima. “We cannot sit by and allow hundreds of thousands of people, many of them young, to die needless deaths. I urge governments to ensure that every man, women and child living with HIV gets regular supplies of antiretroviral therapy—something that’s literally a life-saver.”
Sources:
Jewell B, Mudimu E, Stover J, et al for the HIV Modelling consortium, Potential effects of disruption to HIV programmes in sub-Saharan Africa caused by COVID-19: results from multiple models. Pre-print, https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.12279914.v1, https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.12279932.v1.
Hogan B, Jewell B, Sherrard-Smith E, et al. The potential impact of the COVID-19 epidemic on HIV, TB and malaria in low- and middle-income countries. Imperial College London (01-05-2020). doi: https://doi.org/10.25561/78670.
Stover J, Chagoma N, Taramusi I, et al. Estimation of the Potential Impact of COVID-19 Responses on the HIV Epidemic: Analysis using the Goals Model. Pre-print. medRxiv 2020.05.04.20090399; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.04.20090399
WHO
The World Health Organization provides global leadership in public health within the United Nations system. Founded in 1948, WHO works with 194 Member States, across six regions and from more than 150 offices, to promote health, keep the world safe and serve the vulnerable. Our goal for 2019-2023 is to ensure that a billion more people have universal health coverage, to protect a billion more people from health emergencies, and provide a further billion people with better health and wellbeing.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS Mediatel. tel. +41 22 791 4237
communications@unaids.org
WHO Media
Tarik Jašarević
tel. tel. +41 79 367 6214
jasarevict@who.int
WHO Media
Sarah Russell
tel. tel. +41 79 598 6823
russellsa@who.int
Press centre
Download the printable version (PDF)


Press Release
UNAIDS urges countries to stay focused on HIV prevention during the COVID-19 pandemic
06 May 2020 06 May 2020Overstretched health systems, lockdowns, loss of livelihoods and fewer employment opportunities could increase unprotected sex, sexual violence and exploitation, transactional sex and sex work, leading to an increase in new HIV infections
GENEVA, 6 May 2020—Despite the global progress made in HIV prevention, with new HIV infections falling by 40% since the peak in 1997, hard-won gains are in danger of being reversed by the COVID-19 pandemic sweeping around the world.
In the light of the COVID-19 pandemic, UNAIDS is urging countries to remain steadfast in their HIV prevention efforts and ensure that people can continue to access the services they need to stay HIV-free, discrimination-free and violence-free and to be able to enjoy their sexual and reproductive health and rights.
“COVID-19 is impacting almost every country and community, but the global HIV epidemic hasn’t gone away,” said Winnie Byanyima, UNAIDS Executive Director. “People are still having sex. People are still using drugs. During the COVID-19 pandemic, everyone must be given the tools they need to be safe and to protect themselves from HIV. Human rights are a cornerstone of HIV prevention and must be a cornerstone of the COVID-19 response.”
Three new documents on HIV prevention published by UNAIDS and partners in the Global HIV Prevention Coalition look at how to maintain and prioritize HIV prevention services in the context of COVID-19. They look at the critical measures needed to keep the most vulnerable alive and healthy, including the measures required to prevent and address violence against women and children, to keep the supply of critical commodities available and to sustain the livelihoods of the world’s poorest.
The documents explain that the range of options to prevent HIV—condoms, both male and female, lubricants, sterile needles and syringes and opiate substitution therapy for people who inject drugs, pre-exposure prophylaxis and post-exposure prophylaxis and treatment as prevention—are just as valid now as ever. Innovative ways of getting HIV prevention commodities to the people who need them must be found—dispensing longer-term quantities of prevention supplies, allowing distribution centres to remain open during lockdowns and protecting community distribution points are but a few possibilities.
In addition to hampering HIV prevention and treatment services, UNAIDS is concerned that the COVID-19 epidemic may increase the vulnerability of people to HIV. The widespread loss of livelihoods and fewer employment opportunities could mean that transactional sex, sex work and sexual exploitation will increase, putting people at increased risk of contracting HIV unless they have the means to protect themselves.
As well as HIV prevention commodities, the sustained availability of services and support programmes for the prevention of HIV, prevention of gender-based violence and promotion of sexual and reproductive health and rights as essential services is critical. HIV counselling and testing services, the screening and treatment of sexually transmitted infections, continuity of access to sexual and reproductive health services, peer and other community outreach services, psychosocial support services, drop-in centres for key and vulnerable populations, comprehensive sexuality education and sexual violence protection are all vital to preserving the HIV prevention response. The lockdowns imposed during the COVID-19 response have resulted in alarming increases in reports of domestic and intimate partner violence against women and violence outside the home, necessitating urgent reinforcement of prevention, protection and support services for gender-based and sexual violence.
Since social distancing and lockdowns have all but stopped face-to-face service delivery, UNAIDS is urging the introduction of innovative means through which people can access services. Physical meetings can be made safer by using appointment systems that do not allow too many people in a facility at the same time, while holding meetings and education sessions virtually and the use of telephone hotlines and SMS services all have a role to play to both keep people safe from the new coronavirus and to allow them to continue getting the help they need to stay free from HIV. HIV self-testing is a safer way to carry out HIV testing that reduces contact with other people and reduces the service burden on health facilities.
Community organizations and networks have long been essential for the AIDS response, owing to the central role they play in raising awareness, providing information, dispelling myths and countering misinformation and service delivery for marginalized and vulnerable populations. Now more than ever, community-led actors should be supported to innovate, deliver and be recognized as essential service providers for both the HIV and COVID-19 responses.
Forty years in responding to HIV have provided valuable lessons, notably that the COVID-19 pandemic will not affect everyone equally and that the most marginalized, including key populations, will be the most affected. Across the three new documents, UNAIDS urges countries to take a human rights approach and prioritize the needs of the most marginalized populations during COVID-19, including maintaining critical HIV prevention services.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton-Knott
tel. +41 79 514 6896
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS Media
tel. +41 22 791 4237
communications@unaids.org
Press centre
Download the printable version (PDF)


Press Release
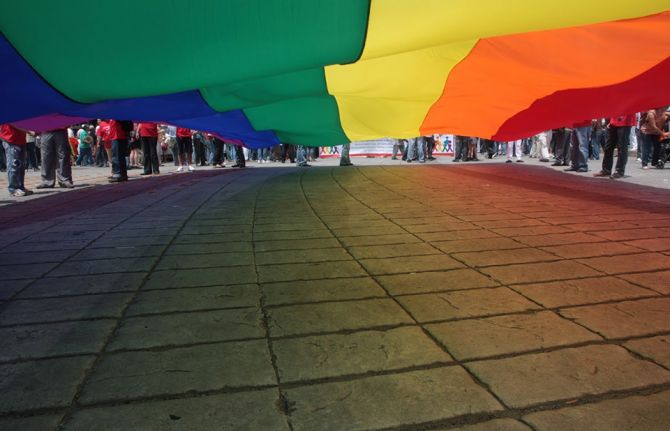
UNAIDS and MPact are extremely concerned about reports that LGBTI people are being blamed and abused during the COVID-19 outbreak
27 April 2020 27 April 2020UNAIDS and MPact call on governments and partners to protect, support and respect the human rights of LGBTI people during the response to COVID-19
GENEVA, 27 April 2020—UNAIDS and MPact Global Action for Gay Men’s Health and Rights are extremely concerned that lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex (LGBTI) people are being singled out, blamed, abused, incarcerated and stigmatized as vectors of disease during the COVID-19 pandemic. UNAIDS and MPact are also deeply troubled that this discriminatory action is compounding the challenges that LGBTI people already face in accessing their rights, including safe and quality health services.
“HIV has taught us that violence, bullying and discrimination only serve to further marginalize the people most in need,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “All people, regardless of their sexual orientation, gender identity or gender expression, are entitled to the right to health, safety and security, without exception. Respect and dignity are needed now more than ever before.”
In Belize, reports have detailed abuse by the police of a gay man who was arrested, humiliated and beaten for breaking a curfew imposed to curb the spread of the coronavirus. The 25-year-old was living with HIV and is believed to have died as a result of complications sustained from injuries inflicted by the police.
“We are receiving reports that government and religious leaders in some countries are making false claims and releasing misinformation about COVID-19 that has incited violence and discrimination against LGBTI people,” said George Ayala, Executive Director of MPact. “Organizations and homes are being raided, LGBTI people are being beaten, and there has been an increase in arrests and threatened deportation of LGBTI asylum seekers.”
In Uganda, 20 LGBTI people were recently arrested in a raid on a shelter, which police authorities claimed was due to their disobeying social distancing procedures. In the Philippines, three LGBTI people were among a group who were publicly humiliated as punishment for breaking the curfew. After segments of the incident went viral online, the police captain was forced to apologize for singling out the LGBTI group members and asking them to dance and kiss each other.
“There is also growing concern over privacy and confidentiality in the way governments are using Internet-based technologies and smartphones to monitor people’s movements during lockdowns or curfews,” Mr Ayala added. “Gay men and gender non-conforming people are often the first targets and among the most impacted by increased policing and surveillance efforts.”
For some LGBTI people, self-isolation and physical distancing can be particularly challenging, even dangerous. Many LGBTI people face violence and/or ill-treatment while sheltering in homes with unaccepting family members. LGBTI people may also suffer from intimate partner violence while staying at home, without the ability to report cases of abuse to the police owing to fear of repercussions. Isolation can also exacerbate pre-existing mental health challenges, common among LGBTI people, including loneliness, depression, anxiety and suicidal ideation.
The COVID-19 pandemic leaves many gay men and transgender women without adequate tools for taking control of their sexual health and rights. Gay men account for nearly 20% of all new HIV infections and are 22 times more likely to become infected with HIV than other men. Transgender women shoulder a risk of acquiring HIV that is 12 times higher than the general population.
Stay at home orders, especially when implemented without flexibilities, compound the difficulties these groups already experience in accessing antiretroviral therapy and HIV prevention and gender-affirming services, including hormone therapies. This is especially true for LGBTI people who are poor, unemployed, homeless or marginally housed.
UNAIDS and MPact are urging countries to:
- Denounce misinformation that scapegoats, slanders or otherwise blames LGBTI people for the spread of COVID-19.
- Stop raids on LGBTI-led organizations, shelters and spaces and desist from arresting people based on their sexual orientation, gender identity or gender expression.
- Ensure that all measures to protect public health are proportionate, evidence-informed and respect human rights.
- Prevent the use of state surveillance on LGBTI people’s personal communication technologies.
- Invest in the COVID-19 response, while safeguarding funds and HIV/sexual health programmes that are inclusive and sensitive to the needs of LGBTI people.
- Safeguard continued access to life-saving medical support, including harm reduction, condoms and lubricant, preexposure prophylaxis, antiretroviral therapy, hormone replacement therapies and mental health services for LGBTI people.
- Provide flexible service delivery options, from multimonth dispensing to community delivery and virtual consultation and support options.
- Consider designating community-led service organizations as essential service providers so that they can provide flexible, safe delivery of key services.
- Include LGBTI people in national social protection schemes, including income support.
- Increase access to appropriate emergency and safe housing for homeless and recently evicted LGBTI people.
- Engage LGBTI people in public health planning and messaging around COVID-19.
- Implement safety monitoring and hacking mitigation during virtual meetings.
Now more than ever, we must stand together to protect and promote the health and human rights of LGBTI people worldwide.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
MPact
MPact Global Action for Gay Men’s Health and Rights was founded in 2006 by a group of activists concerned about HIV-related disparities as well as stigma discrimination, violence, and criminalization experienced by gay men and other men who have sex with men in all parts of the world. MPact is now an established international advocacy network dedicated to ensuring equitable access to HIV services to all gay men, while promoting health and human rights. Directly linked with nearly 150 community-led organizations across 62 countries and thousands of other advocates through its various social media platforms. MPact accomplishes its mission by: watchdogging governments, funders, and other decision makers; strengthening capacities of community-led organizations and healthcare providers; supporting the proliferation of networks led by gay men; conducting and commissioning research; and facilitating inter-regional information exchange.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton-Knott
tel. +41 79 514 68 96
bartonknotts@unaids.org
MPact, Oakland, USA
Greg Tartaglione
gtartaglione@mpactglobal.org
Resources
Press centre
Download the printable version (PDF)


Press Release
UNAIDS calls for a human rights approach to the COVID-19 outbreak that puts communities at the centre
20 March 2020 20 March 2020GENEVA, 20 March 2020—UNAIDS is calling on countries to adopt a human rights-based approach in responding to the global outbreak of COVID-19 that puts communities at the centre and respects the rights and dignity of all. To help guide governments, communities and other stakeholders in planning and implementing measures to contain the pandemic, UNAIDS has produced a new guidance document that draws on key lessons from the response to the HIV epidemic: Rights in the time of COVID-19: lessons from HIV for an effective, community-led response.
The new guidance from UNAIDS is grounded in international human rights law and obligations and makes it clear that responding to an epidemic is not a question of balancing public health and human rights but rather that a successful and effective response requires us to adhere to human rights principles. The guidance has been developed by a group of international experts from communities, the public health arena, academia and the United Nations.
“Successful responses to global epidemics are always grounded in a respect for human rights and community leadership,” said Winnie Byanyima, UNAIDS Executive Director. “Countries that have made the biggest inroads in reducing the impact of HIV have done so by adopting approaches that empower communities to screen, test and seek treatment if necessary and to protect themselves and others from acquiring the virus.”
The guidance presents key lessons from the AIDS response that are crucial for an effective human rights-based approach to public health emergencies. They range from tackling stigma and discrimination faced by affected individuals and communities to prioritizing measures for reaching the most vulnerable, removing human rights barriers, establishing trust between communities and public health authorities and protecting critical frontline medical staff.
As the document recognizes, epidemics tend to expose and exacerbate existing inequalities in society, with their impact often felt most among marginalized and vulnerable groups of people. Financial and other barriers that prevent people from seeking medical help and advice when they need to must be removed, both for their own good and for improved broader public health outcomes.
The guidance also warns against blanket compulsory travel restrictions and criminal sanctions against people affected by epidemics such as COVID-19. Such measures tend to have a disproportionate effect on the most vulnerable and create more barriers to health. Restrictions that are imposed must respect human rights and be necessary, proportionate, evidence-informed and of limited duration. Empowering people to protect themselves and others through voluntary measures can have a greater effect.
“This is a serious and difficult situation for everyone,” said Ms Byanyima, “To come through, we must draw on our valuable experience from responding to other global epidemics, such as HIV: ground the response in human rights, engage communities and leave no one behind.”
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.




Press Release
UNAIDS and United Nations Volunteers further joint collaboration
09 March 2020 09 March 2020GENEVA, 9 March 2020—UNAIDS and the United Nations Volunteers Programme (UNV) have signed a memorandum of understanding to foster closer collaboration between the two organizations. Under the new memorandum of understanding, UNAIDS and UNV will work together to promote volunteering and engage United Nations Volunteers who are committed to supporting people living with and affected by HIV.
“Volunteers have played a critical role in the response to HIV since the earliest days of the epidemic,” said Tim Martineau, UNAIDS Deputy Executive Director, Management and Governance, a.i. “UNAIDS recognizes their importance, values their engagement and will continue to support their contribution in joining global efforts to end AIDS.”
Over the past 10 years, 97 United Nations Volunteers have served with UNAIDS across 36 countries, working to stop new HIV infections, ensure that everyone living with HIV has access to treatment, protect and promote human rights and produce data for decision-making.
“HIV is much more than a health issue. It is an issue of development and social justice, which cuts across so many of the Sustainable Development Goals,” said Olivier Adam, Executive Coordinator of UNV. “This is where UNV comes in—our volunteers are uniquely placed to engage people and deliver on the 2030 Agenda through global, regional, national and community-level implementation.”
International UN Volunteer Tobias Volz joined the UNAIDS Country Office for Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh in 2018, where he helped to develop and implement Live2Luv, a youth-led social media initiative that gives young people in Nepal a platform to voice their concerns, ask questions and challenge taboos about sexual and reproductive health.
“Live2Luv in Nepal strives to achieve an environment where Nepali youth can openly ask questions about sex, sexuality and contraception and get the right answers,” said Mr Volz. “Because adolescents need access to age-appropriate comprehensive sexuality education, in this youth-led movement young teachers will educate and inspire others.”
UN Volunteer Tian Liang recently served as a Communications Officer in UNAIDS’ China office, “UNV gave me an excellent opportunity to use my professional skills to create awareness among the public on the AIDS response and eliminate public bias and misunderstanding of AIDS,” said Mr Liang.
United Nations Volunteers
The United Nations Volunteers (UNV) programme contributes to peace and development through volunteerism worldwide. We work with partners to integrate qualified, highly motivated and well supported UN Volunteers into development programming and promote the value and global recognition of volunteerism. www.unv.org
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.


Press Release
Forty years into the HIV epidemic, AIDS remains the leading cause of death of women of reproductive age—UNAIDS calls for bold action
05 March 2020 05 March 2020Gender discrimination and violence, gaps in education and lack of economic empowerment and protection of sexual and reproductive health and rights are blocking progress
GENEVA/JOHANNESBURG, 5 March 2020—Ahead of International Women’s Day, UNAIDS has launched a new report showing that the stark inequalities and inequities between men and women are continuing to make women and girls more vulnerable to HIV. We’ve got the power urges governments to do more to empower women and girls and fulfil their human rights.
“The HIV epidemic holds a mirror up to the inequalities and injustices faced by women and girls and how the gaps in rights and services are exacerbating the epidemic,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “This is unacceptable, it is avoidable and it must end.”
Twenty-five years ago, governments took the historic step of adopting the Beijing Declaration and the Platform for Action, the most comprehensive and progressive global policy road map for fulfilling the human rights of women and girls and achieving gender equality.
Progress has been made in key areas. More girls are in school and gender gaps in primary schooling are closing globally, in some countries there are more women involved in political leadership and other countries have worked to protect women’s rights in legislation. HIV treatment has also been scaled up, so that by mid-2019 there were more than 24 million people living with HIV on treatment, including more than 13 million women aged 15 years and over.
The report shows, however, that many of the promises made to improve the lives of women and girls around the world have not been kept. Almost 40 years into the response, AIDS is still the leading cause of death for women aged between 15 and 49 years and around 6000 young women aged between 15 and 24 years acquire HIV every week.
We’ve got the power outlines some critical areas to address, including eliminating violence against women. In areas with a high HIV prevalence, intimate partner violence has been found to increase the risk of women acquiring HIV by 50%. Being HIV-positive can also be a trigger for violence, with women living with HIV frequently reporting violence from intimate partners, family and community members and in health services.
The report highlights that outside of sub-Saharan Africa, most women at risk of HIV belong to marginalized communities, such as sex workers, women who inject drugs, transgender women and women in prison. However, gender inequality, stigma and discrimination, criminalization, violence and other human rights violations continue to prevent them from accessing the services they need. Laws and policies need to be reformed in order to end harmful criminalization and coercive practices based on people’s sexuality, sexual activity, HIV status and gender.
For the AIDS response to be fully effective, policies and services must answer to what woman and girls want and need. This includes ensuring adolescent-focused approaches and peer support systems and that rights, gender and non-violence components are integrated into comprehensive sexuality education. Data show that in 2019 adolescents younger than 18 years needed parental or guardian consent in 105 of 142 countries in order to take an HIV test and in 86 of 138 countries they needed consent to access HIV treatment and care.
Surveys from 2013 to 2018 also show that knowledge of HIV prevention remains worryingly low, particularly among women and girls. In sub-Saharan Africa, the region most affected by HIV, seven out of 10 young women did not have comprehensive knowledge about HIV. In contrast, countries that do invest in scaling up effective HIV prevention programmes show impressive results. When Lesotho provided a comprehensive package of HIV prevention programmes it saw new HIV infections among women and girls fall by 41% between 2010 and 2018.
There are huge gaps in education more generally. Studies show that keeping girls in school can have a protective effect against HIV. When Botswana extended mandatory secondary education, it found that each additional year of schooling after year 9 was associated with a 12% reduction in girls’ risk of acquiring HIV. However, nearly one in three adolescent girls from the poorest households around the world has never been to school.
The economic autonomy of women is crucial in its own right and an important component of the AIDS response, yet women still have far fewer economic opportunities than men and shoulder most unpaid care and domestic work. Only 88 countries of 190 had laws mandating equal pay for equal work. Ensuring legal protections to end gender discrimination and guaranteeing women equality before the law are critical to advancing the response to HIV.
“Women and adolescent girls are demanding their rights,” said Ms Byanyima. “Governments must act on those demands by providing resources and services to protect their rights and properly respond to their needs and perspectives.”
The report highlights a number of ways forward. These include investing in HIV policies and programmes proven to foster gender equality, investing in education, including comprehensive sexuality education and the economic empowerment of women and girls, reforming laws that uphold the equal rights of all women and girls, including measures to end stigma and discrimination, violence and criminalization directed at women and girls, holistic care and dignified treatment, the meaningful participation of women in all decision-making relating to HIV programming and supporting the leadership and engagement of women and young people in decision-making at all levels of the AIDS response.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton-Knott
tel. +41 79 514 6896
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS Media
tel. +41 22 791 4237
communications@unaids.org
Press centre
Download the printable version (PDF)


Press Release
UNAIDS calls for zero discrimination against women and girls
01 March 2020 01 March 2020GENEVA, 1 March 2020—On Zero Discrimination Day, which is commemorated every year on 1 March, UNAIDS is calling for an end to discrimination against women and girls and for equal rights, opportunities and treatment.
Despite progress in some areas, in 2020 coercive practices, discriminatory legislation and gender-based violence are just some of the human rights violations that are continuing to have a disproportionate impact on the lives of women and girls around the world. UNAIDS is highlighting areas where change is urgently needed: equal participation in political life; human rights and laws that empower; economic justice—equal pay for equal work; ending gender-based violence; provide health care without stigma or barriers; equal and free access to primary and secondary education; and climate justice.
“Feminism, human rights and zero discrimination are values shared across the world,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “They express our humanity, our recognition that we share a vision for a better future, and they are central to ending AIDS.”
Globally, at least one in three women and girls have experienced violence in their lives, with adolescent girls experiencing higher rates of intimate partner violence than adult women overall. This figure hides deep disparities, with more than 50% of women in some countries reporting violence just in the past 12 months.
Although some countries have made progress towards greater gender equality, discrimination against women and girls still exists everywhere. We know that without equal opportunities early on, without access to education, inequality will persist. Yet, nearly one in three adolescent girls aged between 10 and 19 years from the poorest households globally has never been to school.
Inequalities, discrimination and violence continue to be enabled within the very structures of society. In many countries, laws that discriminate against women and girls remain in force—in areas of work, property, criminal law and sexual and reproductive health and rights, among others.
More than 80 countries criminalize some aspect of sex work, and women are disproportionately affected by laws that criminalize drug use. Meanwhile, laws that uphold women’s basic rights and protect them against harm and unequal treatment are far from the norm. For example, only 88 out of 190 countries have laws regarding equal pay for work of equal value for men and women. Intersecting with other forms of discrimination, on income, race, ethnicity, disability, sexual orientation and gender identity, these rights violations disproportionately harm women and girls.
Numerous government commitments to end violence and discrimination against women and girls have been made over the years, yet hundreds of millions of women and girls continue to be subjected to discrimination, abuse and violence, at huge cost to themselves and to their families, communities, societies and economic development.
“We need to transform our societies so that no one is second class,” said Ms Byanyima. “We must end gender-based violence, inequality and insecurity, and ensure that women and girls have equal access to education, health, public life and employment.”
For this transformation, we need women in roles of leadership, at the community level as well as nationally, regionally and globally. Representation of women’s interests is central to changing structural inequalities. Yet, in 2019, less than a quarter of parliamentarians were women.
Compounding these inequalities are the burdens of unpaid care and domestic work, unequal property and inheritance rights and limited financial autonomy. It is estimated that women carry out three quarters of care work in the household—work that is still not given recognition for its importance in society and the economy and remains unpaid.
Ensuring that women’s rights are protected, ending discrimination against women and girls and removing discriminatory laws will be central to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals and ensuing equity and equality for all.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton-Knott
tel. +41 22 791 1697
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS Media
tel. +41 22 791 4237
communications@unaids.org
