



Press Release
To help ensure the end of AIDS, leaders need to move away from punitive approaches to people who use drugs
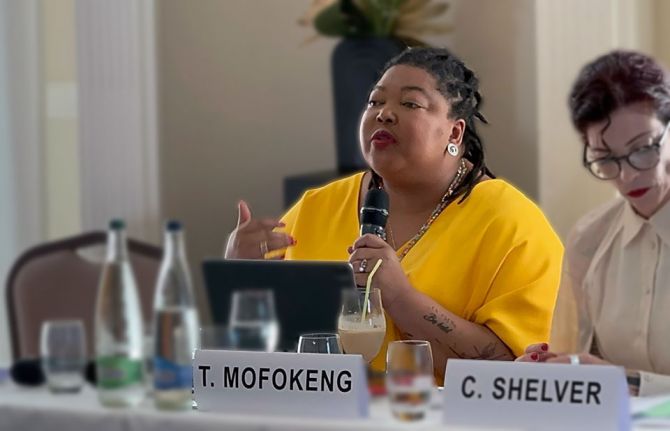
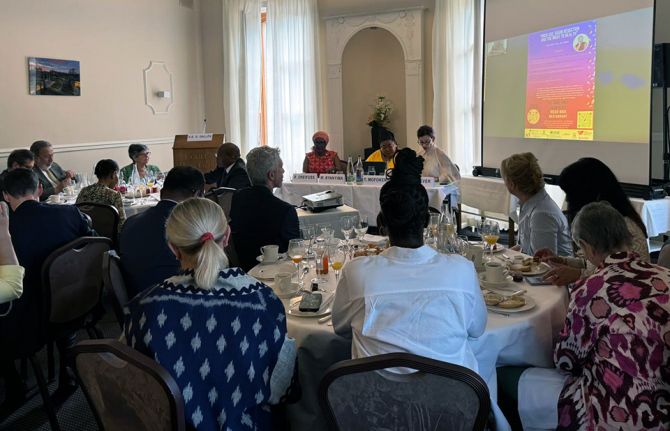
26 June 2024 26 June 2024GENEVA, 26 June 2024—UNAIDS welcomes the recent report by Dr Tlaleng Mofokeng, Special Rapporteur on the Highest Attainable Standard of Physical and Mental Health, which was presented to the 56th session of the UN Human Rights Council. The report, on Drug Use, Harm Reduction and the Right to Health, demonstrates the public health necessity of moving away from punitive approaches to people who use drugs.
Notable, in particular, are three recommendations of the Special Rapporteur’s report that are critical to ending AIDS as a public health threat:
- Decriminalization of the possession of drugs for personal use.
- Ensuring the availability, accessibility, acceptability and quality of harm reduction services for people who use drugs.
- Ensuring that peer-led initiatives have the necessary political and policy support and sufficient and stable resourcing.
Currently, many people who inject drugs continue to be left behind by the global HIV response. The risk of acquiring HIV is 14 times higher than it is for the adult population generally. In contrast, countries which have successfully scaled up harm reduction services have seen significant declines in HIV infections among people who use drugs.
Harm reduction services need to be accessible and acceptable to all who use them. Currently, whilst women who use drugs have a higher prevalence of HIV than men who use drugs, harm reduction services are still often not designed with women’s particular requirements in mind. As the Special Rapporteur on the Right to Health’s report recommends to states: “Design harm reduction services so that they provide suitable environments for women who use drugs, including by providing integrated sexual and reproductive health care, information and services, and childcare”.
Law reform is essential because the evidence shows that even when services are available and appropriate, punitive laws obstruct their use. Criminalization of drug use is associated with needle sharing and avoidance of harm reduction programmes, and increased risk of HIV.
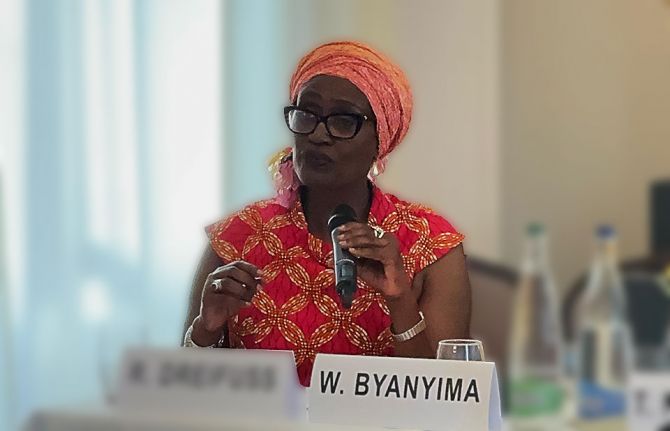
Community leadership in programme design is vital for programme effectiveness. As UNAIDS Executive Director Winnie Byanyima noted today at the special side event with Dr Tlaleng Mofokeng: “Barriers to accessing services can only be overcome if the communities living with, affected by and vulnerable to HIV are supported to lead. This includes communities of people who use drugs, sex workers, gay men and other men who have sex with men, transgender people and people living with HIV. We will continue to leave people behind if we do not support communities in the lead in both service delivery and law reform.”
Global and national approaches to drug policies are starting to change, and this excellent report by the UN Special Rapporteur on the Right to Health will help accelerate this small but important and growing wave of changes. As this report notes, the FRESH project, for example, is engaging transgender women in harm reduction programming, with UNAIDS support. Kenya is one of the countries which has scaled up services, and currently has more than 10 public opioid agonist therapy programmes and 35 drop-in centres with needle-syringe programmes, as well as take-home naloxone, pre-exposure prophylaxis and HIV self-testing services. This year, the Commission on Narcotic Drugs adopted, for the first time, a resolution recognizing the need for harm reduction.
Punitive approaches have hurt public health, including the HIV response. Evidence-based approaches will help enable the world to end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030. UNAIDS pays tribute to Dr Tlaleng Mofokeng, and stands with communities as they issue a call to leaders worldwide: “Support, don’t punish”.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.




Press Release
UNAIDS and Global Fund sign a new strategic framework for their collaboration to end AIDS
24 June 2024 24 June 2024GENEVA, 24 June 2024— UNAIDS Executive Director, Winnie Byanyima, and Executive Director of The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria (the Global Fund), Peter Sands, signed a new strategic framework for cooperation and collaboration to end AIDS (2024 –2028). The agreement renews the organizations’ longstanding partnership and aligns ongoing collaboration with the most recent United Nations General Assembly Political Declaration on HIV and AIDS: Ending Inequalities and Getting on Track to End AIDS by 2030.
“The longstanding partnership between UNAIDS and the Global Fund has been instrumental in supporting many millions of people living with or vulnerable to HIV to enjoy better health and well-being through improved access to essential services,” said Winnie Byanyima, UNAIDS Executive Director. “We at UNAIDS are excited to continue building our collaboration with the Global Fund as we head toward our common goal of ending AIDS.”
The new strategic framework puts people and communities at the centre and aims to unite countries, communities and partners across and beyond the HIV response to take prioritized actions to accelerate progress towards the vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths.
“Our strong collaboration, especially at country level, makes a huge difference in the fight against AIDS,” said Peter Sands, Executive Director of the Global Fund. “Our counterparts at UNAIDS play a crucial role on the ground: they help put communities living with and affected by HIV at the center of the response and ensure that rights-based approaches are widely adopted.”
The Global Fund Strategy (2023–2028) Fighting Pandemics and Building a Healthier and More Equitable World is fully aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals and UNAIDS’ Global AIDS Strategy (2021–2026) End Inequalities, End AIDS, which guides the global AIDS response. It calls on all actors to scale up and sustain global and domestic investments to achieve the strategy’s ambitious targets and commitments for 2025 as well as put the world on course to end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030.
Collaboration under the new agreement will focus on reducing the inequalities that drive the AIDS epidemic and closing the HIV prevention and treatment gaps that are preventing progress towards ending AIDS. It will also prioritize people who are not yet accessing life-saving HIV services.
The common approach supports a renewed focus on primary prevention, addressing structural drivers of HIV infection and AIDS-related deaths, and challenging inequities and human rights and gender-related barriers to services including stigma, discrimination and criminalization. It leverages new HIV prevention and treatment modalities, precision public health approaches, as well as support synergies between HIV services and related areas of health. In addition, the framework continues longstanding support to strengthen countries’ capacity to measure their epidemics and monitor their responses, and act on the data to drive results. There will also be a push for countries to map out the longer-term sustainability of the HIV response through stronger health systems, better-integrated services for HIV, and more streamlined donor contributions.
The Global Fund
The Global Fund is a worldwide partnership to defeat HIV, TB and malaria and ensure a healthier, safer, more equitable future for all. They raise and invest more than US$5 billion a year to fight the deadliest infectious diseases, challenge the injustice that fuels them, and strengthen health systems and pandemic preparedness in more than 100 of the hardest hit countries. They unite world leaders, communities, civil society, health workers and the private sector to find solutions that have the most impact, and they take them to scale worldwide. Since 2002, the Global Fund partnership has saved 59 million lives. Learn more at The Global Fund.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDSCharlotte Sector
sectorc@unaids.org
The Global Fund
Ann Vaessen
ann.vaessen@theglobalfund.org
Partner


Press Release
UNAIDS urges sub-Saharan African countries and global partners to ensure children living with HIV are on life-saving treatment and to stop new infections
14 June 2024 14 June 2024GENEVA, 14 June 2024—On the International day of the African Child this 16 June, UNAIDS is urging African governments and global partners to provide treatment for children living with HIV and to stop new infections among children. The latest data show that only 56% of children living with HIV were on life-saving antiretroviral therapy in 2022 in sub-Saharan Africa compared to 83% of adults globally. Without access to treatment, 50% of infants living with HIV will die before their second birthday.
“As sub-Saharan Africa continues to carry the highest burden of HIV, children are not spared. Over 1.3 million children are living with HIV in the region and too many do not have access to life-saving treatment,” said Ms Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “This highlights the urgency with which we need to tackle this pandemic among children and ensure access to life-saving treatment. No child should be left behind.”
Children are among the age group hardest to reach with HIV testing which is hampering efforts to diagnose and treat children living with HIV. Around 70 000 children died of AIDS-related illnesses in 2022 in sub-Saharan Africa because they did not have access to antiretroviral treatment.
In addition, many children are still becoming infected with HIV in sub-Saharan Africa. Across sub-Sharan Africa, around 110 000 children became infected in 2022 alone. While some countries like Namibia, which has recently reached a key milestone in the pathway toward eliminating vertical transmission of HIV and hepatitis B, are making fast progress, this is not the case in many other countries, particularly in Western and Central Africa including Nigeria, Ghana, Cameroon and the Democratic Republic of Congo which still account for some of the highest numbers of children newly infected with HIV.
“We know the path that ends AIDS. With all the science available, there is no reason for any child to die of AIDS in 2024. So too, we can ensure that all babies are born HIV free and stay HIV free. It is vital to ensure that pregnant and breastfeeding women have all the support they need to access medicine to avoid the transmission of HIV to babies while mothers are pregnant and breastfeeding,” said Ms Winnie Byanyima. “We need to redouble efforts in countries to end AIDS in children and close the HIV treatment gap between adults and children.”
Countries are working to end AIDS in children and this work is supported by the work of UNAIDS and its Cosponsors including UNICEF, the World Health Organization, and partners including PEPFAR, the Global Fund, the Elizabeth Glaser Pediatric AIDS Foundation (EGPAF), the Gates Foundation, Global Alliance to End AIDS in Children and others.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Related links


Press Release
UNAIDS commends Mexico's ban on conversion therapy
12 June 2024 12 June 2024UNAIDS has applauded the decision by Mexico to ban the practice of so-called "conversion therapy".
"The stigma and discrimination that so-called ‘conversion therapy’ perpetuates have damaged public health. Mexico's move to end this harmful practice will help secure public health. All countries should follow Mexico’s example," said Luisa Cabal, UNAIDS Regional Director for Latin America and the Caribbean.
Health and human rights experts have condemned so-called “conversion therapy” for causing severe psychological distress. In 2012, the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) noted that such therapies had no medical justification and represented a severe threat to health and human rights. In 2015, the joint statement by UN agencies condemned “abuse in medical settings, including unethical and harmful so-called ‘therapies’ to change sexual orientation.” In 2016, the World Psychiatric Association found that "there is no sound scientific evidence that innate sexual orientation can be changed." In 2020, the Independent Forensic Expert Group (IFEG) declared that offering such therapy is a form of deception, false advertising, and fraud. In 2020, the report on conversion therapy by the UN Independent Expert on sexual orientation and gender identity called for "a global ban on practices of 'conversion therapy'”. So-called “conversion therapy” is false and harmful, and needs to be ended everywhere.
UNAIDS experience has shown that stigma and shame drive people away from essential health services and support systems, including from HIV prevention, testing, treatment, and care. Protecting the human rights of every person, UNAIDS research shows, is essential for protecting public health, because it enables inclusive and equitable access to health services without discrimination.
"The evidence is clear,” said Ms Cabal. “Stigmatizing practices harm public health. Ensuring inclusion, acceptance and respect for the human rights of everyone is vital to protect everyone’s health. Stigma kills, and solidarity saves lives.”
Region/country





Press Release
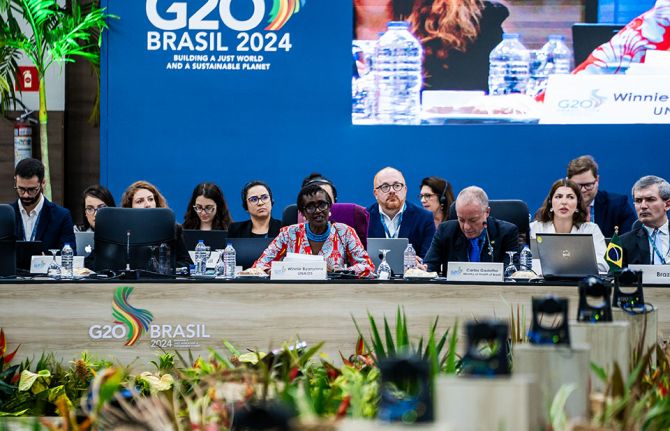
UNAIDS Executive Director and Inequality Council urge G20 to back bold network on medicine production and address the social determinants of pandemics
06 June 2024 06 June 2024SALVADOR, BRAZIL, 6 June 2024—At the G20 preparatory meeting in Brazil, Executive Director of UNAIDS and Under-Secretary-General of the United Nations, Winnie Byanyima, today urged governments to support a new G20 Alliance, proposed by the Brazilian government, to enable life-saving medicines to be produced in every part of the world. Co-Chair of the Global Council on Inequality, AIDS, and Pandemics Sir Michael Marmot also called on G20 delegates to address the social determinants of pandemics, such as education and human rights, as a concrete part of the G20’s pandemic preparedness efforts.
The medicines initiative aims to create a global alliance of local and regional manufacturers of drugs, vaccines and other health technologies and unite a diversified network of local and regional producers to ensure an adequate supply of medicines and technologies for everyone, everywhere.
Ms Byanyima called on the G20 to ensure that the alliance takes a bold approach that strengthens efforts to fight dengue and other neglected diseases, improves global defences against future pandemics, and accelerates access to the latest technologies against HIV.
“Focusing together on neglected diseases and the major killers of vulnerable people is not only strategic, it can deliver during future pandemics,” said Ms Byanyima. “We can be thankful that, for all its devastation, COVID-19 responded to a vaccine, unlike HIV. There is no reason to believe the next pandemic will be like COVID-19. We need to build capacity for vaccines and treatment.”
The responses to many diseases that impact vulnerable populations – from Ebola to Mpox to HIV – would benefit greatly from this initiative, Ms Byanyima told governments today.
“The alliance can supercharge the HIV response. It can supercharge the production pipeline for innovations,” said Ms Byanyima. “An alliance could also build capacity where it is not. The majority of people living with HIV, who get up every day and take that pill, live in Africa. But few of those drugs are actually made in African countries.”
“Brazil’s leadership and experience in this area has inspired this global effort. And we need the support of the whole G20 to make it a success.”
The agenda of the G20 meeting on health is helping to push global health policy towards tackling the systemic inequalities that drive ill-health. UNAIDS is coordinating a Global Council on Inequality, AIDS and Pandemics that is gathering evidence on how inequalities deepen and prolong pandemics, including HIV and COVID-19. That evidence is being shared with policymakers at the G20 and other international forums.
On Monday, world-renowned expert Sir Michael Marmot gave a keynote address the G20 meeting on the potential of focusing concretely on the social determinants to strengthen pandemic preparedness, predict the severity of future pandemics, and improve the efficacy of responses.
“Improving health leads to a better economy. And the way to improve health is not just to invest in healthcare, but in the social determinants of health,” Professor Marmot said. “For example, in Botswana, there is clear evidence that the longer young people remain in education, the lower the rates of HIV.”
Addressing social determinants, building manufacturing capacity, and enabling people everywhere to access the whole range of HIV prevention and treatment options, including the latest long-acting technologies, is vital for ensuring the end of AIDS as a public health threat. The G20 initiatives would play a key role in achieving that objective in a sustainable way, while also contributing to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals and supporting efforts to quickly respond to the next pandemic.
Notes for editors
Brazil's main proposal for the G20 Health Working Group is to establish the creation of an Alliance for Regional Production and Innovation. This initiative aims to establish a network that brings together key actors, including countries, academia, private sector, and international organizations, for research and development and production of vaccines, medicines, diagnostics, and strategic supplies to combat diseases with strong social determinants and that mainly affect vulnerable populations, such as dengue, malaria, tuberculosis, Chagas disease, and leprosy. For more information on the G20 Health Working Group, see the G20 website: https://www.g20.org/en/tracks/sherpa-track/health
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Learn more
Op-ed by Winnie Byanyima
Region/country


Press Release
UNAIDS welcomes governments’ commitment to end AIDS, tackle gender-based violence, discrimination and inequalities
25 March 2024 25 March 2024Resolution on ‘Women, the Girl Child and HIV and AIDS’ updated, strengthened and adopted by consensus at the 68th session of the Commission on the Status of Women
GENEVA/NEW YORK, 25 March 2024—On 22 March, governments attending the 68th session of the Commission on the Status of Women (CSW) adopted, by consensus, a resolution focused on advancing the rights and empowerment of women and girls as part of efforts to end AIDS.
The updated resolution 60/2, Women, the Girl Child and HIV and AIDS, underscores the urgent need to prioritize the health and rights of adolescent girls and young women in the context of the ongoing global AIDS pandemic. It recognizes that adolescent girls and young women are still disproportionately affected by HIV due to various socio-economic factors, including gender inequalities, poverty, and lack of access to education and healthcare.
The resolution underscores the imperative of advancing gender equality as central to ending AIDS, and reaffirms the commitments made in the 2021 United Nations General Assembly Political Declaration on HIV and AIDS. The resolution calls for all governments to enact and intensify the implementation of laws and policies to eliminate all forms of gender-based violence, as well as end HIV-related stigma and discrimination against women and girls. It also calls for promoting active and meaningful participation and leadership of women and girls living with HIV in the AIDS response.
Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS, expressed optimism and her profound appreciation for the adoption of the resolution, stating, "By committing to prioritizing the health and rights of women and girls in all their diversity and addressing HIV comprehensively, leaders have helped safeguard the health of women and girls, which will result in a more equitable and resilient future.”
Nyaradzayi Gumbonzvanda, Deputy Executive Director of UN Women, a cosponsoring organization of UNAIDS which was instrumental in organizing and ensuring a successful outcome of CSW said, “Empowering women, securing rights and achieving equality is an imperative.”
UNAIDS applauds the leadership of Southern African Development Community (SADC) and Angola as its current chair for successfully championing the update of the resolution which was initially adopted in 2016. The updated resolution will continue to serve as a guiding framework for governments, communities and civil society groups, and all stakeholders as they collaborate to safeguard the rights of women and girls living with, at risk of and affected by HIV.
Crucially, UNAIDS emphasizes the importance of translating the commitments outlined in the resolution into concrete actions at the national, regional, and global levels. Efforts must focus on closing the gender gap in HIV prevention, treatment, care and support, while also addressing the underlying social, economic, and structural factors that perpetuate gender-based discrimination, violence, and inequalities and increase the vulnerability of women and girls to HIV.
UNAIDS remains steadfast in its commitment to working collaboratively with governments, civil society, and other partners to create a world where the rights and dignity of all women and girls are respected, protected, and fulfilled, including women and girls living with, at risk of and affected by HIV.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS New YorkRupa Bhadra
tel. +1 646 468 4129
bhadrar@unaids.org
UNAIDS Geneva
Sophie Barton Knott
tel. +41 79 5146896
bartonknotts@unaids.org

Press Release
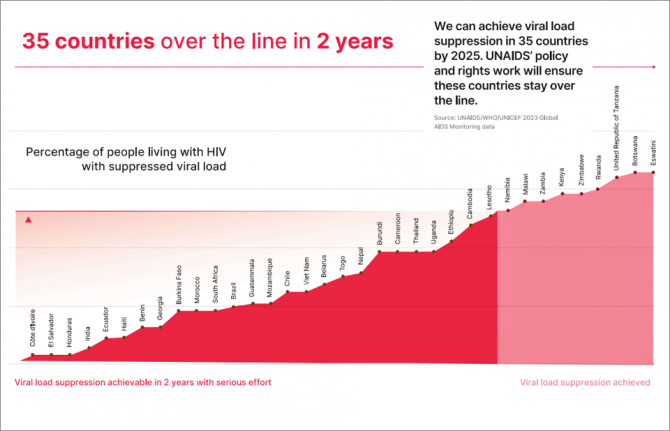
With a modest increase in investment UNAIDS can get 35 countries over the line to end their AIDS pandemics by 2025
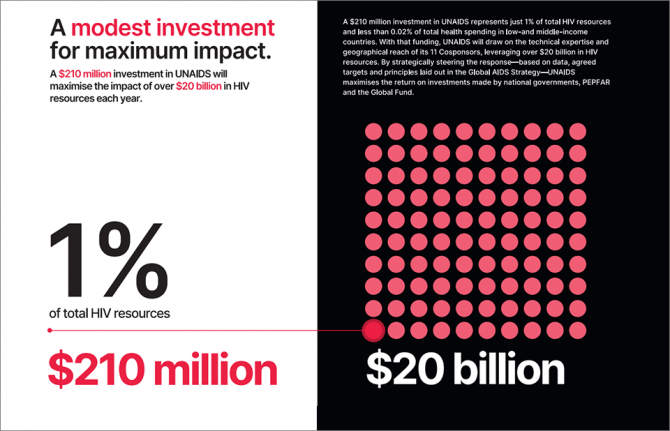
28 March 2024 28 March 2024UNAIDS needs to increase funding to just 1% of the US$ 20 billion HIV resources to effectively support countries in their goal of ending AIDS by 2030
GENEVA, 28 March 2024—UNAIDS is urging donors for a modest increase in funding to ensure that 35 countries can end their AIDS pandemics by 2025, five years ahead of the 2030 target. Current funding for UNAIDS is at US$ 160 million, less than 50% than the resources available in 2015. For maximum impact UNAIDS estimates it will need US$ 210 million annually which represents less than 0.02% of total health spending in low- and middle-income countries.
“UNAIDS has remained a steadfast and dependable partner, advocating and leveraging the strengths of the UN system to catalyze action, secure commitments, mobilize stakeholders, generate authoritative data, empower communities, address vulnerabilities, and tackle barriers,” said Ruth Laibon-Masha, Chief Executive Officer, National Disease Control Council of Kenya. “Let us seize this historic moment, where we are united in our consensus that we need UNAIDS to be fully functional as we have no doubt of the contribution of UNAIDS to global health and its centrality to ending AIDS as a public health threat. Kenya reaffirms our commitment to UNAIDS by honoring our pledge to contribute funds in 2024 and invite other implementing and donor countries not to be left behind by also increasing their contributions.”
UNAIDS projects that fully funding the Joint Programme would enable 35 countries to achieve the viral load suppression targets by 2025. That achievement would save 1.8 million lives, prevent 5.7 million new HIV infections by 2030 and establish a solid foundation for the world to end AIDS by 2030.
“If UNAIDS was not there, we would all be asking for UNAIDS to be established. While we celebrate the progress we have made, we still need a very strong and well-resourced UNAIDS to continue to drive that progress.” said Ambassador John Nkengasong, U.S. Global AIDS Coordinator and Senior Bureau Official for Global Health Security and Diplomacy. “A generational threat requires sustained leadership - sustained leadership that comes with the sustained commitment to provide financing for UNAIDS. So it is always our commitment from the United States that we make UNAIDS stronger and will continue to make UNAIDS that body that provides that Northern Star for all of us.”
“We rely on UNAIDS to support the voice of communities most affected by HIV in national HIV policies and decision-making processes as well as in efforts to improve access to services and address stigma and discrimination and gender inequity” said Peter Sands, Executive Director of the Global Fund. “Ensuring that UNAIDS is adequately resourced is critical to achieving continued progress in controlling HIV.”
As Mary Mahy, Director of Data for Impact, UNAIDS explains, “Diseases go through a period of increasing new infections, and over time, after interventions are implemented, new infections start to decline and countries reach a point of disease control then elimination, and eventually eradication. But with HIV we have not achieved disease control globally and some countries are still in the increasing infections stage. So there is still a considerable amount of work to be done in the HIV response to achieve HIV disease control, elimination and eradication.”
In 2022, every minute someone died of AIDS, 4000 young women and girls aged between 15 and 24 became infected with HIV every week, and of the 39 million people living with HIV more than 9 million do not have access to HIV treatment.
“Pandemics tend to go through cycles of panic and neglect. But health security can only be delivered when we break these cycles and deliver and sustain the gains that we have made together,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “With a modest increase in funding, over the next two years, UNAIDS can support 35 countries in reaching the 95-95-95 targets – and help sustain the gains. This will be an outstanding global achievement.”
UNAIDS has developed a value proposition which highlights three key messages for the 2024–2025 period:
- We know how to end AIDS as a public health threat. Taking this path is a political and financial choice.
- A modest investment in UNAIDS will deliver maximum impact at the national and global levels.
- UNAIDS is uniquely placed as the lead of the global HIV response. Investment in UNAIDS is vital to invest to end AIDS, fight inequalities and save lives.
UNAIDS is leading on the HIV response sustainability agenda, supporting countries to ensure well resourced, people centred and human rights-based HIV programmes that are increasingly funded through domestic resources. The sustainability agenda encompasses political, programmatic and financial sustainability, developed in close collaboration with PEPFAR, the Global Fund and other donors, countries and communities.
The agenda will consider the implications of the growing financial and debt crises faced by many low- and middle-income countries which are also highly affected by HIV. Approximately 60% of the resources for HIV responses in low- and middle-income countries came from domestic sources in 2022, compared to 50% in 2010. UNAIDS has a critical role in ensuring that political, programmatic and financial commitments for the HIV response are sustained.
“We all want the Joint Programme to continue to lead the AIDS response towards 2030,” said Kenya's Ambassador to the United Nations office in Geneva and Chair of UNAIDS Programme Coordinating board Cleopa K. Mailu. “It is the priority we make to the vulnerable people who need our support to lead meaningful and full lives. We must be able to find a collective solution to close the funding gap. Any moment we spend speaking of unsustainable funding for UNAIDS is a moment lost to save a life, prevent a new infection or a death.”
By fully funding UNAIDS and drawing on the technical expertise and geographical reach of its 11 United Nations Cosponsors, UNAIDS can continue to strategically lead and steer the response to HIV, based on data, agreed targets and principles laid out in the Global AIDS Strategy 2021-2026. UNAIDS can maximize the return on investments made by governments, PEPFAR and the Global Fund, and work hand in hand with countries to end their AIDS pandemics by 2030 and ensure sustainability into the future.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Help us end AIDS




Press Release
UNAIDS urges Indian Ocean Island countries to strengthen HIV prevention to end AIDS
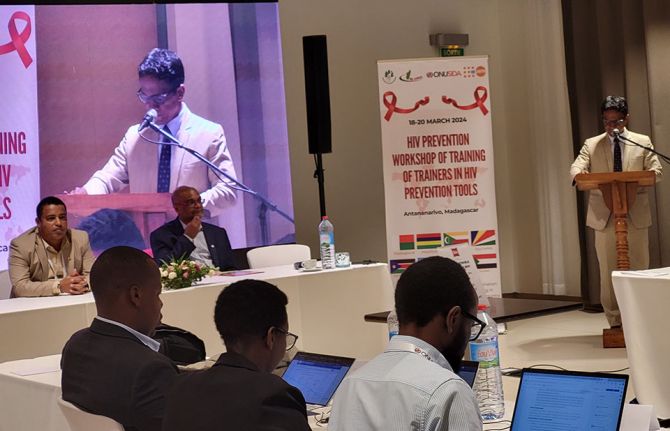
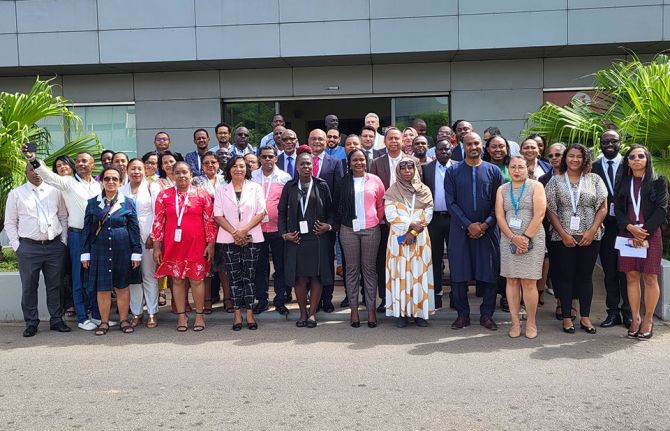
27 March 2024 27 March 2024ANTANANARIVO/GENEVA, 27 March 2024—Despite progress across most of sub-Saharan Africa, UNAIDS warns that gaps in HIV prevention are driving new HIV infections in the Indian Ocean Countries (IOC) and several other countries in Africa. The critical gaps in HIV prevention were the focus of a workshop organized by UNAIDS and UNFPA which was hosted in Madagascar between 18 and 20 March to address some of the barriers to accelerating progress.
Insufficient focus on HIV prevention in a number of African countries including Egypt, Madagascar, Angola, Sudan and South Sudan has resulted in these countries not achieving the proportionate declines in new infections seen in the rest of the region.
For example, the increase in the number of new infections in a country like Madagascar for example, is in stark contrast to the downward trend in Botswana which has seen a 66% decline in new HIV infections since 2010 and 36% decline in AIDS-related deaths during the same period. As a result, Botswana—along with Eswatini, Rwanda and Zimbabwe— are on the path to end AIDS having achieved the global 95-95-95 targets through strong HIV prevention and treatment interventions.
Madagascar, one of the poorest countries in the region, has been hit by cyclical natural disasters including drought and cyclones, making it difficult for the country to recover and mount an effective response to HIV. Madagascar recorded a 151% increase in the number of new HIV infections since 2010, and a 279% increase in AIDS-related deaths during the same period. In addition, just 18% of the estimated 70 000 people living with HIV in Madagascar had access to treatment in 2022, and 3200 people died of AIDS-related illnesses. Sudan and South Sudan are also falling behind on HIV prevention and treatment efforts. Inequalities are exacerbating people’s vulnerability to HIV.
“Local research indicates increases in new HIV infections among key populations, including people who use drugs, and among young women and girls. This could be attributable to many factors including drug routes, recurring cyclones and deep poverty in some areas that is making people more vulnerable to HIV infections,” said Professor Zely Randriamanantany, Madagascar’s Minister of Public Health. “We need our international partners to invest with us before it's too late. This prevention focus is very welcome indeed."
“It is clear from our visits to communities and from speaking to health specialists in Madagascar, that the HIV epidemic is changing. The persistent rise in new infections in Madagascar since 2010, for example, shows that it could spread rapidly if we do not stop it in its tracks immediately,” said Anne Githuku-Shongwe, UNAIDS Regional Director for Eastern and Southern Africa. “We know the path that ends AIDS. It’s not a miracle. It requires strong political and financial support.”
Gaps identified in some countries include a lack of data that would point to where HIV prevention efforts need to focus. Data gathering interventions are key to implementing evidence-informed and effective programmes. Some countries are also lacking commodities, including HIV testing kits and condoms.
“Inadequate investment in HIV responses is holding back ending AIDS as a public health threat,” said Jude Padayachy, UNAIDS Country Director for Comoros, Madagascar, Mauritius and Seychelles. “We need to accelerate the HIV response in the Indian Ocean Island states by ensuring all the basics—making sure people are informed about HIV and how to prevent it, and making sure people have access to HIV prevention services and commodities, such as condoms. We also need to make sure that people who are HIV-positive know their status and get the treatment they need.”
UNAIDS is committed to support countries to accelerate political leadership, investments and better data for prevention.
The meeting in Madagascar brought together HIV experts and programme leaders from a number of countries across Africa to learn from each other and to review and strengthen their national plans on HIV prevention to support countries in scaling up their HIV responses. The meeting included teams from Comoros, Egypt, Madagascar, Rwanda, Sudan and South Sudan.
Participants explored ways to improve data collection to help develop more of an understanding of the dynamics of their HIV epidemics to ensure an effective, evidence-informed, human rights-based response. They also drafted national assessments which will serve as a guide to facilitate dialogues with communities, governments, and partners. This will aid in refining strategies and setting priorities to implement ambitious HIV prevention plans. UNAIDS will continue to support countries in their internal assessments to strengthen their HIV responses.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS JohannesburgBathsheba OKWENJE
tel. + 27 (0) 72 895 5174
okwenjeb@unaids.org
UNAIDS Johannesburg
Robert SHIVAMBU
tel. +27 (0) 83 608 1498
shivambuh@unaids.org
Our work
Region/country



Press Release
Reductions in new HIV infections in several Global HIV Prevention Coalition countries, but global progress needs to be accelerated
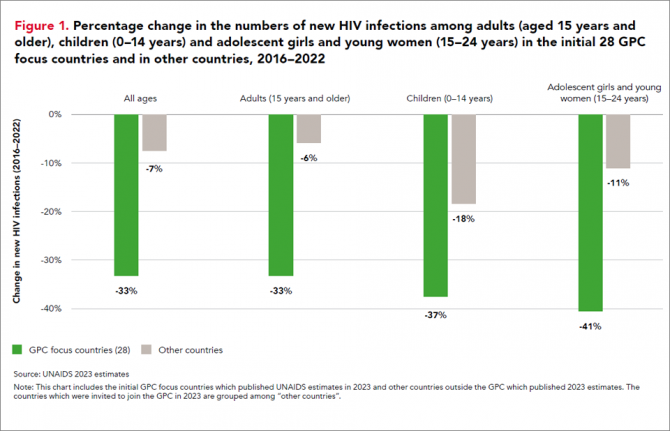
13 March 2024 13 March 202413 March 2024—A new report, HIV Prevention: From Crisis to Opportunity shows that HIV infections continue to decline in countries that are part of the Global HIV Prevention Coalition (GPC) faster than in the rest of the world.
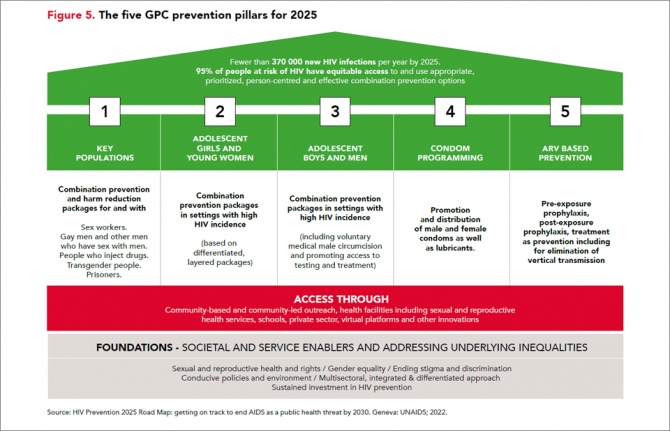
Eleven GPC focus countries have reduced their annual number of new HIV infections by at least 66% since 2010. By comparison, the average reduction in new HIV infections since 2010 globally is 38%. The GPC is a coalition of 38 countries working together to accelerate declines in new HIV infections to achieve the target of having 95% of the people who are at risk of HIV accessing effective combination prevention options.
The GPC countries that have prioritised primary prevention and treatment and that have focused on reaching people most at risk have secured the strongest consistent declines in new HIV infections.
Globally, progress in HIV prevention has been highly uneven and a majority of the world’s countries are not currently on track to achieve the 2025 targets. Indeed, several countries are experiencing prevention crises with low access to services and face record rising new HIV infections.
“The findings of this report offer crucial lessons for action,” said Angeli Achrekar, Deputy Executive Director Programme, UNAIDS. “The report shows that sustained political leadership, investment in effective HIV prevention programmes, and an enabling policy environment are crucial to end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030.”
Declines in new HIV infections have been boosted by the cumulative impact of combination HIV prevention options and increased access to antiretroviral treatment which has also increased viral suppression in people living with HIV. People who are on treatment and are virally supressed cannot transmit HIV.
“It’s remarkable to see what has been achieved in the AIDS response in the past 20 years. But the progress to date has not been equitable and is not yet sustainable, and we must never confuse progress with being sure of success,” said Mitchell Warren, GPC co-chair and Executive Director, AVAC. “Our progress is fragile, and what we’ve achieved today could slip away even more quickly than it was achieved if we let complacency take hold.”
Key populations and adolescent girls and young women are still at high risk of new infections
HIV incidence remains unacceptably high among populations where gaps in HIV prevention investments persist. This includes key populations in all regions globally and adolescent girls and young women in parts of sub-Saharan Africa.
Around 3100 young women and girls aged 15-24 became newly infected with HIV every week in sub-Saharan Africa in 2022 and HIV incidence declined less rapidly than it has among young men. Only 43% of the sub-national areas in which there is elevated HIV incidence among young women are being reached with dedicated prevention programmes for young women.
Although GPC countries have shown solid gains in reducing new HIV infections, challenges remain worldwide in reaching key populations most at risk of new HIV infections including men who have sex with men, sex workers and people who inject drugs. Every week, more than 11 000 new HIV infections occur among key populations and their sexual partners globally.
Only 44% of sex workers, 28% of gay men and other men who have sex with men, and 37% of people who inject drugs accessed two or more HIV prevention services in the previous three months according to median values reported by GPC countries ––against a target of 90%.
HIV prevention is being obstructed by shortfalls in prevention financing, and by punitive laws. Social stigma, violence, discrimination and social exclusion are barriers to key populations’ access to health-care services and information, exacerbating their risk of acquiring HIV. Law reform is a crucial enabler of prevention programmes. Protecting the human rights of everyone is vital for protecting the health of everyone.
Investments in both condom and voluntary medical male circumcision programmes, which are both effective in preventing HIV, have fallen in some of the countries with the largest HIV epidemics. In addition, breakthrough HIV prevention options such as pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), medicine to prevent HIV, are still only available to a small fraction of the people who need them.
There are unprecedented opportunities for HIV prevention in 2024. There is a growing array of prevention options including existing tools and new long-acting prevention technologies, as well as country examples of how to implement prevention at scale and increase choices available to communities.
HIV Prevention programmes need to be at scale, efficient and equitable. The actions that are needed for success and sustainability are known, have been shown to work, and have been agreed: collaborate, follow science, tackle inequalities, protect everyone’s rights, let communities lead, and invest in what is needed. Sliding back on resourcing or inclusion would hurt everyone. Solidarity will benefit everyone. Communities, countries and international partners can prevent new infections – together.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Our work


Press Release
At the 68th Commission on Status of Women UNAIDS calls for action to achieve gender equality and end AIDS
11 March 2024 11 March 2024GENEVA/NEW YORK, 11 March 2024 - UNAIDS is gearing up for the 68th session of the Commission on the Status of Women (#CSW68) which begins today and will run until 22 March 2024. #CSW68, the United Nations largest annual gathering on gender equality and women’s empowerment, is being held this year under the priority theme, Accelerating the achievement of gender equality and the empowerment of all women and girls by addressing poverty and strengthening institutions and financing with a gender perspective.
Despite progress, no country has achieved gender equality to date, and violations of women’s human rights and gender-based violence are continuing to fuel the AIDS pandemic. The world is off track to meet the gender targets set out in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and in many of the world’s poorest countries, the debt crisis is squeezing out investment in education, health, and social protection, particularly hurting women and girls.
Around the world today, 129 million girls are out of school, denying them lifesaving information on how to protect themselves from HIV. Every three minutes, an adolescent girl or young woman (15-24 years) acquired HIV in 2022 in sub-Saharan Africa, and across Africa, AIDS remains the leading cause of death among women of reproductive age.
"There can be no more excuses. Ending AIDS among women and girls is not only a moral imperative but also a strategic priority for achieving the Sustainable Development Goals,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “Only by protecting and investing in the rights of women and girls can we protect their health, and only by protecting women’s health can we end the AIDS pandemic. We must seize this opportunity to accelerate progress towards a world where every woman and girl can, not just survive, but thrive."
During #CSW68 UNAIDS will be co-hosting several key events including a high level meeting co-convened by the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg and Education Plus (a joint initiative of UNAIDS, UNESCO, UNFPA, UNICEF and UN Women) which will mobilize government, partners and stakeholders to accelerate scaled up actions on women’s rights and leverage girls’ education for gender equality and HIV prevention across Africa.
UNAIDS is urging renewed action and anticipates strong outcomes from #CSW68. UNAIDS looks forward to the partnerships that will be forged to accelerate progress towards gender equality and ending AIDS as a global public health threat.
UNAIDS remains steadfast in its commitment to working collaboratively with governments, civil society, and other partners to create a world where the rights and dignity of all women and girls are respected and protected, including women and girls living with, at risk of and affected by HIV.
#CSW68, hosted by the United Nations, will convene leaders, advocates, governments, civil society organizations, activists and experts to discuss, agree on actions and investments that can end women’s poverty and advance gender equality.
Follow the Education Plus event live on Tuesday 12 March at 08:00 – 09:30 EST - Making Education Investment Cases Work for Gender Equality and HIV Prevention
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS New YorkRupa Bhadra
tel. +1 646 468 4129
bhadrar@unaids.org
UNAIDS Geneva
Sophie Barton Knott
tel. +41 79 5146896
bartonknotts@unaids.org
