Cosponsors


Feature Story
Building country-led sustainable HIV responses
20 December 2024
20 December 2024 20 December 2024What does the HIV response look like beyond the 2030 targets to end AIDS? For the past year, UNAIDS has been working with partners and over 30 countries to develop country-led roadmaps for the sustainability of HIV prevention, treatment and care services far into the future.
Part of the sustainability journey includes reaching the global goal of ending AIDS in the next five years. According to a recent World Bank report, despite an early COVID-19 spending peak, per capita government health spending has steadily declined in low- and lower middle-income countries. Urgent action is needed in many countries to ensure reaching the health Sustainable Development Goals remains possible by 2030.
UNAIDS’s new sustainability approach, developed jointly with the US President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) and the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria (GF) in early 2024, focuses on five core areas. These are political leadership and commitment; enabling laws and policies; sustainable and equitable financing; science-driven, effective and high-impact HIV services and solutions; and systems built to deliver. The specific methods look different in each country, but all have equity and communities at the center.
“A multi-sectoral approach remains critical to the HIV response particularly in this last mile as we accelerate prevention and close gaps that require us to address the complex inequalities that persist,” said Anne Githuku-Shongwe at UNAIDS.
As part of this initiative, UNAIDS and partners are supporting countries to create and implement sustainability roadmaps. The roadmaps identify key changes countries can take to shift towards self-reliant, efficient and impactful HIV responses both in the short- and long-term.
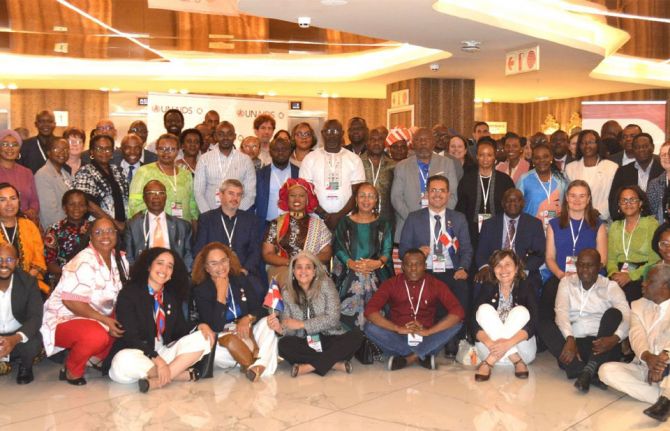
Representatives from 22 countries in Sub-Saharan Africa and the Dominican Republic gathered recently in Johannesburg, South Africa to hone their roadmaps during a workshop hosted in October by The South African National AIDS Council in collaboration with UNAIDS, PEPFAR and the GF.
“While it is valuable that we come together to learn and share insights, it is crucial to recognize the level of responsibility each of us carries in our respective countries. We are not here simply to exchange ideas, but to take on a leadership role in driving meaningful change,” said Thembisile Xulu of the South African National AIDS Council as she addressed the participants.
During the workshop, countries shared experiences and learned from each other about their individual sustainability journeys. In addition, countries agreed to establish a virtual peer learning network to facilitate future cross-border partnerships and share successes and challenges in moving towards sustainability. Some of the findings so far along the journey include the necessity of high-level political support, coordinated multi-sectoral efforts and diversified funding sources.
Furthermore, countries recommended that development partners craft consistent messages about their ongoing commitment levels to fund HIV and health services. The need for transparent, responsible and inclusive conversations was emphasized by all in Johannesburg when discussing the transition from donor financed to country financed responses.
“The fiscal space for HIV is tightening, and we need to be pragmatic as we work to sustain the response with a focus on simplification and efficiency,” said Sarah Dominis from the U.S. State Department Bureau of Global Health Security and Diplomacy, Office of Financial and Programmatic Stability. “The future HIV response will be led by country governments in partnership with community and private sector partners. PEPFAR is not going away but will focus on supporting countries to sustain the HIV response, aligning to the vision they have committed to in their roadmaps.”
As the roadmaps roll out publicly, governments are recognizing the role of communities in the long-term response. For example, Tanzania’s roadmap identifies that community-led organizations play a pivotal role in community mobilisation, facilitating social and behaviour change, addressing social/cultural norms, primary HIV prevention interventions, adherence to antiretroviral treatment and retention in care. As a result, the roadmap lists actions to bolster communities, such as scaling up the network of community health workers and reinforcing community-led monitoring programs.
“When we talk about HIV sustainability we need to go back to the basics. It's about planning around the lives of PLHIV. Communities are always at the centre of service delivery, demand creation and monitoring. There is the opportunity for us all to tap into the infrastructure and willingness of communities to provide treatment and prevention services - through strong sustainable partnerships,” said Sibongile Nkosi from The Global Network of People Living with HIV.
This past World AIDS Day, ten countries launched their sustainability roadmaps, and more will follow in early 2025. To follow the process, visit: https://sustainability.unaids.org/
Related documents






Feature Story
Resilience amid crisis: strengthening the HIV response for displaced communities in Ethiopia
02 December 2024
02 December 2024 02 December 2024Ethiopia faces a triple crisis of conflict, climate change, and displacement that impedes the capacity to provide essential health and other humanitarian assistance to those in need, including people living with HIV.
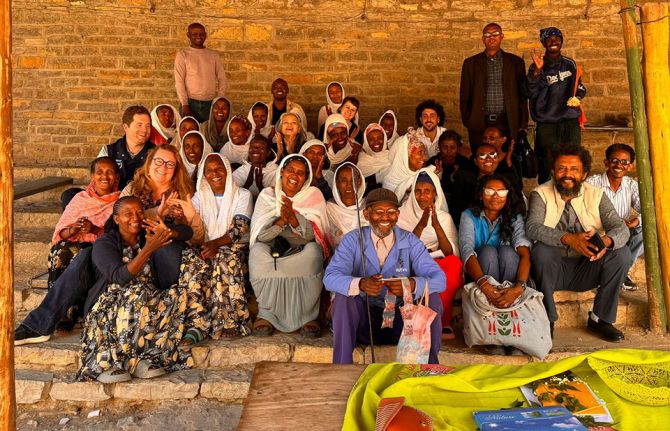
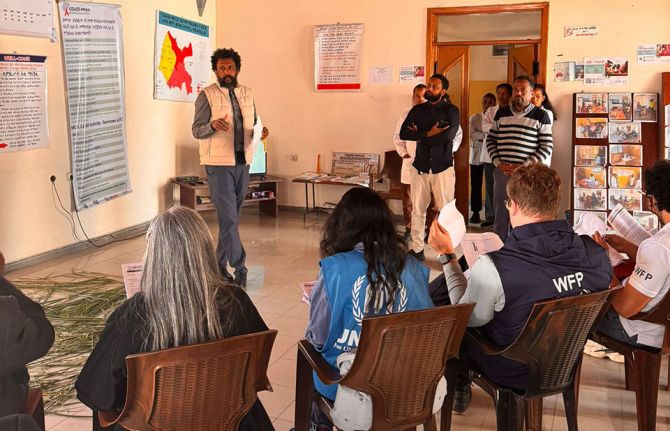
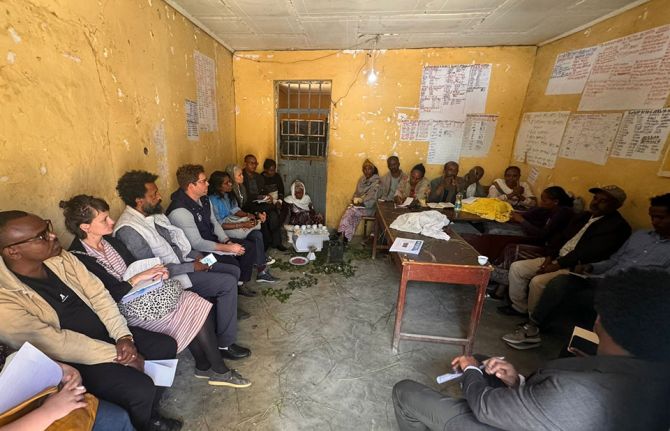
With support from 2Gether 4 SRHR, UNAIDS and partners recently organised a joint mission to learn about the humanitarian response and to identify the challenges that persist. The findings of the mission will help update the guidelines on Addressing HIV in Humanitarian Settings, a crucial resource for all actors working on HIV in emergency settings, providing evidence-based recommendations for integrating HIV into the different sectors of humanitarian responses.
Ethiopia hosts more than 1 million refugees, predominantly from South Sudan, Somalia, Eritrea and Sudan, the majority of whom live in 24 refugee camps established across five regional states, and 80,000 of whom reside in the capital Addis Ababa. In addition, the country has 4.4 million internally displaced persons (IDPs) and over 1.5 million IDP returnees.
The team visited two of the regions hardest hit by humanitarian crises, grappling with rising HIV rates: Tigray and Gambella. In Tigray, just 5 kilometers from the capital Mekelle, lies Seba Kare (70 Kare) IDP camp—a settlement hosting over 20,000 people displaced by the conflicts in the western and eastern parts of the region. Seba Kare represents both the resilience of its inhabitants and the dire challenges of prolonged displacement. The camp, initially intended as temporary shelter for six months, has now housed many families for over four years. Cramped conditions, insufficient food, limited access to education, and inadequate healthcare services are daily realities for residents. Despite the tireless efforts of humanitarian partners on the ground, the growing needs of the displaced population far exceed the resources available.
Among the most pressing gaps is the lack of comprehensive healthcare, particularly for people living with HIV. In humanitarian crises, critical services for HIV and sexual and reproductive health are often sidelined, overshadowed by the urgent need for food, shelter, and disease control. Healthcare is restricted to primary services. Care for chronic conditions, such as HIV, is referred to government hospitals. This means that all patients, IDP or not, must pay for transportation as well as services and purchase vital medical supplies on their own—an impossible burden for many.
Despite the continuous advocacy efforts in support of the decentralization of services and outreach interventions at camp-level, government-owned facilities outside the camp remain the only viable option for IDPs in need of health services.
The refugee camp of Jewi—in the western province of Gambella which has the highest HIV burden across Ethiopia—is equipped with its own antiretroviral therapy center. However, like in Tigray, Gambella faces significant challenges in providing HIV testing and treatment. Limited mobility within and beyond the camps, due to the costs of transport for clients and a shortage of ambulances in medical emergencies, combined with resource constraints at health centres, often results in treatment interruptions and high rates of loss to follow-up.
Adding to the crisis, the recent reduction in donor funding has severely impacted the quality of health services in the camps. The gender-based violence (GBV) center run by International Medical Corps will soon close due to funding cuts, leaving no other GBV services available outside of health services.
The situation for women and youth in Gambella is especially concerning. Limited educational and employment opportunities, compounded by rising HIV infections, put them at higher risk of infection due to the adoption of negative coping mechanisms, including substance abuse. The high rates of new HIV infections exacerbate these existing challenges, underscoring the urgent need for sustained interventions to improve health services, livelihoods, and social inclusion for refugees and host communities in the region. “There are many young and vulnerable people who need protection, shelter, food, income, education – and HIV prevention, testing, treatment and care. We must make sure to rebuild health and social services and fill the current resources gap,” said Tina Boonto, UNAIDS Ethiopia Country Director.
As international organisations step up their efforts to address HIV in humanitarian settings, there is a coordinated push in Ethiopia, at both the federal and regional levels, to ensure that the health needs of people living with HIV are met, even in the most challenging circumstances. The Ministry of Health, with support from UNAIDS, is developing an HIV Baseline Survey in Humanitarian Settings and a comprehensive National HIV/Sexual and Reproductive Health Guiding Document. This initiative is a substantial step towards safeguarding the rights and well-being of people living with HIV across the country.
"Ethiopia's progress in addressing HIV is inspiring,” said Maheswari P Murugayia, Public Health Officer and Global HIV Focal Point at UNHCR. “Tackling HIV in humanitarian settings is not just a priority— it’s a necessity for ensuring the health and well-being of displaced populations.”
Region/country
Related
 Zambia - an HIV response at a crossroads
Zambia - an HIV response at a crossroads

24 February 2025
 Status of HIV Programmes in Botswana
Status of HIV Programmes in Botswana

20 February 2025


Press Release
UNAIDS calls for an end to violence against women and girls. No excuses
25 November 2024 25 November 2024GENEVA, 25 November 2024—Gender-based violence persists as one of the most appalling violations of human rights. It also thwarts efforts to end AIDS as a public health threat because intimate partner violence is linked with a heightened risk of HIV acquisition among women and undermines access to testing and treatment.
Globally, one in eight women and girls experiences sexual violence before the age of 18. Harmful gender norms, low prioritization of safe, qualitative and affordable sexual and reproductive health services, as well as fragile health systems heighten women’s risk of contracting HIV and prevent access to HIV services.
In addition, women and girls living with HIV are too often stigmatized by health service providers. They also experience pressure not to have children, forced and coerced sterilization or termination of a pregnancy. All violations of human rights.
“We must counter patriarchy and poverty to keep girls in school and we must provide women and girls safe spaces, economic opportunities and ensure their recognition and leadership,” said Winnie Byanyima, UNAIDS Executive Director.
“We must also fight rigid gender norms and stereotypes that perpetuate unhealthy masculinity and violence based on gender."
Gender-related killings of women and girls are the deadliest outcome of gender-based violence with a woman being killed every 11 minutes. This is unacceptable. In 2022, the number of women and girls killed intentionally – nearly 89,000 – is the highest yearly number recorded in the past 20 years. Women from key populations – transgender women, sex workers, and LGBTQ+ human rights defenders - are also at particular risk of femicide according to the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights (IACHR).
On the International Day for the Elimination of Violence against Women this year, the campaign kicked off with the theme ‘UNiTE to End Violence against Women and Girls: Towards Beijing +30.’ These 16 Days of Activism remind us that 30 years after the Beijing declaration - a blueprint for achieving gender equality and women’s and girls’ rights everywhere - the world is far from such a gender equal world.
UNAIDS remains committed to working collaboratively with governments, business, civil society, communities and especially women’s movements and networks to create a world where the rights and dignity of all women and girls are respected and protected, including women and girls living with, at risk of and affected by HIV.
Started in 1991, the 16 Days of Activism against Gender-Based Violence is an international campaign that kicks off on 25 November, the International Day for the Elimination of Violence against Women, and runs until 10 December, Human Rights.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.


Press Release
Climate emergency risks worsening AIDS epidemic, UN warns at COP29
21 November 2024 21 November 2024Countries facing “triple funding crisis” of insufficient climate finance, insufficient HIV funding, and crippling debt
GENEVA/BAKU, 21 November 2024—The climate crisis could disrupt HIV services and lead to increasing HIV risk for some of the most vulnerable populations, the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) and United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) have warned at the COP29 Climate Conference in Baku, Azerbaijan.
In a new report, the UN agencies warn that eroded public health infrastructure, heightened prevalence of diseases that interact with HIV, food insecurity, water scarcity, and the mass displacement of people – all likely to intensify due to climate change – could drive new HIV infections and lead to more AIDS-related deaths.
“The progress we have made tackling AIDS is fragile – and it could be unwound by runaway climate change,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “Some of the most climate vulnerable countries also have the highest HIV burden, and are the countries in the greatest debt, compounding injustice on injustice. We need to find ways to ease the triple funding crisis of AIDS, climate, and debt, and invest in the communities on the front lines of these intertwined crises.”
Many of the countries at the sharp end of climate change are also facing the worst impacts of the AIDS epidemic, and climate change is likely to exacerbate the inequalities of AIDS, UNAIDS says. Of the 4,000 adolescent girls and young women aged between 15 and 24 years newly infected with HIV every week, 3,100 live in Sub-Saharan Africa, where severe heatwaves and drought could leave whole regions uninhabitable.
HIV-focused institutions are responding, with 70% of financing from the Global Fund to Fight HIV, Tuberculosis and Malaria set to go to 50 of the most climate-vulnerable countries. But many of these countries are facing a triple funding crisis, with insufficient climate finance, a US$ 9.5billion gap in HIV funding, and the crushing burden of sovereign debt.
Almost half of humanity live in countries spending more on servicing debt than on healthcare. In Western and Central Africa, countries are spending seven times more on repaying debt than on health. With 71% of public climate financing coming as loans rather than grants, the climate crisis will only make this problem worse.
Last year, Malawi was hit by Cyclone Freddy amid a cholera outbreak just as the nation was recovering from COVID-19. Some of the worst hit regions were those with the highest burden of HIV. Around 37 000 people living with HIV were displaced by the storm, forced to navigate overwhelmed services and shortages of medicines – and this is just one of many examples of how climate change is already impacting the HIV response.
At the report launch on the sidelines of the COP29 Climate Conference in Baku, governments will be urged to tackle inequalities, build proper leadership and governance systems, and provide sustainable financing to prevent a climate-induced AIDS crisis.
“At COP29 we can see increasing recognition that the climate crisis is compounding existing health challenges” said Marcos Neto, Director, Bureau of Policy & Programme Support, UNDP. “The AIDS response has shown us what is possible when communities most impacted, governments and institutions unite. By embedding HIV and health considerations into climate action, we can protect hard-won progress, build resilience for the future, and leave no one behind.”
Notes
On Thursday 21 November, UNAIDS and UNDP are hosting a discussion on HIV and climate change at COP29 in Baku, Azerbaijan at the Azerbaijan Pavillion from 14:00-15:00 AZT.
The Climate Crisis and HIV: A Policy Brief from UNDP and UNAIDS is available here.
UNDP
UNDP is the leading United Nations organization fighting to end the injustice of poverty, inequality, and climate change. Working with our broad network of experts and partners in 170 countries, we help nations to build integrated, lasting solutions for people and planet. Learn more at undp.org or follow at @UNDP.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.


Feature Story
Women living with HIV in China unite to confront discrimination
14 October 2024
14 October 2024 14 October 2024There are around 1.4 million people living with HIV in China and women make up around 23.7% of them, according to the latest data from Chinese health authorities. Among those living with HIV are pregnant women who are in a particularly vulnerable position due to the stigma surrounding the disease.
In order to counter such stigma and discrimination, women living with HIV and Hepatitis B came together at The Voice of Resilience event to tell their stories and to call for additional resources for community-based organizations (CBOs) working on the frontlines providing services for women living with and affected by HIV.
In 2023 alone, more than 5,000 pregnant women were diagnosed with HIV and over 400,000 with hepatitis B, and some of them were diagnosed at very late stage to be able to receive HIV services to prevent transmission to their children, according to China’s National Health Commission. Even though services are in place to prevent the transmission of HIV to their babies, discrimination, including denial of healthcare, obstructs women from accessing such services.
“I received a call from the doctor telling me that I couldn’t receive services from their hospital because I was HIV positive,” explained Xia Jing, one of the mothers, after she went to a general hospital in Beijing for a routine maternal exam. She still cannot hold her tears when she remembers her traumatic experience. She challenged back and told the doctor r that under the law they had no right to reject her.
She was eventually referred to Beijing’s You’an Hospital, a designated hospital for infectious diseases and people living with HIV where she delivered her baby. Now she is a happy mother of a four-year-old boy. Doctor Zhu Yunxia was the doctor who helped Jing deliver her baby. Dedicated to her job for more than 30 years, she is proud of having helped so many women deliver healthy babies. She calls for empathy with people facing discrimination and unfair treatment and urges all people to look at women living with HIV without prejudice.
“Stigma undermines public health objectives by creating barriers to accessing health and social services and can reduce the quality of the services that members of affected communities receive,” said Mark Vcislo, the First Secretary at Canadian Embassy to China, which has supported the work to tackle stigma. He called for breaking down “the prejudices that can prevent and deter marginalized communities, including persons living with HIV, from accessing the health and social services they need and deserve.”
Community-based organizations (CBO) are vital support for women living with HIV. Sister Xin, for instance, who herself received help from community volunteers when she was first diagnosed with HIV, created Firefly, a community-based organization that has help more than 20,000 women living with HIV in the last 20 years. Zhang Yu whose CBO supports women living with HIV in rural areas of China’s southwestern Yunnan Province, called for more resources for CBO’s work. “CBOs are struggling with their survival due to lack of resources,” she said. “I sincerely hope the government, the charity organizations and everybody can support us to continue our work.”
China has developed a strong and ambitious plan to significantly reduce the transmission rates of HIV, syphilis, and hepatitis B by 2025 outlined in China Women’s Development Plan and Healthy China 2030. China has achieved around 99 percent national screening rates among pregnant women living with HIV over the past five years. In 2023 alone, more than 9 million pregnant women have received HIV testing services.
The Chinese government has partnered with UN agencies for the “last mile” by building a patient-centred and family-centred community service model to enable a holistic set of services and help break the barriers for both mothers and infants.
“Thanks to the combination of development of technology and social progress, women living with HIV can today give birth to healthy babies,” said Sister Xin.
Read the profile of the storytellers and more unsung community heroes committed to helping mothers and babies: http://www.unaids.org.cn/page122?_l=en&article_id=1233.
Region/country
Related
 Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia
Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia

24 February 2025

Press Statement
UNAIDS calls for a rapid international response to mpox based on rights and an equitable access to vaccines and treatments
19 August 2024 19 August 2024GENEVA, 19 August 2024—UNAIDS is calling on the international community to respond swiftly and decisively to the World Health Organization’s declaration of the mpox outbreak in several African countries as a public health emergency of international concern. The move came after the Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC) made a similar declaration for the region.
“The emergence of a new and more contagious variant of mpox, and the devastating impact it is having on communities, across Africa, especially those most vulnerable including from HIV and AIDS, is alarming,” said Angeli Achrekar, UNAIDS Deputy Executive Director, Programme. “We must call on international efforts to focus on ensuring vaccines and treatments are accessible and available to all who need them and draw on the experience of the AIDS movement to ensure a response rooted in solidarity, compassion, inclusion, and equity.”
Many communities affected by mpox face discrimination, similar to people who are affected by HIV and AIDS. Stigma and discrimination undermine epidemic responses, driving people with symptoms underground and hindering efforts to protect public health. UNAIDS urges people to show compassion and solidarity to people affected, not intolerance and discrimination. We at UNAIDS, across the entire Joint Programme, also emphasize the crucial role of involving communities in every stage of the response—from development to implementation and monitoring.
The emergence of the 2024 mpox variant once again demonstrates the need for international, multisectoral coordination and solidarity to end pandemics. The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS, is committed to bring its expertise and support to countries to help. UNAIDS urges all media covering the crisis to follow the regular updates being issued by WHO and Africa CDC.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.


Press Statement
Joint UN statement calling for sexual and reproductive health and rights for all
11 July 2024 11 July 2024In April, at the United Nations Headquarters in New York, governments renewed their commitment and determination to accelerate the implementation of the Programme of Action of the 1994 International Conference on Population and Development (ICPD), the principles of which are embedded in the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including commitments to ensure universal access to sexual and reproductive health-care services and to advance reproductive rights.1
Significant progress has been made over the past three decades. Since 1990, the number of women using modern contraception has doubled. Since 2000, maternal mortality has declined by 34 per cent. By 2022, access to HIV treatment had averted an estimated 20.8 million deaths globally. More recently, however, this progress has stalled and in some instances is reversing. Looking forward, the prospect of continued progress is far from guaranteed. The ongoing effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, persistent and increasing conflict, climate change, rising inequalities and deepening polarization are all undermining access to quality, essential health services. These setbacks demand urgent action.
Women and girls are disproportionately affected by these challenges, hindering their right to make informed decisions and exercise full bodily autonomy without coercion, violence or discrimination – fundamental human rights. Equitable and sustainable access to human rights–based sexual and reproductive health interventions and information remains beyond the reach of many – especially marginalized women, adolescent girls and those living in humanitarian crises and conflict zones. The latest data show that close to half of women of reproductive age cannot make their own informed decisions about whether or when to become pregnant, and many still lack the autonomy and agency to fully exercise their reproductive rights.
On World Population Day, as UN agencies mandated to advance the health and rights of all people and ensure no one is left behind, we call upon the global community, including governments, donors, civil society organizations, and the private sector to strengthen access to a comprehensive package of sexual and reproductive health services as part of universal health coverage, delivered through resilient health systems including at the primary healthcare level. We underscore the need to implement evidence-based, normative guidance to strengthen access to affordable, high quality and rights-based care. To ensure services are acceptable to all, efforts are needed to eliminate stigma and discrimination and dismantle harmful social and gender norms.
We also call for accelerated access to comprehensive sexuality education and strengthened action across social sectors, such as education and gender, to enhance the health and well-being of girls and women throughout their lives. Promoting comprehensive sexual and reproductive health and rights is not only the right thing to do – it is also the smart thing to do. Investing in women’s and girls’ reproductive rights and agency and expanding access to services is proven to have remarkable returns, including in terms of social wellbeing, economic prosperity and peace, which our world so desperately needs. Additional financing from all sources – domestic, international, public, private – is essential to create long-term positive outcomes for women and girls.
We must also urgently support the increasing efforts of young people, women and communities to speak up about sexual and reproductive health concerns and to design and deliver solutions that respond to their needs and to the realities of a changing world, where climate change in particular, affects sexual and reproductive health and rights. An inclusive, bottom-up approach to designing and delivering health interventions with and for communities can deliver more sustainable results and reach those who are furthest left behind.
We urge the public and private sectors to collaborate in exploring cutting-edge technologies like telemedicine, artificial intelligence, big data analytics and predictive modeling to bridge geospatial gaps and expand access to essential services, particularly in remote and underserved areas. At the same time, we call on innovators to address the risks inherent in these new technologies, including gender gaps in access, technology-facilitated gender-based violence, and systematic biases embedded in tech design.
Finally, we call upon governments, communities, civil society organizations and the private sector to unite to prioritize universal access to comprehensive sexual and reproductive health, in ways that advance gender equality and promote the full realization of human rights, in line with the groundbreaking vision of the ICPD Programme of Action. We ask for more than a commitment, more than business as usual — this is an appeal to collaborate and innovate in ways that ensure everyone can realize their rights to health, dignity and security. As we head towards the Summit of the Future at the United Nations General Assembly in September, now is the time to act boldly and decisively, forging a path towards a more just, equitable and sustainable world for all.
Thirty years ago in Cairo, 179 governments adopted a framework that recognized sexual and reproductive health and reproductive rights and the empowerment of women and girls as foundational pillars of sustainable development – the landmark Programme of Action of the International Conference on Population and Development. As UN agencies, we stand together committed to advancing comprehensive sexual and reproductive health and rights, which are integral to everyone’s right to the enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health and essential for the achievement of gender equality.
[1] https://www.un.org/development/desa/pd/content/regional-reviews-icpd-programme-action
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.


Press Release
Unfinished business: only the urgent and accelerated delivery of HIV services will keep the promise of ending AIDS in children by 2030
22 July 2024 22 July 2024Despite significant gains in many countries, critical gaps continue to undermine efforts to end AIDS in children
GENEVA/MUNICH, 22 July 2024—Despite progress made in reducing HIV infections and AIDS-related deaths among children, a new report released today by the Global Alliance for Ending AIDS in Children by 2030 shows that an urgent scale up of HIV services in countries worst affected by the pandemic is required to end AIDS by 2030.
The report, Transforming Vision Into Reality, shows that programmes targeting vertical transmission of HIV have averted 4 million infections among children aged 0-14 years old since 2000. Globally, new HIV infections among children aged 0-14 years old have declined by 38% since 2015 and AIDS-related deaths have fallen by 43%.
Among the 12 Global Alliance countries, several have achieved strong coverage of lifelong antiretroviral therapy among pregnant and breastfeeding women living with HIV, with Uganda nearing 100%, United Republic of Tanzania at 98%, and South Africa at 97%. Mozambique has achieved 90% coverage, with Zambia at 90%, Angola at 89%, Kenya at 89%, Zimbabwe at 88%, and Cote d'Ivoire at 84%.
“I applaud the progress that many countries are making in rolling out HIV services to keep young women healthy and to protect babies and children from HIV,” said UNAIDS Executive Director, Winnie Byanyima. “With the medicines and science available today, we can ensure that all babies are born – and remain – HIV-free, and that all children who are living with HIV get on and stay on treatment. Services for treatment and prevention must be ramped up immediately to ensure that they reach all children everywhere. We cannot rest on our laurels. The death of any child from AIDS related causes is not only a tragedy, but also an outrage. Where I come from, all children are our children. The world can and must keep its promise to end AIDS in children by 2030.”
Global Alliance countries are innovating to overcome barriers and accelerate progress towards ending AIDS in children. However, despite advances neither the world nor Global Alliance countries are currently on track to reach HIV-related commitments for children and adolescents and the pace of progress in preventing new HIV infections and AIDS-related deaths among children has slowed in recent years.
“Accelerating the delivery and uptake of HIV services for children and adolescents is a moral obligation, and a political choice,” said Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, Director-General of the World Health Organization. “Twelve countries are demonstrating they have made that choice, but significant challenges remain. While we have made progress in increasing access for pregnant women to testing and treatment to prevent vertical transmission of HIV, we are still far from closing the paediatric treatment gap. We need to further strengthen the collaboration and reach of the Global Alliance, and we must do this work with focus, purpose and in solidarity with all affected mothers, children, and adolescents.”
Around 120 000 children aged 0-14 years old became infected with HIV in 2023, with around 77 000 of these new infections occurring in the Global Alliance countries. AIDS-related deaths among children aged 0-14 years old numbered 76 000 globally with Global Alliance countries accounting for 49 000 of these unnecessary deaths. Vertical transmission rates remain extremely high in some locations, particularly in Western and Central Africa, with rates exceeding 20% in countries including Nigeria and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
“In the fight against HIV, we must do a much better job for children,” said Peter Sands, Executive Director of the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria, which provides funding for HIV programmes in over 100 countries through a country-led partnership model. “In support of national programmes, we have been procuring the latest dolutegravir-based paediatric treatment regimens at negotiated prices. Our investments in laboratory systems are helping ensure exposed infants are rapidly tested and that those that test positive are quickly initiated on age-appropriate antiretroviral treatment. Differentiated testing and treatment approaches are helping close the diagnostic gap and ensuring more child-centred service delivery.”
It is concerning that the treatment gap between adults and children continues to widen.
“Just 57 per cent of children living with HIV receive life-saving treatment, compared to 77 per cent of adults,” said UNICEF Associate Director HIV/AIDS, Anurita Bains. “Without early and effective testing and treatment, HIV remains a persistent threat to the health and well-being of children and adolescents and puts them at risk of death. To close the treatment gap, we must support governments to scale up innovative testing approaches and ensure children and adolescents living with HIV receive the treatment and support they need.”
In 2023, there were 210 000 new infections globally among young women and girls aged 15—24 years old (130 000 in Global Alliance countries), four times higher than the 2025 goal set at 50 000. Preventing new infections among this age group is critical both to protect the health and wellbeing of young women and to reduce the risk of new infections among children.
Gender inequalities and human rights violations are increasing women’s vulnerability to HIV and diminishing their ability to access essential services. Globally, nearly one in three women have encountered some form of violence during their lifetime, with adolescent girls and young women disproportionately affected by intimate partner violence. In the four Global Alliance countries with available data, countries are not currently on track to achieve the target of ensuring that by 2025 less than 10% of women, key populations and people living with HIV experience gender-based inequalities and gender violence.
"It has been remarkable to see how many more children's lives can be saved when all stakeholders and partners come together to commit to end AIDS in children. While much progress has been made, notably through the successful introduction of pediatric dolutegravir, large gaps still remain across the pediatric cascade and we must recommit ourselves with purpose and innovation to fulfill the promises we have made by 2025 and beyond,” said Ambassador John N. Nkengasong, United States Global AIDS Coordinator and Special Representative for Global Health Diplomacy.
The Global Alliance for Ending AIDS in Children by 2030 was launched in 2022 by WHO, UNICEF and WHO to reinvigorate the paediatric HIV agenda. It has now grown, and in addition to the United Nations agencies, the alliance includes civil society movements, including the Global Network of People living with HIV, national governments in the most affected countries, and international partners, including PEPFAR and the Global Fund. Twelve countries are members: Angola, Cameroon, Côte d'Ivoire, The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Kenya, Mozambique, Nigeria, South Africa, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDSMichael Hollingdale
hollingdalem@unaids.org
UNICEF
Lazeena Muna-Mcquay
lmunamcquay@unicef.org
WHO
Sonali Reddy
reddys@who.int
The Global Fund
Ann Vaessen
ann.vaessen@theglobalfund.org
PEPFAR
Veronica Davison
davisonv@state.gov




Feature Story
Girls’ education for HIV prevention at 1st Pan-African Conference on Girls’ and Women’s Education in Africa
08 July 2024
08 July 2024 08 July 2024Girls’ education as a tool to prevent HIV infection has been centered at the 1st African Union Pan-African Conference on Girls’ and Women’s Education in Africa. This followed African leaders designating education as the 2024 African Union theme of the year.
At a high-level side event hosted by the Education Plus Initiative on the first day of conference held at the African Union Commission in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, leaders, girls’ and women’s networks and advocates called for greater investments in girls’ education.
“Some people claim that providing girls with secondary education is too expensive. Such claims fail to consider the exponentially higher cost of not educating them,” said UNAIDS Executive Director, Winnie Byanyima. “We can get all our girls and boys to complete secondary education; that should be our legacy."
UNICEF calculates that 34 million girls in sub-Saharan Africa are out of secondary school. According to the Global Education Monitoring (GEM) Report 2023, in all regions in Africa, there are more girls out of school at the secondary level than boys, with gender disparities worsening as children move up to higher levels of education in favour of boys over girls. In sub-Saharan Africa, less than half of adolescent girls complete secondary education, their percentage standing at 42% and there has been no progress at all in closing this gap in the past 20 years. Sub-Saharan Africa is the region furthest from parity at the expense of girls, with no progress since 2011 at the lower secondary level and since 2014 in upper secondary.
Gender is a key factor linked to disparities in enrolment, retention, completion, and learning outcomes through social conditioning, gender-based differences in parental expectations and education-related investments, child marriages and early childbearing, female genital mutilation, child labour, gender-based violence, period poverty and discrimination.
More than forty years into the HIV response, Africa remains an epicenter of the AIDS epidemic with adolescent girls and young women being disproportionately affected. Every week 3100 adolescent girls and young women acquired HIV in sub-Saharan Africa. Every three minutes, an adolescent girl or young woman aged 15-24 years acquired HIV in 2022 in sub-Saharan Africa. Adolescent girls and young women aged 15-24 years in the region were more than three times as likely to acquire HIV than their male peers in 2022.
UN agencies, African Union representatives, government ministers, and young women leaders called for accelerated actions to translate commitments to action through leveraging girls' education for gender equality and preventing HIV, child marriage, teenage pregnancies, violence, gender-related stigma and discrimination in Africa.
Speakers emphasized the connection between health and education. Ministers spoke about key policy reforms and best practices aimed at promoting girls' education, including creating safe and inclusive school environments, strategies to get girls into secondary school, and the readmission policy that addresses high dropout rates due to pregnancy. UN co-leads emphasised the need for improved collection of data disaggregated by sex and other relevant population characteristics to better understand educational participation, progression, and learning, and using gender-sensitive data for policymaking and planning.
Other issues highlighted included the integration of digital literacy programs into the secondary education and vocational training curriculum to facilitate smooth transitions from school to employment; integrate gender equality into all aspects of the education system, including curriculum-based comprehensive sexuality education and life skills, address gender-based violence within schools and discriminatory laws and practices, and access to information, non-discriminatory HIV and sexual and reproductive health services access.
Young women leaders spoke on the role of partnerships and young women's leadership. Participants highlighted the upcoming 30th anniversary of the Beijing Declaration as an opportunity moment to accelerate accountability and commitments, as well as the CSW Resolution 60/2, Women, the Girl Child and HIV and AIDS as significant mechanisms to address political and resource gaps so no woman or girl is behind in the HIV response.
Education Plus is a rights-based, gender-responsive action agenda to ensure adolescent girls and young women have equal access to quality secondary education, alongside key education and health services and support for their economic autonomy and empowerment. Co-led by five UN agencies, the initiative builds on existing frameworks like the Transforming Education Summit, the Continental Education Strategy for Africa (CESA) and the Dakar Education for All (EFA) Declaration to push for access and completion of education for women and girls in Africa.
Quotes
" Some people claim that providing girls with secondary education is too expensive. Such claims fail to consider the exponentially higher cost of not educating them. We know the consequences when girls can’t finish secondary school: higher risks of sexual violence, early marriage, unwanted pregnancy, complications in pregnancy and childbirth, and HIV infection. But when a girl completes secondary school, it helps her to be safe and strong. If all girls complete secondary education, adolescent pregnancy could be cut by 75% and early marriage could be virtually eliminated. An extra year of secondary school can increase women’s eventual wages by 15-25%. We can get all our girls and boys to complete secondary education; that should be our legacy."
We must recognize the intersecting challenges girls face, including HIV. They face extraordinarily high levels of HIV infections. Women and girls represented 63% of all new HIV infections in Africa in 2022. Empowering girls with knowledge is key to ending AIDS as a public health threat. Education is the best HIV prevention tool available.”
“African nations should ensure that young people not only gain vital knowledge but also acquire life skills, values, attitudes, and make decisions in order to live healthy and fulfilled lives. Through the AU strategy, we will see increased awareness about the importance of investing in education and the health of children and adolescents.”
“Girls’ education is not only a right, but will also result in broad socio-economic development for countries. We are creating a safe and conducive environment for adolescent girls and young through the criminalization of child marriage, FGM, school-related gender-based violence, and sexual harassment, particularly sexual exploitation perpetrated by teachers. We provide life skills and comprehensive sexuality education in schools and ensure an inclusive school environment for children with disabilities, with specific attention to girls. We have enhanced social protection strategies, including cash transfers to poor households to ensure that girls go to school and are not engaged in care work and child labour.”
“Girls who dropped out due to early pregnancies or early unwanted pregnancies are readmitted. We have a national girls’ education strategy aimed at facilitating the pace at which Malawi may achieve sustainable development goals. We emphasize universal primary education, the promotion of gender equality and empowering women.”
“We are trying to remove the cultural norm barriers and negative gender stereotypes that contribute to gender-based violence and discrimination against adolescent girls and young women with a male engagement strategy. Inclusive education provides special provisions for the less privileged and disadvantaged children and youth; user-friendly infrastructure, teaching and learning materials and provision of expert teachers.”
“Education is a human right. The Education Plus Initiative is driving policy changes in Africa. Education Plus seeks to keep adolescent girls and young women in school by simply unequivocally saying no to child marriage, no to violence, no to HIV infections, no to gender-related stigma, and of course, no to harmful practices. We want to keep girls in secondary education and make sure they stay there and complete their education. We do that by supporting sexual and reproductive health and rights, comprehensive sexuality education and work for integration HIV awareness, preventing and managing learners pregnancies and addressing school-related gender-based violence.”
“We need to scale up effective interventions to increase HIV knowledge and transform gender norms, and hence girls’ access to services. We should explore the potential of innovative solutions offered by digital technologies to mobilize and provide young women and adolescent girls with comprehensive HIV information. Let's do more, particularly for those girls living with HIV to be meaningfully engaged in the HIV response. Young women must have a formal seat and a safe space to raise their needs. let's move from rhetoric to action.”
“The numbers are unfortunately very clear: highest adolescent pregnancy rates of the world are in sub-Saharan Africa, highest percentages of women first married or in union before 18, young women more than 3 times as likely of HIV infection, or unacceptably high rates of justification of wife beating among adolescents. Fortunately, we benefit from a strong set of political commitments and strategies to face these issues. There is the Education Plus Initiative, the WCA Commitment for Educated, Healthy and Thriving Adolescents and Young People, the ESA Commitment, and the AU Continental Strategy on Education for Health and Wellbeing of Young People in Africa. It is high time to convert the commitments and strategies in concrete results for adolescent girls and young women.”
“Girls need an affirming environment. Where there's ignorance, there's a lot of resistance to education and sexuality education in the curriculum. We need to engage to change the environment, talking with parents, men and boys, community members and leaders for them to have access to information because they have a great influence on the lives of these young people. We need inclusive advocacy, especially the rural grassroots and true localization of information and interventions.”
Our work
Related
 Zambia - an HIV response at a crossroads
Zambia - an HIV response at a crossroads

24 February 2025


Press Release
UNAIDS urges sub-Saharan African countries and global partners to ensure children living with HIV are on life-saving treatment and to stop new infections
14 June 2024 14 June 2024GENEVA, 14 June 2024—On the International day of the African Child this 16 June, UNAIDS is urging African governments and global partners to provide treatment for children living with HIV and to stop new infections among children. The latest data show that only 56% of children living with HIV were on life-saving antiretroviral therapy in 2022 in sub-Saharan Africa compared to 83% of adults globally. Without access to treatment, 50% of infants living with HIV will die before their second birthday.
“As sub-Saharan Africa continues to carry the highest burden of HIV, children are not spared. Over 1.3 million children are living with HIV in the region and too many do not have access to life-saving treatment,” said Ms Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “This highlights the urgency with which we need to tackle this pandemic among children and ensure access to life-saving treatment. No child should be left behind.”
Children are among the age group hardest to reach with HIV testing which is hampering efforts to diagnose and treat children living with HIV. Around 70 000 children died of AIDS-related illnesses in 2022 in sub-Saharan Africa because they did not have access to antiretroviral treatment.
In addition, many children are still becoming infected with HIV in sub-Saharan Africa. Across sub-Sharan Africa, around 110 000 children became infected in 2022 alone. While some countries like Namibia, which has recently reached a key milestone in the pathway toward eliminating vertical transmission of HIV and hepatitis B, are making fast progress, this is not the case in many other countries, particularly in Western and Central Africa including Nigeria, Ghana, Cameroon and the Democratic Republic of Congo which still account for some of the highest numbers of children newly infected with HIV.
“We know the path that ends AIDS. With all the science available, there is no reason for any child to die of AIDS in 2024. So too, we can ensure that all babies are born HIV free and stay HIV free. It is vital to ensure that pregnant and breastfeeding women have all the support they need to access medicine to avoid the transmission of HIV to babies while mothers are pregnant and breastfeeding,” said Ms Winnie Byanyima. “We need to redouble efforts in countries to end AIDS in children and close the HIV treatment gap between adults and children.”
Countries are working to end AIDS in children and this work is supported by the work of UNAIDS and its Cosponsors including UNICEF, the World Health Organization, and partners including PEPFAR, the Global Fund, the Elizabeth Glaser Pediatric AIDS Foundation (EGPAF), the Gates Foundation, Global Alliance to End AIDS in Children and others.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.



