Epidemiology
Documents
Western and Central Europe and North America regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
There has been a 24% drop in the annual number of new HIV infections in western and central Europe and North America since 2010, and the number of AIDS-related deaths has declined by 34%. Numbers of new HIV infections among sex workers and their clients, however, have not declined at the same rate. Despite data showing ongoing progress in HIV prevention, persistent social and economic factors, including stigma and discrimination, continue to cause health disparities, compromising the health and well-being of people from marginalized communities. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 UNAIDS urges that all essential HIV services must continue while U.S. pauses its funding for foreign aid
UNAIDS urges that all essential HIV services must continue while U.S. pauses its funding for foreign aid

01 February 2025
Documents
Western and Central Africa regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
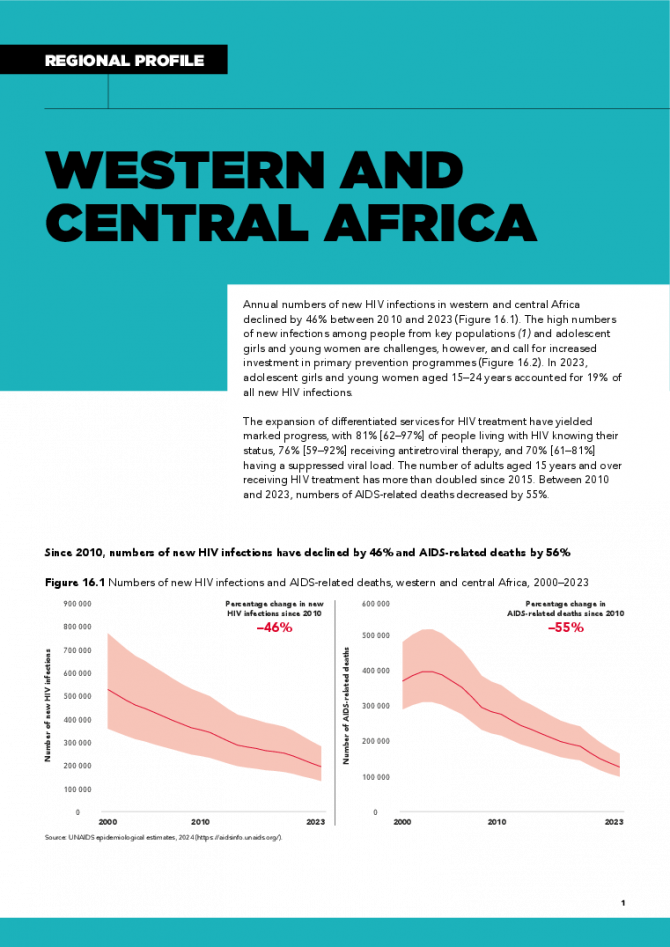
Annual numbers of new HIV infections in western and central Africa declined by 46% between 2010 and 2023. The high numbers of new infections among people from key populations and adolescent girls and young women are challenges, however, and call for increased investment in primary prevention programmes. In 2023, adolescent girls and young women aged 15–24 years accounted for 19% of all new HIV infections. The expansion of differentiated services for HIV treatment have yielded marked progress, with 81% [62–97%] of people living with HIV knowing their status, 76% [59–92%] receiving antiretroviral therapy, and 70% [61–81%] having a suppressed viral load. The number of adults aged 15 years and over receiving HIV treatment has more than doubled since 2015. Between 2010 and 2023, numbers of AIDS-related deaths decreased by 55%. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
 Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment
Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment

21 January 2025
Documents
Middle East and North Africa regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
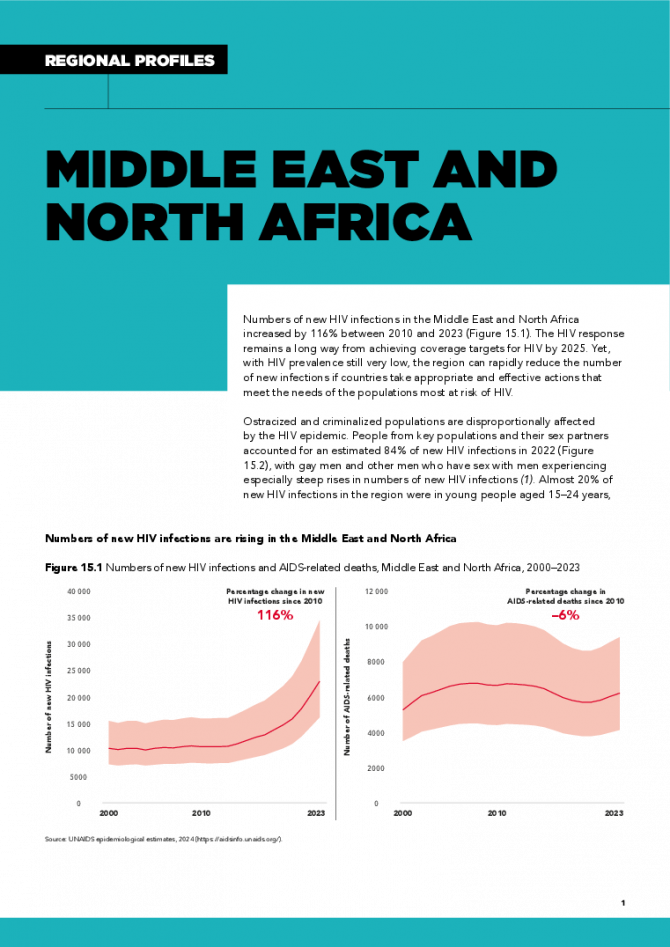
Numbers of new HIV infections in the Middle East and North Africa increased by 116% between 2010 and 2023. The HIV response remains a long way from achieving coverage targets for HIV by 2025. Yet, with HIV prevalence still very low, the region can rapidly reduce the number of new infections if countries take appropriate and effective actions that meet the needs of the populations most at risk of HIV. Ostracized and criminalized populations are disproportionally affected by the HIV epidemic. People from key populations and their sex partners accounted for an estimated 84% of new HIV infections in 2022, with gay men and other men who have sex with men experiencing especially steep rises in numbers of new HIV infections. Almost 20% of new HIV infections in the region were in young people aged 15–24 years, the majority of them male (55%). These epidemic patterns underscore the need for scaled-up HIV interventions for people from key populations and especially young people, and for reducing the societal and structural barriers that limit their access to needed services. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
 Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment
Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment

21 January 2025
Documents
Latin America — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
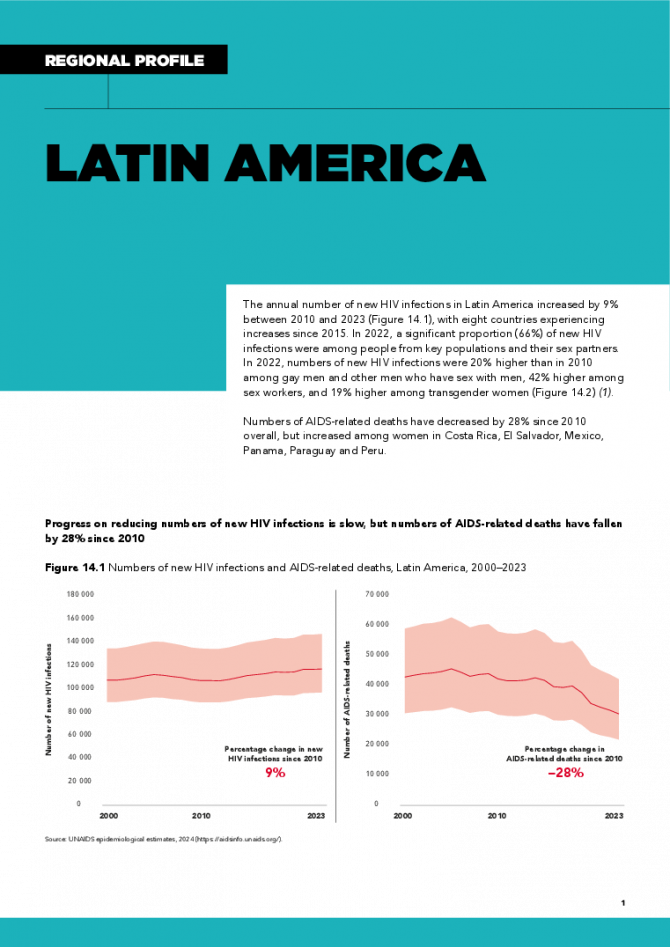
The annual number of new HIV infections in Latin America increased by 9% between 2010 and 2023, with eight countries experiencing increases since 2015. In 2022, a significant proportion (66%) of new HIV infections were among people from key populations and their sex partners. In 2022, numbers of new HIV infections were 20% higher than in 2010 among gay men and other men who have sex with men, 42% higher among sex workers, and 19% higher among transgender women. Numbers of AIDS-related deaths have decreased by 28% since 2010 overall, but increased among women in Costa Rica, El Salvador, Mexico, Panama, Paraguay and Peru. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 The critical impact of the PEPFAR funding freeze for HIV across Latin America and the Caribbean
The critical impact of the PEPFAR funding freeze for HIV across Latin America and the Caribbean
19 February 2025
Documents
Eastern and Southern Africa regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
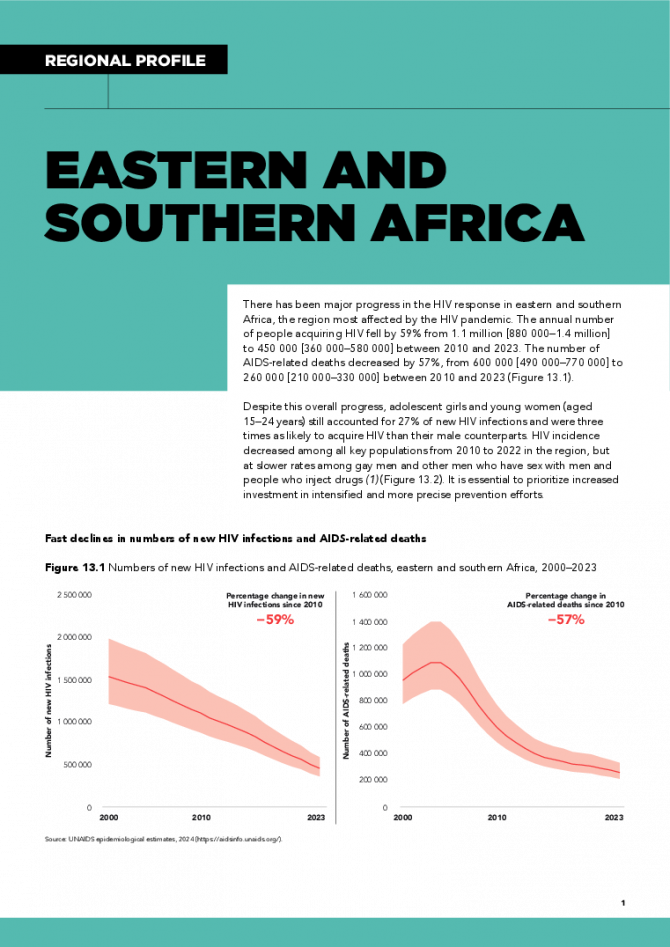
There has been major progress in the HIV response in eastern and southern Africa, the region most affected by the HIV pandemic. The annual number of people acquiring HIV fell by 59% from 1.1 million [880 000–1.4 million] to 450 000 [360 000–580 000] between 2010 and 2023. The number of AIDS-related deaths decreased by 57%, from 600 000 [490 000–770 000] to 260 000 [210 000–330 000] between 2010 and 2023. Despite this overall progress, adolescent girls and young women (aged 15–24 years) still accounted for 27% of new HIV infections and were three times as likely to acquire HIV than their male counterparts. HIV incidence decreased among all key populations from 2010 to 2022 in the region, but at slower rates among gay men and other men who have sex with men and people who inject drugs. It is essential to prioritize increased investment in intensified and more precise prevention efforts. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 Zambia - an HIV response at a crossroads
Zambia - an HIV response at a crossroads

24 February 2025
 Status of HIV Programmes in Botswana
Status of HIV Programmes in Botswana

20 February 2025
 Government ensures continuity of treatment in Malawi
Government ensures continuity of treatment in Malawi

10 February 2025
Documents
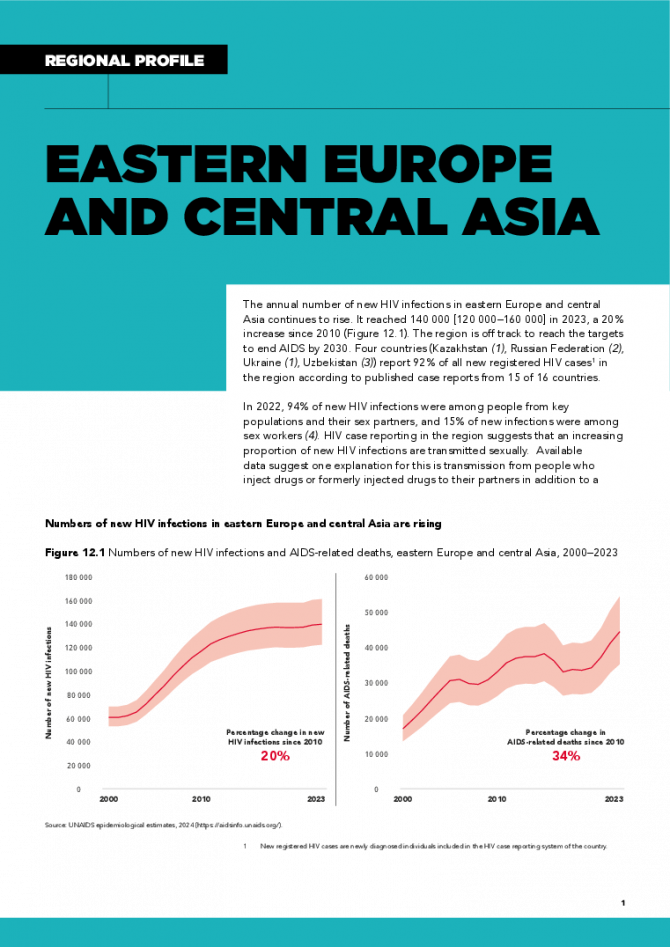
Eastern Europe and Central Asia regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
The annual number of new HIV infections in eastern Europe and central Asia continues to rise. It reached 140 000 [120 000–160 000] in 2023, a 20% increase since 2010 . The region is off track to reach the targets to end AIDS by 2030. Four countries (Kazakhstan, Russian Federation, Ukraine, Uzbekistan) report 92% of all new registered HIV cases in the region according to published case reports from 15 of 16 countries. In 2022, 94% of new HIV infections were among people from key populations and their sex partners, and 15% of new infections were among sex workers. HIV case reporting in the region suggests that an increasing proportion of new HIV infections are transmitted sexually. Available data suggest one explanation for this is transmission from people who inject drugs or formerly injected drugs to their partners in addition to a growing recognition of transmission among men who have sex with men. Unsafe drug injecting practices are a key factor in the region’s epidemic, representing 27% of new HIV infections. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery
Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery

20 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
Documents
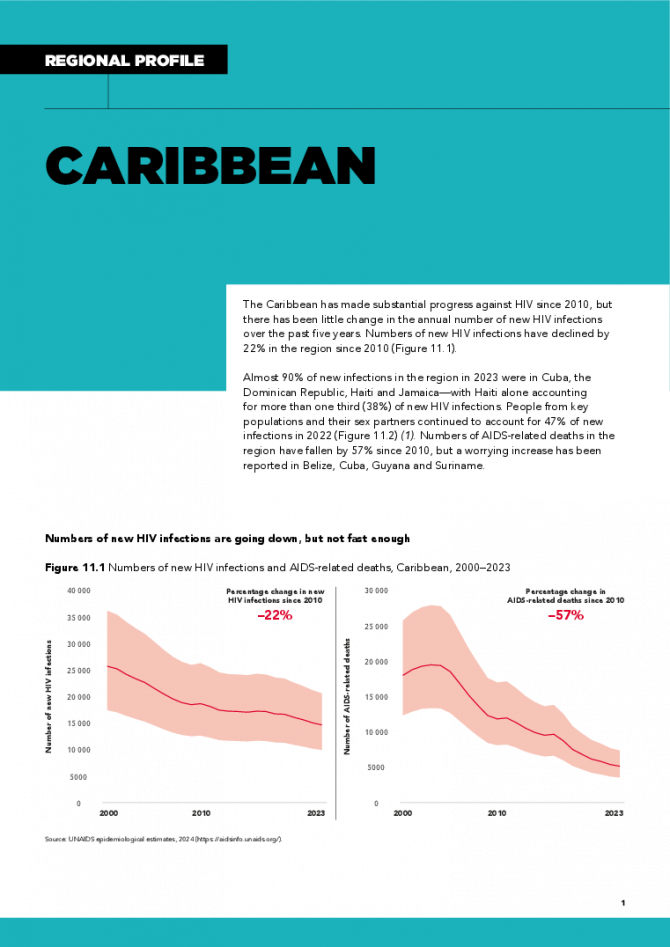
Caribbean regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
The Caribbean has made substantial progress against HIV since 2010, but there has been little change in the annual number of new HIV infections over the past five years. Numbers of new HIV infections have declined by 22% in the region since 2010. Almost 90% of new infections in the region in 2023 were in Cuba, the Dominican Republic, Haiti and Jamaica—with Haiti alone accounting for more than one third (38%) of new HIV infections. People from key populations and their sex partners continued to account for 47% of new infections in 2022. Numbers of AIDS-related deaths in the region have fallen by 57% since 2010, but a worrying increase has been reported in Belize, Cuba, Guyana and Suriname. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
 Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment
Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment

21 January 2025
Documents
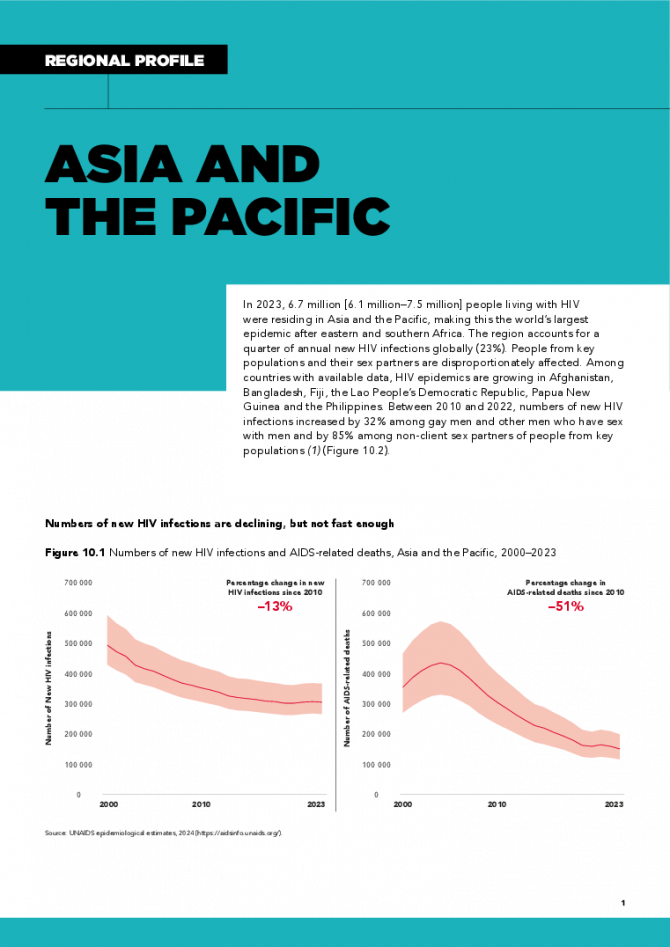
Asia and the Pacific regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
In 2023, 6.7 million [6.1 million–7.5 million] people living with HIV were residing in Asia and the Pacific, making this the world’s largest epidemic after eastern and southern Africa. The region accounts for a quarter of annual new HIV infections globally (23%). People from key populations and their sex partners are disproportionately affected. Among countries with available data, HIV epidemics are growing in Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Fiji, the Lao People’s Democratic Republic, Papua New Guinea and the Philippines. Between 2010 and 2022, numbers of new HIV infections increased by 32% among gay men and other men who have sex with men and by 85% among non-client sex partners of people from key populations. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia
Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia

24 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
Documents
2024 global AIDS report — The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
This UNAIDS 2024 report brings together new data and case studies which demonstrate that the decisions and policy choices taken by world leaders this year will decide the fate of millions of lives and whether the world’s deadliest pandemic is overcome. Related links: Press release | Special web site | Executive summary | Fact sheet | Video playlist | Epidemiology slides | Data on HIV | Annex 2: Methods Regional profiles: Asia and the Pacific | Caribbean | Eastern Europe and Central Asia | Eastern and Southern Africa| Latin America | Middle East and North Africa | Western and Central Africa | Western and Central Europe and North America Thematic briefing notes: People living with HIV | Gay men and other men who have sex with men | Transgender people | Sex workers | People who inject drugs | People in prisons and other closed settings | Adolescent girls and young women | Other translations: German
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025
 UNAIDS urges that all essential HIV services must continue while U.S. pauses its funding for foreign aid
UNAIDS urges that all essential HIV services must continue while U.S. pauses its funding for foreign aid

01 February 2025





Press Release
UNAIDS Executive Director and Inequality Council urge G20 to back bold network on medicine production and address the social determinants of pandemics
06 June 2024 06 June 2024SALVADOR, BRAZIL, 6 June 2024—At the G20 preparatory meeting in Brazil, Executive Director of UNAIDS and Under-Secretary-General of the United Nations, Winnie Byanyima, today urged governments to support a new G20 Alliance, proposed by the Brazilian government, to enable life-saving medicines to be produced in every part of the world. Co-Chair of the Global Council on Inequality, AIDS, and Pandemics Sir Michael Marmot also called on G20 delegates to address the social determinants of pandemics, such as education and human rights, as a concrete part of the G20’s pandemic preparedness efforts.
The medicines initiative aims to create a global alliance of local and regional manufacturers of drugs, vaccines and other health technologies and unite a diversified network of local and regional producers to ensure an adequate supply of medicines and technologies for everyone, everywhere.
Ms Byanyima called on the G20 to ensure that the alliance takes a bold approach that strengthens efforts to fight dengue and other neglected diseases, improves global defences against future pandemics, and accelerates access to the latest technologies against HIV.
“Focusing together on neglected diseases and the major killers of vulnerable people is not only strategic, it can deliver during future pandemics,” said Ms Byanyima. “We can be thankful that, for all its devastation, COVID-19 responded to a vaccine, unlike HIV. There is no reason to believe the next pandemic will be like COVID-19. We need to build capacity for vaccines and treatment.”
The responses to many diseases that impact vulnerable populations – from Ebola to Mpox to HIV – would benefit greatly from this initiative, Ms Byanyima told governments today.
“The alliance can supercharge the HIV response. It can supercharge the production pipeline for innovations,” said Ms Byanyima. “An alliance could also build capacity where it is not. The majority of people living with HIV, who get up every day and take that pill, live in Africa. But few of those drugs are actually made in African countries.”
“Brazil’s leadership and experience in this area has inspired this global effort. And we need the support of the whole G20 to make it a success.”
The agenda of the G20 meeting on health is helping to push global health policy towards tackling the systemic inequalities that drive ill-health. UNAIDS is coordinating a Global Council on Inequality, AIDS and Pandemics that is gathering evidence on how inequalities deepen and prolong pandemics, including HIV and COVID-19. That evidence is being shared with policymakers at the G20 and other international forums.
On Monday, world-renowned expert Sir Michael Marmot gave a keynote address the G20 meeting on the potential of focusing concretely on the social determinants to strengthen pandemic preparedness, predict the severity of future pandemics, and improve the efficacy of responses.
“Improving health leads to a better economy. And the way to improve health is not just to invest in healthcare, but in the social determinants of health,” Professor Marmot said. “For example, in Botswana, there is clear evidence that the longer young people remain in education, the lower the rates of HIV.”
Addressing social determinants, building manufacturing capacity, and enabling people everywhere to access the whole range of HIV prevention and treatment options, including the latest long-acting technologies, is vital for ensuring the end of AIDS as a public health threat. The G20 initiatives would play a key role in achieving that objective in a sustainable way, while also contributing to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals and supporting efforts to quickly respond to the next pandemic.
Notes for editors
Brazil's main proposal for the G20 Health Working Group is to establish the creation of an Alliance for Regional Production and Innovation. This initiative aims to establish a network that brings together key actors, including countries, academia, private sector, and international organizations, for research and development and production of vaccines, medicines, diagnostics, and strategic supplies to combat diseases with strong social determinants and that mainly affect vulnerable populations, such as dengue, malaria, tuberculosis, Chagas disease, and leprosy. For more information on the G20 Health Working Group, see the G20 website: https://www.g20.org/en/tracks/sherpa-track/health
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.