Topics



Press Release
UNAIDS rallies faith leaders in support of the HIV response at the Vatican in Rome
13 February 2025 13 February 2025ROME/GENEVA, 13 February 2025—Today, the Executive Director of UNAIDS Winnie Byanyima met with leaders in the Catholic Church as part of a global effort to mobilize voices of faith to stand up in a moment of crisis for the AIDS response.
Speaking to communities of faith at events in Vatican City Ms Byanyima said, “Two weeks ago, the world’s biggest AIDS relief programme was paused. 20 million people living with HIV rely on the United States Government for the medication they need to stay alive and prevent HIV infection. A humanitarian waiver was issued allowing some lifesaving medicines to be distributed. That is welcome. But the programme’s future remains uncertain.”
HIV clinics around the world have shuttered and HIV prevention and treatment programmes have been derailed. Without funding from the United States, within four years, 6.3 million people will die and 8.9 million will newly acquire HIV. Around 370 000 babies will acquire HIV, and without treatment, half will not live to see their second birthday.
The AIDS movement has been through this before. When people were dying from neglect in the early days of HIV in Africa, Asia, and Latin America it was the churches that stepped up to care for the sick and dying. Catholic Leaders have called urgently for the restoration of HIV programmes and other crucial international funding.
“The church has a powerful voice that reaches into communities around the world,” said Ms Byanyima. “We need the voice of faith and the leadership of faith in the world that we are in today–this time to defend the global AIDS response and lifesaving programmes like PEPFAR. Human life is sacred–and today, it hangs in the balance.”
The AIDS response has recently been presented with a game-changing opportunity. In 2024, Gilead announced that its breakthrough medicine lenacapavir can prevent HIV with injections just twice a year. If made available and affordable to all in need, this could present the opportunity to end what has been the deadliest pandemic in generations.
“Humanity has made incredible progress tackling AIDS. But let me be clear. Without funding for the HIV response, we risk losing all we have gained and could see a resurgent AIDS pandemic. And if we want national governments to plug the gap, we must give them the means to do so and support a sustainable transition,” said Ms Byanyima.
Even before the US announcement, the AIDS response had a financing gap of US$ 9.5 billion. UNAIDS estimates that US$ 29.3 billion is needed to get countries on track and end the AIDS pandemic by 2030.
“That is why at the Vatican today we are also focused on enabling low- and middle-income countries to raise domestic funding for the HIV response. Proper taxation and relieving the crushing burden of debt are critical.”
UNAIDS will continue to partner with the United States, other donors and countries most affected by HIV to ensure a robust and sustainable response to HIV and to achieve our collective goal of ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030.
UNAIDS is documenting the Impact of recent U.S. shifts on the global HIV response online.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.

Feature Story
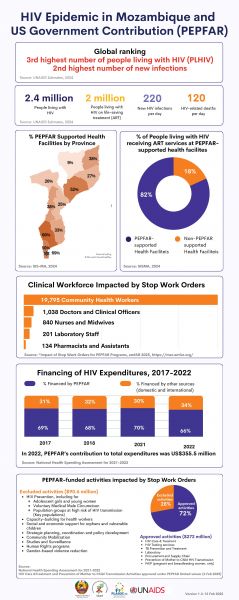
HIV Epidemic in Mozambique and US Government Contribution (PEPFAR)
18 February 2025
18 February 2025 18 February 2025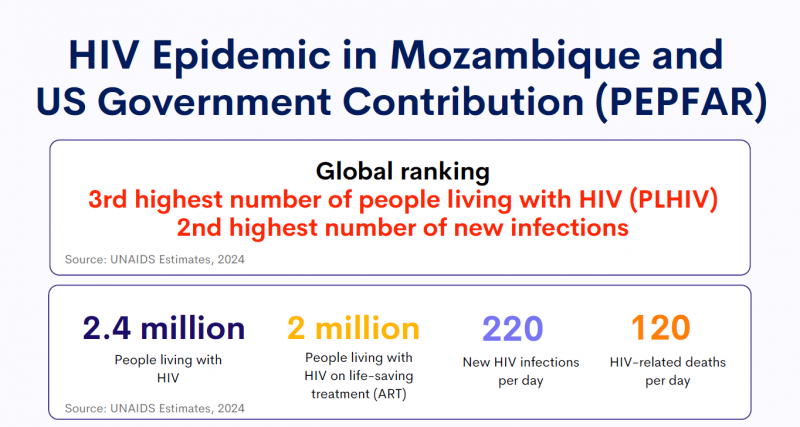
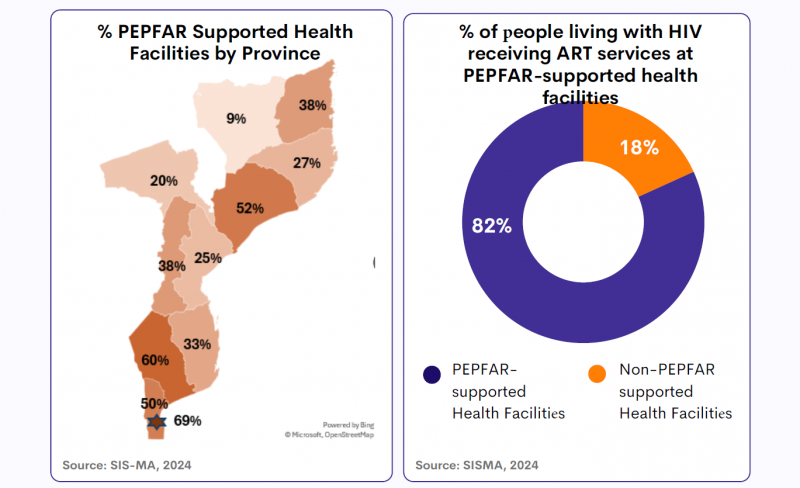

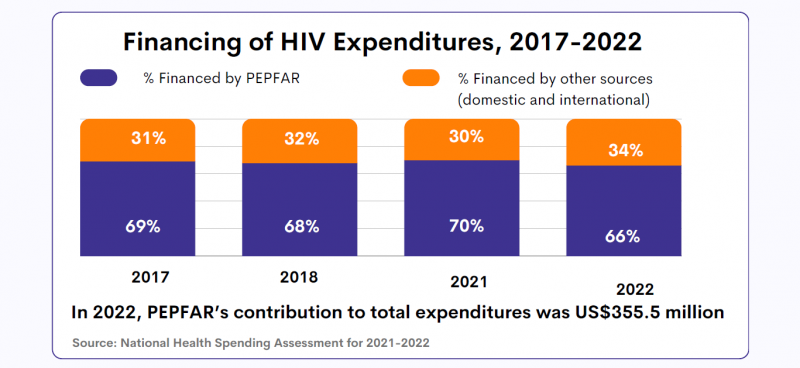
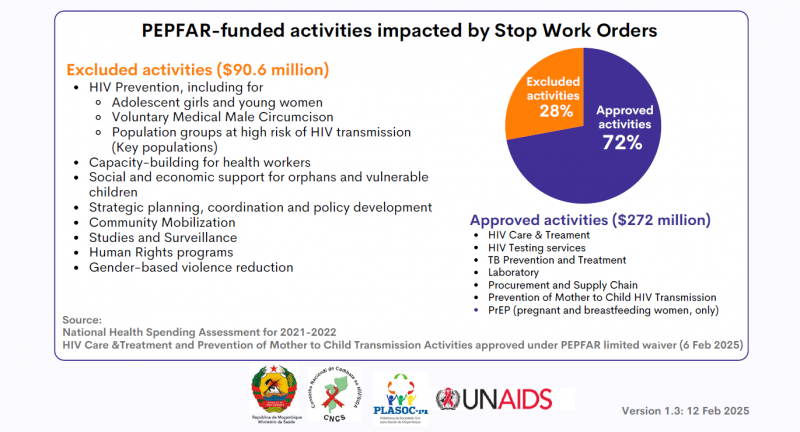
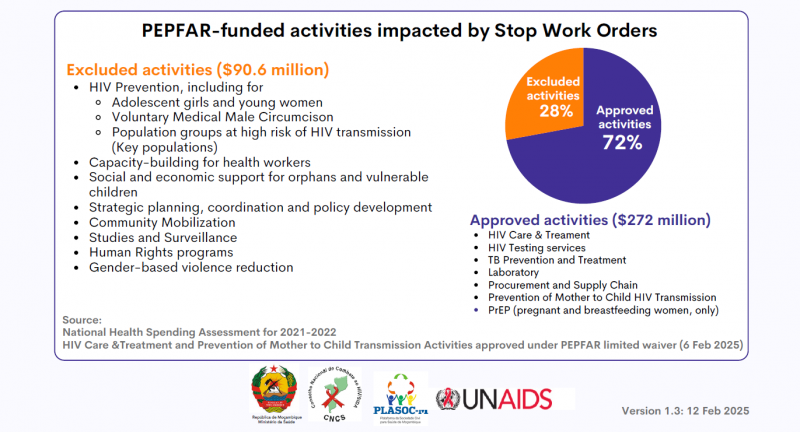
HIV epidemic in Mozambique and US Government contribution (PEPFAR)
Region/country


Press Statement
UNAIDS urges countries to invest in HIV prevention as key to ending AIDS
13 February 2025 13 February 2025Despite proven effectiveness, UNAIDS is alarmed by a decrease in condom use in several countries
Geneva, 13 February 2025– On International Condom Day, UNAIDS and partners are calling for HIV prevention efforts to be stepped up. In 2023, around 3,500 people became newly infected with HIV every day, bringing the total number of people newly infected in 2023 to 1.3 million.
One of the most effective, low-cost HIV prevention tools available today are condoms which are 98% effective when used correctly and consistently. Condom use has averted an estimated 117 million new HIV infections globally from 1990 to 2019 however, new data reveal that there has been a decline of 6-15% in condom use in a number of countries, according to the Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS), a Condom Landscape Analysis, and the World Health Organization (WHO.)
For the past few years, the estimated global public sector and subsidized condom procurement declined by an average of 30% from peak procurement in 2011. This decline occurred despite the population in Africa growing to an estimated 400 million since 2010. As a consequence, fewer free or subsidized condoms are available per capita in Africa now than a decade ago.
"Condoms are a critical part of a comprehensive approach to HIV prevention and public health.. We also want to make sure medical breakthroughs like long-acting HIV medicines are affordable and accessible to all to give people most at risk additional HIV prevention options,” said Angeli Achrekar, UNAIDS Deputy Executive Director for Programmes.
Public and international investment in condom distribution, education, and social marketing has decreased in recent years. As a result, a new generation of young people has not been exposed to condom promotion.
As new drugs and injectable HIV prevention methods gain ground in the next few years, condoms as well as PrEP (pills for people who may be at risk of acquiring HIV), voluntary medical male circumcision and treatment remain essential to achieving global health targets related to HIV and sexual and reproductive health.
Your Health. Your Power. Your Choice. Your Future.
International Condom Day is a reminder of the importance of protecting one’s own health. This year's theme focuses on the importance of ensuring equitable access to condoms, combating myths and misconceptions, and encouraging open conversations about preventing new HIV infections.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Watch: The truth about condoms
Our work

Feature Story
A crisis unfolding: hard-won progress in Ethiopia’s HIV response at risk
13 February 2025
13 February 2025 13 February 2025Ethiopia has made significant progress in its HIV response in recent years and is on track to reach the UNAIDS 95-95-95 targets with 90% of people living with HIV in the country being aware of their HIV status; 94% of those diagnosed with HIV receiving antiretroviral (ARV) therapy; and 96% of people on ARV therapy achieving viral suppression.
But now, that progress is at risk. The recent pause in United States foreign assistance poses a direct threat to the lives and well-being of thousands of people living with HIV in Ethiopia and millions globally. Critical services are grinding to a halt, leaving people who rely on them facing an uncertain and dangerous future.
Ethiopia is heavily reliant on external funding for its AIDS response. PEPFAR provides 53% of HIV funding in the country. In 2023, UNAIDS’ estimates show that there were 610 000 people living with HIV in Ethiopia, 510 000 of whom were accessing antiretroviral treatment.
For women living with HIV, uncertainty is growing. Limited and unclear communication from healthcare providers and policymakers has left them in the dark about treatment changes, medication availability, and service disruptions. With no clear answers, they are forced to rely on rumors, fueling fear and anxiety.
“We don’t know what’s happening. Are services being cut permanently? Will we still get our medication next month? No one is telling us anything,” one woman shared.
To make matters worse, case workers and counsellors—once a vital source of medical and emotional support—are disappearing. These professionals were more than healthcare providers; they were trusted confidants who ensured women received care in a stigma-free environment. Their absence is leaving many feeling abandoned.
“They understood our struggles, checked in on us, and made sure we had what we needed,” another woman explained. “Without them, we feel forgotten.”
As services become increasingly unreliable, distress and fear are taking hold.
Shortages and desperate measures
Funding cuts bring shortages, and for women living with HIV, the fear of running out of medication is overwhelming. Access to antiretroviral therapy (ART) is essential—it keeps people alive. Yet many are already facing supply disruptions, and whispers of medication shortages are spreading panic.
“If I can’t get my medicine, what happens to me?” one woman asked. Women living with HIV who have been healthy for years now fear an uncertain future where their treatment is no longer guaranteed. People living with HIV who do not access antiretroviral therapy will eventually develop AIDS and die. To cope, many have resorted to stockpiling medication, traveling long distances and spending entire days at clinics in hopes of securing extra supplies. While understandable, this survival strategy comes at a heavy cost—disrupting work, family life, and daily routines. No one should have to live in fear of their next refill. The urgent need for stable, uninterrupted HIV treatment cannot be overstated.
Adding to the crisis, shortages extend beyond medication. The dwindling supply of test kits, including viral load tests, is threatening the future of diagnosis and monitoring. These tests are crucial to ensure that people living with HIV maintain undetectable viral levels, reducing transmission risks and protecting their health.
Fears have also been expressed around the availability of medications for HIV prevention, particularly for the prevention of vertical transmission of HIV. If the current pause in the supply of medical resources continues, the availability of these vital medications could be severely compromised, putting the lives of women and children at even greater risk. For women living with HIV who are pregnant, a lack of lifesaving medications for themselves also means their children can be born with HIV even though this is entirely preventable.
Without test kits and prevention measures, undiagnosed and untreated cases could rise dangerously. “We can’t afford to go backward,” one woman said.
A Plea for Action
The voices of these women reveal a stark and urgent reality—funding cuts have left people living with HIV in a state of uncertainty, with no clear path forward.
"Urgent intervention is needed,” stressed Tina Boonto, Country Director for UNAIDS Ethiopia. “UNAIDS is gathering information and developing funding solutions to address the shortfall, with proposals for both the government and external partners to ensure continuity of critical services. We hope Ethiopia's government will step up and lead in covering these essential services. We must act now to safeguard gains that have been made and succeed in securing sustainable support to people living with HIV."
While the future remains uncertain, one thing is clear: without swift action, the hard-won progress in Ethiopia’s HIV response is at risk.
Impact of recent U.S. shifts on the global HIV response
Region/country


Press Release
UNAIDS urges that all essential HIV services must continue while U.S. pauses its funding for foreign aid
01 February 2025 01 February 2025GENEVA, 1 February 2025— The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) is urging for a continuation of all essential HIV services while the United States pauses its funding for foreign aid.
On 29 January, UNAIDS welcomed the news that United States Secretary of State, Marco Rubio, had approved an “Emergency Humanitarian Waiver,” allowing people to continue accessing lifesaving HIV treatment funded by the U.S. in 55 countries worldwide. More than 20 million people - two-thirds of all people living with HIV accessing HIV treatment globally - are directly supported by the United States President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR).
While continuity of HIV treatment is essential, services must continue to be monitored, and oversight provided for quality. Other critical HIV services for people, especially marginalized people including children, women, and key populations, must continue. Last year, PEPFAR provided over 83.8 million people with critical HIV testing services; reached 2.3 million adolescent girls and young women with HIV prevention services; 6.6 million orphans, vulnerable children, and their caregivers received HIV care and support; and 2.5 million people were newly enrolled on pre-exposure prophylaxis to prevent HIV infection.
Since PEPFAR was created, the United States has been steadfast in its leadership in the fight against HIV. The U.S. has saved millions of lives through its programmes, particularly in the countries most affected by HIV. PEPFAR has had remarkable results in stopping new infections and expanding access to HIV treatment – and this must continue.
Globally, there are 1.3 million people that are newly infected with HIV every year, 3,500 every day. Young women and girls in Africa are at alarming high risk of HIV, where 3,100 young women and girls aged 15 to 24 years become infected with HIV every week and at least half of all people from key populations are not being reached with prevention services.
Pregnant women in high HIV prevalent areas must be tested for HIV to determine whether they are living with HIV so they can protect their baby by taking antiretroviral therapy prior to birth. As a result, babies will be born HIV-free.
Many organizations providing services for people living with HIV that are funded, or partly funded, by PEPFAR have reported they will shut their doors due to the funding pause with lack of clarity and great uncertainty about the future. UNAIDS is evaluating the impact and will provide routine and real-time updates to share the latest global and country information, data, guidance, and references.
“PEPFAR gave us hope and now the executive order is shattering the very hope it offered for all people living with HIV and our families. As communities we are in shock with the continued closure of clinics. We resolutely demand that all our governments come in haste to fill the gap in human resources needed at the moment to ensure sustainability of HIV service delivery,” said Flavia Kyomukama, Executive Director at National Forum of People Living with HIV Network Uganda (NAFOPHANU).
Zimbabwe`s umbrella network of people living with HIV (ZNNP+) stated that the implementation of stop work orders has led to significant fears, including reduced access to essential services, loss of community trust and long-term health outcomes.
As the waiver is effective for a review period of all U.S. foreign development assistance, future coverage of HIV services - including for treatment - remains unclear and the lives of the millions of people supported by PEPFAR are in jeopardy and could be at stake.
Anele Yawa, General Secretary for the Treatment Action Campaign is worried. "The PEPFAR-fund freeze will take South Africa and the world back in terms of the gains we have made in our response to HIV,” he said. "We are asking ourselves how are we going to cope in the next three months as people are going to be left behind in terms of prevention, treatment and care."
At a moment when the world can finally get the upper hand on one of the world’s deadliest pandemics, aided by new long-acting HIV prevention and treatment medicines coming to market this year, UNAIDS urges the U.S. to continue its unparalleled leadership and accelerate, not diminish, efforts to end AIDS.
UNAIDS looks forward to partnering with the United States, other donors and countries most affected by HIV to ensure a robust and sustainable response to HIV and to achieve our collective goal of ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Region/country


Press Statement
UNAIDS welcomes the decision by the US Secretary of State to continue life-saving HIV treatment and convenes partners to assess and mitigate impacts on HIV services
29 January 2025 29 January 2025GENEVA, 29 January 2025— The United States Secretary of State, Marco Rubio, has approved an “Emergency Humanitarian Waiver”, which will allow people to continue accessing HIV treatment funded by the US across 55 countries worldwide. More than 20 million people living with HIV, representing two-thirds of all people living with HIV receiving treatment globally, are directly supported by the United States President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) - the world’s leading HIV initiative.
“UNAIDS welcomes this waiver from the US government which ensures that millions of people living with HIV can continue to receive life-saving HIV medication during the assessment of US foreign development assistance,” said UNAIDS Executive Director, Winnie Byanyima. “This urgent decision recognizes PEPFAR’s critical role in the AIDS response and restores hope to people living with HIV.”
In recent days, the US Department of State announced an immediate 90-day funding pause for all foreign assistance, including for funding and services supported by PEPFAR. The executive order announcing a “90-day pause in United States foreign development assistance for assessment of programmatic efficiencies and consistency with United States foreign policy” was one of the first major foreign policy decisions of the new administration. This waiver approves the continuation or resumption of “life-saving humanitarian assistance” which applies to core life-saving medicine and medical services, including HIV treatment, as well as to supplies necessary to deliver such assistance.
UNAIDS will continue efforts to ensure that all people living with or affected by HIV are served and that other key components of PEPFAR’s life-saving efforts, including service delivery and services for HIV prevention, care, and support for orphans and vulnerable children are continued.
UNAIDS is serving in its essential role to mobilize and convene partners, governments, and communities across the globe at the country level to assess and mitigate the impact of the pause on the continuity of essential HIV services.
UNAIDS has encouraged President Donald J. Trump to prioritize the U.S. Government’s leadership in the global HIV response to achieve the shared goal of ending AIDS.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Region/country
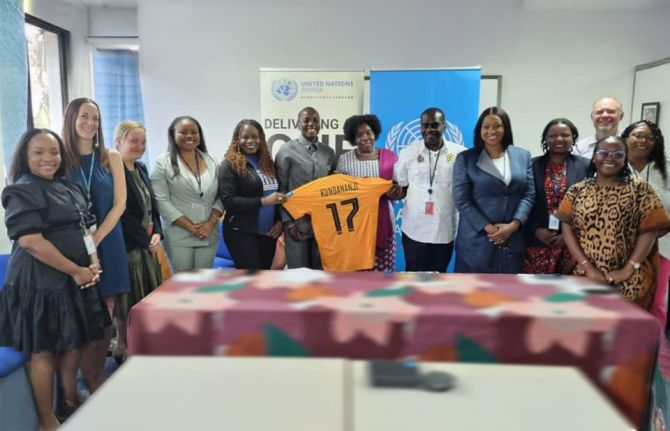


Press Release
Zambian football star Racheal Kundananji named UNAIDS Goodwill Ambassador for Education Plus in Zambia
23 January 2025 23 January 2025GENEVA/LUSAKA, 30 January 2025—Zambian football star Racheal Kundananji has been appointed as a UNAIDS Goodwill Ambassador to champion the fight to end AIDS as a public health threat in Zambia.
In her new role, Ms Kundananji will work with UNAIDS to champion HIV prevention, advocate for girls’ education to help reduce new HIV infections and sexually transmitted infections. She will also highlight the importance of preventing teenage pregnancy and advocate for an increase in HIV testing and access to health services for young people.
“I am so happy to be collaborating with UNAIDS to end AIDS as a public health threat in my country Zambia,” said Ms Kundananji. “Achieving this will require a collective effort, including ensuring that all young people in Zambia, particularly girls, remain in secondary education to reduce their risk of HIV infection and provide them with better economic opportunities.”
Ms Kundananji is already using her platform to drive change. She founded the Racheal Kundananji Legacy Foundation to harness the power of sport to address gender-based violence, sexual and reproductive health, and child marriage, demonstrating her deep commitment to empowering women and girls and tackling gender inequality.
“Ms Kundananji shares UNAIDS’ vision of ending AIDS as public health threat in Zambia by 2030,” said Isaac Ahemesah, UNAIDS Country Director for Zambia. “That world is possible. Leaders must ensure that girls stay in school and increase political and financial support to end the AIDS epidemic, by stopping new HIV infections and ensuring that everyone who needs treatment for HIV has access.”
United Nations Resident Coordinator for Zambia, Ms. Beatrice Mutali, praised Ms Kundananji’s dedication to advancing and promoting HIV awareness, testing, prevention and the Education Plus Initiative, which promotes girls’ school attendance. She also called for gender equality in sports, emphasizing the need for equal pay for equal work for women and men in all fields.
Ms Kundananji shattered the global women’s football transfer record, becoming the most expensive player in the history of women’s football. She is the first African footballer - male or female - to break the world transfer record. Now playing for Bay FC, an American professional women's soccer team based in the San Francisco Bay Area, she competes in the prestigious National Women's Soccer League, solidifying her place as a trailblazer on the global football stage.
Ms Kundananji has represented the Zambian National team since 2018 at the African Cup of Nations, FIFA World Cup Qualifiers and the Olympic qualifiers. Ms Kundananji has also played for Madrid Club de Fútbol Femenino among others.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Region/country


Press Statement
UNAIDS encourages President Donald J. Trump to continue the strong leadership of the United States of America in the global AIDS response
22 January 2025 22 January 2025GENEVA, 22 January 2025—UNAIDS congratulates President Donald J. Trump as the 47th President of the United States of America.
“Under President Trump’s leadership, the United States of America has the opportunity to accelerate the global HIV response and end AIDS by 2030,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS.
During President Trump’s first administration, he demonstrated strong leadership in the fight against AIDS by launching the groundbreaking initiative Ending the HIV Epidemic in the US and reaffirming the United States of America's steadfast commitment to the United States President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR), the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria (Global Fund), and the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS).
For more than two decades, the United States Government has led in the global HIV response, saving more than 26 million lives. The country's unwavering commitment to addressing HIV stands as a global gold standard of leadership.
Since the start of the AIDS pandemic, innovations led by the United States in HIV prevention and treatment technologies have saved millions of lives around the world.
Today, we are on the brink of ending AIDS thanks to advances in developing long-acting medicines which both prevent and treat HIV. These new medicines give us a real shot at ending AIDS with the United States of America at the forefront. UNAIDS is poised and ready to work side by side with the new Administration to save millions of lives by bringing these new medicines swiftly to scale.
The United States Government’s partnership with UNAIDS remains an indispensable force for progress and accountability in the global HIV response. UNAIDS looks forward to further strengthening its collaboration with the United States to achieve our shared goal of ending AIDS.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Region/country


Feature Story
Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment
21 January 2025
21 January 2025 21 January 2025Grabbing his helmet, Hadi Timotius gets in the back of his colleague’s scooter to pay a routine visit to a woman who is taking her HIV treatment again. Hadi oversees the ‘Lost and Link’ initiative at JIP, a national network of people living with HIV in Indonesia.
Region/country
Related


Press Release
UNAIDS calls on leaders at Davos to commit to rapid global access to revolutionary new long-acting HIV medicines
21 January 2025 21 January 2025UNAIDS urges speed and compassion urging pharmaceutical companies to enable access to new, life-saving medicines
DAVOS/GENEVA, 21 January 2025—Today, at the World Economic Forum’s annual meeting in Davos, Switzerland the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) has warned that new long-acting HIV prevention – and potentially treatment – medicines can help usher in the end of AIDS if corporate and political leaders move quickly and urgently to prioritise access for all low and middle-income countries.
Lenacapavir, produced by Gilead Sciences, has proved to be more than 95% effective in preventing HIV with just two doses a year and the company is now conducting trials of once-yearly shots. ViiV Healthcare has the injectable medicine Cabotegravir, administered once every two months to prevent HIV, which is already being used in some countries. Month-long vaginal rings are also in use and longer acting pills and vaginal rings are being trialled.
“These new technologies offer us a real shot at ending AIDS by 2030,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS and Under-Secretary-General of the United Nations. “But it comes with a caveat—only if pharmaceutical companies, governments, international partners and civil society unite around an HIV prevention and treatment revolution, can we use these medicines to their full potential and end AIDS much sooner than we previously thought.”
The breakthrough long-acting medicines could stem new HIV infections and are already being used to suppress the virus for some people living with HIV. But their potential can’t be unlocked unless everyone, everywhere who could benefit has access.
UNAIDS is urging pharmaceutical companies to move faster and ensure “affordable pricing and generic competition” in the market for the new HIV medicines. “We have no problem with profit, but we will not stand for profiteering,” said Ms Byanyima.
Gilead and ViiV have licensed generics manufacturing to a number of countries, which is to be applauded, but they are moving too slowly. Generics aren’t expected until next year- and many countries have been left out. Nearly all of Latin America, a region of rising HIV infections, has been excluded. In addition, to provide for the whole world, Gilead has licensed just six companies to make generic versions of the medicine – with no producer in sub-Saharan Africa. To make these medicines widely available and affordable, more generic production is needed.
Gilead has not announced a price for lenacapavir for prevention. However, used as treatment in the United States, the medicine can cost around US$ 40 000 per year per person. One study suggests that, if 10 million people are reached, generics could cost just $40 per person per year, a thousand times less.
At the end of 2023 only 3.5 million people are using pre-exposure prophylaxis. UNAIDS goal is to reach 10 million with preventative HIV medicine by the end of 2025. “This is possible, said Ms Byanyima, “But only if we have ambition. Look at injectable contraceptives—72 million women around the world accessed them in 2022. Look at COVID-19 vaccines in rich countries – 4.5 billion people were vaccinated in a year. Why can we not have the same ambition for HIV? We did it for HIV treatment and we can do it for prevention. We have done it before – and we can do it again.”
Today, 30 million of the 40 million people living with HIV are now on treatment—a huge, but long-awaited achievement which destroyed families and cost far too many lives.
While these new medicines are not a cure or a vaccine, they could halt the HIV pandemic.
The Global Fund to fight AIDS, TB and Malaria and the US President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) recently announced a deal to get lenacapavir to 2 million people over the next three years. Which is a good start but not ambitious enough.
"Science has delivered a miraculous new tool: medicines that prevent HIV infection with injections just twice a year and which could work for treatment too,” said Ms Byanyima. “We must do better this time. Either companies step up, or governments step in. This is our shot to end AIDS – and we cannot afford to miss it."
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDSSophie Barton-Knott
tel. +41 79 514 6896
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS
Joe Karp-Sawey
tel. +44 74 2898 5985
karpsaweyj@unaids.org