

Feature Story
Early infant diagnosis of HIV: changing lives for mothers and infants
07 December 2017
07 December 2017 07 December 2017Mahabad Asanova’s first daughter was found to be living with HIV after being rushed to hospital with a high fever. For her second pregnancy, Ms Asanova had to wait 18 months before finding out that her son was HIV-negative.
By the time of her third pregnancy, however, things had changed dramatically. Within a month of her birth, Ms Asanova had been told that her daughter was HIV-negative. A revolutionary method of HIV testing of infants, dried blood spot (DBS) testing, had by then been introduced, significantly cutting the time for diagnosis.
“Waiting 18 months to know about the HIV status of my child was terrible,” Ms Asanova said. “I’m so relieved—dried blood spot testing completely changed my life.” Before DBS, children had to wait a year or more to be tested.
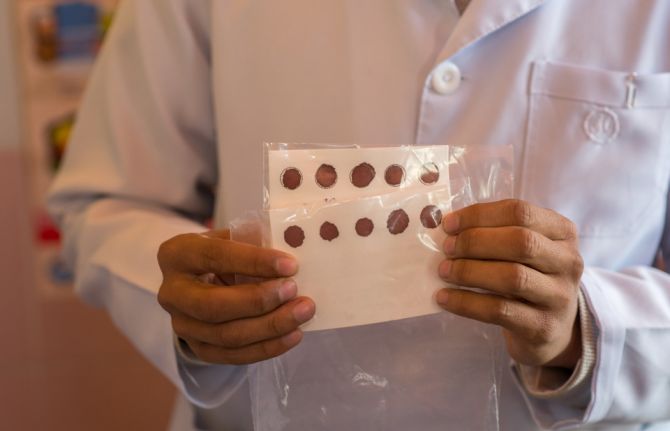
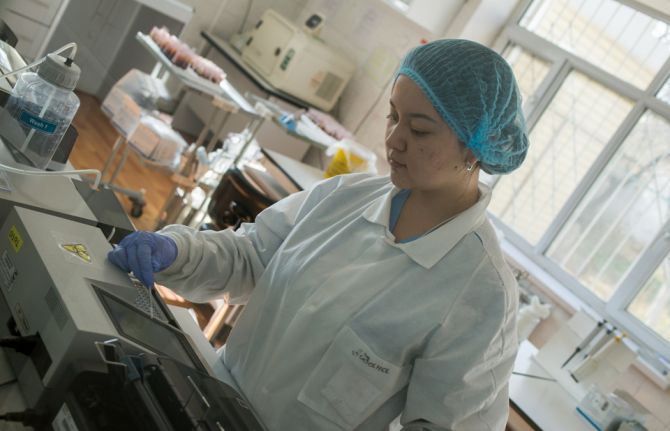
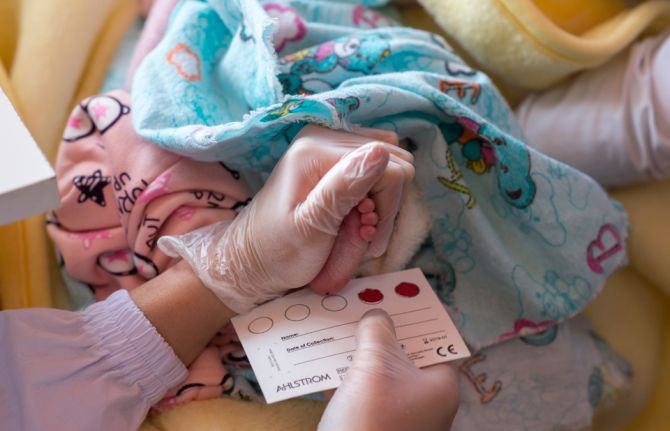
DBS is simple: no sophisticated equipment or invasive testing methods are needed. After a prick on the newborn’s heel, a drop of blood is collected on filter paper and dried. The sample is sent to a laboratory for testing and the results are known before the infant is a month old, allowing infants living with HIV to be treated immediately with life-saving antiretroviral medicines.
“Before dried blood spot testing was widely introduced in 2013 in Kyrgyzstan, only around 15% of infants were diagnosed early,” said Edil Tilekov, HIV Programme Officer for the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF). “In 2017, that figure grew to nearly 90%.”
Today, HIV science and diagnostics are becoming ever-more sophisticated. UNICEF is promoting point-of-care HIV diagnostic methods for infants that would yield an HIV diagnosis a mere two hours after collecting blood.
The introduction of DBS and improved training for doctors has helped to defuse some of the stigma against people living with HIV.
“Stigma among medical staff began to decrease as antiretroviral medicines were integrated into the primary health-care system,” Elmira Narmatova, Director of the Osh Oblast AIDS Centre, said. “It became more like a chronic disease, mortality declined.”
Children who are treated early fare better and the more the medicines work, the more confident parents become. Today, in part as a result of DBS, more than 95% of children living with HIV in Osh, Kyrgyzstan, access antiretroviral therapy.
Yet pockets of resistance remain. Despite early diagnosis, not all infants receive the medicines they need. “We are interviewing parents and medical staff to find out why some parents still don’t want to give their infants antiretroviral medicines,” said Mr Tilekov.
Informal conversations already provide clues: resistance may be due to religion, to scepticism about immunization or even to urban myths.
“Although much has been done to provide parents with information and train medical staff, there is still a lack of resources and trained personnel, so some parents will slip through the net and might not be briefed properly about side-effects,” said Mr Tilekov. “So, if their infants lose weight or don’t eat well after starting antiretroviral therapy, parents blame the medicines.”
When an infant or mother is tested for HIV in Osh, the laboratory sends the results to the Osh AIDS Centre, a pleasant house set among trees in a leafy suburb, its gates open in welcome. The hallways are decorated with images of the popular Vitaminka fairy tale, a comic strip that helps health workers and parents explain to children the importance of taking their antiretroviral medicines regularly.
By providing child-friendly spaces and psychosocial support in addition to medical treatment, the centre makes parents feel welcome and encourages them to visit, pick up prescribed medication and get tested regularly.
The centre, upgraded by the Ministry of Health together with UNICEF and UNAIDS with support from the Government of the Russian Federation, now treats more than 200 children and a psychologist provides psychosocial support to children living with HIV.
Away from social pressures and among friends, parents can exchange hopes for the future and find much needed support at the centre.
Ms Asanova looks relaxed as her fingertips touch across her lap, her olive-green dress contrasting with her cream-coloured hijab. Mahabad Asanova isn’t her real name, since she still worries about stigma and discrimination beyond the centre’s walls. But she isn’t afraid anymore, even though she is now expecting another child. Whatever happens, thanks to DBS, she will no longer face painful months of waiting for a diagnosis.



