


Press Statement
UNAIDS welcomes the adoption of a crucial resolution recognizing harm reduction measures at the UN Commission on Narcotic Drugs
22 March 2024 22 March 2024VIENNA/GENEVA, 22 March 2024— UNAIDS welcomes the adoption of a key resolution today at the 67th session of the United Nations Commission on Narcotic Drugs (CND), recognizing harm reduction for the first time as an important part of an effective public health response. The resolution encourages member states to develop and implement harm reduction measures to minimize the adverse public health and social consequences of the non-medical use of illicit drugs. UNAIDS congratulates the CND and the CND Chair for this historic milestone.
The resolution represents a landmark in political commitment to a rebalancing of drug policy towards a public health approach. Such a shift is critical to meeting the targets in the 2021-2026 Global AIDS Strategy.
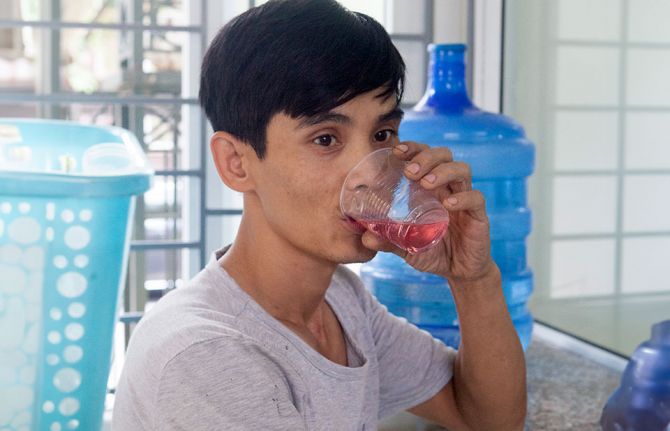
Harm reduction is a “a comprehensive package of evidence-based interventions, based on public health and human rights, including needle syringe programmes (NSPs), opioid agonist maintenance therapy (OAMT) and naloxone for overdose management. Harm reduction also refers to policies and strategies that aim to prevent major public and individual health harms, including HIV, viral hepatitis and overdose, without necessarily stopping drug use.” (World Health Organization, 2022).
Since 2018 only five countries have reported achieving the target of providing 200 sterile needles and syringes per person who inject drugs. In that same timeframe only three countries reported achieving the target of 50% coverage of opioid agonist maintenance therapy among people who inject drugs.
The criminalization of drug use and possession for personal use in at least 145 countries, along with stigma, discrimination and violence, continues to restrict both the provision of and access to life-saving harm reduction services.
A failure to invest in harm reduction services or remove the structures that inhibit access, including those relating to gender, have led to a situation where HIV prevalence among people who inject drugs is 7 times that of the rest of the population, and people who inject drugs have the highest incidence globally of any key or vulnerable population. In countries with data, median HIV prevalence among women who inject drugs is almost twice that of men who use drugs.
Under the UN Common Position on Drugs, UNAIDS collaborates with other UN agencies and partners with governments, community-led organizations and donors to increase the provision of harm reduction services and remove harmful laws and policies which create barriers to accessing such services, such as the criminalization of possession of drugs for personal use. UNAIDS works to ensure all efforts relating to drug policy are in conformity with international human rights, as outlined in the international guidelines on human rights and drug policy.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
