


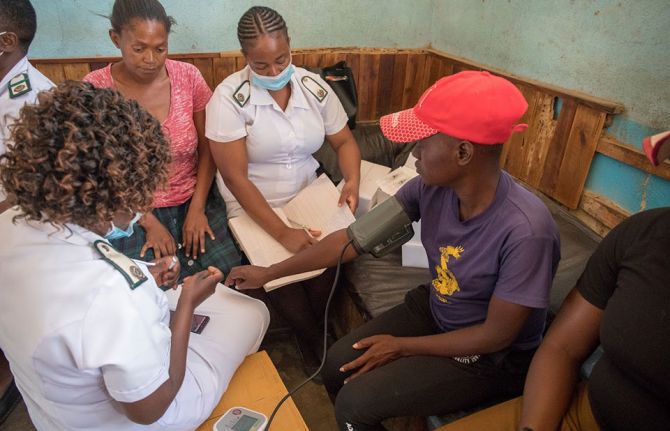
Press Statement
UNAIDS calls for rights-based and people-centred universal health coverage
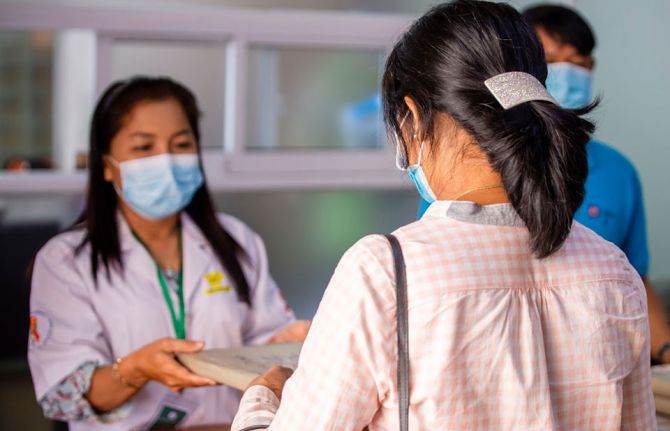
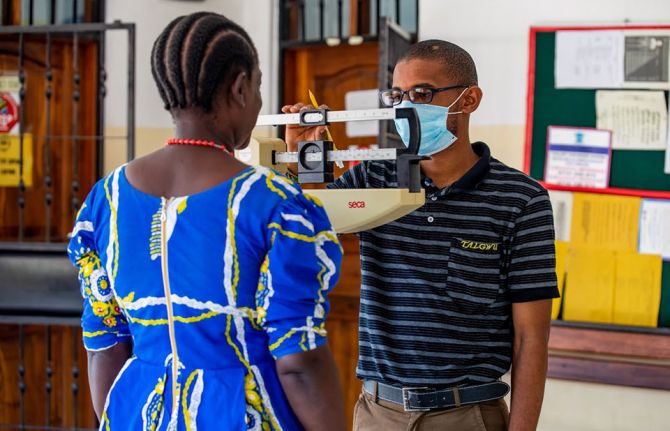
12 December 2020 12 December 2020GENEVA, 12 December 2020—The world is only 10 years away from the deadline for the universal health coverage target of the Sustainable Development Goals. Only 10 years away from when everyone should have access to quality essential health services and access to safe, effective, quality and affordable essential medicines and vaccines. But that target seems as far away as ever. In 2017, less than half of the world’s people were covered by essential health services, and if current trends continue it is estimated that only 60% of the global population will enjoy universal health coverage by 2030.
On Universal Health Coverage Day, UNAIDS is calling for the world to meet its obligation— universal health coverage, based on human rights and with people at the centre.
“Health for all: protect everyone” is the theme for this year’s Universal Health Coverage Day, making it clear that health is a fundamental human right.
“It’s a disgrace that inequalities are still impacting the ability of people to access health care,” said Winnie Byanyima, UNAIDS Executive Director. “Health is a human right, but it is so often denied, especially to the most vulnerable, the marginalized and the criminalized.”
Someone’s socioeconomic status, gender, age, sexual orientation, citizenship or race can affect their ability to access health services. Like the HIV response, equality lies at the heart of universal health coverage and progressing towards universal health coverage means progressing towards equity, social inclusion and cohesion. A rights-based and people-centred approach to universal health coverage can help to ensure equitable health for all.
COVID-19 has shown that public health systems have been neglected in many countries around the world. In order to promote health and well-being, countries need to invest in the core functions of health systems, including public health, as common goods for health.
“Money should never determine someone’s access to health,” added Ms Byanyima. “No one should be pushed into poverty by paying for health services. User fees must be abolished and health for all paid for from public funds.”
Even before the COVID-19 pandemic hit, the global AIDS response was off track, in part because of a long-term underinvestment in health systems. Universal health coverage and the end of AIDS cannot be achieved and sustained without resilient and functioning health systems that can respond to the needs of everyone, without stigma and discrimination.
The HIV response has shown that communities make the difference. During the COVID-19 pandemic, community-led organizations, including communities of people living with HIV, around the world have mobilized to protect the vulnerable, working with governments to keep essential services going.
Communities have campaigned for multimonth dispensing of HIV treatment, organized home deliveries of medicines and provided financial assistance, food and shelter to at-risk groups. Communities are part of systems for health and are fundamental to attaining universal health coverage. They must be better recognized and supported for their leadership, their innovation and their immense contribution towards health for all.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton-Knott
tel. +41 79 514 68 96
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS Media
tel. +41 22 791 4237
communications@unaids.org
Our work
Press centre
Download the printable version (PDF)


Press Statement
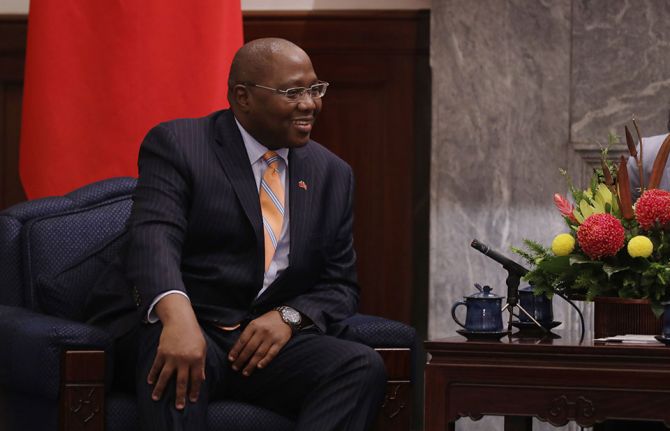
UNAIDS saddened by the death of Ambrose Dlamini, Prime Minister of Eswatini
14 December 2020 14 December 2020GENEVA, 14 December 2020—UNAIDS is saddened by the death of the Prime Minister of Eswatini, Ambrose Dlamini, who has died after testing positive for the new coronavirus.
“The HIV response has lost a champion,” said Winnie Byanyima, UNAIDS Executive Director. “He was a friend of UNAIDS and helped to steer his country to great successes in the HIV response. We will miss him.”
Mr Dlamini took an active role in the response to HIV in Eswatini, and the National AIDS Council and the Country Coordinating Mechanism in Eswatini of the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria reported directly to him.
Mr Dlamini was present for the launch of Seizing the moment, a UNAIDS report on the global AIDS epidemic, in July 2020, at which he spoke about Eswatini’s success in surpassing the 90–90–90 targets, whereby 90% of people living with HIV know their HIV status, 90% of people who know their HIV-positive status are accessing treatment and 90% of people on treatment have suppressed viral loads.
“We have achieved 95–95–95,” he said. “We cannot rest on our successes, nor be discouraged by setbacks. We must ensure that no one is left behind. We must close the gaps. We are aiming for 100–100–100,” he added.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.


Press Statement
UNAIDS calls on countries to put human rights first to beat pandemics
10 December 2020 10 December 2020Human Rights Day message from Winnie Byanyima, UNAIDS Executive Director
I invite you to join us on Human Rights Day, and every day, as we take action to reform our systems, to recover better and to fight for everyone’s rights.
The COVID-19 crisis has demonstrated once again how quickly rights violations can arise in an emergency. Inequalities that have too long been ignored were laid bare and exacerbated during the response to the pandemic. And yet we have learned from the AIDS response that it is only where rights are respected, protected and fulfilled that countries can make progress against an epidemic and build fairer societies.
Sex workers, gay men and other men who have sex with men, transgender people and people who use drugs were often targeted by law enforcement during lockdowns, exposed to high rates of violence, omitted from social protection and financial support mechanisms and denied access to health services because community-led organizations were frequently deemed as non-essential.
There are 69 countries that still criminalize same-sex sexual relations, 92 that criminalize HIV transmission, exposure and non-disclosure and 32 that criminalize transgender people. Almost every country in the world continues to criminalize drug use and aspects of sex work. If it wasn’t clear before, it should be now—this is not just an HIV issue, but one of fundamental equality and human rights.
The criminal law is a heavy and blunt instrument. It must be used with great care and sparingly. Used badly, it can harm when we need to help, it can oppress when we need to enable, and far from being neutral, it creates and amplifies existing discrimination and inequalities.
We need to transform our justice systems and change our laws. The law should work for everyone and protect everyone. Law reform can take time, but we can already act now to put a moratorium on arrests where criminal laws and their enforcement breach international human rights norms.
On Human Rights Day, let us commit to ending the inequalities and injustices that fuel AIDS and other pandemics.
UNAIDS is one of the founding members of the Global Partnership for Action to Eliminate HIV-Related Stigma and Discrimination, along with the United Nations Development Programme, UN Women, the Global Network of People Living with HIV and now the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria. This year, 18 countries have joined the partnership. Next year we will be expanding further.
Our work


Press Statement
UNAIDS calls for the elimination of the neglected pandemic of violence against women and girls
25 November 2020 25 November 2020GENEVA, 25 November 2020—Today, on the International Day for the Elimination of Violence against Women, UNAIDS is calling for the world to urgently scale up efforts to eliminate the neglected pandemic of violence against women and girls in all their diversity, a widespread human rights violation that affects one in three women at least once in their life.
Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, it was estimated that globally 243 million women and girls aged 15–49 years had been subjected to sexual and/or physical violence perpetrated by an intimate partner in the past 12 months. Evidence shows that the COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in significant increases in gender-based violence in nearly all countries.
“The growing evidence confirms that the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic are not gender-neutral,” said Winnie Byanyima, UNAIDS Executive Director. “The impacts of lockdowns and travel restrictions imposed in many countries to curb the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic, the failure to designate sexual and reproductive health services and services for survivors of violence as essential services, and the undermining of women’s economic security have compounded the barriers for women and girls experiencing abuse, especially those who are trapped at home with their abusers.”
Adolescent girls and young women are also increasingly being subjected to early marriage and trafficking, missing out on education because of school closures and lacking access to comprehensive sexuality education and sexual and reproductive health services, including contraception and abortion, as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
COVID-19 is increasing violence against women and amplifying existing gender inequalities, further exacerbating HIV risks and vulnerabilities for women, at the same time that access to gender-based violence services, as well as HIV and other sexual and reproductive health services, are being reduced or are unavailable during the pandemic. Violence against women is a major factor driving risks for HIV—in areas with a high HIV burden, such as sub-Saharan Africa, women subjected to intimate partner violence are 50% more likely to be living with HIV. And men who are perpetrators of violence against women tend to be at higher risk of HIV themselves and to use condoms less frequently, thus increasing the risk of HIV transmission.
Violence, or the potential for it, discourages many women and adolescent girls living with HIV from disclosing their HIV status to their partners, families and health-care providers, making it more difficult for women and girls to stay on HIV treatment.
Gender-based violence restricts women’s and girls’ decision-making and erodes their sexual and reproductive health and rights, including deciding if, how, when and with whom they have sex, their ability to protect their health and their ability to access HIV prevention services and stay on treatment.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has reflected once again just how unacceptable it is to continue with half measures and unmet commitments to ending violence against women,” added Ms Byanyima. “If we are serious about achieving gender equality, and ending AIDS, preventing gender-based violence must finally become a global, national and local priority.”
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton-Knott
tel. +41 79 514 68 96
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS Media
tel. +41 22 791 4237
communications@unaids.org


Press Statement
World AIDS Day 2020 message from UNAIDS Executive Director Winnie Byanyima
01 December 2020 01 December 2020World AIDS Day 2020 will be like no other.
COVID-19 is threatening the progress that the world has made in health and development over the past 20 years, including the gains we have made against HIV.
Like all epidemics, it is widening the inequalities that already existed.
Gender inequality, racial inequality, social and economic inequalities. We are becoming a more unequal world.
I am proud that over the past year the HIV movement has mobilized to defend our progress, to protect people living with HIV and other vulnerable groups and to push the coronavirus back.
Whether campaigning for multimonth dispensing of HIV treatment, organizing home deliveries of medicines or providing financial assistance, food and shelter to at-risk groups, HIV activists and affected communities have again shown they are the mainstay of the HIV response. I salute you!
It is the strength within communities, inspired by a shared responsibility to each other, that has contributed in great part to our victories over HIV.
Today, we need that strength more than ever to beat the colliding epidemics of HIV and COVID-19.
Friends, in responding to COVID-19, the world cannot make the same mistakes it made in the fight against HIV, when millions in developing countries died waiting for treatment.
Even today, more than 12 million people are still waiting to get on HIV treatment and 1.7 million people became infected with HIV in 2019 because they could not access essential services.
That is why UNAIDS has been a leading advocate for a People’s Vaccine against the coronavirus.
Global problems need global solidarity.
As the first COVID-19 vaccine candidates have proven effective and safe, there is hope that more will follow, but there are serious threats to ensuring equitable access. We are calling on companies to openly share their technology and know-how and to wave their intellectual property rights so that the world can produce the successful vaccines at the huge scale and speed required to protect everyone and so that we can get the global economy back on track.
Our goal of ending the AIDS epidemic was already off track before COVID-19. We must put people first to get the AIDS response back on track. We must end the social injustices that put people at risk of contracting HIV. And we must fight for the right to health. There is no excuse for governments to not invest fully for universal access to health. Barriers such as up-front user fees that lock people out of health must come down.
Women and girls must have their human rights fully respected, and the criminalization and marginalization of gay men, transgender people, sex workers and people who use drugs must stop.
As we approach the end of 2020, the world is in a dangerous place and the months ahead will not be easy.
Only global solidarity and shared responsibility will help us beat the coronavirus, end the AIDS epidemic and guarantee the right to health for all.
Thank you.
Winnie Byanyima
Executive Director of UNAIDS
Under-Secretary-General of the United Nations
World AIDS Day 2020 playlist
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.


Press Statement
UNAIDS welcomes Suki Beavers as UNAIDS Director of Gender Equality, Human Rights and Community Engagement
16 November 2020 16 November 2020GENEVA, 16 November 2020—UNAIDS is delighted to announce the appointment of Suki Beavers to the position of Director, Gender Equality, Human Rights and Community Engagement in UNAIDS Programme Branch.
Ms Beavers will be joining from the National Association of Women and the Law in Canada, where in her position as Executive Director, she led efforts to develop high quality feminist legal analysis and law reform strategies to advance the rights and empowerment of women in all their diversity.
“With a wealth of experience in women’s rights and empowerment, sexual and gender-based violence, sexual and reproductive health, and human rights Ms Beavers will be a huge asset to UNAIDS,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “Her passion and dedication in standing up for the rights of women and the most vulnerable will be invaluable in advancing UNAIDS work in these critical areas.”
In her new role Ms Beavers will be leading UNAIDS work to address human rights challenges, including stigma and discrimination, inequality and violence against women and girls, misuse of criminal law and punitive approaches which remain among the main barriers to effective HIV responses. She will also oversee UNAIDS work on achieving gender equality, advancing women’s empowerment and fulfilling the sexual and reproductive health and rights of women and girls. In addition, she will be leading work to support the critical role of community action in advocacy, participation and coordination of AIDS responses and service delivery.
“I am honoured to be joining UNAIDS, especially now as we work to scale up the global, regional, national and local efforts required to advance the rights of women and girls, end stigma and discrimination, and strengthen and expand community engagement as critical components of the HIV response,” said Ms Beavers.
UNAIDS would also like to thank Luisa Cabal for assuming the role of interim Director of the Department since June 2019.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Press centre
Download the printable version (PDF)
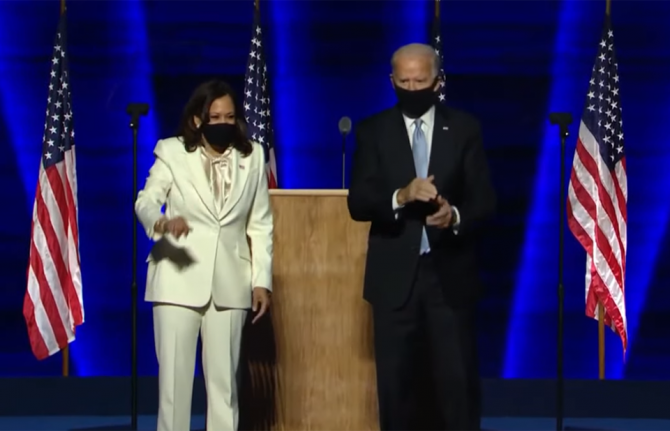


Press Statement
UNAIDS congratulates President-elect Joe Biden and Vice President-elect Kamala Harris on their election
10 November 2020 10 November 2020GENEVA, 10 November 2020—UNAIDS congratulates President-elect Joe Biden and Vice President-elect Kamala Harris on the recent election results in the United States of America.
“UNAIDS looks forward to working with the new United States administration on the challenge of ending AIDS, for which there is still no vaccine and no cure,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “The colliding pandemics of COVID-19 and HIV are evidence that global solidarity and shared responsibility is needed now more than ever before to ensure that no one is left behind and that medicines, services and solutions can be accessed equitably.”
In 2019, around 1.7 million people became infected with HIV and 690 000 people died of AIDS-related illnesses. UNAIDS and the United States Government have collaborated closely since the inception of UNAIDS in 1996, to accelerate progress towards global HIV prevention and treatment targets in the countries most affected by HIV.
Through the United States President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR), the United States Government has invested more than US$ 85 billion in the global response to HIV, the largest commitment by any nation to address a single disease. Strong bipartisan support for investments to end AIDS across successive administrations and effective, data-driven and evidence-informed HIV programming through PEPFAR and investments to the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, TB and Malaria, have enabled millions of men, women and children to live longer, healthier lives.
To ensure continued success towards ending AIDS, concerted, strategic efforts in the months and years ahead will be needed, especially at a moment when COVID-19 threatens the health of people all around the world. To end these dual pandemics UNAIDS looks forward to continuing to work closely with the United States for a safer, healthier world.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton-Knott
tel. +41 79 514 6896
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS Media
tel. +41 22 791 4237
communications@unaids.org
Press centre
Download the printable version (PDF)
Region/country

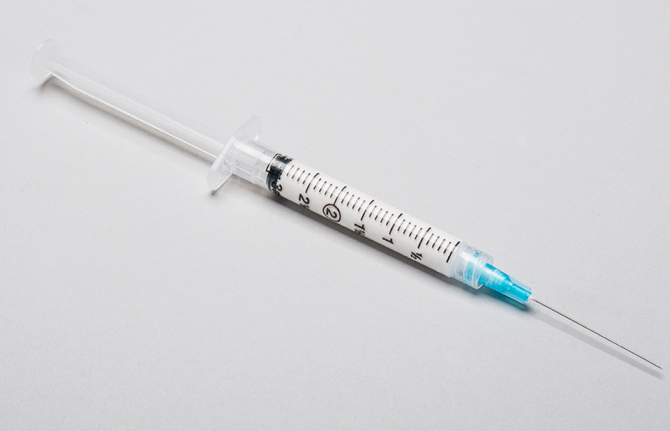
Press Statement
UNAIDS hails new results showing that long-acting injectable medicines are highly effective in preventing HIV among women
09 November 2020 09 November 2020GENEVA, 9 November 2020—UNAIDS is strongly encouraged by new study results showing that the antiretroviral medicine cabotegravir, which is administered by injection every two months, prevents HIV among women. The study shows that the long-acting injections among women in sub-Saharan Africa were 89% more efficient in preventing HIV compared to daily tablets of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP).
“These results are hugely significant. UNAIDS has long been calling for additional, acceptable and effective HIV prevention options for women, and this could be a real game-changer,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “If donors and countries invest in rolling out access of injectable PrEP to women at higher risk of HIV, new infections could be dramatically reduced.”
The trial enrolled over 3200 women aged between 18 and 45 years who were at higher risk of acquiring HIV in Botswana, Kenya, Malawi, South Africa, Eswatini, Uganda and Zimbabwe. The trial was halted early on the recommendation of the Data and Safety Monitoring Board due to clear statistical evidence showing that the injectable medicine is more effective than a daily pill.
Four HIV infections occurred among women randomly assigned to the cabotegravir injectable arm of the study, compared to 34 infections in the arm that was randomly assigned to daily oral PrEP. The risk of HIV was ninefold lower with cabotegravir injections than with daily oral PrEP.
The study results are important and timely as more methods to prevent HIV among women at higher risk of HIV are urgently needed, including methods that do not depend on daily or near-daily pill-taking, condom use or abstention from sex. The development of alternative methods to prevent HIV, and more adherence-friendly schedules than are currently available, will increase the HIV prevention choices and acceptability for women and reduce new HIV infections.
“UNAIDS congratulates everyone involved in this landmark study,” said Ms Byanyima. “Like with a COVID-19 vaccine, we now must work to ensure that these life-changing injections are accessible, affordable and equitably distributed to people who choose to use them.”
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton-Knott
tel. +41 79 514 6896
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS Media
tel. +41 22 791 4237
communications@unaids.org
Learn more
Press centre
Download the printable version (PDF)
Region/country
- West and Central Africa
- Benin
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Equatorial Guinea
- Gabon
- Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea-Bissau
- Guinea
- Liberia
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Senegal
- Sierra Leone
- Togo
- Eastern and Southern Africa
- Angola
- Botswana
- Comoros
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mauritius
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Rwanda
- Seychelles
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Eswatini
- Uganda
- United Republic of Tanzania
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
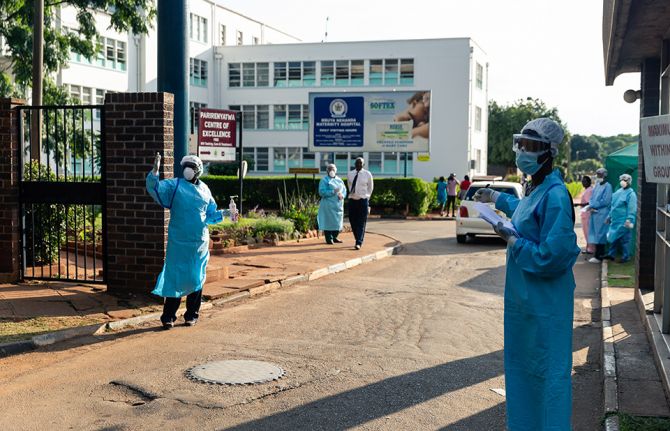


Press Statement
UNAIDS supports a temporary WTO waiver from certain obligations of the TRIPS Agreement in relation to the prevention, containment and treatment of COVID-19
15 October 2020 15 October 2020GENEVA, 15 October 2020—Today, the World Trade Organization’s Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Council meets to consider a proposal presented by the Governments of South Africa and India for a temporary waiver of certain TRIPS obligations in order to facilitate an appropriate response to COVID-19. The aim is to create certainty and clarity, guaranteeing freedom to operate, innovate, procure and scale up manufacturing capacities in essential health technologies at the required scale. The waiver would reduce transaction costs and eliminate key barriers across the research and development cycle and the supply chain for the access and delivery of health technologies to prevent, diagnose and treat COVID-19.
“UNAIDS fully supports this proposal, which reflects the urgency and global health emergency that COVID-19 represents,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “Its adoption will enable countries to work together to establish national and multilateral strategies to promote innovation of, and access to, medicines, diagnostics, vaccines and other health technologies.”
Global solidarity and shared responsibility have been recognized as fundamental principles that guide the United Nations system response. There is a growing consensus that universal access to health care, and to COVID-19 health technologies, must be a global public good.
In response to the colliding pandemics of COVID-19 and HIV, UNAIDS has adopted a multisectoral and people-centred approach in order to protect the gains for people living with and affected by HIV and to drive progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals. The AIDS community knows that in order to tackle public health threats a focus on inequality is essential, including inequalities in access to solutions, whether vaccines, diagnostics or therapeutics.
“We cannot repeat the painful lessons from the early years of the AIDS response, when people in wealthier countries got back to health, while millions of people in developing countries were left behind,” Ms Byanyima added. “If we continue with business as usual we will fail in delivering fair access to COVID-19 treatments for all those in need. Yet fair access is the human right of everyone, no matter the colour of their skin, the money in their pocket or the country they live in.”
A range of solutions will be needed in order to ensure equal access and to unlock supply. UNAIDS calls for support for the multilateral solutions that are on the table and for collaboration through fostering the transfer of technology and mass-producing health products, using a public health lens.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
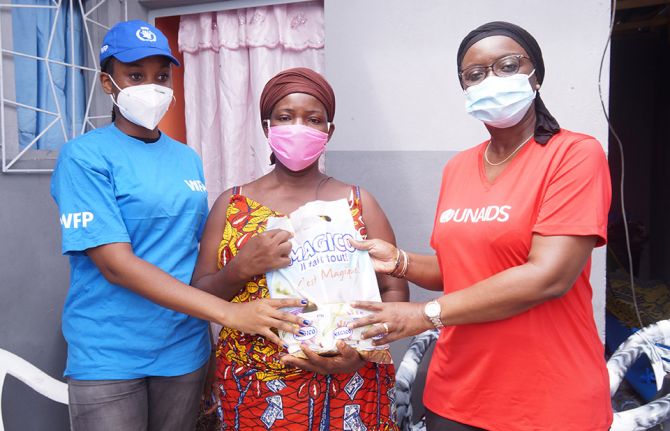
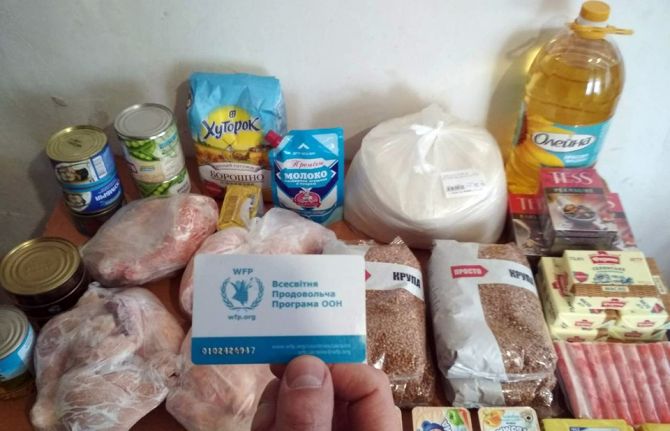
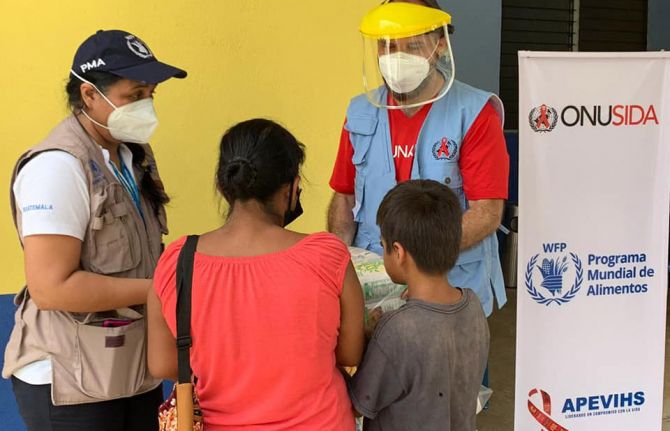




Press Statement
UNAIDS congratulates the World Food Programme on being awarded the Nobel Peace Prize
09 October 2020 09 October 2020GENEVA, 9 October 2020—UNAIDS sends its heartfelt congratulations to the World Food Programme (WFP) for being awarded the 2020 Nobel Peace Prize. WFP’s efforts to ensure food security for all, particularly the most vulnerable women, men and children, including people living with HIV, have saved countless lives and prevented hunger and starvation in countries all around the world.
“We are so proud of WFP’s achievement and are honoured to have WFP as one of our Cosponsors, working with us to end AIDS,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “We will continue to work closely together to achieve our shared goals of zero hunger, zero new HIV infections, zero AIDS-related deaths and zero discrimination for all.”
For people living with HIV, food and nutrition are critical components of care and support. WFP’s work on HIV includes nutritional recovery for malnourished people living with HIV, support at the individual and household levels, supplying food, cash and vouchers, and linking food and health systems. As part of its HIV and tuberculosis programmes in 29 countries, WFP also links clients with social protection programmes and livelihood strengthening activities in order to ensure that health gains can be sustained in the long term, as people living with HIV need to stay on treatment for life.
WFP’s efforts have improved the lives of people living with and affected by HIV and have advanced access and adherence to HIV treatment. UNAIDS thanks WFP for its work and collaboration and congratulates WFP on its well-merited achievement of being awarded the Nobel Peace Prize.
Additional information on WFP’s work on HIV is available here.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton-Knott
tel. +41 79 514 6896
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS Media
tel. +41 22 791 4237
communications@unaids.org
