

Press Statement
UNAIDS welcomes Kenya’s High Court judgement in landmark case of involuntary sterilization of women living with HIV
20 December 2022 20 December 2022GENEVA, 20 December 2022—UNAIDS welcomes the judgement by the High Court of Kenya at Nairobi recognizing that coerced sterilization of women living with HIV is a violation of their human rights.
The judgement follows a case brought forward in 2014 by a Kenyan woman living with HIV who was coerced by professionals at a health facility to undergo tubal ligation thus taking away her ability to have children. The High Court found that the performance of this operation without consent amounted to a violation of her rights to non-discrimination, to dignity, to health and to family.
“This decision is an important step in protecting the sexual and reproductive health and rights of women living with HIV,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “UNAIDS stands ready to work with all governments to ensure such practices are eliminated completely and that women living with HIV are able to access health services without stigma or discrimination.”
UNAIDS intervened in this case with an amicus curiae (friend of the court) brief that informed the Kenyan High Court on the health guidelines and human rights standards that each country must follow to respect, protect and guarantee the human rights of people living with HIV, and the impact that such involuntary practices can have on the HIV response. The Kenyan Legal and Ethical Issues Network on HIV/AIDS (KELIN) and the African Gender and Media Initiatives Trust (GEM) were also petitioners in this case.
HIV-related stigma and discrimination has a significant impact on the health, lives and well-being of people living with or at risk of HIV. Stigma and discrimination hinders the HIV response by limiting access to broader sexual and reproductive health and other health services. UNAIDS continues to work daily to ensure that governments invest in preventing and responding to violations linked to the forms of intersectional discrimination to which people living with HIV have been subjected.
The plaintiff in the case stated, “This was never about the money. I wanted to fight for justice for myself and all women who have had this experience, and to ensure this does not happen to other women who are living with HIV who need access to reproductive health services.”
“This case is an important moment for reproductive justice and the feminist movement. Coercive sterilization of women living with HIV is a violation of women’s most fundamental human rights and undermines effective HIV responses,” said UNAIDS Country Director for Kenya, Medhin Tsehaiu. “It is only through a human rights approach that we will end AIDS as a public health threat.”
A rights-based approach includes the right to start a family and have children, the right to decide the number and spacing of their children, the right to reproductive autonomy and the right to access quality services to support their reproductive health choices, based on their informed, safe and voluntary consent. These are fundamental human rights that belong to all women, regardless of HIV status, and are guaranteed in global and regional treaties.
“We welcome the court’s decision and although it took a long time, we are happy that the court found the client’s rights had been violated, and particularly the finding of discrimination on the basis of sex and HIV status,” said Allan Maleche, Executive Director, KELIN.
The Global AIDS Strategy 2021–2026: End Inequalities, End AIDS includes a central role for the promotion of human rights, gender equality and dignity, free from stigma and discrimination for all people living with and affected by HIV. It is a commitment by UNAIDS to an ambitious vision to end gender inequalities and realize human rights, including the right to health, calling on all partners and stakeholders in the HIV response in all countries to transform unequal gender norms and end stigma and discrimination.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Region/country


Press Statement
UNAIDS welcomes the appointment of Erika Castellanos as Executive Director of GATE
13 December 2022 13 December 2022GENEVA, 13 December 2022—UNAIDS warmly welcomes the appointment of Erika Castellanos as the new Executive Director of GATE (Global Action for Trans Equality). GATE works to ensure justice and equality for trans, gender diverse and intersex communities through strategic partnerships with diverse global entities, including UNAIDS and other United Nations bodies and mechanisms.
Born in Belize, Erica started her activism focusing on the rights of people living with HIV and sex workers. She brings to her work her lived experience as a transgender woman living with HIV and as a member of different communities of key populations.
“Erika Castellanos is an internationally recognized and highly respected HIV and human rights activist. UNAIDS appreciates our partnership with Erika as a civil society delegate to our Programme Coordinating Board" said Winnie Byanyima, UNAIDS Executive Director. “GATE’s work as a trans-led organization has been critical to foster the engagement of trans, gender diverse and intersex communities in the AIDS response. We look forward to continuing our work with Erika and GATE in addressing the inequalities affecting these communities”.
Erika Castellanos joined GATE in April 2017 as Director of Programs. In February 2022, she took the role of Interim Executive Director during which time she has continued to solidify GATE’s position as a global leader in trans, gender diverse and intersex advocacy.
Erika has served various positions at national, regional and global levels including as Executive Director of the Collaborative Network for Persons Living with HIV (C-NET+) – Belize, Vice-Chair of the Board of the Global Network of People Living with HIV (GNP+), board member of the HIV Justice Network and co-chair of the ViiV Positive Action program for men who have sex with men and transgender people. In 2018, Erika was the first openly transgender advocate to be appointed to the Board of the Global Fund, as part of the communities delegation.
Erika will begin her new role as GATE’s Executive Director on 1 January 2023.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Our work




Press Statement
UNAIDS welcomes strong funding commitments from the United Kingdom and from Ireland
13 December 2022 13 December 2022CHAING MAI/GENEVA, 13 December 2022—UNAIDS welcomes confirmation from the United Kingdom that it will be increasing its funding to UNAIDS from £2.5 million in 2021 to £8 million in 2022.
UNAIDS also welcomes plans being finalized for a multi-year funding agreement between UNAIDS and Ireland for the period 2023 to 2026.
In recent weeks, a series of donors have been announcing funding commitments to UNAIDS.
The decisions were shared at the 51st meeting of UNAIDS Programme Coordinating Board being held in Chaing Mai, Thailand, and will help provide to secure predictable and timely funding to UNAIDS to enable UNAIDS to deliver on the Global AIDS Strategy 2021-2026.
“We warmly welcome the United Kingdom’s decision to announce further funding to UNAIDS, and Ireland’s multi-year commitment, which underscore both countries’ bold commitment to end AIDS and tackle the inequalities that continue to drive the pandemic,” said the Executive Director of UNAIDS Winnie Byanyima. “The United Kingdom and Ireland are valued and steadfast partners to UNAIDS, and their support allows us to provide the leadership and coordination that the global HIV response requires at this critical time.”
Both the United Kingdom and Ireland share UNAIDS commitment to an equality based, evidence driven approach to ending AIDS which champions the rights of women, girls and the key populations most vulnerable to HIV infection.
Thank you to the United Kingdom for contributing a further £8 million to UNAIDS.
— UNAIDS (@UNAIDS) December 13, 2022
We are grateful for the UK's partnership and support, and for their commitment to the AIDS response. #PCB51 pic.twitter.com/tnd61NKWoi
We are pleased to be finalizing a multi-year funding agreement with Ireland, as announced at #PCB51.
— UNAIDS (@UNAIDS) December 13, 2022
Thank you Ireland for your support and your longstanding commitment to the AIDS response. Together we can #endAIDS by 2030! pic.twitter.com/pLAwYjR631
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.


Press Statement
UNAIDS congratulates Barbados on its decision to repeal colonial-era laws that criminalised same sex sexual relations
13 December 2022 13 December 2022GENEVA, 13 December 2022—UNAIDS welcomes the judgement by the High Court in Barbados to strike down the country’s colonial-era gross indecency and buggery laws that criminalised consensual same-sex relations.
“This historic decision is a significant step towards protecting the human rights and dignity of LGBT people in Barbados,” said Luisa Cabal, UNAIDS Regional Director for Latin America and the Caribbean. “It will also strengthen the country’s HIV response by helping to reduce stigma and discrimination faced by LGBT people and increasing the uptake of HIV testing, treatment and prevention services.”
Under section 9 of the Barbados Sexual Offences Act, punishment could lead to life imprisonment for men engaging in same-sex sexual activity. Under section 12, both men and women were criminalised and liable to up to 10 years imprisonment. Laws that punish consensual same sex relations, in addition to contravening the human rights of LGBT people, act as a barrier to improving health outcomes, including in the HIV response. Such laws sustain stigma and discrimination against LGBT people and stop LGBT people seeking and receiving healthcare for fear of being punished or detained. Decriminalisation saves and changes lives and builds stronger societies.
Barbados becomes the third Caribbean country this year to announce the repeal of such discriminatory legislation. The case was filed by two Barbadian LGBT advocates with local organisation Equals Barbados providing community support, and the regional LGBT umbrella organisation, the Eastern Caribbean Alliance for Diversity and Equality, convening the process.
Earlier this year, courts in Antigua and Barbuda and St Kitts and Nevis also struck down as unconstitutional laws that criminalised gay men and other men who have sex with men. There now remain six countries in the Caribbean that criminalize gay sex between consenting adults, all of them former British colonies. They are Dominica, Grenada, Guyana, Jamaica, St. Lucia, and St. Vincent and the Grenadines.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Our work
Region/country


Press Statement
International Human Rights Day: ending the AIDS pandemic means respecting human rights for all
10 December 2022 10 December 2022GENEVA, 10 December 2022—On International Human Rights Day, UNAIDS is highlighting that the AIDS pandemic will only be ended if the human rights of all people are fully respected.
UNAIDS is emphasising the need for law and policy reform to ensure the human rights of people living with HIV, women and girls, and all marginalised populations, including gay men and other men who have sex with men, transgender people, people who use drugs, and sex workers.
“It’s clear that when communities of people suffer from human rights violations, the response to HIV is undermined,” said UNAIDS Executive Director, Winnie Byanyima.
Multiple and intersecting inequalities that drive the HIV pandemic are exacerbated by, and exacerbate, human rights violations. A UNAIDS report released ahead of World AIDS Day, Dangerous Inequalities, revealed how human rights violations hamper the AIDS response.
Stigma and discrimination, criminalization and marginalization are driving new infections among key populations by blocking access to HIV prevention, treatment and care services. Around the world, 68 countries still criminalize same sex relationships, which prevents tailored service outreach to communities most affected by the pandemic and deters people from visiting public health facilities. In sub-Saharan Africa, studies have shown that in countries where they are criminalised, HIV prevalence is many times higher among gay men and other men who have sex with men and sex workers, compared to countries where they are not. In 2021, 70% of all new HIV infections worldwide were among key populations and their sexual partners.
UNAIDS supports the Global Network of People Living with HIV (GNP+) in its #NotACriminal campaign against the dehumanising and denigrating impact of laws that criminalise identities and health status. During its World AIDS Day campaign this year, UNAIDS has been urging countries to challenge the inequalities driving the AIDS pandemic by equalizing access to HIV services.
In 2021, a young woman or girl aged 15—24 years old acquired HIV every two minutes. In sub-Saharan Africa, this group is three times more likely to acquire HIV than adolescent boys and young men of the same age group. These inequalities are not inevitable. Enabling girls to complete secondary education dramatically reduces their vulnerability to HIV, and when countries take measures to tackle gender-based violence and secure access to key services, their risk of HIV infection further decreases.
“Respect for the human rights of all people is key to overcoming the AIDS pandemic,” said Ms Byanyima.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
UN High Commissioner for Human Rights Volker Türk


Press Statement
UNAIDS welcomes the recent decision of the government of the Republic of Kazakhstan to remove the remaining legal barriers for people living with HIV to adopt children
07 December 2022 07 December 2022The 2020 Kazakhstan Code on Public Health and Health Care System guaranteed the right of people living with HIV to adopt children. However, certain bylaw regulations remained that created barriers for people living with HIV to enjoy the right to adopt children. On 1 December 2022, the day the world commemorated World AIDS Day, the Ministry of Health removed this remaining barrier.
UNADS welcomes this progressive action as reaffirmation of Kazakhstan’s continuing commitment to eliminate stigma and discrimination against people living with and affected by HIV.
UNAIDS Country Director in Kazakhstan Gabriela IONASCU said, “Living with HIV is no longer seen as an impediment to adopting and raising children. By excluding HIV from the list of diseases that prevent people from adopting children or becoming guardians or foster parents, Kazakhstan is taking bold steps to advance in the right direction: ensuring human rights for all, including for people living with HIV.”
It furthermore underlines Kazakhstan’s commitment to guaranteeing human rights for all leaving no one behind, including activities under the framework of the Global Partnership for Action to Eliminate All Forms of HIV-Related Stigma and Discrimination which the Republic of Kazakhstan joined in 2021 among 30 other pilot countries.
“Similar changes in legislation were made in other eastern European and central Asian countries, including the Kyrgyz Republic, the Republic of Moldova, the Russian Federation, and Ukraine. UNAIDS reaffirms its commitment to provide technical assistance and expert support to advance progress to end AIDS in Kazakhstan and support all people living with and affected by HIV across the region,” said Eamonn Murphy, UNAIDS Deputy Executive Director and Regional Director for Eastern Europe and Central Asia
Note: The decree of the Ministry of Health of The Republic of Kazakhstan
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Region/country


Press Statement
Australia and UNAIDS strengthen partnership to advance the end of AIDS
02 December 2022 02 December 20222 December 2022
UNAIDS and the Australian Government have signed a new five-year strategic partnership agreement to advance efforts to respond to HIV in the Asia-Pacific region. The agreement will help to intensify efforts to get back on track to end AIDS by 2030, by addressing the inequalities that hamper the global HIV response.
As part of the agreement, Australia will commit AUD 25 million from 2022 to 2027 to support the global effort to ending AIDS, and to improve HIV outcomes for people in Asia-Pacific.
While Asia-Pacific has seen remarkable progress, many challenges remain. The COVID crisis interrupted vital services across the region, hurting progress. New HIV infections in the region are rising again for the first time in a decade. Key populations, LGBTQI communities, and people with disabilities continue to face unequal access to medicine and healthcare, along with enduring stigma. These inequalities have hindered the HIV response.
The agreement will assist communities and countries to tackle those inequalities, advancing proven approaches which help equalize access to HIV prevention, testing, treatment and care. The agreement recognizes the role of UNAIDS in providing international leadership and coordination to guide the HIV response. It builds on the strengths and experiences of Australia and UNAIDS to ensure strong partnership engagement.
The partnership will enable a robust and sustainable response to HIV which is integrated into the wider context of health and sustainable development in the Asia–Pacific region.
“Australia is a longstanding and valued partner of UNAIDS, said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. This new agreement will help us to build on this partnership and draw on our collective expertise to end AIDS by 2030.”
“The Australian Government is investing in our long-standing partnership with UNAIDS,” said Senator the Hon Penny Wong, Minister of Foreign Affairs. “Our five-year partnership builds upon our efforts to recover lost ground during the COVID pandemic and set our region, and the world, back on the path to ending HIV/AIDS.”
In 2021, 650 000 people were lost to AIDS and 1.5 million people newly acquired HIV. Through bold international action to tackle the inequalities which drive it, the world can end AIDS by 2030.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Region/country


Press Statement
UNAIDS welcomes the decriminalisation of same sex relations by Singapore's Parliament
01 December 2022 01 December 2022Responding to the scrapping of the colonial era law which had criminalised gay men, UNAIDS Regional Director for Asia and the Pacific region Taoufik Bakkali said:
“Everyone benefits from decriminalisation. The end of the criminalisation will save lives.
In all countries which have criminalised gay men, it has had the consequence of obstructing access to vital services. Laws which punish consensual same sex relations, as well as contravening the human rights of LGBT people, are a major barrier to improving health outcomes, including in the HIV response. Punitive legislation embeds stigma and discrimination against LGBT people, and deters LGBT people from seeking healthcare for fear of being denounced to the authorities and facing punishment and detention.
The international momentum to scrap colonial punitive laws will inspire other countries to follow. The evidence is clear: if we are to protect the health of everyone, such harmful laws have no future."
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Our work
Region/country


Press Statement
World AIDS Day 2022 — Message from Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS
29 November 2022 29 November 2022World AIDS Day is a moment to honour over 40 million lives lost to AIDS, take stock of the AIDS response, and commit to ending AIDS.
This week we launched a powerful new report, Dangerous Inequalities. In it, we called the world’s attention to a painful reality: currently, we are not on track to end AIDS by 2030, and the reason is inequality.
But there is good news: by equalizing, we can end AIDS.
Firstly:
We must equalize for women and girls to reduce their HIV risks.
In sub-Saharan Africa, adolescent girls and young women are three times more likely to be infected with HIV than boys and men of the same age. The driving factor is inequality.
Enabling girls to stay in school until they complete secondary education reduces their vulnerability to HIV infection by up to 50%. When we include comprehensive sexuality education and other measures for girls’ empowerment then their risk is reduced even further. That is why 12 African countries have come together in the Education Plus Initiative, supported by the United Nations to make this happen.
Beyond this, we must combine services for sexual and reproductive health together with services for preventing and responding to sexual and gender-based violence and HIV.
They must be designed to work for all women and girls, in all their diversity.
We must equalize for marginalised people.
Discrimination against marginalised people is hurting the HIV response. Globally, gay men and other men who have sex with men are 28 times more likely to be infected with HIV. People who inject drugs have 35 times the risk, sex workers 30 times the risk, and transgender women 14 times the risk.
We will not end AIDS unless we can end it for everyone.
The evidence is clear: when you decriminalise, people will come forward for services. Decriminalisation saves lives.
Here are two examples:
In South Africa, where same sex relationships are legal, gay men are 60% more likely to be living with HIV but in Uganda where gay men are criminalized, they are 240% more likely.
In Thailand, where same sex relationships are legal, gay men are 11-times more likely to living with HIV than other men, but in Malaysia where gay men are criminalized, they are 72-times more likely.
But here is the good news. There is a growing momentum from Asia to Africa to the Caribbean, for decriminalizing same sex relationships. In recent years, Angola, Bhutan, and Botswana. In the past few months alone, St. Kitts and Nevis, Singapore, Antigua and Barbuda. In 68 countries these laws still exist. Let’s consign these harmful and colonial laws to history.
But we don’t only need to decriminalise, we need to fight stigma.
Stigma is the sentence passed by society on people for who they are. And it kills.
We need to end stigma for people living with HIV and for marginalised communities. We need every leader – political leaders, faith leaders, traditional leaders, cultural leaders.
Rise. Equalize.
Thirdly:
An inequality that breaks my heart is that against children living with HIV. With the science that we have today, no baby should be born with HIV and no child who has HIV should be without treatment. But today, while three quarters of adults living with HIV are on treatment, only half of children are. This is intolerable.
We will not allow this shameful and avoidable injustice to continue. That is why the United Nations, international partners, civil society and governments from the 12 countries with the highest burden have come together and formed the Global Alliance to end AIDS in Children. We are moving. Tanzania will host the official launch early next year.
Lastly and crucially.
To end AIDS, we must tackle the inequalities in resourcing.
The COVID-19 crisis and the war in Ukraine have increased inequality worldwide. Every day, G20 countries receive 136 million dollars in debt repayments from poor countries in the South. Meanwhile in these countries debt repayments are 4 times more than they spend on health and twice what they spend on education.
In the midst of a crisis of debt, austerity and inequality hitting developing countries, some rich countries have cut back aid for global health and are considering even deeper cuts.
This is not right. Now is not the time to step away, it is the time to step up.
Remember: it is through international solidarity that we reduced inequalities in financing and made amazing gains against AIDS including bringing more than 28 million people onto life-saving treatment. And we must complete the job.
On World AIDS Day, UNAIDS joins with people living with HIV and communities around the world in one shared call to action: Equalize.
Equalize access to rights, equalize access to services, equalize access to resources, equalize access to the best science and medicine.
This is how we will end AIDS.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.

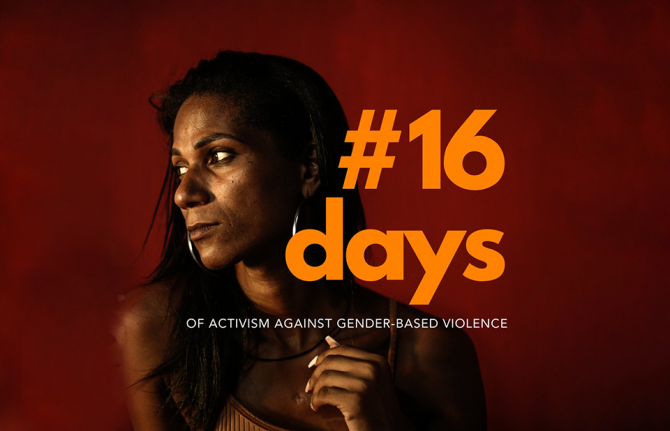
Press Statement
UNAIDS urges world to unite to end gender-based violence against women and girls
25 November 2022 25 November 2022GENEVA, 25 November 2022—On the International Day for the Elimination of Violence Against Women, UNAIDS is calling on the world to unite to end gender-based violence in all its forms and to challenge the gender inequities driving the HIV pandemic.
“Violence against women and girls is our individual and collective shame—a gross violation of human rights happening on an epic scale,” said UNAIDS Executive Director, Winnie Byanyima. “This pandemic of violence continues to drive thousands of new HIV infections every week and is making the end of AIDS much harder to achieve. It is a systemic issue that must be addressed at every level of society.”
Last year, 4900 young women or adolescent girls aged 15—24 became infected with HIV every week. One in three women and adolescent girls around the world have suffered physical and/or sexual violence from their husbands, male partners or strangers. This violence often takes place in their homes and neighbourhoods, where they should be safest. And this staggering statistic doesn’t include the millions more women and girls facing other forms of gender-based violence and harmful practices such as child and forced marriage, female genital mutilation and sexual violence.
In countries with high HIV prevalence, intimate partner violence can increase the chances of women acquiring HIV by up to 50%. Violence or the fear of it blocks women’s access to services and their ability to negotiate condom use with perpetrators, disclose their HIV status or stay on HIV treatment. Keeping girls in school is one way to decrease their exposure to violence and reduces their risk of HIV infection by 50%.
The World Health Organization has named violence against women a global health problem of epidemic proportions. Yet, decades after the Universal Declaration of Human Rights adopted on 10th December 1948 and The Convention on the Elimination of all Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) instituted in 1979—the world is still talking about eliminating violence against women.
Today marks the beginning of 16 Days of Activism Against Gender Based Violence whose theme this year is UNITE! Activism to end violence against women and girls.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
