Cosponsors


Feature Story
Government leaders reaffirm their commitment to accelerate HIV prevention efforts to reduce new HIV infections
10 November 2023
10 November 2023 10 November 2023With just two years left to attain the 2025 HIV prevention target of fewer than 370 000 new HIV infections annually, the world is not on track. In 2022, 1.3 million people became infected with HIV – the urgency to accelerate progress cannot be overemphasized. The Global HIV Prevention Coalition co-convened by UNAIDS and UNFPA ensures a strengthened and sustained political commitment for primary prevention across key policy makers and programme implementers. It includes countries such as Botswana, Cameroon, Eswatini, Lesotho, Malawi, Rwanda South Africa, and Zimbabwe – which have reduced new HIV infections by more than 70% since 2010.
However, there were disparities across populations and regions. No significant declines were seen among key populations (sex workers, men who have sex with men and people who inject drugs).
Globally, 4,000 new HIV infections occurred among adolescent girls and young women aged 15-24 years, every week – 3,000 of these occurred in Sub-Saharan Africa. Approaches and investments for HIV prevention are currently insufficient to meet global targets.
The directors of National AIDS Coordinating Agencies, Ministry of Health HIV leads from the Global HIV Prevention Coalition focus countries and development partners were convened by the HIV Prevention Leadership Forum, with support from UNAIDS and UNFPA, to reinforce their commitment to stopping new HIV infections. This is part of efforts to ensure effective implementation of expanded HIV programmes with a focus on key and priority populations .
During the meeting, each country identified commitments that they will drive and will be held accountable for in 2024 as well as technical level actions necessary for programme optimization. Donors and global technical partners identified opportunities for technical and financial resources available at country level to supplement national resources to drive the action plans.
The first lady of Namibia and UNAIDS Special Advocate for Adolescent Girls, and Young Women, Her Excellency Monica Geingos urged the country leaders in the HIV response to adapt solutions tailored to their national needs culturally, socio-economically, and politically. Whilst strengthening global collaboration, leaders should strengthen partnerships across sectors within the countries. Success in HIV prevention is possible, however, not only does it require leadership at government level, but also communities must lead.
The Global Prevention Coalition co-chair and former Minister of Health of Botswana, Prof. Sheila Tlou encouraged government leaders to follow the science, make data-driven decisions and ensure community leadership and participation in HIV prevention programming. This will secure gains made, bridge disparities and expedite progress needed for success in HIV prevention.
Dr Ruth Laibon Masha, Co-Chair of the HIV Multi-Sector Leadership Forum and Director, National Syndemic Disease Control Council, underscored the need to secure gains made by extraordinary leaders from multiple sectors who have played a crucial role in advancing the HIV movement and achieving significant progress. “By continuing to lead from the front we can work together towards the goal of delivering a future free of new HIV infections and AIDS-related deaths. It’s time to recommit and finish the race against time “, she added.
Vice Minister, National Disease Control and Prevention Administration (NDCPA) affirmed China’s commitment towards strengthened multisectoral leadership and promotion of a nationally led HIV prevention and health agenda.
Quotes
“In this moment, community leadership counts, country leadership counts in making the commitments of this meeting and our Action Plans a reality”
“While scientists, policymakers and funders will continue to drive and be essential to this work, it’s community leadership and mobilization that will end this epidemic. But no matter how good the science or community leadership, HIV will not end if we don’t have significant policy change to reverse criminalization and lessen stigmatization of affected populations. If we can’t protect human rights, then we can’t end HIV. This is never just about the virus—it’s about people, and the people must lead.”
Our work


Press Statement
The United Nations welcomes the Supreme Court’s decision to decriminalize same sex relations in Mauritius
04 October 2023 04 October 2023This will speed up progress to end the AIDS pandemic and save lives.
GENEVA, 4 October 2023—The United Nations in Mauritius—which includes UNAIDS, UNFPA, OHCHR, UNDP and WHO—welcome today’s ruling by the Supreme Court of Mauritius that a discriminatory law criminalizing consensual same sex relations is unconstitutional and will be immediately struck from the legal code. Previously, under Section 250 of the Mauritian Criminal Code (which dated back to 1898) anyone convicted could have faced up to five years in prison.
“The Supreme Court today overturned an obsolete colonial law and demonstrated its commitment to non-discrimination and leaving no-one behind,” said Lisa Singh, United Nations Resident Coordinator in Mauritius. “The UN in Mauritius and internationally welcomes the decision of Mauritius to join the growing list of African countries protecting the human rights of everyone, including LGBTQI+ people.”
The ruling noted that “Section 250 was not introduced in Mauritius to reflect any indigenous Mauritian values but was inherited as part of our colonial history from Britain. Its enactment was not the expression of domestic democratic will, but was a course imposed on Mauritius and other colonies by British rule.” It also noted that a growing number of countries have decriminalized consensual same sex sexual relations, including the United Kingdom which overturned its law in 1967.
“Mauritius' decision to decriminalize homosexuality is an important step forward for public health and a step towards equal rights, respect and dignity for the LGBTQI community,” said Anne Githuku-Shongwe, Director of UNAIDS’ Regional Support Team for Eastern and Southern Africa. “UNAIDS applauds Mauritius for today’s decision which will mean that men who have sex with men will have much easier access to the health and social services they need without fear of arrest or criminalization. Work will need to continue to break down the barriers of stigma and discrimination towards the LGBTQI community, but today’s ruling is a positive step in the right direction. It will save lives.”
Mauritius becomes the latest in a growing list of countries to declare that laws which have criminalized LGBTQI people are unconstitutional. However, UNAIDS estimates that 66 countries still have laws which criminalize consensual same sex relations. In addition to contravening the human rights of LGBTQI people, these laws impede access to health and social services, including HIV services. Such laws fuel stigma and discrimination against LGBTQI people and put them under constant fear of being punished or detained.
The case was brought forward by Abdool Ridwan Firaas Ah Seek, President of Arc-en-Ciel, the largest and longest-standing organisation in Mauritius championing the human rights of LGBTQI people, and was supported by partners including the Human Dignity Trust.
Civil society organizations, especially community-led organizations, are at the forefront of a global wave of progress that advances access to health for all. UNAIDS urges all countries to decriminalise same sex sexual relations. Decriminalization saves and changes lives.
Maneesh Gobin, Attorney General and Minister of Foreign Affairs and Regional Integration in Mauritius said, “In keeping with its internationally acclaimed respect for the rule of law, Mauritius will indeed report to United Nations Member States at the next cycle of the Universal Periodic Review.” The Universal Periodic Review is a unique mechanism of the Human Rights Council that calls for each UN Member State to undergo a peer review of its human rights records every 4.5 years.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Our work
Learn more
Region/country


Feature Story
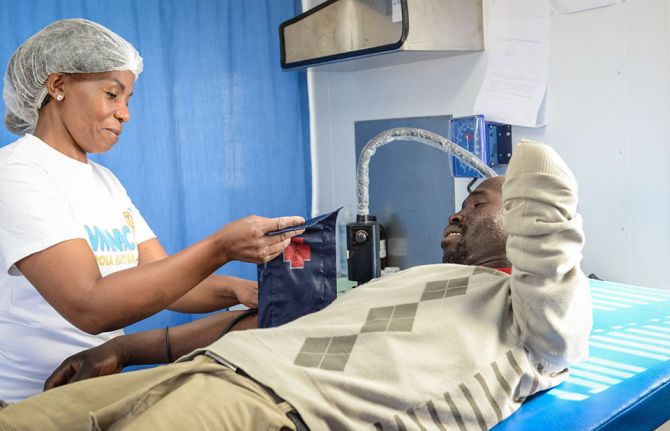
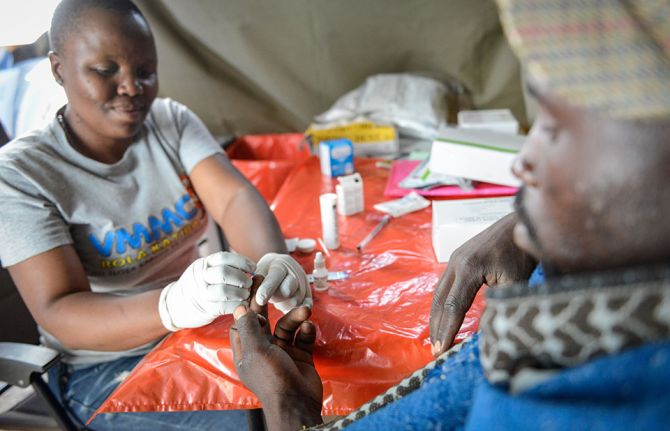
Voluntary medical male circumcision shown to be highly cost-effective, highlighting the need to intensify scale up and sustainability
27 September 2023
27 September 2023 27 September 2023UNAIDS’ Global AIDS Update The Path that Ends AIDS underscores 2 main challenges faced by voluntary medical male circumcision (VMMC) programmes: diminished funding and low coverage among men in their twenties and older. Since VMMC was recommended by WHO and UNAIDS in 2007 as key to HIV prevention in high-prevalence settings, about 35 million men have accessed services across the 15 VMMC priority countries. While this shows good progress, the Global AIDS update highlights that VMMC coverage remains far from reaching the 90% global coverage target for impact in many subnational areas of priority countries. Additionally, funding has declined by almost half since 2020 from approximately US dollars 285 million to US dollars 147 million for the 15 countries funded by the United States President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR). But questions have arisen about VMMC’s cost-effectiveness under growing coverage of other biomedical interventions, such as antiretroviral treatment.
“We need strong political leadership to scale up implementation of VMMC programmes; tackle the inequalities holding back progress; and ensure sufficient and sustainable funding” said Angeli Achrekar, UNAIDS Deputy Executive Director of Programmes. “Countries that are putting people and communities first in their policies and programmes are already leading the world on the journey to ending AIDS by 2030.”
Voluntary medical male circumcision is a simple, safe procedure that has proven to reduce the risk of HIV transmission by up to 60% in heterosexual men. But is it cost effective? For how long must policy makers continue to promote VMMC among adolescent boys and adult men across VMMC priority countries? This is what a group of researchers investigated.
Now published in The Lancet Global Health and using 5 existing mathematical HIV models, the researchers aimed to assess whether providing VMMC for the next 5 years would continue to be a cost-effective use of HIV programme resources in sub-Saharan Africa. The models applied assumptions based on HIV epidemiology in VMMC priority countries focusing on Malawi, South Africa, and Zimbabwe. The impact and cost-effectiveness were projected over 50 years to capture clients’ lifetime HIV exposure and infection.
Findings reveal that a continuation of VMMC was cost-effective even in regions with low HIV incidence; VMMC was cost-effective in 62% of settings with HIV incidence of less than 1 per 100 person-years in men aged 15–49 years, increasing to 95% with HIV incidence greater than 10 per 100 person-years They underscored VMMC’s importance in continuing to avert HIV infections and related healthcare costs over time.
While details of the results varied by country and model (see Box1), overall VMMC was shown to be highly cost-effective and even cost saving in nearly all countries and scenarios.
| Box 1 Varying results across countries
|
The authors concluded that despite the scale-up of antiretroviral therapy and low HIV incidence in some settings, the continuation of VMMC for at least the next 5 years is cost-effective in almost all settings considered in this study.
“Clearly, intensified efforts and commitments are needed to scale up VMMC while at the same time sustaining these services to reach men and boys,'' said Dr Meg Doherty, Director of WHO’s Global HIV, Hepatitis and STI Programmes. “The new Global AIDS report shows a widening gap for men that is important to recognize and address efficiently and effectively for their own health and to reduce new infections.’’
These analyses support a call to action on intensified efforts to reach men and boys in general and for continued funding for VMMC programmes. The discussion on VMMC sustainability is crucial. UNAIDS and WHO are urging countries to intensify their efforts in scaling up VMMC to global coverage targets (90%), at the same time address programme sustainability.
In the 2025 HIV Prevention Roadmap, VMMC remains a core component of combination HIV prevention under the pillar of men and boys. It is not only cost-effective, but also, cost-saving in many settings. Accordingly, continued progress towards male circumcision coverage targets in all the VMMC priority countries must be accelerated
Our work
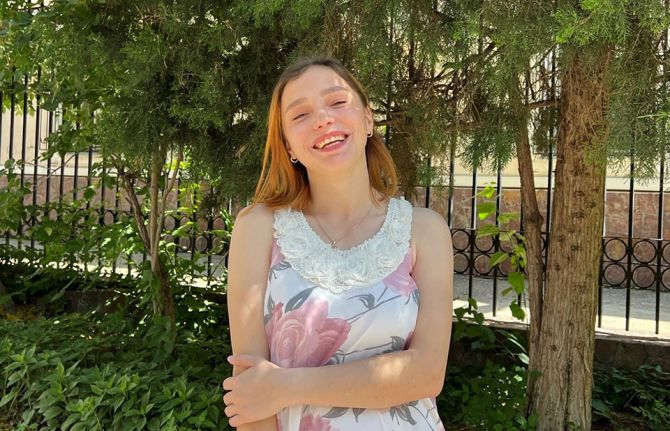
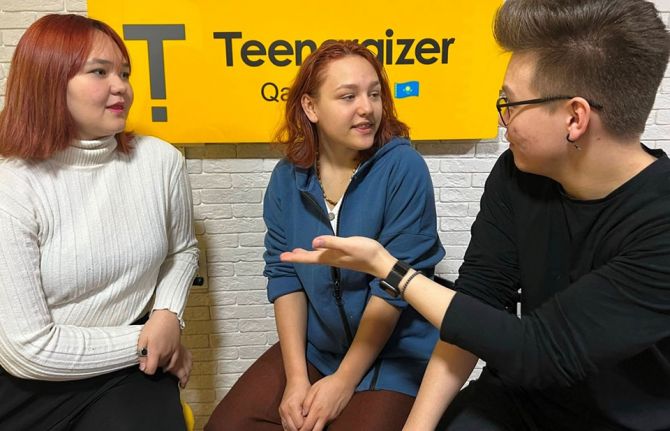




Feature Story
Young role models combat HIV stigma in Central Asia
22 June 2023
22 June 2023 22 June 2023Last year, Elina Kruglova made a bold decision. She disclosed her HIV status during the casting of a popular reality TV show in Uzbekistan.
“I disclosed my status right at the casting because the project lasted for several months, and I needed to take medicine daily,” she said. “I made the decision to be honest and mustered up the courage. I thought they wouldn't accept me, but I passed the casting," Ms Kruglova explained.
In her second-year student in the Faculty of Agricultural Economics at Tashkent State Agrarian University in Uzbekistan, she grew up in an orphanage. She was the first child living with HIV in her country to start antiretroviral (ARV) therapy seventeen years ago. Despite facing stigma, she has been taking life-saving medicine daily.
Uzbekistan struggles with HIV-related stigma and discrimination.
According to the recent Multiple Indicator Cluster Survey (MICS) in Uzbekistan, 76% of women aged 15-49 in the country would refuse to purchase vegetables from a vendor living with HIV and would not accept children living with HIV attend school with other children. Prejudice is fuelled by a lack of knowledge; only 14% of women in the same age group possess comprehensive information about HIV. Uzbekistan's HIV cases have steadily risen by 44 % in the last six years (31,088 in 2016 to an estimated 45,000 in 2022.)
Throughout the TV show, Ms Kruglova shared her experiences of being an orphan and living with HIV. Over time she became an inspiration for young people and those living with HIV.
"When the TV episode aired, I started contemplating how people would perceive me, what they would say, and how they would react,” she recalled. “Psychologists were working with us during the project, which made it easier for me to handle the pressure."
To her surprise, people positively reacted when they recognized her on the streets, and she received numerous supportive messages from people living with HIV via Instagram.
"I am grateful for the trust they placed in me " she said.
For her, the Tashkent day-care center for children and families affected by HIV supported by UNICEF and UNAIDS played a crucial role in her life. It provided a safe haven, gave guidance throughout her childhood and teenage years. The center's support group, the professional consultations, and master classes helped her develop practical life skills. She is optimistic about the future and believes that people can change their attitudes towards HIV with the right information and education. In her mind, hiding only makes things worse.
Aida Muravyova knows all about the power of disclosing her HIV status.
She is a 16-year-old school student in Kazakhstan and learned about her HIV status when she was 6 years old. Although advised against disclosing her status at school and extracurricular activities, Aida chose a different path. She shared her HIV status with her classmates in school and took on the role of breaking down the myths and misconceptions surrounding HIV in front of her peers and adults.
“When I was told about my HIV diagnosis, I thought to myself, 'Okay, I have red hair, I have HIV, I take pills... what else?!'"
Ms Muravyova found solace through the Teenergizer Movement, a youth-led initiative supported by the Kazakhstan Government, UNICEF, UNAIDS and other donors. Teenergizer aims to empower young people living with HIV. It created a safe space for young women like her to connect, have fun, and share experiences without shame or stigma. The movement has reached many young people in the country, creating a ripple effect of reliable information and support.
When Teenergizer came along, Ms Muravyova invited classmates to join. "They got valid information, learned with me, and even conducted training sessions,” she said. “The most gratifying part was when one of my classmates' mothers, initially frightened by my HIV status, learned about HIV through her child's participation in Teenergizer.”
Her friend told her that her family had an open conversation, hashed out concerns, and now everything is okay.
Gender assessments conducted in several countries of Central Asia, including Kazakhstan, confirmed that gender inequality, stereotypes, customs and practices increase women’s vulnerability to HIV as well as limit their choices and expose them to socioeconomic and health difficulties.
Ms Muravyova refuses to let her HIV status define her or limit her dreams.. "I have seen many people living with HIV, but never in my field of Electrical and Aerospace Engineering... I want to change that perception and demonstrate that living with HIV can be different, cool, and interesting."
The UNAIDS Regional Policy and Equality Officer in Central Asia, Elena Kiryushina, sees role models like Elina and Aida as well as community networks as key.
“Promoting leadership among adolescent girls and young women, fostering positive masculinities in boys and men, providing care and support to adolescents living with HIV, especially those who lost parents and access to comprehensive sexuality education in and out of schools, and supporting gender-transformative approaches are essential steps to address HIV and gender-related stigma and to build foundation for the gender equality in Central Asia and beyond,” she said.
UNAIDS and partners believe empowering women and girls and challenging cultural norms is crucial to address HIV stigma and ensure equal access to support and health services.
Ms Muravyova has one mantra. “Speak, and don't be afraid!,” she said. “We are together, and together we'll make it through.”
Region/country
Related




Feature Story
Supporting women and girls affected by gang violence in Haiti
29 June 2023
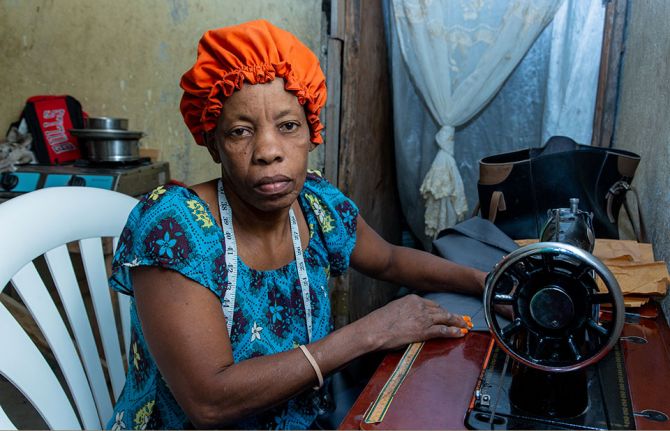
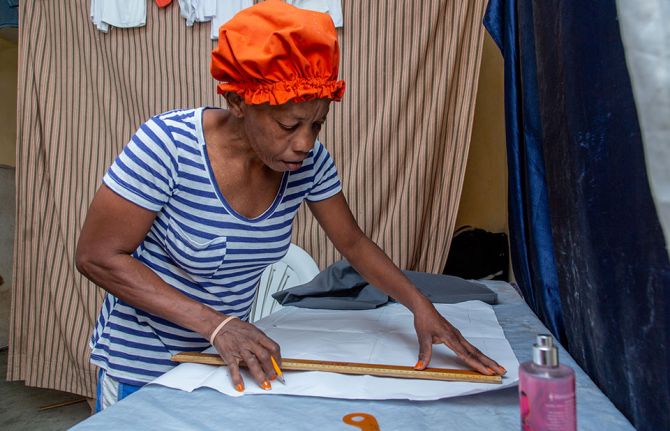
29 June 2023 29 June 2023At Refuge des Femmes d'Haiti, a small women's community-based organization in the commune of Croix-des-Bouquets, Port-au-Prince, Martha Norcimè, a 34-year-old pregnant woman from the nearby commune of Delmas, completes her training in sewing and macramé—a form of textile produced using knotting techniques.
She is part of a group of vulnerable women deeply affected by the gang violence and warfare that has impacted several areas of the capital since early 2022. Most of her peers came from Croix-de-Bouquets. All of them—including women with HIV—living in challenging circumstances, who have seen their livelihood completely disappear throughout these past two years as violence rose.
"I will soon give birth to my first child. I used to sell food and cleaning products that I was buying on the Haitian-Dominican border between Jimani and Malpasse, and I was then selling in markets in the city and in my neighborhood,” recalls Martha. “But I could no longer continue, given the blockade of the North city entry controlled by armed gangs. So many women traders are raped, kidnapped, or robbed by them."
In the fall of 2022, a joint UN project coordinated by the UNAIDS Country Office in Haiti, with participation from UNFPA, UNDP, and UNICEF, has been launched in partnership with Refuge des Femmes d’Haiti and with the support of FOSREF, a Haitian non-governmental organization. The goal is to support women and girls living this daily reality by empowering and giving them the tools to remain healthy and overcome the feminization of HIV in Haiti.
Haiti’s significant gains made over the past decade in controlling its HIV epidemic are now under threat, particularly in the capital, where a third of the 11.8 million Haitians reside. The brunt of an ongoing socio-economic and security crisis triggered by the assassination of former President Jovenel Moïse in July 2021 is borne by adolescent girls, young and adult women.
The feminization of HIV has long been a feature of the Haiti pandemic with HIV prevalence for females at 2.3%, compared to 1.6% among men. Still, the continuing multi-faced and profound crisis, fueled by such levels of violence, is exposing thousands of women to HIV infection.
In October 2022, a joint human rights report published by the United Nations Integrated Office in Haiti (BINUH) and the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR), entitled Sexual violence in Port-au-Prince: a weapon used by gangs to instill fear denounced collective rape by gangs in the capital as a weapon of war. In May 2023, research conducted by the Global Initiative Against Transnational Organized Crime in Cité-Soleil, another impoverished commune in Port-au-Prince deeply hit by gang activity, found that 80% of the women and girls who participated in the study had been victims of one or more forms of gender-based violence by one or multiple perpetrators.
"We work closely with UN Agencies to support women, victims of violence, make them financially independent and thus reduce the feminization of HIV, sexual and gender-based violence and maternal and neonatal mortality," says Novia Augustin, President of Ref-Haiti, and of the Federation of Women Organizations for the Equality and Human Rights (FEDOFEDH). "Difficulties are several, but the biggest is insecurity and the lack of financial resources. My motivation comes from our results: When I look at the satisfaction on the faces of the women we have accompanied, the recognition they show, I tell myself that it is worth it, despite all the difficulties encountered and the risks incurred."
Martha recalls how Novia opened the door to her for intensive training every day from 8 a.m. to 4 p.m. At the time, she was already pregnant. And despite the pregnancy-related fatigue, she did not miss a single day of class. “I can sew skirts, bonnets, blouses and even sandals!" she says proudly. "But I can't do anything now because of this crisis. Sometimes I even miss my pre-natal appointments with the doctor just because I am afraid to go out."
Besides training, Ref-Haiti also included discussions on HIV risk and prevention, gender-based violence, sexual and reproductive health, family planning, and cholera. The awareness-raising activities targeted women beneficiaries and hundreds of young girls of other affected communes.
"We are working to support an integrated health response for women and girls so severely affected by gang violence and by socio-economic inequality”, says Christian Mouala, UNAIDS Country Director for Haiti. “We are proud of women-led local organizations such as Refuge des Femmes and their immeasurable efforts to support women to overcome the challenges they face."
All photos by UNDP Haiti
Region/country
Related




Feature Story
Virtual course on HIV, gender and human rights: empowering medical teachers in Guatemala
18 May 2023
18 May 2023 18 May 2023The University of San Carlos de Guatemala (USAC) Faculty of Medical Sciences, in collaboration with UNAIDS, the World Health Organization (WHO), and the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), launched an online course titled "Conceptos clave sobre VIH, Género y Derechos Humanos" (Key Concepts on HIV, Gender, and Human Rights). The four-module course is designed to provide teaching staff with detailed knowledge about key concepts related to HIV, its treatment and prevention, and the national and international legal framework guiding the response to HIV, as well as the gender and human rights dimensions of the epidemic.
With an estimated three new HIV infections each day in Guatemala and only 73% of the estimated 31,000 people living with HIV receiving antiretroviral treatment and persisting high level of stigma and discrimination towards people living with HIV, the course is a significant step towards addressing the country's HIV challenges. The course aims to provide teaching staff and students with the necessary resources to promote, protect, and fulfill the human rights of adults, adolescents, and children living with or at risk of acquiring HIV, in all their diversity.
The course consists of 140 hours of study, including 70 hours of theory and 70 hours of practice, and will be undertaken between May and August 2023. Course participants will join virtual classes and synchronous group workshops and will have to submit the required tasks according to a work schedule.
The course covers four modules: Module 1 - Update on HIV and AIDS; Module 2 - National and international legal framework for the response to HIV; Module 3 - Health sector Policy framework for HIV response; Module 4- Key concepts on gender and human Rights.
During the inauguration, Marie Engel, UNAIDS Country Director, expressed her hope that participants would enjoy taking the course as much as she and other partners had in developing it. She also emphasized that "the course will be enriched with participants' individual knowledge and experiences, their doubts and concerns. There is obviously a lot of knowledge and wisdom among course participants that the facilitators will strive to capture."
Dr. José María Gramajo, General Coordinator of the USAC Faculty of Medical Sciences' Area of Teachers and Postgraduate training, highlighted that "this refresher course will contribute to the professional development of faculty teachers, sharing with them the latest knowledge about innovations related to HIV prevention, detection, and care, and ensuring an in-depth understanding of cross-cutting issues relevant to HIV and other public health problems."
Teaching staff and students are catalysts with the power to change the national response to HIV. As stated by Dr. Mirna Herrarte, Coordinator of the national HIV, STI, and AIDS program, "I am glad to know that there are so many professionals who want to know more about HIV. In the country, HIV treatment schemes are constantly reviewed. As an anecdote, Guatemala had more than 200 antiretroviral schemes a year ago. Under my leadership, we have reduced those schemes by 75%."
Inequalities persist in the most basic health and HIV services, such as access to screening, treatment, and condoms. USAC's collaborative initiative is an important step towards ensuring that all sectors, including academia, are engaged in ending social, economic, and legal inequities. The University of San Carlos de Guatemala is the largest and oldest university in Guatemala, and the only national and public university in the Central American country.
Watch
Region/country
Related



Press Release
UNAIDS calls for access to HIV prevention, treatment and care in prisons, including access to life saving harm reduction services
07 May 2023 07 May 2023Harm reduction policies and practices help people who are using drugs to stay alive and protect them from HIV and Hepatitis C
Released ahead of International Harm Reduction Day - 7 May 2023
GENEVA, 5 May 2023—Many prison systems are struggling to cope, with overcrowding, inadequate resources, limited access to healthcare and other support services, violence and drug use. In 2021, the estimated numbers of people in prisons increased by 24% since the previous year to an estimated 10.8 million people, increasing the strain on already overstretched prison systems.
Drug use is prevalent in prisons. UNAIDS Cosponsor, the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), estimates that in some countries up to 50% of people in prisons use or inject drugs. Unsafe drug injecting practices are a major risk factor for the transmission of HIV and hepatitis C due to limited access to harm reduction services, including condoms, clean needles and syringes, and a lack of comprehensive drug treatment programs, particularly opioid agonist therapy.
People in prison are 7.2 times more likely to be living with HIV than adults in the general population. UNAIDS reports that HIV prevalence among people in prisons increased by 13% since 2017, reaching 4.3% in 2021. Although data are limited, it is thought that around one in four of the total prison population has hepatitis C.
“Access to healthcare, including harm reduction services, is a fundamental human right, and no one should be denied that right because they are incarcerated,” said Eamonn Murphy, UNAIDS Regional Director for Asia Pacific and Eastern Europe and Central Asia. “Prisons are too often ignored in countries' efforts to respond to HIV. A multisectoral, multifaceted approach is urgently needed to save lives, which includes access to clean needles and syringes, effective treatment for dependence on opioid drugs and reducing stigma and discrimination.”
Both drug use and HIV infection are more prevalent among women in prison than among imprisoned men. In particular, women who use drugs and sex workers are overrepresented in prisons. Highlighting the urgent need to scale up the implementation of community-led harm reduction services for women who use drugs and women in prison.
Ms Ghada Waly, Executive Director of UNODC, said, “It is time to put compassion at the heart of our responses. To take a more serious look at de-penalization and alternatives to incarceration for minor drug offenses, focusing instead on treating and rehabilitating. To use a gender-sensitive lens when looking at women and girls who use drugs, and to ensure that they have equal access to treatment. To reach out to young people, who are using drugs more than ever before, understand their vulnerabilities to substance abuse, and help them be part of the solution. To stand with marginalized and vulnerable people, including people in prisons who are underserved by treatment programmes, and people who inject drugs, who are far more likely to be living with HIV, yet far less likely to access life-saving services”.
Among the countries reporting on prisons to UNAIDS in 2019, just 6 of 104 countries had needle and syringe programmes in at least one prison; only 20 of 102 countries had opioid substitution therapy programmes in at least one prison, 37 of 99 countries had condoms and lubricants in some prisons.
UNAIDS, UNODC, and WHO have long supported expanding harm reduction services to all prisons. However, according to Harm Reduction International, only 59 countries globally provide opioid agonist therapy in prisons.
Some countries have made huge progress in recent years. Despite the challenges faced by the influx of refugees and the repercussions of the war in Ukraine, Moldova, (which has an HIV prevalence of 3.2% in its prisons, compared to 0.4% among the general population) has committed significantly more resources into its prison systems.
In the early 2000’s few of its prisons provided harm reduction services. Today all of the country’s 17 penitentiaries provide harm reduction services including, methadone (an opioid agonist therapy), access to psychiatrists, doctors and treatment programmes, needle and syringe exchange and HIV prevention, testing, treatment and care.
Svetlana Plamadeala, UNAIDS Country Director in Moldova said, “It’s about putting people front and center, treating them as equals and taking on a solid, public health approach, grounded in human rights and evidence.”
UNAIDS, UNODC, UNFPA, WHO, ILO and UNDP recommend 15 comprehensive and essential interventions to save lives and ensure effective HIV programming in prisons. These include HIV prevention, testing and treatment, condoms, lubricant, opioid agonist therapy and post-exposure prophylaxis. However, this is only part of the solution. UNAIDS also recommends that countries amend their laws to decriminalize the possession of drugs for personal use.
UNAIDS has set ambitious targets for 2025 which include: 95% of people in prisons and other closed settings who know their HIV status, 95% who know their status are on treatment; and 95% on treatment are virally suppressed; 90% of prisoners used condoms at last sexual activity with a non-regular partner; 90% of prisoners who inject drugs used sterile needles and syringes at last injection; and that 100% of prisoners have regular access to appropriate health system or community-led services.
UNAIDS advocates that communities take an active role in planning, providing and monitoring HIV services. However, this is not always facilitated in prison settings. Without community engagement it will be impossible to reach the global AIDS targets.
For more information on Moldova’s work on HIV in prisons please read Moldova expands harm reduction services to all prisons and watch https://youtu.be/JQYtnsiJKs0
Fact sheet: UNAIDS Human rights fact sheet on HIV in prisons
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaCharlotte Sector
tel. +41 79 500 8617
sectorc@unaids.org
UNAIDS Eastern Europe and Central Asia
Snizhana Kolomiiets
kolomiietss@unaids.org
UNAIDS Geneva
Sophie Barton Knott
tel. +41 79 514 6896
bartonknotts@unaids.org
Watch: Moldova expands Harm Reduction services to all prisons




Feature Story
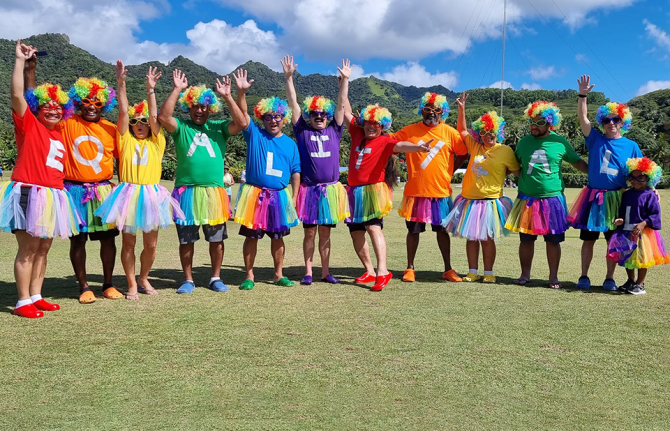
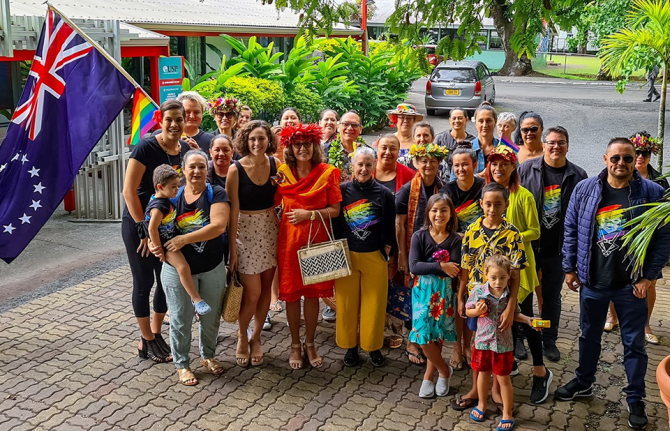
Cook Islands’ original path toward equality
27 April 2023
27 April 2023 27 April 2023On April 14th members of the Cook Islands rainbow community assembled at parliament with colourful flags and cautious optimism. It turned out to be the day they’d been working toward for the last twelve years. Parliament removed laws prohibiting consensual sex between men, striking out sections of the Crimes Act that had been on the books since the turn of the 20th century.
“This decision by Cook Islands is part of a wave of global progress around abolishing harmful laws,” noted UNAIDS Asia Pacific Regional Director, Eamonn Murphy.
“This was a huge historical moment,” said Valery Wichman, President of the Te Tiare Association, the nation’s oldest lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) organisation. “It’s not just a win for the community, but also a shift in terms of our nation maturing and upholding the constitutional rights of all people.”
Ms Wichman, an attorney and public servant, is also an akava'ine—a Māori word meaning transgender woman. She attests that the anti-LGBT laws which made so-called “sodomy” and “indecent acts” punishable by imprisonment reinforced prejudices. This contributed to the LGBT community’s exclusion, harassment and bullying. She has herself experienced being mocked and assaulted.
“A lot of people chose not to live here. It was too hard for them to endure their family’s and society’s judgment. The idea that you are not worthy has carried down from parents to children and has affected how we have been treated by our peers. A lot of trans women have not gone to the doctor because they have been misgendered and have felt disrespected. There have been cases where they ended up dying,” she said.
The journey toward law reform started in 2011. The spark was the discriminatory response to the nation’s first HIV diagnosis. Te Tiare led the advocacy charge with support from organisations including the Cook Islands Family Welfare Association.
A Crimes Bill drafted around 2013 removed the discriminatory clauses. In 2017 parliament set up a Standing Committee to review its raft of proposed revisions. Support for civil society to prepare submissions outlining public health grounds for reforms was provided by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), the lead agency amongst the United Nations Joint Programme on HIV and AIDS working on effective democratic governance and issues affecting sexual and gender minorities.
But following a political change the next year, the committee’s Chair recommended retaining the ban on gay sex. What’s more, he proposed a new section criminalising sex between women. The bill remained in limbo for years. Reform efforts seemed to hit a wall.
A strategy of public dialogue and political engagement rooted in Cook Islands culture enabled a breakthrough. Pride Cook Islands (PCI) was formed as a sister organisation to Te Tiare, focusing on this public advocacy branch of work.
“Obviously we are in a unique situation as a small, conservative, religious population,” PCI President, Karla Eggelton began. “The work of advocacy becomes more delicate when you are living beside people making these decisions for you. We welcomed support from international allies, but we knew we had to do this our own way and have our own approach that is mindful of the situation and culture we live in.”
First TCI tackled messaging. There were deep deliberations around word choice. The mandate was to keep the conversation simple. Ultimately the cause was framed as an equality issue. The rallying cry became, ‘don’t make us criminals in our own country’.
The organisation stayed in communication with policymakers on both sides of aisle. They not only explained their position, but sought to understand politicians’ concerns.
The group met with traditional leaders who are grassroots decision-makers. Village communities were invited to have conversations during public meetings.
“It offered an opportunity for us to understand the misperceptions. We were able to explain that all we are asking for is to not be made criminals. People said, ‘we don’t want to send you to jail, we love our neighbours and our family’,” Ms Eggelton remembered.
The organisation’s patron is Lady Tuaine Marsters whose husband, Sir Tom Marsters, is the British King’s Representative. Lady Marsters frequently attended consultations. Other spokespersons included parents and people with standing in the church. At times supporters were invited to simply stand in solidarity. But anyone who would speak was carefully prepared.
“We spent hours articulating what we would say. We reaffirmed our pledge to not become emotional. We had to keep each other in check to make sure we did not say anything we could regret,” Ms Eggelton outlined.
Then came an effort to increase visibility. The call for equality was largely coming from the LGBT community. They needed other people to demand the same. So PCI embarked on a campaign for people to show their support either by lending their voice to the public dialogue or flying the rainbow flag. The group distributed free flags, urging people to fly one for their daughter, son or grandchild. From restaurants to bars, t-shirts to earrings, the display of support resonated.
A first-of-its-kind pride ad on TV, newspapers and radio challenged Cook Islanders: “We are good enough to be your teachers, nurses, choreographers, dressmakers and orators… but not good enough in the eyes of the law. We are already part of your community, we are just asking you to recognise us as equals.”
This visibility and advocacy work was supported by UNDP through the Being LGBTI in Asia and the Pacific program. PCI developed a project to strengthen the digital capacities of community organisations. A critical outcome was the Pride Pledge Cook Islands initiative with the business community which provides visible safe spaces for LGBT people.
“The UNDP support was instrumental in promoting acceptance and awareness and utilising digital tools to share our message,” Ms Eggelton said.
TCI conducted frequent polls to gauge public sentiment. At the start of the process they lagged behind reform opponents. But by the time would-be Prime Minister, Mark Brown, made an election promise to change the law last year, public sentiment had tilted.
“Once we were able to establish that it was really about equality, then we saw a changing of the tide,” Ms Eggelton reflected.
Ultimately the entire government bench voted in favour of an Amendment Bill while opposition leader, Tina Brown, and two of her Members of Parliament also supported.
Renata Ram, UNAIDS Country Director for Fiji and the Pacific, noted that seven other countries in the Pacific region retain laws criminalising same-sex relations.
“The Cook Islands example proves that along with law reform we can have national dialogues about inclusion, justice and equity,” Ms Ram said.
At a national ceremony marking the end of the South Pacific cyclone season the rainbow community gathered once more, this time to give thanks.
“We want to make sure people understand our gratitude for everything that has transpired and for everyone who worked hard to achieve this,” Ms. Eggelton said. “Our community is now recognised through the eyes of the law as being equal. Now people can feel safe, not like second class citizens.”
Our work
Region/country
Related
 Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia
Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia

24 February 2025




Feature Story
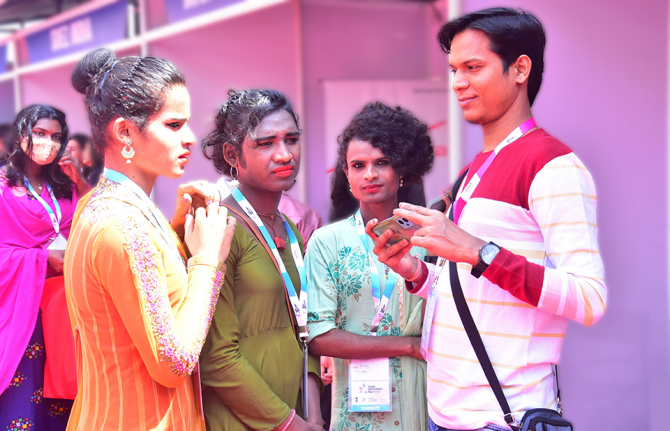
Beyond transgender visibility: India works toward employment equity
31 March 2023
31 March 2023 31 March 2023Ratrish Saha is a transgender woman from Kolkata, India. Even with seven years’ work experience, she was anxious about applying for a new job last year.
“Finding a job is never easy being a transgender woman. I would get rejected with statements like ‘currently no LGBT hiring is going on’ or ‘we do not have facilities to accommodate a trans individual in our office’,” she recalled. But through the Transgender Welfare Equity and Empowerment Trust or TWEET Foundation, she was paired with suitable opportunities in corporations that have received sensitivity training. She soon landed the position of associate consultant for Siemens Technology in Bangalore.
She said of the interview process: “I only talked about my skills and no gender explanations were included in those conversations.” An ecstatic Ms. Saha says she is “grabbing the opportunity… putting my all into it”.
Transgender people in India now have a new pathway toward dignified work thanks to a collaborative effort between communities, government and development partners.
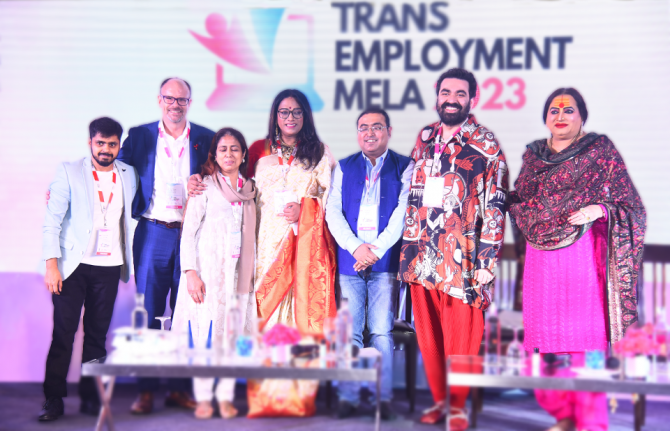
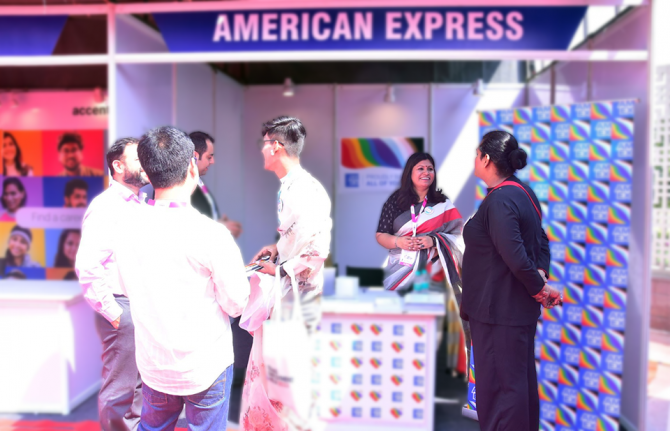
Ahead of the International Day of Transgender Visibility, the UNAIDS Country Office for India and United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) supported the Trans Employment Mela (Job Fair) in New Delhi. The initiative was jointly hosted by the National Institute of Social Defence, Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, TWEET Foundation and In Harmony, a diversity consulting firm.
The programme aims to accelerate the socio-economic inclusion of the trans community by bringing awareness about their issues to mainstream corporations and providing a platform to connect them with job roles in inclusive organisations.
“Not only does this approach provide an opportunity for dialogue between government representatives, civil society organisations, and businesses, but it facilitates access to skills training, career counselling, entrepreneurship support and mentorship support,” Maya Awasthi, Co-Chair and Co-founder of TWEET Foundation explained.
India’s 2019 Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act prohibits employment discrimination against trans people in either the public or private sectors. While stakeholders point to aspects of the law that could be strengthened, they acknowledge that the wide-ranging anti-discrimination provision creates a pathway toward building a more inclusive culture and pursuing redress when rights are violated.
Addressing employment access inequality is relevant to the HIV response. In 2021 HIV prevalence among transgender people in India was 3.8%, almost 20 times the national average. A study commissioned by India’s National Human Rights Commission found that in 2017 just six percent of transgender people were formally employed in either the private or non-governmental organisation (NGO) sector. About 5% engaged in sex work and domestic labour respectively. Thirteen percent sold food and other items while 11% reported begging.
“There are many ways in which higher paying and consistent work can reduce HIV vulnerability,” explained UNAIDS Country Director for India, David Bridger. “By addressing the inequalities that have unfairly pushed trans people away from opportunities, we can help build a more empowered community in which people fulfil their potential, enjoying better health and wellbeing in the process.”
The 2017 Human Rights Commission study found that around half the transgender population never attended school. Several development partners are supporting initiatives to provide the community with education opportunities in a stigma-free environment as well as skills training to promote self-reliance.
Aarav Singh is a transman who had been out of work for six months. He was able to score a human resource internship at Roop Automotives through the Trans Employment Mela.
“This is a sensitised, trans inclusive organisation where I've faced zero issues with documentation. Not only me but my friends have scored great opportunities with some of the leading trans inclusive companies,” he said. “I hope this continues.”
But while the Trans Employment Mela beneficiaries acknowledge the community dimension of their challenge, in other respects they feel like any other hopeful young professional or recent graduate.
Yumnam Thawalngamba Meetei completed an MBA in 2022 but found it difficult to get a management position “or even a small job”.
“With the help of TWEET Foundation I got into Mahindra Logistics Limited as an Executive for Talent Management and Organisational Development in Mumbai. I am thankful for this job to pave a path for my success,” he said.
Region/country
Related
 Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia
Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia

24 February 2025

Press Statement
UNAIDS urges world to unite to end gender-based violence against women and girls
25 November 2022 25 November 2022GENEVA, 25 November 2022—On the International Day for the Elimination of Violence Against Women, UNAIDS is calling on the world to unite to end gender-based violence in all its forms and to challenge the gender inequities driving the HIV pandemic.
“Violence against women and girls is our individual and collective shame—a gross violation of human rights happening on an epic scale,” said UNAIDS Executive Director, Winnie Byanyima. “This pandemic of violence continues to drive thousands of new HIV infections every week and is making the end of AIDS much harder to achieve. It is a systemic issue that must be addressed at every level of society.”
Last year, 4900 young women or adolescent girls aged 15—24 became infected with HIV every week. One in three women and adolescent girls around the world have suffered physical and/or sexual violence from their husbands, male partners or strangers. This violence often takes place in their homes and neighbourhoods, where they should be safest. And this staggering statistic doesn’t include the millions more women and girls facing other forms of gender-based violence and harmful practices such as child and forced marriage, female genital mutilation and sexual violence.
In countries with high HIV prevalence, intimate partner violence can increase the chances of women acquiring HIV by up to 50%. Violence or the fear of it blocks women’s access to services and their ability to negotiate condom use with perpetrators, disclose their HIV status or stay on HIV treatment. Keeping girls in school is one way to decrease their exposure to violence and reduces their risk of HIV infection by 50%.
The World Health Organization has named violence against women a global health problem of epidemic proportions. Yet, decades after the Universal Declaration of Human Rights adopted on 10th December 1948 and The Convention on the Elimination of all Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) instituted in 1979—the world is still talking about eliminating violence against women.
Today marks the beginning of 16 Days of Activism Against Gender Based Violence whose theme this year is UNITE! Activism to end violence against women and girls.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.






