Epidemiology
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 UNAIDS urges that all essential HIV services must continue while U.S. pauses its funding for foreign aid
UNAIDS urges that all essential HIV services must continue while U.S. pauses its funding for foreign aid

01 February 2025
Documents
Dangerous inequalities: World AIDS Day report 2022
29 November 2022
This report, which marks World AIDS Day 2022, unpacks the impact that gender inequalities, inequalities faced by key populations, and inequalities between children and adults have had on the AIDS response. It is not inevitable, however, that these inequalities will slow progress towards ending AIDS. We know what works—with courage and cooperation, political leaders can tackle them. Read press release. Report introduction available in languages, including Arabic, French, Russian, Spanish.
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025


Press Release
Inequalities are blocking the end of the AIDS pandemic, say UN
29 November 2022 29 November 2022DAR ES SALAAM / GENEVA, 29 November 2022—Analysis by the UN ahead of World AIDS Day reveals that inequalities are obstructing the end of AIDS. On current trends the world will not meet agreed global targets on AIDS. But the new UNAIDS report, Dangerous Inequalities, shows that urgent action to tackle inequalities can get the AIDS response on track.
UNAIDS set out earlier this year that the AIDS response is in danger—with rising new infections and continuing deaths in many parts of the world. Now, a new report from UNAIDS shows that inequalities are the underlying reason why. It shows how world leaders can tackle those inequalities, and calls on them to be courageous to follow what the evidence reveals.
Dangerous Inequalities unpacks the impact on the AIDS response of gender inequalities, of inequalities faced by key populations, and of inequalities between children and adults. It sets out how worsening financial constraints are making it more difficult to address those inequalities.
The report shows how gender inequalities and harmful gender norms are holding back the end of the AIDS pandemic.
“The world will not be able to defeat AIDS while reinforcing patriarchy,” said UNAIDS Executive Director Winnie Byanyima. “We need to address the intersecting inequalities women face. In areas of high HIV burden, women subjected to intimate partner violence face up to a 50% higher chance of acquiring HIV. Across 33 countries from 2015-2021 only 41% of married women aged 15-24 could make their own decisions on sexual health. The only effective route map to ending AIDS, achieving the sustainable development goals and ensuring health, rights and shared prosperity, is a feminist route map. Women’s rights organizations and movements are already on the frontlines doing this bold work. Leaders need to support them and learn from them.”
The effects of gender inequalities on women’s HIV risks are especially pronounced in sub- Saharan Africa, where women accounted for 63% of new HIV infections in 2021.
Adolescent girls and young women (aged 15 to 24 years) are three times more likely to acquire HIV than adolescent boys and young men of the same age group in sub-Saharan Africa. The driving factor is power. One study showed that enabling girls to stay in school until they complete secondary education reduces their vulnerability to HIV infection by up to 50%. When this is reinforced with a package of empowerment support, girls’ risks are reduced even further. Leaders need to ensure all girls are in school, are protected from violence which is often normalized including through underage marriages, and have economic pathways that guarantee them a hopeful future.
By interrupting the power dynamics, policies can reduce girls’ vulnerability to HIV.
Harmful masculinities are discouraging men from seeking care. While 80% of women living with HIV were accessing treatment in 2021, only 70% of men were on treatment. Increasing gender- transformative programming in many parts of the world is key to halting the pandemic. Advancing gender equality will benefit everyone.
The report shows that the AIDS response is being held back by inequalities in access to treatment between adults and children. While over three quarters of adults living with HIV are on antiretroviral therapy, just over half of children living with HIV are on the lifesaving medicine. This has had deadly consequences. In 2021, children accounted for only 4% of all people living with HIV but 15% of all AIDS-related deaths. Closing the treatment gap for children will save lives.
Discrimination against, stigmatization and criminalization of key populations are costing lives and preventing the world from achieving agreed AIDS targets.
New analysis shows no significant decline in new infections among gay men and other men who have sex with men in both the western and central Africa and eastern and southern Africa regions. Facing an infectious virus, failure to make progress on key populations undermines the entire AIDS response and helps explain slowing progress.
Around the world, over 68 countries still criminalize same sex sexual relations. Another analysis highlighted in the report found that gay men and other men who have sex with men who live in African countries with the most repressive laws are more than three times less likely to know their HIV status than their counterparts living in countries with the least repressive laws, where progress as far more rapid. Sex workers who live in countries where sex work is criminalized have a 7 times greater chance to be living with HIV than in countries where sex work is legal or partially legalized.
The report shows progress against inequalities is possible and highlights areas where the AIDS response has made remarkable progress. For example, while surveys among key populations often highlight lower service coverage among key populations, three counties in Kenya have achieved higher HIV treatment coverage among female sex workers than among the general population of women (aged 15-49 years). This has been helped by strong HIV programming over many years, including community-led services.
“We know what to do to end inequalities,” said Ms Byanyima. “Ensure that all of our girls are in school, safe and strong. Tackle gender based violence. Support women’s organisations. Promote healthy masculinities—to take the place of the harmful behaviours which exacerbate risks for everyone. Ensure services for children living with HIV reach them and meet their needs, closing the treatment gap so that we end AIDS in children for good. Decriminalize people in same-sex relationships, sex workers, and people who use drugs, and invest in community-led services that enable their inclusion — this will help break down barriers to services and care for millions of people.”
The new report shows donor funding is helping catalyse increased domestic funding: increases in external HIV funding for countries from PEPFAR and the Global Fund during 2018-2021 were correlated with increases in domestic funding from a majority of national governments. New investments to address HIV-related inequalities are urgently needed. At a moment when international solidarity and a surge of funding is most needed, too many high-income countries are cutting back aid for global health. In 2021, funding available for HIV programmes in low- and middle-income countries was US$ 8 billion short. Increasing donor support is vital to getting the AIDS response back on track.
Budgets need to prioritize the health and well-being of all people, especially vulnerable populations that are most affected by HIV-related inequalities. Fiscal space for health investments in low- and middle-income countries needs to be expanded, including through substantial debt cancellation and through progressive taxation. Ending AIDS is far less expensive than not ending AIDS.
In 2021, 650 000 people were lost to AIDS and 1.5 million people newly acquired HIV.
“What world leaders need to do is crystal clear,” said Ms Byanyima. “In one word: Equalize. Equalize access to rights, equalize access to services, equalize access to the best science and medicine. Equalizing will not only help the marginalised. It will help everyone.”
WATCH REPORT LAUNCH
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.




Feature Story
Eastern Europe and Central Asia may face an accelerated increase in new HIV infections and AIDS-related deaths because of the humanitarian crisis gripping the entire region
28 October 2022
28 October 2022 28 October 2022Global shocks, including the COVID-19 pandemic and the war in Ukraine, have further exacerbated risks for the HIV response in Eastern Europe and Central Asia. The growing HIV epidemic and several waves of migration and refugee crises in the region require urgent and considerable efforts to ensure access to essential HIV services for all people in need. Officials and community representatives from several countries of the region have discussed how to address those challenges using the recommendations of the new Global AIDS Report “In Danger’ during the launch of the Report in Almaty, Kazakhstan.
When the Republic of Moldova faced the first wave of refugees from the war in Ukraine, with 500 000 people passing through within the first few months, there was not much time to prepare.
Svetlana Popovichi, National Treatment Coordinator in the Republic of Moldova, explained: “The Government prepared a legislative framework so that all people, regardless of their residence and available documents, have access to necessary HIV services. Civil society and community organizations worked day and night to connect us to people in need. Together with partners, despite the huge flow, we provided all the necessary services, including PrEP and treatment for pregnant women. We were able to quickly redesign our treatment plans so that everyone—our people and refugees—living with HIV had equal access to treatment and services.”
“This is our universal recommendation for countries in crisis,” said Gabriel Ionascu, UNAIDS Country Director in Kazakhstan. “All people, including foreigners, have to have access to HIV services, otherwise the infection will spread further.”
According to Azamat Dysenov, Director of the Treatment Department in the Ministry of Health of Kazakhstan, the availability of antiretroviral medicines for Kazakhstan citizens living with HIV in the country is 100%. Treatment and prevention programmes are funded from the state budget and available for all Kazakh people free of charge. He said: “Today we are facing new challenges, including active migration movements. We are ready to strengthen cooperation with neighbouring countries, maximize the potential of civil society, and work together to remove barriers to access to HIV services for all who need them.”
“Stigma and discrimination towards people living with HIV and other vulnerable groups, which are worsening during the humanitarian crisis, continue to be the major block to an effective response to the HIV epidemic in this region,” said Eamonn Murphy, UNAIDS Deputy Executive Director and Regional Director for Eastern Europe and Central Asia. “HIV transmission, exposure and nondisclosure are criminalized in all countries. While the majority of countries have decriminalized same-sex sexual relations, stigma against gay men and other men who have sex with men remains common.”
According to the UNAIDS Global AIDS Update: In Danger, in 2021, 160 000 [130 000–180 000] people were newly infected with HIV in Eastern Europe and Central Asia, a 48% increase since 2010. The number of AIDS-related deaths in the region in 2021, at 44 000 [36 000–53 000], is 32% higher than in 2010, despite expanding HIV treatment coverage and availability of new prevention methods and measures to control opportunistic infections. According to UNAIDS, in 2020, 54% of new HIV diagnoses in the region were detected at the late stage (CD4+ <350 cells), which is 10% more than in 2018.
Amir Shaikezhanov, an activist and AmanBol Project Director in Kazakhstan, said it is important to remember “there are people behind these facts and figures. Stigma is difficult to measure, but it hugely impacts access to HIV services for different groups. My friend just recently died from AIDS because he was not ready to disclose his gay status and HIV-positive status, even to doctors.”
The “transgender community has been excluded and not visible for a long time. It is great that the report pays attention to this group, including to a high level of stigma towards transgender people,” said Victoria Primak, a transgender activist in Kazakhstan.
According to the UNAIDS report, COVID-19 exposed an epidemic of violence against women across the region. Baktygul Ismailova, Director of the Network of Women Living with HIV in Kyrgyzstan, emphasized that women living with HIV need protection from violence at all levels.
The report’s recommendations for the region include maximizing the availability of community-led, people-centred services; removing punitive and discriminatory laws, especially those criminalizing HIV and people from key populations; national action; and international solidarity in providing sustainable financing.
“Over the past two years, community organizations have proven their ability to adapt quickly to new challenges, address problems quickly in crisis situations, and provide people with the necessary HIV services. We are ready to take on all the work of providing services to key groups. We have people, experience, knowledge and understanding of what exactly and how exactly needs to be done. Give us this opportunity!” urged Nurali Amanzholov, Leader of the Central Asian Association of People Living with HIV.
Recent developments in the region, including the war in Ukraine, massive waves of refugees and migration, humanitarian challenges and economic slowdown, bring additional challenges in providing HIV and other health-care services to all people in need and ensure sustainable financing. Domestic funding for the HIV response in the region may slow down, and countries that still depend on international resources will not be able to ensure the sustainability of AIDS programmes.
“Consolidated efforts of countries and increased support from the international community are urgently needed,” said Eamonn Murphy.
Watch: launch event (English interpretation)
Watch: launch event (Russian)
Region/country
Related
Documents
Executive summary — In Danger: UNAIDS Global AIDS Update 2022
27 July 2022
Progress in prevention and treatment is faltering around the world, putting millions of people in grave danger. Eastern Europe and central Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East and North Africa have all seen increases in annual HIV infections over several years. In Asia and the Pacific, UNAIDS data now show new HIV infections are rising where they had been falling. Action to tackle the inequalities driving AIDS is urgently required to prevent millions of new HIV infections this decade and to end the AIDS pandemic. See also: Full report | Fact sheet | Epi slides | Microsite | Press release | Arabic translation of the report summary
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
Documents
2021 UNAIDS Global AIDS Update — Confronting inequalities — Lessons for pandemic responses from 40 years of AIDS
14 July 2021
UNAIDS report shows that people living with HIV face a double jeopardy, HIV and COVID-19, while key populations and children continue to be left behind in access to HIV services. Read the press release | Data slides | This document is also available in Arabic
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025
 UNAIDS urges that all essential HIV services must continue while U.S. pauses its funding for foreign aid
UNAIDS urges that all essential HIV services must continue while U.S. pauses its funding for foreign aid

01 February 2025
Documents
2021 World AIDS Day report — Unequal, unprepared, under threat: why bold action against inequalities is needed to end AIDS, stop COVID-19 and prepare for future pandemics
29 November 2021
This document is also available in Arabic
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
Documents
UNAIDS data 2021
29 November 2021
Documents
The response to HIV in western and central Africa
29 October 2021
The HIV response across western and central Africa is improving, but not fast enough to end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030. Over the past year, the COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted HIV and other health services, and it has highlighted the vulnerability of people in the region to public health, climatic, socioeconomic and security shocks, along with the pressing need for inclusive social protection systems.
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 Impact of the pause of US foreign assistance in Côte d'Ivoire
Impact of the pause of US foreign assistance in Côte d'Ivoire

19 February 2025
 Government mitigation measures in Cameroon
Government mitigation measures in Cameroon

09 February 2025

Update
Financial shortfalls hold back the HIV response in western and central Africa
25 October 2021
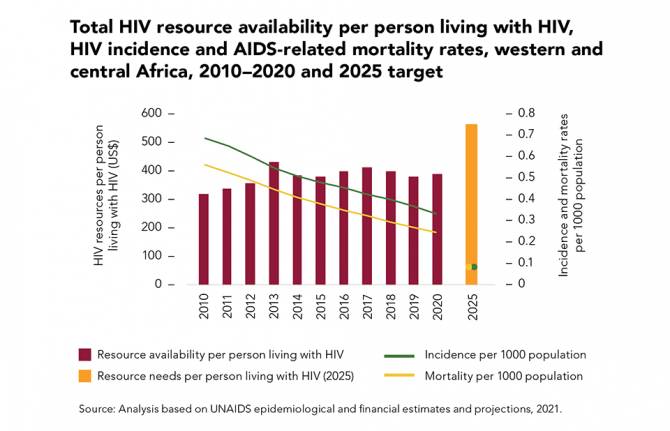
25 October 2021 25 October 2021Underinvestment in the HIV responses of low- and middle-income countries was a major reason why the global targets for 2020 were missed. Financial resource availability during the past five years was consistently below the resources needed, and in 2020 it was 29% less than the US$ 26 billion target for that year (in constant 2016 US dollars).
In western and central Africa, large resource shortfalls and continued reliance on out-of-pocket expenditures (such as user fees for health services) are associated with more modest declines in the incidence of HIV infection and the rate of AIDS-related mortality compared to eastern and southern Africa, where a combination of domestic and international investments has fuelled the rapid expansion of HIV prevention, testing and treatment in areas with a high burden of HIV, resulting in strong and steady reductions in the rate of HIV infections and AIDS-related mortality.
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 Impact of the pause of US foreign assistance in Côte d'Ivoire
Impact of the pause of US foreign assistance in Côte d'Ivoire

19 February 2025
















