Epidemiology
Related
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
Slide deck - 2024 global AIDS update
22 July 2024
Core epidemiology slides
22 July 2024

Update
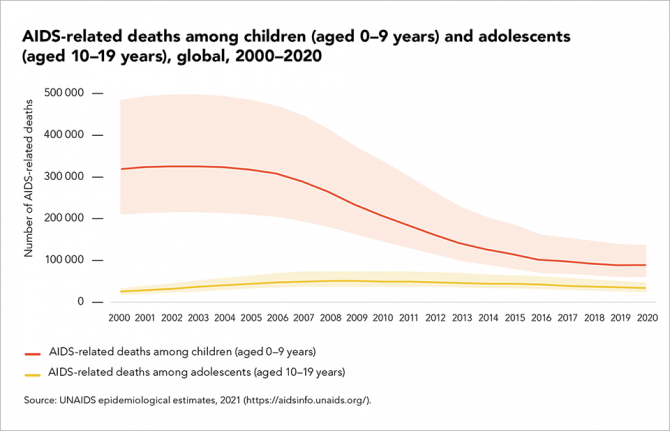
Slow progress on AIDS-related deaths among adolescents
04 October 2021
04 October 2021 04 October 2021Current inequalities in HIV testing and treatment for children living with HIV and trends in historical coverage of services to prevent vertical (mother-to-child) transmission of HIV are driving year-on-year trends in AIDS-related mortality.
Reductions in AIDS-related deaths among children and adolescents are steepest among children aged 0 to 9 years (a 60% decline since 2010), reflecting both improvement in efforts to prevent new vertical infections and efforts to diagnose and treat children in the months following childbirth and during breastfeeding.
However, among adolescents (aged 10–19 years), progress is slower, with AIDS-related deaths declining just 37% over the same period.
The single biggest paediatric treatment challenge is to rapidly find children living with HIV who were missed at birth or during breastfeeding and link them to care. Scale-up of rights-based index, family and household testing and self-testing, and integrating HIV screening with other child health services, can help close this gap.
Our work
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025


Press Release
UNAIDS report shows that people living with HIV face a double jeopardy, HIV and COVID-19, while key populations and children continue to be left behind in access to HIV services
14 July 2021 14 July 2021People living with HIV are at a higher risk of severe COVID-19 illness and death, yet the vast majority are denied access to COVID-19 vaccines. Key populations and their sexual partners account for 65% of new HIV infections but are largely left out of both HIV and COVID-19 responses—800 000 children living with HIV are not on the treatment they need to keep them alive
GENEVA, 14 July 2021—The UNAIDS Global AIDS Update 2021, launched today, highlights evidence that people living with HIV are more vulnerable to COVID-19, but that widening inequalities are preventing them from accessing COVID-19 vaccines and HIV services.
Studies from England and South Africa have found that the risk of dying from COVID-19 among people living with HIV was double that of the general population. In sub-Saharan Africa, which is home to two thirds (67%) of people living with HIV, less than 3% had received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine by July 2021. At the same time, HIV prevention and treatment services are eluding key populations, as well as children and adolescents.
COVID-19 vaccines could save millions of lives in the developing world but are being kept out of reach as rich countries and corporations hold on tightly to the monopoly of production and delivery of supplies for profit. This is having a severe impact around the world as health systems in developing countries become overwhelmed, such as in Uganda, where football stadiums are being turned into makeshift hospitals.
“Rich countries in Europe are preparing to enjoy the summer as their populations have easy access to COVID-19 vaccines, while the global South is in crisis,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “We have failed to learn the lessons of HIV, when millions were denied life-saving medicines and died because of inequalities in access. This is totally unacceptable.”
The new UNAIDS report shows how COVID-19 lockdowns and other restrictions have badly disrupted HIV testing—in many countries this has led to steep drops in HIV diagnoses, referrals to care services and HIV treatment initiations. In KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa, for example, there was a 48% drop in HIV testing after the first national lockdown was imposed in April 2020. There were also fewer new HIV diagnoses and a marked drop in treatment initiation. This occurred as 28 000 HIV community health-care workers were shifted from HIV testing to COVID-19 symptom screening.
The report, Confronting inequalities, shows that in 2020 the 1.5 million new HIV infections were predominantly among key populations and their sexual partners. People who inject drugs, transgender women, sex workers and gay men and other men who have sex with men, and the sexual partners of these key populations, accounted for 65% of HIV infections globally in 2020. Key populations accounted for 93% of new HIV infections outside of sub-Saharan Africa, and 35% within sub-Saharan Africa. However, they remain marginalized and largely out of reach of HIV services in most countries.
The report shows that many of the 19 countries that achieved the 90–90–90 targets by 2020 have been leaders in differentiated service delivery, where facility-based services are complimented by community-led services. Most have also included key populations as central to their responses. In Estonia, for example, the expansion of comprehensive harm reduction services was followed by a 61% countrywide reduction in HIV infections and a 97% reduction in new HIV infections among people who inject drugs.
HIV testing and treatment has been scaled up massively over the past 20 years. Some 27.4 million of the 37.7 million people living with HIV were on treatment in 2020. However, gaps in service provision are much larger for children than for adults. In 2020, around 800 000 children aged 0–14 years who were living with HIV were not on HIV treatment. Treatment coverage was 74% for adults but just 54% for children in 2020. Many children were not tested for HIV at birth and remain unaware of their HIV status, making finding them and bringing them into care a major challenge.
Confronting inequalities also shows that women and girls in sub-Saharan Africa continue to be at a higher risk of HIV infection, with gender inequality and gender-based violence at the centre of that risk. Gender inequalities and gender-based violence rob women and girls of their fundamental human rights, including the right to education, health and economic opportunities. This increases their risk of HIV infection and blocks access to services. In sub-Saharan Africa, adolescent girls and young women account for 25% of all new HIV infections despite representing just 10% of the population.
Poverty and lack of schooling are also formidable barriers to health and HIV services. The report shows how family planning services for women and voluntary medical male circumcision for men and boys are much less likely to be accessed by people living in poverty. In 2020, the number of voluntary medical male circumcisions dropped by more than 30% in 15 priority countries in eastern and southern Africa.
Poverty is also a driver of migration, which has been shown to severely impact access to HIV services and puts lives in danger as migrants flee conflict and poverty in the hope of safety and economic security.
“Billionaires are sailing their yachts in the same Mediterranean waters that migrants are drowning in,” said Winnie Byanyima. “How can we stand by and let this be the “new normal”. We must confront these horrific inequalities and put the emphasis back on respect for basic, fundamental human rights.”
Inequalities are not naturally occurring. They are the result of policy and programmatic actions that divide rather than include. For example, key populations are marginalized and criminalized for their gender identities and expression, sexual orientation and livelihoods. New analysis included in the report shows a positive correlation between better HIV outcomes and the adoption of laws that advance non-discrimination. A study from sub-Saharan Africa found that HIV prevalence among sex workers was 39% in countries that criminalized sex work, compared to 12% in countries where sex work was partially legalized.
“We are 40 years into the fight against HIV. Both the successes and the failures have taught us that we cannot prepare for or defeat a pandemic unless we tear down inequalities, promote people-centred, rights-based approaches and work together with communities to reach everyone in need,” said Ms Byanyima.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Documents
Global commitments, local action
03 June 2021
After 40 years of AIDS, charting a course to end the pandemic. Read press release


Press Release
Forty years on and new UNAIDS report gives evidence that we can end AIDS
03 June 2021 03 June 2021UNAIDS urges world leaders to adopt a bold political declaration on HIV at the United Nations General Assembly High-Level Meeting on AIDS, being held in New York and online next week, and to commit to achieving a new set of targets for 2025 to end AIDS by 2030
NEW YORK/GENEVA, 3 June 2021—Four decades after the first cases of AIDS were reported, new data from UNAIDS show that dozens of countries achieved or exceed the 2020 targets set by the United Nations General Assembly in 2016—evidence that the targets were not just aspirational but achievable.
The report shows that countries with progressive laws and policies and strong and inclusive health systems have had the best outcomes against HIV. In those countries, people living with and affected by HIV are more likely to have access to effective HIV services, including HIV testing, pre-exposure prophylaxis (medicine to prevent HIV), harm reduction, multimonth supplies of HIV treatment and consistent, quality follow-up and care.
“High-performing countries have provided paths for others to follow,” said Winnie Byanyima, the Executive Director of UNAIDS. “Their adequate funding, genuine community engagement, rights-based and multisectoral approaches and the use of scientific evidence to guide focused strategies have reversed their epidemics and saved lives. These elements are invaluable for pandemic preparedness and responses against HIV, COVID-19 and many other diseases.”
Globally, the report shows that the number of people on treatment has more than tripled since 2010. In 2020, 27.4 million of the 37.6 million people living with HIV were on treatment, up from just 7.8 million in 2010. The roll-out of affordable, quality treatment is estimated to have averted 16.2 million deaths since 2001.
Deaths have fallen in large part due to the roll-out of antiretroviral therapy. AIDS-related deaths have fallen by 43% since 2010, to 690 000 in 2020. Progress in reducing new HIV infections has also been made, but has been markedly slower—a 30% reduction since 2010, with 1.5 million people newly infected with the virus in 2020 compared to 2.1 million in 2010.
The report underscores that countries with punitive laws and that do not take a rights-based approach to health punish, ignore, stigmatize and leave key populations—which make up 62% of new HIV infections worldwide—on the margins and out of reach of HIV services. For example, almost 70 countries worldwide criminalize same-sex sexual relationships. Gay men and other men who have sex with men, sex workers, transgender people, people in prison and people who inject drugs are left with little or no access to health or social services, allowing HIV to spread among the most vulnerable in society.
Young women in sub-Saharan Africa also continue to be left behind. Six out of seven new HIV infections among adolescents aged 15–19 years in the region are among girls. AIDS-related illnesses remain the leading cause of death among women aged 15–49 years in sub-Saharan Africa.
COVID-19 has shown the fragility of the health and development gains made over the past decades and has exposed glaring inequalities. To get the world on track to end AIDS by 2030, the global AIDS community and UNAIDS have used an inequalities lens to develop an ambitious and achievable strategy with new targets to reach by 2025. Ending inequalities requires HIV responses that can reach the populations currently being left behind.
If reached, the targets will bring HIV services to 95% of the people who need them, reduce annual HIV infections to fewer than 370 000 and AIDS-related deaths to fewer than 250 000 by 2025. This will require an investment of US$ 29 billion a year by 2025. Each additional US$ 1 of investment in implementing the global AIDS strategy will bring a return of more than US$ 7 in health benefits.
UNAIDS urges the United Nations General Assembly to commit to the targets in a new political declaration on HIV at the fifth United Nations General Assembly High-Level Meeting on AIDS, taking place from 8 to 10 June 2021.
“The world cannot afford to underinvest in pandemic preparedness and responses,” said Ms Byanyima. “I strongly urge the United Nations General Assembly to seize the moment and commit to taking the actions needed to end AIDS.”
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Watch


Press Release
United Nations Secretary-General calls for a greater focus on ending inequalities to end AIDS
30 April 2021 30 April 2021Forty years since the first AIDS cases were reported and just weeks before the United Nations General Assembly High-Level Meeting on AIDS, the United Nations Secretary-General has released a new report with recommendations and targets to get the world back on track to end AIDS
NEW YORK, 30 April 2021—The United Nations Secretary-General, António Guterres, has warned that despite intensive action and progress made against HIV in some places and population groups, HIV epidemics continue to expand in others and issued a set of 10 key recommendations.* If followed by all countries, this will end the AIDS pandemic as a public health threat by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. In a new report, Addressing inequalities and getting back on track to end AIDS by 2030, the United Nations Secretary-General urges the world to address the inequalities that are slowing progress.
“It is imperative to break out of an increasingly costly and unsustainable cycle of achieving some progress against HIV but ultimately not enough to bring about an end to the pandemic,” said Mr Guterres in the report. “Inequalities are the key reason why the 2020 global targets were missed. By ending inequalities, transformative outcomes can be achieved for people living with HIV, communities and countries.”
The global targets set out in the General Assembly’s 2016 Political Declaration on Ending AIDS were missed by a long way, allowing the AIDS pandemic to grow in many regions and countries. The staggering 1.7 million new HIV infections that occurred in 2019 are more than three times higher than the 2020 target of less than 500 000 new infections. In addition, the 690 000 AIDS-related deaths in 2019 far exceed the 2020 target of reducing deaths to fewer than 500 000 a year.
“Ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030 is still within reach—many countries are showing that rapid progress against HIV is possible when evidence-informed strategies and human rights-based approaches are adopted,” said UNAIDS Executive Director Winnie Byanyima. “But it requires bold political leadership to challenge and address the social injustices and inequalities that continue to make certain groups of people and entire communities highly vulnerable to HIV infection.”
The report notes that COVID-19 has caused additional setbacks. The United Nations Secretary-General warned that COVID-19 is not an excuse for missing AIDS targets, but rather a stark warning to the countries that they can no longer afford to underinvest in pandemic preparedness and responses.
At the same time, the COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the many spill-over benefits of HIV investments in health and development. Community-led service delivery pioneered by the HIV response is helping to overcome the extraordinary impediments created by COVID-19.
The set of 10 recommendations to get the world back on track include: addressing inequalities and reaching all people living with or at risk of HIV infection to reduce the annual new HIV infections to under 370 000 and annual AIDS-related deaths to under 250 000 by 2025; prioritizing HIV prevention to ensure that 95% of people at risk of HIV infection have access to effective HIV prevention options by 2025; and eliminating new HIV infections among children.
The report underscores that addressing social and structural factors that perpetuate inequalities is key. It highlights, for example, how gender inequality, underpinned by harmful gender norms, restricts women’s use of HIV and sexual and reproductive health services by perpetuating gender-based violence and limiting decision-making power, including the ability of women and girls to refuse unwanted sex, negotiate safer sex and mitigate HIV risk.
It also shows how vulnerable, marginalized and criminalized communities, such as gay men and other men who have sex with men, people who use drugs, sex workers, transgender people, prisoners and migrants, also remain at higher risk of HIV infection than the general population because they are not receiving essential information and HIV treatment, prevention and care services.
The United Nations Secretary-General describes how communities of people living with, at risk of and affected by HIV are the backbone of the HIV response. Initiatives led by people living with HIV, women, key populations, young people and other affected communities have identified and addressed key inequalities and service gaps, advocated for the rights of their constituents and expanded the reach, scale and quality of health services.
In the report, Mr Guterres applauds UNAIDS’ recently adopted Global AIDS Strategy 2021–2026: End Inequalities, End AIDS. “The lessons from the countries, cities and communities that successfully fast-tracked their HIV responses over the last five years are at the heart of the UNAIDS Global AIDS Strategy 2021–2026,” said Mr Guterres. “The global AIDS community and UNAIDS have used an inequalities lens to develop the strategy, with new targets that are ambitious, granular and tailored to reach the furthest behind first.”
The report comes 25 years after the creation of UNAIDS and describes how COVID-19 has exposed social inequalities and health system weaknesses. The United Nations Secretary-General says that the world should leverage the experience from responding to the AIDS pandemic to strengthen health systems across the world and improve pandemic preparedness. He also calls for enhanced global solidarity to close the HIV resource gap and increase annual HIV investments in low- and middle-income countries to US$ 29 billion by 2025.
*The 10 recommendations in the United Nations Secretary-General’s report:
- Reduce and end the acute and intersecting inequalities that are obstructing progress to end AIDS.
- Prioritize HIV prevention and ensure that 95% of people at risk of HIV infection have access to and use appropriate, prioritized, person-centred and effective combination prevention options by 2025.
- Close gaps in HIV testing, treatment and viral suppression that are limiting the impact of HIV responses and achieve by 2025 the 95–95–95 testing and treatment targets within all subpopulations, age groups and geographic settings, including children living with HIV.
- Eliminate vertical HIV transmission and end paediatric AIDS.
- Put gender equality and the human rights of women and girls in all their diversity at the forefront of efforts to mitigate the risk and impact of HIV.
- Implement the GIPA (Greater Involvement of People Living with HIV/AIDS) principle and empower communities of people living with HIV, women, adolescents and young people and key populations to play their critical HIV response roles.
- Respect, protect and fulfil the human rights of people living with, at risk of and affected by HIV and ensure by 2025 that less than 10% of people living with HIV and key populations experience stigma and discrimination.
- Enhance global solidarity to close the HIV response resource gap and increase annual HIV investments in low- and middle-income countries to US$29 billion by 2025.
- Accelerate progress towards universal health coverage and strong primary health care systems, build forward better and fairer from COVID-19 and humanitarian crises, and strengthen global health security and future pandemic preparedness.
- Leverage the 25 years of experience, expertise and mandate of the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) in building multisectoral, multi-stakeholder and rights-based collaborative action to end AIDS and deliver health for all as global public good.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton-Knott
tel. +41 79 514 6896
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS Geneva
Michael Hollingdale
tel. +41 79 500 2119
hollingdalem@unaids.org
Press centre
Download the printable version (PDF)


Feature Story
Epidemiological Well-Being conference opens in Moscow
20 April 2021
20 April 2021 20 April 2021The Epidemiological Well-Being international conference, which will draw attention to the need for stronger health systems and preparedness against epidemics in the light of the colliding COVID-19 and HIV pandemics, opened today in Moscow, Russian Federation. The aims of the conference include discussions on the progress made against infectious diseases globally, highlighting interim results for reaching the goal of ending AIDS by 2030 and coming up with recommendations for sustainable approaches to combating infectious diseases.
The conference was opened by Anna Popova, Head of the Federal Service for Surveillance on Consumer Rights Protection and Human Wellbeing (Rospotrebnadzor), who emphasized the importance of effective international cooperation. “In a critical situation of the rapid spread of the new coronavirus, countries around the world rallied for one goal—to defeat a common enemy, the COVID-19 pandemic. We realized how important it is to maintain a constant dialogue and prompt exchange of information on outbreaks of infectious diseases, to conduct scientific research and confirm laboratory data for the diagnosis of infections,” she said.
The President of the Russian Federation, Vladimir Putin, and the Deputy Prime Minister of the Russian Federation, Tatyana Golikova, sent welcoming words to the participants and organizers.
Winnie Byanyima, the UNAIDS Executive Director, welcomed the decision of the Russian Government to convene the conference in a video statement, saying, “I am grateful for the Russian Federation’s engagement as a United Nations Member State on the UNAIDS Programme Coordinating Board, your strong commitment to ending AIDS and your support to UNAIDS’ efforts of ending AIDS in eastern Europe and central Asia.”
She also expressed hope that the targets in the new Global AIDS Strategy 2021–2026 will be reflected in the Russian Federation’s state strategy against HIV. Ms Byanyima also called on the governments participating in the conference, “To engage in the negotiations in New York on a bold, new, ambitious political declaration that does not lower the bar and will advance the momentum to end AIDS by 2030.”
Shannon Hader, the UNAIDS Deputy Executive Director for Programme, addressed the participants of the conference. “While COVID-19 has increased and exacerbated many of the inequalities that were already perpetuating new HIV infections and AIDS-related deaths, it has also shown the critical importance of lessons from the HIV response—science, community leadership, the importance of public health advocacy and the critical importance of an all-of-government, all-of-society approach to end pandemics.”
The conference includes more than 20 sessions on critical aspects of combating epidemics and is hosted by Rospotrebnadzor with the support of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and in cooperation with UNAIDS.
Related links
Region/country
Related
 Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery
Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery

20 February 2025


Feature Story
Addressing inequalities can decrease HIV prevalence
15 March 2021
15 March 2021 15 March 2021The gaps in HIV responses and resulting HIV infections and AIDS-related deaths lie upon faultlines of inequality.
Data from 46 countries in sub-Saharan Africa show a positive relationship between HIV prevalence and income disparity. After controlling for education, gender inequality and income per capita, a one-point increase in a country’s 20:20 ratio—which compares how much richer the top 20% of a given population is to the bottom 20% of that population—corresponds to a two-point increase in HIV prevalence.
HIV prevalence and income inequality, sub-Saharan African countries, 2019
Our work

Feature Story
Towards 10–10–10 in eastern Europe and central Asia
15 March 2021
15 March 2021 15 March 2021The recent regional launch of the global AIDS report 2020, Prevailing against pandemics by putting people at the centre, in eastern Europe and central Asia provided a platform for the proposal of a joint revision of social and legal enablers in the region to achieve the proposed 2025 targets. UNAIDS Cosponsors, governments and civil society partners presented their views on the issue and the joint action to be taken.
Based on the regional data, the 90–90–90 treatment cascade in the region is far off the targets, having reached only 70–44–41. Lev Zohrabyan, the UNAIDS Strategic Information Adviser for Eastern Europe and Central Asia, noted that one of the reasons for this is late diagnosis: in 2019, 53% of all new HIV cases in the region were registered in the later stages. In his opinion, it shows that testing strategies need revision and require enabling societal conditions.
Societal and service enablers have been given prominence in the proposed 2025 targets; in particular, it is outlined in the 10–10–10 targets that:
- Less than 10% of countries have punitive legal and policy environments that deny access to justice.
- Less than 10% of people living with HIV and key populations experience stigma and discrimination.
- Less than 10% of women, girls, people living with HIV and key populations experience gender inequality and violence.
Achieving these goals includes having enabling laws, policies and public education campaigns that dispel the stigma and discrimination that still surrounds HIV, empower women and girls to claim their sexual and reproductive health and rights and end the marginalization of people at higher risk of HIV infection.
“Interventions in these areas create conditions for people to be more active in HIV testing, seek help and start antiretroviral therapy immediately upon diagnosis, adhere to a treatment regimen or proactively seek HIV prevention services, including pre-exposure prophylaxis,” said Mr Zohrabyan.
Rosemary Kumwenda, the Regional HIV/Health Team Leader at the United Nations Development Programme Istanbul Regional Hub, presented an analysis of the legislation in the eastern Europe and central Asia region on the criminalization of HIV and key populations, noting that the situation in the region remains unfavourable for an effective HIV response. The criminal codes have changed in many countries, but discriminatory laws are changing very slowly. Although many countries revisited their legislation regarding HIV exposure, HIV transmission is criminalized in virtually every country in the region. The Russian Federation and Belarus remain “leaders” in the criminalization of HIV and key populations. Criminal penalties for sex between adult men remain in Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan. The biggest challenge for the region, where more than 48% of new HIV cases are among people who inject drugs, is the criminalization of drug use and possession.
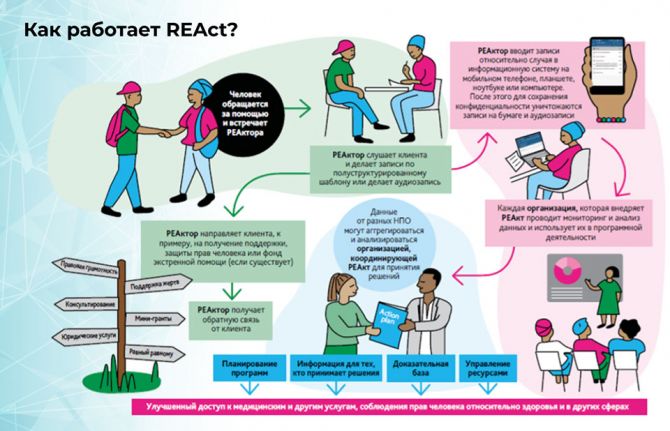
In the presentation An Inventory of Existing Tools for Creating a Favourable Social and Legal Environment in the Eastern Europe and Central Asia Region, given by Tatiana Deshko, the Director of the Department of International Programs, ICF Alliance for Public Health, Ukraine, the ReACT mechanism, which comprehensively works for the rights of key populations, was presented. ReACT (Rights, Evidence, Actions) is the programme’s principle for monitoring violations of rights and is being implemented in 37 cities in seven countries of the region with the support of the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria (Global Fund). Cases of rights violation are registered in a mobile application and then lawyers work with specific cases at the individual level or at the system level of revising legislation. Last year, about 2000 cases were registered. The analysis shows that law enforcement agencies are the primary violators of the rights of key populations in almost all countries, using threats, intimidation, illegal detention and abuse of authority. The health-care system, with denials of medical services, discrimination based on HIV status or disclosure of HIV status, is ranked after law enforcement. “Strategic analysis of cases based on the ReACT-collected data allows not only help for specific people to protect their rights but also formulating recommendations for revising legislation in countries,” said Ms Deshko.
As part of the discussion of the second 10, Alexandra Volgina, the Manager of the Global Partnership for Action to Eliminate All Forms of HIV-Related Stigma and Discrimination, Global Network of People Living with HIV, spoke about the People Living with HIV Stigma Index 2.0 study and the role of the Global Partnership for Action to Eliminate All Forms of HIV-Related Stigma and Discrimination.
Four countries of the region, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, the Republic of Moldova and Ukraine, have entered the Global Partnership for Action to Eliminate All Forms of HIV-Related Stigma and Discrimination. “If we compile the ReACT system, the Stigma Index and other instruments you’ll get a clear picture of what exactly needs to be done to make a difference. We need to address this issue jointly, all partners together. If we change the situation in the area of stigma and discrimination, we will be able to stop the epidemic,” said Ms Volgina.
An example of such an integrated approach, from data to policies and action, was shared by Evghenii A. Golosceapov, a member of the Equality Council in the Republic of Moldova, the first state institution in the post-Soviet countries dealing with discrimination against various groups.
As part of the Equality Council’s work, studies on the People Living with HIV Stigma Index were carried out, where, through public opinion polls and in-depth interviews, categories of people who are marginalized by society were determined. People living with HIV ranked the second among those categories, after lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex people. The Equality Council also uses data from the People Living with HIV Stigma Index, the ReACT registration system and research on the legal environment on HIV.
On this comprehensive basis, more than 70 recommendations on practical steps in the field of legislative changes were developed. These data were used to develop a new national HIV programme and a country proposal to the Global Fund. In addition, the Equality Council considers specific cases of discrimination and complaints (e.g. dismissal due to HIV status) and supports civil society organizations in defending the rights in court. In recent years, the restriction on artificial insemination for people living with HIV has been lifted in the Republic of Moldova, as well as the ban on adoption and guardianship.
All the data collected shape the Roadmap for the Elimination of Discrimination, a government programme in which people living with HIV play a critical role. In the Republic of Moldova, the ScorCard system has also been launched, which allows real-time tracking of the implementation of recommendations and progress towards the adopted targets in reducing stigma and discrimination.
Regional gender gaps in the context of the HIV response were presented by Enkhtsetseg Miyegombo, a Programme Specialist at the UN Women Europe and Central Asia Regional Office.
According to her, the COVID-19 pandemic has largely erased progress in this area and exacerbated existing inequalities: lockdowns disproportionately affected the workload of women who do unpaid domestic work, reduced women’s economic opportunities due to job losses, limited their mobility and increased documented violence against women. These new circumstances were superimposed on existing problems—a lack of awareness about HIV, barriers to discussing safer sex with a partner, revival of patriarchal stereotypes, religious restrictions—as a result of which, women find themselves under growing pressure. Ms Miyegombo highlighted that investment in gender equality programmes is critical to the effectiveness of the regional HIV response.
A study conducted by the Eurasian Women’s Network on AIDS helped to identify the key characteristics of violence and the specifics of organizing assistance to victims of violence in 12 countries of the eastern Europe and central Asia region. The results of the study supplemented the available international data on violence and equipped national civil society organizations with real facts for political advocacy. Elena Rastokina, a specialist in advocacy and community mobilization from the Almaty Model of HIV Epidemic Control project in Kazakhstan, presented successful practices of community-based monitoring in the eastern Europe and central Asia region, concluding that this approach is important as it allows communities to know their rights and barriers and to have systematic data to advocate for systematic change.
Alexander Goliusov, the Director, a.i., of the UNAIDS Regional Support Team for Eastern Europe and Central Asia, stressed that the new 10–10–10 targets are addressing the inequalities that are fuelling the spread of HIV, COVID-19 and other pandemics. “Testing and treatment remain our priorities; however, now our fast track to them lies in combatting inequalities,” he said.
The recording of the launch in Russian and English, along with all presentations and materials, can be found here.
Region/country
Related
 Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery
Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery

20 February 2025
Documents
Prevailing against pandemics by putting people at the centre — World AIDS Day report 2020
26 November 2020
Five years after a global commitment to Fast-Track the HIV response and end AIDS by 2030, the world is off track. A promise to build on the momentum created in the first decade of the twenty-first century by front-loading investment and accelerating HIV service provision has been fulfilled by too few countries. Read press release This document is also available in Arabic
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025











