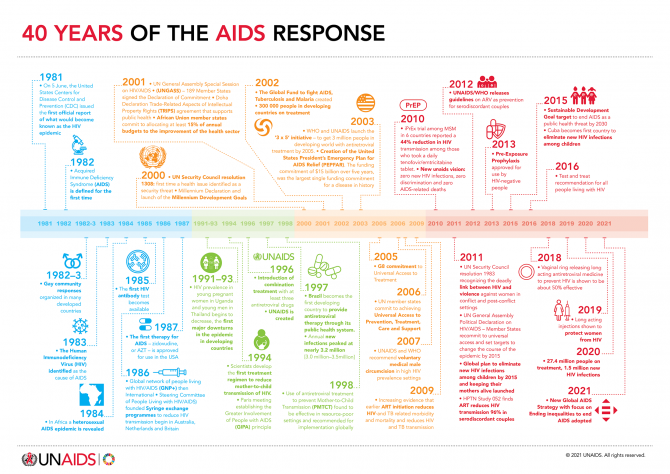
40 years of the AIDS response
Men who have sex with men
14 July 2021
UNAIDS report shows that people living with HIV face a double jeopardy, HIV and COVID-19, while key populations and children continue to be left behind in access to HIV services. Read the press release | Data slides | This document is also available in Arabic

27 February 2025

18 February 2025

01 February 2025
02 June 2021
The 2021-2026 Global AIDS Strategy has bold and critical new targets on realizing human rights, reducing stigma, discrimination and violence and removing harmful punitive laws as a pathway to ending inequalities and ultimately ending AIDS. To aid in the scale up of interventions to remove these societal barriers, UNAIDS has produced a series of fact sheets on human rights in various areas, highlighting the critical need to scale up action on rights. They are a series of short, easy to digest and accessible documents outlining the latest epidemiology, the evidence of the impact of human rights interventions, the latest targets, and international guidelines, recommendations and human rights obligations relating to each topic. Fact sheets: HIV criminalization, HIV and people who use drugs, HIV and gay men and who have sex with other men, HIV and transgender and other gender-diverse people, HIV and sex work, HIV and people in prisons and other closed settings and HIV and stigma and discrimination. This document is also available in Portuguese.
30 January 2025
21 January 2025
17 December 2024
02 December 2024

01 December 2024
26 November 2024




28 October 2021
28 October 2021 28 October 2021The Bangkok Metropolitan Administration (BMA) in Thailand has been awarded the inaugural Circle of Excellence Award at the Fast-Track cities 2021 conference, held recently in Lisbon, Portugal. The Circle of Excellence Award showcases outstanding work in fast-tracking the HIV response and advancing innovative programming to end the AIDS epidemic in cities by 2030.
“To receive the Circle of Excellence Award for Bangkok is a great honour. It demonstrates not only the past achievements but, moreover, the future commitment to accelerate the HIV response and towards ending AIDS in Bangkok. We are proud that innovations have produced remarkable results, particularly same-day antiretroviral therapy and key population-led health services, such as specialized and holistic services for transgender people and the scale-up of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) programmes. These innovations are not only applied in Bangkok but have become models for the region,” said Parnrudee Manomaipiboon, the Director-General of the Department of Health, BMA, during the award ceremony.
Organized by the International Association of Providers of AIDS Care, in collaboration with UNAIDS, the Fast-Track Cities Institute and other partners, the Fast-Track cities conference highlighted successes achieved across the Fast-Track cities network, addressed cross-cutting challenges faced by local stakeholders and shared best practices in accelerating urban HIV, tuberculosis and hepatitis B and C responses.
“Bangkok has put in place a 14-year strategic plan for ending AIDS from 2017 to 2030, which is under the leadership of the Bangkok Fast-Track Committee,” said Pavinee Rungthonkij, the Deputy Director-General, Health Department, BMA. “During COVID-19, BMA and partners have introduced innovations such as multimonth antiretroviral therapy, an express delivery of antiretroviral therapy service, sexually transmitted infection self-sampling and PrEP,” she added. Among other achievements, Bangkok has expanded its PrEP services to 16 municipal public health centres and eight city hospitals and implemented citywide awareness campaigns. PrEP in the City was the first citywide PrEP campaign focusing on transgender people in Asia.
“Significant progress has been made in the HIV response since Bangkok joined the Paris Declaration to end the AIDS epidemic in cities in 2014. It shows that mutual commitments and a strengthened partnership between stakeholders at all levels are key to an effective HIV response. Bangkok will continue to leverage support, scale up innovations and Fast-Track solutions to achieve the 2025 targets and end AIDS by 2030,” said Patchara Benjarattanaporn, the UNAIDS Country Director for Thailand.

21 September 2021
21 September 2021 21 September 2021“My life is now in my hands,” says Erick González, a Venezuelan who has been living in Ecuador for almost a year. For a long time, he has looked for a place where he could feel part of society—he has found that place in Diálogo Diverso.
Based in Quito, the civil society organization created in 2018 works on the protection and promotion of human rights, with an emphasis on gender and lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex (LGBTI) people. Through the Hablemos Positivo (Let’s Talk Positively) initiative, supported by UNAIDS, Diálogo Diverso increased its capacity to respond to the needs of LGBTI migrants during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“There are very few entities working on HIV prevention as well as the other health issues to which we are exposed as part of the LGBTI and migrant community,” said Mr González.
Diálogo Diverso is among the 61 organizations that received grants from the UNAIDS Regional Support Team for Latin America and the Caribbean as part of the Soy Clave: de las Comunidades para las Comunidades (I Am Key: from Communities to Communities) initiative, a platform that aims to promote community-led social solutions to respond to HIV during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“We have received requests from different LGBTI people: Venezuelans, Cubans, Colombians, among others. And we have identified that they all face a very similar migration process,” said Danilo Manzano, the Director and co-founder of Diálogo Diverso, which counts on a team of more than 40 people working in the cities of Quito, Guayaquil, Manta and Cuenca. “But on top of the collective needs as migrants and key populations, it was important to take into account the intersectionality with human rights and the impact of the individual challenges they face in a new country.”
“HIV is one of the reasons why LGBTI people leave the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, given the difficulties in accessing antiretrovirals on a permanent basis, the invisibility of their rights and, on other occasions, hate crimes,” said Andrés Alarcón, an activist with Diálogo Diverso. “This project was born from our experience in serving thousands of LGBTI migrants. And during the pandemic, we identified a particular trend among those living with HIV: lack of information and access to different health services.”
Thanks to a grant provided by UNAIDS, the project delivered hundreds of sexual and reproductive health kits, organized several conversations on health promotion, HIV prevention, sexually transmitted infections and COVID-19 and disseminated a campaign on social networks focused on raising awareness and promoting the human rights of migrant LGBTI people.
“This is a great example of how international organizations, donors and governments can invest in communities so that they can bring social solutions to their own communities while tackling key intersecting issues such as LGBTI rights and migration,” said Guillermo Marquez Villamediana, Senior Community Support Adviser for the UNAIDS Regional Support Team for Latin America and the Caribbean. “Their expertise and outreach capacity have been crucial to keeping the HIV response alive for those most vulnerable during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
One of the highlights of the project was the creation of an alliance between two community-based organizations that work with migrants and refugees in Ecuador, Alianza Igualitaria and Construyendo Igualdad, which extended their reach and allowed them to work with other populations, such as sex workers and young people.
Exclusion based on sexual orientation and gender identity compounds the violations of the human rights of LGBTI migrants and refugees in the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela. According to a study carried out by Diálogo Diverso and the International Organization for Migration in 2020, 43% of LGBTI migrants in the country had experienced exclusion, discrimination or violence. The same study pointed out that LGBTI migrants and refugees find it difficult to access the health system due to lack of information and awareness about it.
“This project gave me knowledge about the possibilities to avoid HIV infection and transmission,” said Reinaldo Mendoza, a Venezuelan migrant who received support from Hablemos Positivo.
Reina Manteña, the President of the Women’s Association of Cantón Milagro, in Ecuador, said that the partnership with Diálogo Diverso in providing technical advice to LGBTI women has been rewarding. “Many compañeras benefited from the kits and the dialogues. Let’s not forget that in the face of this pandemic, health centres were not providing care nor condoms, which are vital for sex workers,” she said. “In addition, we have provided technical support to Venezuelan sex workers so that they could regularize their situation in the country.”
For Mr Manzano and his team in Diálogo Diverso it is gratifying to see these results. “It has never been about quantity, but the quality of the assistance we can offer and its real impact on their lives.”


14 September 2021
14 September 2021 14 September 2021Networks of key populations and community-based organizations in China have called for strengthened collaboration to improve and increase access to Internet-based HIV prevention services.
At the Seminar on Social Organization’s Involvement in Internet-Based HIV/AIDS Prevention, held in Chengdu, China, more than 60 representatives of 45 community-based organizations came together for two days to discuss how to utilize technology and innovations to support the HIV response. In particular, they explored how HIV prevention services can reach a wider range of people and how to encourage key populations to get tested for HIV and initiate treatment if needed.
With the Internet increasingly being used as a source of health information, its potential for delivering HIV prevention services is significant, especially given that services can be delivered anonymously and with minimal cost.
In 2018, according to the government there were 1.25 million people living with HIV in China: 69% of those were aware of their HIV status and 83% of those were accessing treatment. The HIV epidemic in China is concentrated among key populations, particularly among gay men and other men who have sex with men.
Yuan Jizheng, from the Chinese Foundation for Prevention of STD and AIDS, recognized the significant role that Internet companies play in HIV prevention, especially corporations that serve the lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex community, such as Blued, the world’s largest gay dating app. “Companies should continue to advocate for protected sex and HIV prevention and testing, including counselling for key populations and care and support for people living with HIV,” she said.
With more than 8 million active monthly users, apps such as Blued play an important role in promoting HIV services on the Internet among gay men and other men who have sex with men. Such services provide information on HIV prevention through chat room outreach, online partner notifications, online test slips, banner ads, interactive targeted interventions and websites, focusing on populations at higher risk of HIV, including gay men and other men who have sex with men, adolescents and young adults.
Danlan Goodness, a community-based organization affiliated with Blued, launched the Internet + HIV Response initiative four years ago to provide online and offline HIV prevention and treatment services for gay men and other men who have sex with men. Since its inception, 150 community-based organizations from 90 cities in China have joined the platform to provide HIV prevention services through Blued’s new media channels.
The UNAIDS Country Office for China has been working closely with Danlan Goodness to conduct research on Internet-based HIV prevention service strategies for young people and key populations in order to understand better how online services can help to improve service delivery. The research looks at the benefits of Internet HIV prevention services, such as the low cost of delivering content, the ability to reach hidden populations, the potential to erase geographic and social barriers caused by stigma and marginalization and the relative anonymity it provides in seeking information and support online.
“The research findings will be shared with community-based organizations and other related partners to facilitate capacity-building and policymaking in this area,” said Liu Jie, the Community Mobilization Adviser for the UNAIDS Country Office for China.
“The importance of Internet HIV prevention interventions has been magnified during the COVID-19 pandemic, when conventional HIV testing and treatment services were disrupted,” said Kong Lingkun, the President of the Beijing Love without Borders Fund and Chairman of the U = U Anti-AIDS Network of China. “Community-based organizations are willing to work with the government and the private sector, tapping into the potential of Internet HIV prevention interventions to benefit more people,” he added.
At the seminar, community-based leaders and participants exchanged ideas about the challenges and advantages of Internet HIV prevention services, sharing views on overcoming specific difficulties such as data privacy and confidentiality, Internet inaccessibility and ways to enhance cooperation between community-based organizations and the government, international organizations and private corporations.
The forum was co-organized by the Chinese Foundation for Prevention of STD and AIDS, Danlan Goodness, Blued, the UNAIDS Country Office for China, the Chengdu Tongle Social Work Service Centre, the China AIDS Fund for Non-Governmental Organizations and the Sichuan Association of STD and AIDS Prevention and Control.

24 February 2025


12 August 2021
12 August 2021 12 August 2021UNAIDS fully backs calls made today by an eminent group of United Nations experts that Ghana should reject a proposed “family values bill” that targets the country’s lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex community.
After analyzing the draft legislation, the independent experts appointed by the United Nations Human Rights Council concluded that adopting the legislation in its current or any partial form would be tantamount to a violation of a number of human rights standards, including the absolute prohibition of torture.
The experts said that the proposed law seeks to establish a system of State-sponsored discrimination and violence against the LGBTI community.
UNAIDS has already called for the law to be rejected as a gross violation of human rights. It has also warned that the legislation would be a grave setback for the HIV response in driving vulnerable people further away from essential HIV treatment, care and prevention services.
Ghana: Anti-LGBTI draft bill a “recipe for violence” – UN experts
GENEVA, 12 August 2021 — UN human rights experts* urged Ghana’s Government to reject a proposed ‘family values’ bill, saying it seeks to establish a system of State-sponsored discrimination and violence against the LGBTI community. The first reading of the bill took place on 2 August 2021, and its consideration is expected to resume in October 2021.
“The draft legislation argues that any person who deviates from an arbitrary standard of sexual orientation or gender identity is immediately to be considered dangerous, sick or anti-social,” said the experts. “Such laws are a textbook example of discrimination.
“The proposed law promotes deeply harmful practices that amount to ill-treatment and are conducive to torture, such as so-called ‘conversion therapy’ and other heinous violations like unecessary medical procedures on intersex children, and so-called corrective rape for women,” they added.
The independent experts, appointed by the Human Rights Council, presented an analysis of the draft bill to the Ghanaian Government, concluding that adopting the legislation in its current or any partial form would be tantamount to a violation of a number of human rights standards, including the absolute prohibition of torture.
For example, attempts to prevent human rights defenders from organising themselves to defend LGBTI people, and the absolute prohibition of public debate on sexual orientation and gender identity, raises grave concerns about rights to freedom of opinion and expression, and of association. Moreover, the bill in question would essentially legitimize the above instances of violence against LBTI women and reinforce existing gender stereotypes and discrimination against women, which are both cause and consequence of violence against women and girls.
“The consideration of this legislation is deeply perplexing in a country that has been regarded as a champion of democracy in Africa, with an impressive record of achieving certain Millennium Development Goals by 2015,” they said. They cited specific concerns about the MDG goals on health, education, employment, housing and gender justice.
“The draft legislation appears to be the result of a deep loathing toward the LGBTI community. It will not only criminalise LGBTI people, but anyone who supports their human rights, shows sympathy to them or is even remotely associated with them.
“Given that LGBTI people are present in every family and every community it is not very difficult to imagine how, if it were to be adopted, this legislation could create a recipe for conflict and violence.”
ENDS
*The experts: Victor Madrigal-Borloz, Independent Expert on protection against violence and discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity; Reem Alsalem, Special Rapporteur on violence against women, its causes and consequences; Koumbou Boly Barry, Special Rapporteur on the right to education; Irene Khan; Special Rapporteur on the promotion and protection of the right to freedom of expression; Mary Lawlor, Special Rapporteur on the situation of human rights defenders; Nils Melzer, Special Rapporteur on Torture and other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment; Tlaleng Mofokeng, Special Rapporteur on the right of everyone to the enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health; Elina Steinerte (Chair-Rapporteur), Miriam Estrada-Castillo (Vice-chairperson), Leigh Toomey, Mumba Malila, Priya Gopalan, Working Group on arbitrary detention Clément Nyaletsossi Voule, Special Rapporteur on Rights to Freedom of Peaceful Assembly and Association
The Special Rapporteurs, Independent Experts and Working Groups are part of what is known as the Special Procedures of the Human Rights Council. Special Procedures, the largest body of independent experts in the UN Human Rights system, is the general name of the Council's independent fact-finding and monitoring mechanisms that address either specific country situations or thematic issues in all parts of the world. Special Procedures' experts work on a voluntary basis; they are not UN staff and do not receive a salary for their work. They are independent from any government or organization and serve in their individual capacity.
UN Human Rights, country page: Ghana
For more information and media requests please contact Catherine de Preux De Baets (+41 22 917 93 27/ cdepreuxdebaets@ohchr.org) or write to ie-sogi@ohchr.org
For media enquiries regarding other UN independent experts, please contact Renato de Souza (+41 22 928 9855 / rrosariodesouza@ohchr.org).
Follow news related to the UN's independent human rights experts on Twitter @UN_SPExperts.

19 February 2025


GENEVA, 6 July 2021—UNAIDS is deeply concerned by new legislation in Hungary that includes discriminatory amendments against lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex (LGBTI) people.
The amendments include banning the dissemination of content in schools and public service announcements deemed to “promote gender identity different from sex assigned at birth, the change of sex and homosexuality” to people under the age of 18 years. The amendments were tacked on to a popular bill to increase the criminalization of paedophilia, which was signed into law by Hungary’s President, János Áder, on 23 June 2021.
“The association of sexual orientation and gender identity with criminal acts such paedophilia is not only wrong, it is intolerable,” said Winnie Byanyima, the Executive Director of UNAIDS. “To end the AIDS epidemic, we need laws that protect, not harm, already marginalized communities.”
Criminalization and discrimination against LGBTI people hinder the availability, access and uptake of HIV prevention, testing, treatment, and care and support services. Data from UNAIDS show that knowledge of HIV status among gay men and other men who have sex with men who are living with HIV was three times higher in countries with the least repressive LGBTI laws than in countries with the most repressive LGBTI laws.
In response to a recent question on the new law, the United Nations Secretary-General, António Guterres, said, “No discrimination is acceptable in any circumstances, and any discrimination against LGBTIQ+ people is totally unacceptable in our modern societies.”
The new legislation will also present new barriers to addressing discrimination against LGBTI people in school settings. According to the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization’s Global Education Monitoring Report, launched last May, more than half of LGBTI students in Europe have experienced bullying in school at least once based on their sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression or variations of sex characteristics.
The President of the European Commission, Ursula von der Leyen, called the Hungarian bill a “shame”, saying that it “clearly discriminates against people on the basis of their sexual orientation and goes against the fundamental principles of the European Union.”
In the recently adopted Political Declaration on HIV and AIDS: Ending Inequalities and Getting on Track to End AIDS by 2030, United Nations Member States committed to “urgent and transformative action to end the social, economic, racial and gender inequalities, restrictive and discriminatory laws, policies and practices, stigma and multiple and intersecting forms of discrimination, including based on HIV status, and human rights violations that perpetuate the global AIDS epidemic.”
UNAIDS will continue to advocate with legislators, other government authorities and civil society around the world to establish anti-discrimination and protective laws, to eliminate the discrimination and violence faced by LGBTI people and to advance the right to health for all people without exception.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.


GENEVA, 7 July 2021—UNAIDS strongly condemns the attacks on lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex (LGBTI) activists and journalists at Tbilisi Pride’s offices and surrounding areas, which have forced the cancellation of Gay Pride events in the city. UNAIDS expresses its solidarity with all LGBTI people in Georgia.
“The shocking violence suffered by LGBTI activists and journalists in Tbilisi is completely unacceptable,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “The authorities must take urgent measures to protect the human rights of the LGBTI community, including their right to freedom of expression and assembly, and to bring those responsible for the attacks to justice.”
On 1 December 2018, Tbilisi signed the Paris Declaration to end the AIDS epidemic by 2030, joining more than 300 municipalities in the Fast-Track cities initiative, which was initiated by the Mayor of Paris, UNAIDS, IAPAC and UN-HABITAT in 2014. The initiative commits Tbilisi to work closely with communities, including gay men and other men who have sex with men and transgender people, to foster social equality.
The new UNAIDS Global AIDS Strategy 2021–2026: End Inequalities, End AIDS is also clear that stigma and discrimination against LGBTI people violates human rights, deepens inequalities and acts as a critical barrier to ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030. A crucial element of the strategy is to address the challenges faced by key populations (gay men and other men who have sex with men, sex workers, transgender people and people who use drugs) so that less than 10% experience stigma, discrimination and violence by 2025. The strategy calls on countries to take immediate action to reduce stigmatizing attitudes and discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity as a critical element to ending AIDS by 2030.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.


11 June 2021
11 June 2021 11 June 2021Since the United Nations High-Level Meeting on Ending AIDS in 2016, the young key populations’ movement and its visibility have grown considerably in Asia and the Pacific. Through their engagement with national and regional networks of key populations, more and more young people have taken up space in decision-making processes and in mobilizing resources to support local and national organizations. However, despite those important efforts, more needs to be done to meaningfully engage young key populations in the HIV response as leaders, beneficiaries and partners.
UNAIDS data from 2019 alarmingly shows that 27% of all new HIV infections in Asia and the Pacific were among young people. Young gay men and other men who have sex with men accounted for 52% of all new HIV infections among young people. Overall, 99% of new HIV infections among young people were among young key populations and their partners.
A side event held on the sidelines of the United Nations High-Level Meeting on AIDS, held in New York, United States of America, and online from 8 to 10 June, looked at the progress made and challenges in the HIV response and emphasized the critical role of young people in leading change and promoting successful and innovative approaches to the HIV response.
The speakers and panellists stressed that significant barriers exist for young key populations to access HIV testing, treatment and prevention services and routine sexual and reproductive health and rights services in the region. Those barriers include a limited availability of differentiated HIV services for young key populations, stigma and discrimination, punitive laws and other legal barriers that leave young key populations on the margins and out of reach of HIV services. The COVID-19 pandemic continues to widen existing inequalities and service gaps, but thanks to the engagement of community-led organizations, populations at higher risk of HIV, including young key populations, were able to access essential HIV and health services.
The speakers and panellists noted that young people are showing us the way to revolutionize HIV prevention and increase the uptake of HIV services by implementing new strategies and innovations that cater to the specific needs of young people. During the COVID-19 pandemic, organizations led by and serving young people, such as the Lighthouse Social Enterprise in Viet Nam and the Human Touch Foundation in India, have been at the forefront of the HIV response, providing HIV services in partnership with the local government to the communities that need them the most.
The team at the Human Touch Foundation, a community-based organization in Goa, India, that provides care and support to adolescents living with HIV has, since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, organized volunteers to deliver antiretroviral therapy to people’s doorsteps. Moreover, the organization played a critical role in getting the local government to waver public transport costs to ensure that people living with HIV had access to treatment. With the increased anxiety and depression brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic, the Human Touch Foundation offered psychosocial support services to adolescents living with HIV, both in the form of online counselling and in-person consultations.
Similarly, the Lighthouse Social Enterprise, a lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex (LGBTI) organization led by young people based in Hanoi, Viet Nam, has been instrumental in providing differentiated service delivery to young key populations during the COVID-19 pandemic. Some of the services it provides at its clinic include HIV counselling and testing, post-exposure prophylaxis, pre-exposure prophylaxis and antiretroviral therapy. The Lighthouse Social Enterprise also established a referral service to ensure that young key populations are linked with other health services, such as sexually transmitted infection testing and treatment, mental health support and harm reduction services. What makes the Lighthouse Social Enterprise unique is that the clinic is entirely run by young people. Health-care workers are given training by the Lighthouse Social Enterprise team on LGBTI and key population needs and issues in order to ensure that services are youth-friendly and free from stigma and discrimination. Last year, the Lighthouse Social Enterprise provided services to more than 3000 members of young key populations in Viet Nam.
The side event was an opportunity for different organizations led by and serving young people working on HIV-related issues to share experiences and define common strategies to keep HIV on the political agenda at the national and municipal levels.
“What we have learned from the AIDS response is that the voices of communities are key. Many types of youth-led and peer-led programmes provide safe and inclusive platforms for young people and affected communities, to connect, share their experiences, access information and, more importantly, shape responses.”
“Young key populations do play a vital role in the HIV response, yet they continue to be marginalized and are often seen as beneficiaries of programmes, rather than leaders and implementers. It’s essential that young key populations are empowered and meaningfully engaged if we are to end AIDS by 2030.”
“A lot of young key populations lack the fundamental knowledge on HIV and sexual health and do not have adequate information on HIV testing, including harm reduction. Lighthouse implemented Internet-based interventions during COVID-19 and provided differentiated service delivery for young key populations to ensure they had access to youth-friendly HIV services.”