Middle East and North Africa



Feature Story
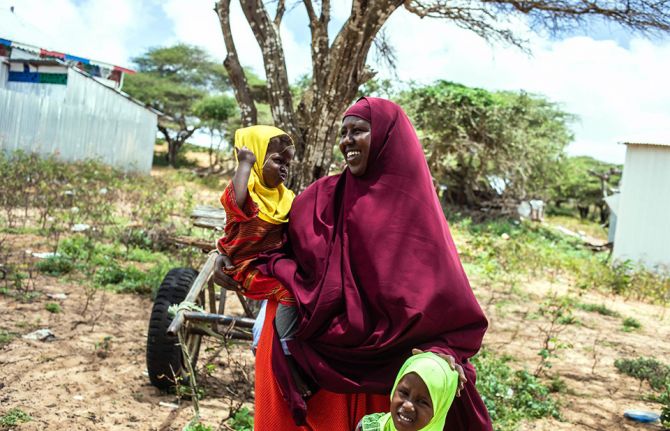
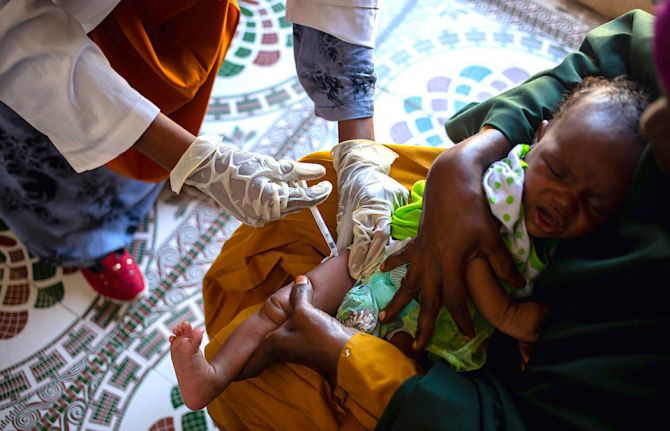
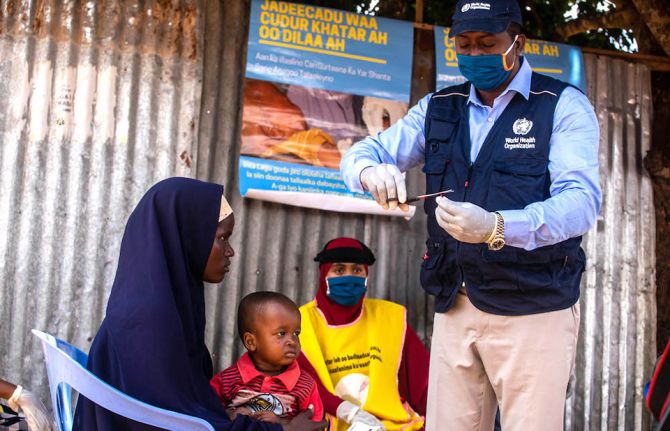
Somalia: building a stronger primary health care system
15 September 2020
15 September 2020 15 September 2020This story was first published by WHO
In the first year of the Stronger Collaboration, Better Health: The Global Action Plan for Healthy Lives and Well-being for All (GAP), 12 signatory agencies have engaged with several countries to help them achieve their major health priorities. The initial focus has been on strengthening primary health care and sustainable financing for health. Somalia is one of the countries where progress under the GAP is most advanced and where its added value has been most clearly demonstrated.
The Somalia country Director and Representative of the World Food Programme, Dr Cesar Arroyo underlined the vital importance of the GAP – through cementing collaboration among the 12 agencies: “The GAP initiative marks a crucial step towards solving health-related challenges in Somalia and offers us an opportunity to strengthen our partnerships across the humanitarian community thereby enhancing operational efficiency, particularly within the COVID-19 context and beyond”.
Three decades of civil war and instability have weakened Somalia’s health system and contributed to it having some of the lowest health indicators in the world. The situation varies from region to region but between 26-70% of Somalia’s 15 million people live in poverty and an estimated 2.6 million people have been internally displaced.
But the Government is committed to using current opportunities to strengthen health and social development. These include implementation of Somali National Development Plan for 2019–2024 and the Somali Universal Health Coverage (UHC) Roadmap, launched in September 2019.
Both plans identify primary health care as the main approach to improving health outcomes in the country. Primary health care provides whole-person care for most health needs throughout the lifespan, ensuring that everyone can receive comprehensive care ─ ranging from health promotion and prevention to treatment, rehabilitation and palliative care ─ as close as possible to where they live.
Working together, the Government of Somalia, GAP agencies and multilateral and bilateral partners have identified 5 priorities for enhanced collaboration to accelerate progress towards UHC.
Says Monique Vledder, Head of Secretariat for the Global Financing Facility for Women, Children and Adolescents: “The launch of the Global Action Plan has helped accelerate momentum across global health agencies to align their support to country partners. In Somalia, the GFF has brought the spirit of the GAP from the global to the country level, convening partners across the federal and local governments, Somaliland, UN agencies, donors and civil society to establish the Health Sector Coordination Committee. Country stakeholders and GAP agencies are now building consensus around a priority package of essential services and critical health system reforms”.
Establishment of a health coordination mechanism
Efforts are underway to set up a coordination mechanism for all health partners to strengthen primary health care and fill gaps in services at the district level, building consensus around a priority package of essential services and critical health system reforms and mapping the availability of services and health workers.
Improving access to a package of high-quality essential health services
The country’s health services package is being updated with support from GAP agencies and other partners, with a focus on prevention and community-based components, communicable and noncommunicable diseases, and mental health.
Strengthening emergency preparedness and response through UHC
Somalia is prone to emergencies from natural disasters and disease outbreaks and is now responding to COVID-19. GAP agencies are exploring opportunities to support the finalization and implementation of components of a National Action Plan for Health Security, which includes strengthening of laboratory and early warning systems and ensuring that a package of essential health services and key commodities are effectively delivered in humanitarian settings.
Strengthening the role and capacity of the Ministry of Health
This is essential to address fragmented health service delivery and funding arrangements; improve institutional capacity for policy-making, regulation, coordination, planning, management and contracting; and use of data in decision-making.
Harnessing the private sector for UHC
Private health services and the pharmaceutical sector are largely unregulated in Somalia but could contribute to improving access and achieving UHC. GAP agencies are exploring opportunities to support the development and operationalization of a strategy for the private health sector, to assess its current role in service delivery and implementation of regulatory frameworks and contracting mechanisms.
“GAP provides us an opportunity to accelerate progress in achieving universal health coverage in Somalia through coordinated action and alignment with development partners and UN agencies. More than ever, we now need to push this agenda as we support the health systems of Somalia recover stronger and better from the COVID-19 pandemic“, said WHO Country Representative in Somalia, Dr Mamunur Malik.
“Our collective engagement in improving access to care for women, children, and other vulnerable groups will be decisive in improving health and well being in the country. Through an integrated, coordinated and collaborative approach such as the GAP, we can also build the required capacity of national and local health authorities to deliver not only cost-effective health interventions using a primary healthcare approach, but also monitor and track porgress of the health-related indicators of sustainable development goal in the country", he added.
Although there are many health and social challenges in Somalia, the GAP is leveraging emerging opportunities to strengthen primary health care to support the country in achieving UHC and other health-related SDGs.
To move these efforts forward, GAP agencies are collaborating with the Government to develop an operational plan. They aim to align this with the new funding that a number of agencies are providing for the response to COVID-19, to support the scale-up of primary health care, including implementation of the package of essential health services.
Region/country
Related
 Government ensures continuity of treatment in Malawi
Government ensures continuity of treatment in Malawi

10 February 2025


Feature Story
UNAIDS supporting people stranded in Egypt to access HIV treatment
29 June 2020
29 June 2020 29 June 2020Hundreds of thousands of people around the world have been stranded abroad due to the bans on flights and border closures imposed to stop COVID-19. As elsewhere, thousands of non-nationals have been stranded in Egypt indefinitely.
Travel restrictions have had many repercussions on the daily lives of non-nationals, putting significant economic pressure on them and potentially putting their well-being at risk.
The UNAIDS Country Office for Egypt has been working on COVID-19 from the start of the pandemic in the country, establishing a direct line of communication with the National AIDS Program and working with it to ensure the continuation of HIV treatment by everyone on it and to help non-nationals in Egypt to get supplies of antiretroviral therapy.
Sophia Bianchi (not her real name) is an Italian tourist stranded in Sharm El Sheikh. “I ordered my antiretroviral treatment in late April from Italy via a courier service. Unfortunately, the shipment was stuck at the airport customs in Cairo for weeks. I contacted UNAIDS and they have been very helpful, following up daily with the Egyptian Ministry of Health and Population to get approval for releasing the shipment and checking on me and my health. They kept pushing through the Eid holidays and it all got resolved in two weeks. It was a stressful time but now I am relieved,” she said.
Antiretroviral therapy is available in Egypt free of charge to all nationals and registered refugees. However, as there is no community-based dispensing, nor private market purchase of antiretroviral medicines, gaps remain in ensuring that non-nationals can access treatment. For this reason, UNAIDS’ work during the COVID-19 pandemic has been essential in bridging the gaps.
There are strict rules on the dispensing of antiretroviral therapy in Egypt—only close family members are able to collect it from the dispensing centre. For Fatima Ahmed (not her real name), a refugee from Yemen who because of chronic illnesses that put her at higher risk from COVID-19 cannot leave her house, this was a significant barrier to accessing her HIV treatment. UNAIDS got in contact with the Egyptian Ministry of Health and Population to get an exceptional approval to dispense her medicine through a nongovernmental organization.
“I have not left the house for more than three months. My family has not been able to support me financially, so I was left without revenue. Thanks to the support of the National AIDS Program and MENA Rosa, a nongovernmental organization, peer supporters have delivered three months of antiretroviral treatment to my doorstep,” said Ms Ahmed.
However, much still remains to be done in reaching out to the most in need in Egypt. UNAIDS in Egypt has been advocating for the right to health and universal health coverage for everyone and is working in partnership with the Egyptian Ministry of Health and Population to ensure treatment for all nationals and non-nationals in the country.
“We believe in the absolute right of everyone to have access to their basic right to health. Ensuring access to antiretroviral therapy during these exceptional times is therefore our upmost priority. We are working relentlessly with our governmental and nongovernmental partners to build long-term policies to ensure treatment and care services for people living with HIV during times of emergency,” said Walid Kamal, the UNAIDS Country Director for Egypt.
Our work
Region/country
Related


Feature Story
“We carry on”
28 February 2020
28 February 2020 28 February 2020“For five years I have been subjected to harassment and threats—rape threats, murder threats, vilification, character assassination, phone calls to my family, to my mom,” said Lebanese television anchor Dima Sadek.
To raise public awareness about sexual harassment and bullying in Lebanon, particularly against female journalists during the recent protests, the Arab Foundation for Freedoms and Equality—UNAIDS’ regional partner on rights and health—has produced a video that sheds light on this human rights abuse committed against many women in the country.
Made in partnership with the HIVOS Women Empowered for Leadership (WE4L) programme, with funding from the Dutch Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the video highlights cases of harassment and assault—reporters whose bodily autonomy has been violated, whose personal telephone numbers have been leaked and who subsequently received rape threats and pornography and who have been verbally and physically attacked while live on television.
“You don’t expect that someone could be this hurtful or that they could say such things. You don’t know them and they don’t know you, but because you differ on politics, they feel they are allowed to talk to you in this way,” said Layal Saad, a reporter.
Since similar attacks, including online bullying and harassment both online and offline, have also been reported by female protesters, the video also seeks to raise awareness about the everyday sexual harassment, bullying and violence that women in general are subjected to, emphasizing the need for policies that allow women to become leaders.
Diana Moukalled, a journalist, explained that legal protection against sexual harassment is needed, since at present there are no laws that criminalize sexual harassment in Lebanon. “Lebanese women are among the most politically marginalized in the world, not just in the region. We see women present on many levels, yet there is a sharp discrepancy between the role of Lebanese women and their representation,” she said.
The video’s title is We Carry On, echoing the sentiment of the many women who watched and reacted to it—a feeling of resilience in the face of adversity and a determination to achieve the social justice demanded by women in Lebanon.
Region/country
Related
 Government ensures continuity of treatment in Malawi
Government ensures continuity of treatment in Malawi

10 February 2025
Documents
The response to HIV in Middle East and North Africa — Global AIDS update 2019
16 July 2019
The epidemic in the Middle East and North Africa continues to grow, with a 10% increase in new infections and a 9% increase in the annual number of AIDS-related deaths between 2010 and 2018. Access to HIV testing, treatment and care in the region is well below the global average. Less than half of people living with HIV are aware of their serostatus, and treatment gaps among men are larger than they are among women in many countries.
Related
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
A shot at ending AIDS — How new long-acting medicines could revolutionize the HIV response
21 January 2025
Indicators and questions for monitoring progress on the 2021 Political Declaration on HIV and AIDS — Global AIDS Monitoring 2025
17 December 2024
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
Take the rights path to end AIDS — World AIDS Day report 2024
26 November 2024


Feature Story
Empowering women living with HIV in Djibouti to live dignified lives
25 July 2019
25 July 2019 25 July 2019Zarah Ali (not her real name) remembers how things changed for the better. “In 2014, I received a loan of 40 000 Djiboutian francs (US$ 250) that I used to develop and improve my garment business. I was also trained in business entrepreneurship, including marketing and customer satisfaction. I import clothes from Dubai and Somaliland and earn a decent income that helps me support my 25-year-old son, my 16-year-old daughter in secondary school and my three-year-old adopted son. I am able to pay for my rent, electricity and water and have decent meals.”
Ms Ali’s loan came from an income-generation programme established by the World Food Programme in collaboration with the United Nations Development Programme, UNAIDS and the national network of people living with HIV in Djibouti (RNDP+). The programme supports the long-term empowerment of, and provides regular incomes to, women living with HIV in Djibouti City. It helps them to achieve financial security and have access to food and improves their access to health-care services. Income-generating activities such as those supported by the programme have a powerful potential to help people living with HIV adhere to antiretroviral therapy and optimize health outcomes.
The loans, ranging from US$ 141 to US$ 438 per person, are for starting or building retail businesses. The beneficiaries, who are selected from among two networks of people living with HIV affiliated to RNDP+ (ARREY and Oui à la Vie – Yes to Life), also receive training on how to run their business. Government support in the form of favourable policies and legislation has been vital to the success of the programme.
Dekah Mohammed (not her real name) now lives a fulfilling life after receiving help from the income-generation programme. Ms Mohammed, who lost her husband to AIDS, lives with six children. After she lost her job in the hospitality sector owing to her deteriorating health and to stigma and discrimination, she started her own clothing business and received a loan of 50 000 Djiboutian francs (US$ 313) to expand her business. The loan was repaid within 10 months. Her business has since expanded into furniture and electronics and she has recruited an employee. “I am no longer a desperate woman. I make enough to take care of my family and dependants,” she said.
The programme has improved the quality of life of many Djiboutian women, allowing them to regain dignity and ensure their financial security. It empowers women and girls to protect themselves from HIV, make decisions about their health, live free from violence and be financially independent.
Building on the belief that empowering women living with HIV and their households to be financially independent strengthens adherence to treatment and leads to more fulfilling and dignified lives, the programme contributes to the World Food Programme’s broader strategic contribution towards ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030.
Region/country
Related


Feature Story
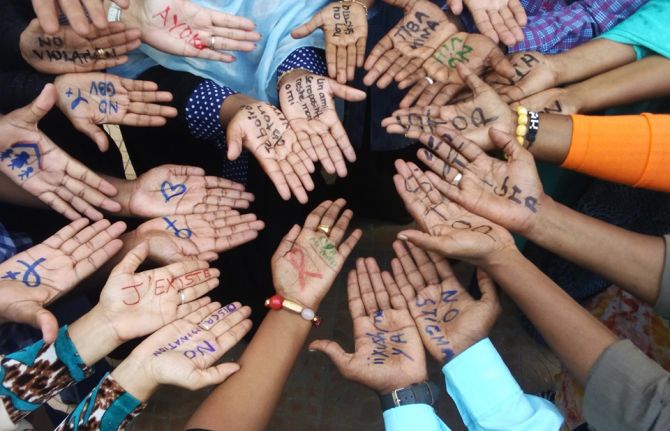
Women lead to reduce the impact of HIV and gender-based violence in the Middle East and North Africa
23 April 2019
23 April 2019 23 April 2019According to the World Health Organization, about one third of women worldwide have experienced violence. In some regions, women who have experienced physical or sexual intimate partner violence are 1.5 times more likely to acquire HIV than women who have not experienced such violence. Among marginalized populations, such as sex workers or transgender women, a high prevalence of violence is linked with higher rates of HIV infection.
In the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region, UNAIDS estimates that around 220 000 people are living with HIV. New infections were up by 12% between 2010 and 2017 and AIDS-related deaths increased by 11% over the same period. The stigma and discrimination associated with HIV as well as high levels of gender-based violence are preventing several countries from making progress against the epidemic. Gender-based violence in the region is strongly associated with harmful gender norms and stereotypes.
In 2018, the LEARN MENA project was launched to provide women with a platform to share experiences and explore the linkages between gender-based violence and HIV in the region. Underpinning the project is the Action Linking Initiatives in Violence against Women and HIV Everywhere (ALIV(H)E) framework, a research project that collates evidence on what works to prevent violence and builds women’s awareness to understand and address linkages between violence against women and HIV.
Through community dialogues led by MENA-Rosa, a regional network of women living with or affected by HIV, women are strengthening their own understanding of the root causes of violence and the links with HIV. The dialogues have highlighted the fact that gender inequality is at the centre of violence against women and an increased risk of HIV infection. For example, through the dialogues it was revealed that some women had never been to school. Many had experienced early or forced marriage. Many women acquire HIV from sexual violence, including within their own marriage.
“Violence is everywhere. Over time, and as you get older, you get to see it as normal,” said an Algerian woman participating in one of the dialogues.
The participants described multiple forms of violence across different settings, including in health-care settings, which impede their access to health care, including to HIV prevention and treatment services.
So far, the project has been implemented in seven countries―Algeria, Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, Morocco, Sudan and Tunisia.
Findings from the project are helping women living with and affected by HIV to advocate for an improved response to the epidemic in the region and for measures to reduce the impact of violence against women. The dialogues have amplified the voices of marginalized women living with and affected by HIV, encouraging decision-makers and partners to build strengthened national community responses. UNAIDS is supporting countries to implement the recommendations and action plans developed from the project.
“MENA-Rosa leaders have learned through this painful process that violence against us should be denounced and not brushed under the carpet,” said Rita Wahab, Regional Coordinator of MENA-Rosa. “Empowerment will help women in all their diversity to know and understand their rights. Our advocates will move forward to expose the links between violence against women and HIV. Gender equality starts at home, grows in society and blossoms in the legal environment.”
LEARN MENA is implemented by UNAIDS, Frontline AIDS and MENA-Rosa, with funding support from USAID. Additional technical support is provided by the Salamander Trust, the lead author of the ALIV(H)E framework.
Region/country
Related
 Government ensures continuity of treatment in Malawi
Government ensures continuity of treatment in Malawi

10 February 2025


Feature Story
Scaling up stigma-free services for women in Egypt
11 April 2019
11 April 2019 11 April 2019When the family and neighbours of Salma Karim (not her real name) found out that she was living with HIV they chased her out of her home. With nowhere to go, she was forced to leave her two young children behind. This is not an uncommon story in Egypt. One in five people living with HIV report being forced to leave their homes by their landlords, family or neighbours.
High levels of stigma and discrimination are one of the key factors driving new HIV infections in the country, which doubled between 2010 and 2016. Women and adolescent girls are often the most vulnerable. Societal norms, gender inequality, economic dependence, legal discrimination and harmful practices affect them disproportionately, making them more vulnerable to HIV and facing greater levels of stigma and discrimination in the event of HIV infection.
In 2016, UNAIDS in partnership with the Egyptian Ministry of Health and Population joined efforts towards a gender-transformative response to the HIV epidemic. With funding from the Dutch government, a pilot project called Enhancing Sexual and Reproductive Health of Women Living with and Affected by HIV was launched. Three years later, the pilot has reached double its intended beneficiaries with stigma-free quality sexual and reproductive health services.
“I lost my first child as I didn’t know I had HIV,” explains Nour Tarek (not her real name). It was in one of the pilot project sites in Giza that she received the support to realize her reproductive rights free from discrimination. “I followed up with the doctor in the hospital and I became pregnant again.”
Thanks to the antiretroviral medicine she received while pregnant, her baby Mona (not her real name) was born HIV-negative. “I still have to test again until she is older to make sure she is fine,” explains Ms Tarek.
Having proved its success, the pilot project is now being scaled up to a third of the country’s governorates. The aim is to deliver high-quality sexual and reproductive health and HIV services for 1300 women living with HIV and 3000 women at higher risk of acquiring HIV. Its focus on building the capacity of health-care providers and civil society organizations will be key to avoiding future stigma and discrimination, which is reported to lead one in four people living with HIV in Egypt not to disclose their HIV status when seeking care.
During his visit to Cairo on 9 April, the Executive Director of UNAIDS, Michel Sidibé, and the Ambassador of the Netherlands to Egypt, Laurens Westhoff, discussed the expansion of the project. Implemented through a new three-year Dutch grant, the scaled-up services will complement national efforts to achieve Egypt’s ambitious new National AIDS Strategy 2018–2022 and the Sustainable Development Goals.
Region/country
Related





Feature Story
UN and AU working together for sustainable development
27 March 2019
27 March 2019 27 March 2019“We cannot have sustainable development without sustaining peace. Neither can we build a secure future for everyone without addressing the root causes of our conflicts and vulnerabilities,” said Amina Mohammed, the United Nations Deputy Secretary-General.
Ms Mohammed was speaking in Marrakech, Morocco, at the twentieth session of the Regional Coordination Mechanism for Africa (RCM–Africa)―a joint United Nations and African Union body that supports African development.
“The United Nations is working with the Africa Union to try to get the 47% of people of the continent still under the poverty line out of poverty, bring energy to the doorsteps of 500 million people without electricity and garner the US$ 60 billion needed to empower African women,” said Vera Songwe, the Executive Secretary of the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa.
The African Union Commissioner for Human Resources, Science and Technology, Sarah Anyang Agbor, encouraged the participants to, “Live by Ubuntu. It is my, your, our responsibility to strengthen collaboration for the reforms.”
Michel Sidibé, the Executive Director of UNAIDS, co-chaired a panel meeting with Ms Anyang Agbor at the RCM–Africa session. During the panel meeting―entitled “Upscaling durable solutions, including addressing the forced displacement–development nexus”―the participants noted that more than a third of the world’s displaced people are in Africa. The participants agreed on the need to understand and address the root causes of displacement and build on what is known to work to break the cycle of vulnerability. Mr Sidibé emphasized that fostering resilient societies means first addressing the challenge of income inequality.
The RCM–Africa session was held on 23 and 24 March.
Region/country
Related
 Government ensures continuity of treatment in Malawi
Government ensures continuity of treatment in Malawi

10 February 2025

Feature Story
Young people to campaign against stigma and discrimination in Egypt
27 February 2019
27 February 2019 27 February 2019Ahead of Zero Discrimination Day, young people came together in Cairo, Egypt, to learn how to respond to HIV-related stigma and discrimination and to hear about how the HIV epidemic affects Egypt and the role that young people can play in the AIDS response.
“The burden of the epidemic is higher on young people. In Egypt, it is for young people to lead the HIV response,” said Walid Kamal, Egypt’s National AIDS Programme Manager.
During a discussion on stigma and discrimination, people living with HIV shared some of their testimonies and experiences, helping to give the participants a deeper understanding of how stigma and discrimination affects people living with HIV.
“It is our responsibility to help people living with HIV feel part of the community,” said one of the participating young people.
“It is not only about AIDS, it is about social justice, equality, the empowerment of women and promoting healthy gender norms,” said Ahmed Khamis, the UNAIDS Country Manager for Egypt.
The participants also learned how to plan, design and implement online awareness and advocacy campaigns on social media.
At the end of the meeting, organized by UNAIDS and the National AIDS Programme and held on 21 February, the young people agreed to lead social media campaigns to highlight the harm caused by stigma and discrimination. Starting on 1 March, Zero Discrimination Day, and running for three weeks, the campaigns will be supported by the UNAIDS country office in Egypt and are endorsed by Egypt’s Ministry of Health and Population.
Region/country
Related
 Government ensures continuity of treatment in Malawi
Government ensures continuity of treatment in Malawi

10 February 2025
Documents
Miles to go - The response to HIV in Middle East and North Africa
12 August 2018
HIV is a hidden epidemic in the Middle East and North Africa. The HIV burden across the region is relatively low, and new HIV infections are largely among key populations that face high levels of stigma, discrimination and criminalization. Almost two thirds of new HIV infections in 2017 were in Egypt, the Islamic Republic of Iran and Sudan. Special efforts are needed to expand and improve the HIV testing and treatment programmes in the Islamic Republic of Iran and Sudan, which accounted for more than 60% of the region’s deaths from AIDS-related illness in 2017.
Related
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
A shot at ending AIDS — How new long-acting medicines could revolutionize the HIV response
21 January 2025
Indicators and questions for monitoring progress on the 2021 Political Declaration on HIV and AIDS — Global AIDS Monitoring 2025
17 December 2024
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
Take the rights path to end AIDS — World AIDS Day report 2024
26 November 2024








