SRH

Update
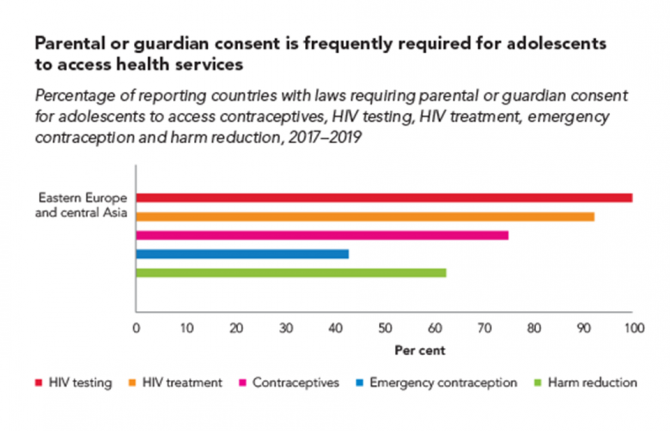
Parental consent undermines the right to health of adolescents
16 March 2020
16 March 2020 16 March 2020Many countries have laws or policies that prevent adolescents from accessing essential health services without the consent of a parent or guardian. The original intention may have been to protect minors, but these stipulations often have the opposite effect and increase the risk of HIV and other health problems among adolescents.
A large proportion of countries across all regions restrict access to HIV testing and treatment for adolescents. In 2019, for instance, adolescents younger than 18 years needed explicit parental consent in 105 of 142 countries in order to take an HIV test. In 86 of 138 reporting countries, they needed such consent to access HIV treatment and care. These kinds of laws and policies also may complicate or hinder adolescent access to pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), a highly effective prevention tool.
Research in sub-Saharan Africa shows that in countries where the age of consent is 15 years or lower, adolescents are 74% more likely to have been tested for HIV in the past 12 months compared with countries where the age of consent is 16 years or higher—with girls especially benefiting from the easier access.
Country-level details on which countries have consent laws can be viewed on the UNAIDS Laws and Policies Analytics web page.
Resources
Documents
We’ve got the power — Women, adolescent girls and the HIV response
05 March 2020
This publication marks the 25th anniversary of the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action. It is dedicated to the women leaders and allied community mobilizers who have devoted their lives to advancing the human rights and dignity of all people affected by the HIV epidemic, and to opposing social injustice, gender inequality, stigma and discrimination, and violence.
Related
 UNAIDS calls for rights, equality and empowerment for all women and girls on International Women’s Day
UNAIDS calls for rights, equality and empowerment for all women and girls on International Women’s Day

06 March 2025
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Documents
No more neglect — Female genital schistosomiasis and HIV — Integrating sexual and reproductive health interventions to improve women’s lives
12 December 2019
Neglected tropical diseases continue to affect people who live under dire socioeconomic conditions in the poorest parts of the world — people who the global health and development community have promised not to leave behind. Female genital schistosomiasis (FGS), is a waterborne neglected tropical disease of poverty affecting 56 million African women and girls. Yet FGS remains underreported, under- and misdiagnosed and largely untreated.
Related
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
A shot at ending AIDS — How new long-acting medicines could revolutionize the HIV response
21 January 2025
Indicators and questions for monitoring progress on the 2021 Political Declaration on HIV and AIDS — Global AIDS Monitoring 2025
17 December 2024
Joint Evaluation of the Global Action Plan for Healthy Lives and Well-being for All (SDG 3 GAP)
16 December 2024
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
Take the rights path to end AIDS — World AIDS Day report 2024
26 November 2024

Press Release
UNAIDS and the LGBT Foundation launch groundbreaking study on happiness, sex and quality of life for LGBTI people
14 May 2019 14 May 2019New global survey aims to fill the data gap on the mental well-being of lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex (LGBTI) people to create better conditions and improve health
GENEVA, 14 May 2019—UNAIDS and the LGBT Foundation have launched an online survey to evaluate happiness, sex and quality of life for LGBTI people. The survey, the first of its kind, is part of a campaign to gain more information and insight into the challenges faced by LGBTI people. The data gathered will help to voice the concerns and advocate for improving the conditions and treatment of LGBTI people, including ensuring access to inclusive health and social services.
“Many lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex (LGBTI) people face stigma and discrimination daily in education, work, health and social settings. We want to understand how this affects wellness, including mental well-being, and also their responses and resiliencies,” said Gunilla Carlsson, UNAIDS Executive Director, a.i. “By examining in depth how economic, socioecological, homophobic and other variables impact the lives of LGBTI people, we will be able to advocate more strongly for meaningful change to improve their lives.”
LGBTI people have to contend with stigma and discrimination and are often faced with a lack of economic opportunities and a lack of access to health and social care. They are also at much higher risk of HIV infection. Estimates show that the risk of acquiring HIV is 27 times higher among gay men and other men who have sex with men and 13 times higher among transgender people, yet studies show that many gay men and other men who have sex with men and transgender people avoid seeking health services for fear of stigma and discrimination.
Although there are studies that evaluate the well-being of LGBTI people through measuring levels of violence, legal status and health―often HIV risk and status―few look at the mental well-being of LGBTI people, which is essential to ensuring their overall health and access to economic opportunities.
Data are also lacking on LGBTI people in Africa, Asia and Latin America, which the survey hopes to address. Available in more than 17 languages, the survey has been distributed through social media to more than 25 million people around the world and will run until the end of July 2019.
“We want progress in lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex (LGBTI) health and well-being. We want it now and this survey will help in this direction. It is a great initiative, where LGBTI people can confidentially speak up and build the knowledge to empower, raise public awareness and advocate, with an ultimate goal of eliminating stigma and discrimination against LGBTI people. It will be extremely helpful to the community,” said Sean Howell, Chief Executive Officer of the LGBT Foundation.
The survey was developed in collaboration with Aix-Marseille University and the University of Minnesota and was designed in collaboration with representatives of the LGBTI community, including people living with HIV. To ensure the highest standards with respect to privacy and the protection of personal data, the survey complies with the General Data Protection Regulation.
To secure and safeguard anonymity, access is provided via a secured weblink, which establishes an encrypted link between a web server and a browser. The research protocol for the survey has been approved by the Research Board of Ethics of Aix-Marseille University and by the Research Ethics Review Committee of the World Health Organization.
The survey is open for participation until 31 July 2019 and takes about 12 minutes to complete.
To participate in this groundbreaking survey, click on the following link: https://www.research.net/r/LGBTHappinessResearch.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton-Knott
tel. +41 22 791 1697
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS Media
tel. +41 22 791 4237
communications@unaids.org
Participate
Press centre
Download the printable version (PDF)
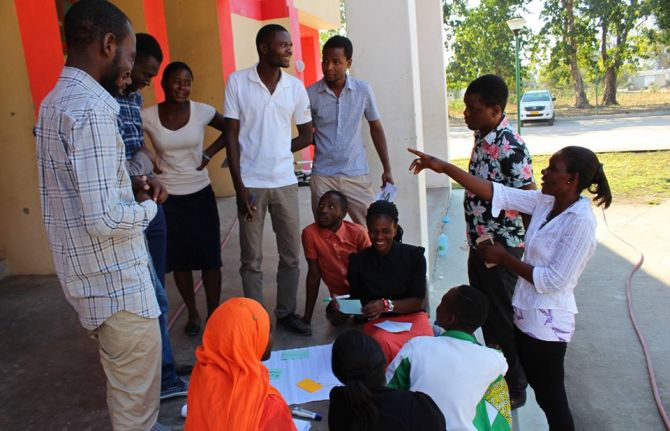
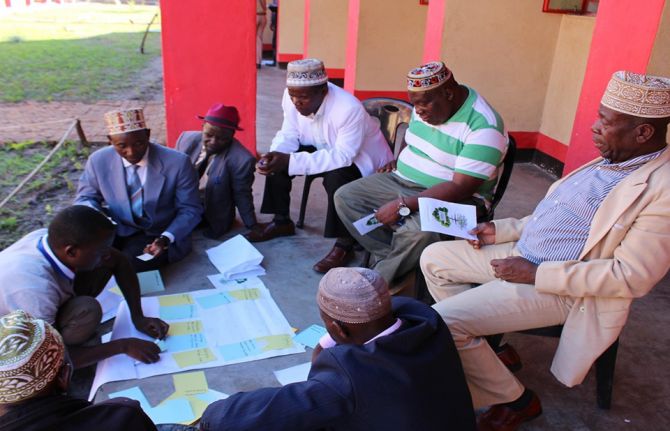




Feature Story
UNAIDS and UN Women working together in Malawi
07 May 2019
07 May 2019 07 May 2019One of the 11 UNAIDS Cosponsors, UN Women is working closely with UNAIDS to improve the lives of women and girls worldwide. In Malawi, for example, UNAIDS and UN Women have partnered to reduce the impact of gender-based violence and mitigate the risk of HIV infection among women and girls.
“UN Women is the youngest of the UNAIDS Cosponsors, and we are delighted to work closely with UNAIDS and other partners under the UNAIDS Unified Budget, Results and Accountability Framework 2016–2021,” says Clara M.W. Anyangwe, the representative of UN Women in Malawi. The Unified Budget, Results and Accountability Framework (UBRAF) is a UNAIDS instrument that maximizes the coherence, coordination and impact of the United Nations response to HIV by combining the efforts of the UNAIDS Cosponsors and UNAIDS Secretariat. Its principal aim is to allocate financial resources to catalyse country-level action in the AIDS response.
With UBRAF funding, UN Women in Malawi has teamed up with an impressive number of partners, including UNAIDS, the Ministry of Gender, Children, Disability and Social Welfare, the National AIDS Commission, the National Law Commission, the United Nations Development Programme, the Malawi Network of AIDS Service Organizations and civil society to implement a project that aims to enhance the national response to sexual and gender-based violence, harmful practices, sexual and reproductive health and rights and HIV.
“Working together as UNAIDS Cosponsors is just a better approach,” says Ms Anyangwe. “There is no single agency that can help the country to achieve the UNAIDS 90–90–90 targets. Instead, each agency has a comparative advantage that they bring to the table. In this case, UN Women brings in the gender dimension and UNAIDS its expertise in the HIV response.”
Malawi has made great progress in reducing new HIV infections. In 2017, there were 39 000 new HIV infections, a 40% reduction since 2010, but 9500 of those were among adolescent girls and young women between the ages of 15 and 24 years. That is more than double the number among men of the same age group.
The project has produced a perception study on the prevailing gender norms that increase violence against women and girls and their risk of HIV infection in Malawi, such as rite of passage practices, sexual cleansing, child marriage, marriage by proxy and transactional sex. An indicator framework has been developed from the findings that will be used to track progress of Malawi’s National Strategic Plan for HIV and AIDS.
An important part of the project is to engage with traditional leaders, including those who facilitate rite of passage practices, and mother and father groups. As a result of the engagements, a framework has been developed that links partners in the local HIV, sexual and reproductive health and rights and sexual and gender-based violence response to monitor and address harmful cultural practices that occur during local rites of passage ceremonies.
A series of intergenerational dialogues that brought together young people, people living with HIV and traditional and faith-based leaders revealed that issues such as lack of access to youth-friendly HIV and sexual and reproductive health and rights services, peer pressure, stigma and discrimination and gender-based violence need to be addressed in order to increase young people’s resilience and empower them to protect themselves against HIV infection.
“We also leveraged UN Women’s global He for She campaign to engage men and boys as partners of women and girls. We were looking particularly to foster a positive masculinity. How can we use masculinity to protect women and girls against harmful practices?” said Ms Anyangwe.
During the dialogues, more than 100 men and boys took the pledge to be He for She champions to promote gender equality and reduce HIV and sexual and gender-based violence. The human rights approach embedded in the project has seen laws and policies that relate to HIV and gender translated into local languages and widely disseminated in affected communities.
Ms Anyangwe insists that leveraging the specific expertise of partners under the UBRAF umbrella is reaping rewards in Malawi.
“It has also been great to have UNAIDS as a member of the Country Coordinating Mechanism of the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria. UNAIDS’ involvement in these mechanisms benefits us all,” she says.
“We really value UN Women’s continued support and partnership in ending HIV and gender-based violence in Malawi,” says Thérèse Poirier, UNAIDS Country Director for Malawi. “It has been beneficial to work as One UN so we don’t confuse our national counterparts by coming in and working separately on different areas of these interconnected and multilayered epidemics,” she said.
Region/country
Related
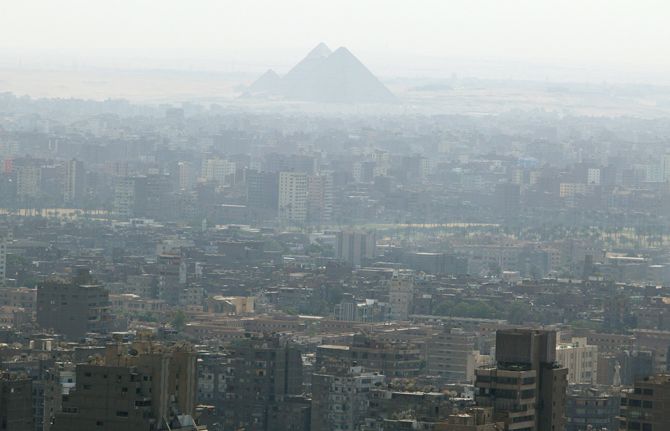


Feature Story
Scaling up stigma-free services for women in Egypt
11 April 2019
11 April 2019 11 April 2019When the family and neighbours of Salma Karim (not her real name) found out that she was living with HIV they chased her out of her home. With nowhere to go, she was forced to leave her two young children behind. This is not an uncommon story in Egypt. One in five people living with HIV report being forced to leave their homes by their landlords, family or neighbours.
High levels of stigma and discrimination are one of the key factors driving new HIV infections in the country, which doubled between 2010 and 2016. Women and adolescent girls are often the most vulnerable. Societal norms, gender inequality, economic dependence, legal discrimination and harmful practices affect them disproportionately, making them more vulnerable to HIV and facing greater levels of stigma and discrimination in the event of HIV infection.
In 2016, UNAIDS in partnership with the Egyptian Ministry of Health and Population joined efforts towards a gender-transformative response to the HIV epidemic. With funding from the Dutch government, a pilot project called Enhancing Sexual and Reproductive Health of Women Living with and Affected by HIV was launched. Three years later, the pilot has reached double its intended beneficiaries with stigma-free quality sexual and reproductive health services.
“I lost my first child as I didn’t know I had HIV,” explains Nour Tarek (not her real name). It was in one of the pilot project sites in Giza that she received the support to realize her reproductive rights free from discrimination. “I followed up with the doctor in the hospital and I became pregnant again.”
Thanks to the antiretroviral medicine she received while pregnant, her baby Mona (not her real name) was born HIV-negative. “I still have to test again until she is older to make sure she is fine,” explains Ms Tarek.
Having proved its success, the pilot project is now being scaled up to a third of the country’s governorates. The aim is to deliver high-quality sexual and reproductive health and HIV services for 1300 women living with HIV and 3000 women at higher risk of acquiring HIV. Its focus on building the capacity of health-care providers and civil society organizations will be key to avoiding future stigma and discrimination, which is reported to lead one in four people living with HIV in Egypt not to disclose their HIV status when seeking care.
During his visit to Cairo on 9 April, the Executive Director of UNAIDS, Michel Sidibé, and the Ambassador of the Netherlands to Egypt, Laurens Westhoff, discussed the expansion of the project. Implemented through a new three-year Dutch grant, the scaled-up services will complement national efforts to achieve Egypt’s ambitious new National AIDS Strategy 2018–2022 and the Sustainable Development Goals.
Region/country
Related
Documents
Translating community research into global policy reform for national action: a checklist for community engagement to implement the WHO consolidated guideline on the sexual and reproductive health and rights of women living with HIV
20 December 2018
This Checklist supports the in-country implementation of the 2017 WHO and UNAIDS Consolidated guideline on the SRHR of women living with HIV. To guarantee the guideline’s effective implementation and fulfil its ground-breaking women-centred spirit and principles, its uptake must include the meaningful engagement of women living with HIV in all their diversity. This guideline was developed with engagement from communities of women living with HIV throughout its development, publication and dissemination. In line with this collaborative process, it discusses implementation issues that laws, policies, health, social and other relevant initiatives and service delivery must address to achieve gender equality and support human rights. The overall objective of this Checklist is to support women living with HIV and community activists who care about the rights of women living with HIV to guarantee effective implementation of the WHO and UNAIDS Consolidated guideline on the SRHR of women living with HIV.
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025

Feature Story
Civil society cooperation network for the Americas and the Caribbean launched
02 November 2018
02 November 2018 02 November 2018A new regional civil society cooperation network for the Americas and the Caribbean to support nongovernmental organizations working to end AIDS was launched on 30 October in Quito, Ecuador. Launched by Coalition PLUS, the initiative will support coordination and capacity-building among community organizations involved in the AIDS responses of North, Central and South America and the Caribbean.
“Although we have HIV services available, people do not have access because they are criminalized and stigmatized. The community movement is helping us to end the conspiracy of silence about discrimination. We need civil society to increase efforts to achieve the progressive policies that will clear the way for us to end AIDS,” said Michel Sidibé, UNAIDS Executive Director.
Since 2014, Coalition PLUS—an international alliance of more than 100 nongovernmental organizations contributing to the AIDS response—has been building and strengthening mechanisms for regional collaboration. Such networks already exist in western Africa, central Africa, the Middle East and North Africa, the Indian Ocean and Europe.
The President of Coalition PLUS, Hakima Himmich, said that the network will increase access by organizations to new resources and approaches relevant to their local contexts. She noted that it was especially important to strengthen civil society’s capacity around addressing the needs of the most vulnerable.
“We have huge challenges around stigma and discrimination against entire populations. In order to achieve epidemic control, we must also address human rights,” said Ms Himmich.
UNAIDS data show that in 2017 key populations and their sexual partners accounted for three quarters of new HIV infections in Latin America and two thirds of new infections in the Caribbean. Gay men and other men who have sex with men and transgender women are disproportionately affected, with a few countries reporting HIV rates of above 15% among those communities.
The activities of the network in the region will be coordinated by the Kimirina Corporation, a Ecuadorian organization focused on people-centred combination prevention and advocacy. Amira Herdoiza, Director of the Kimirina Corporation, explained that the platform will place strong emphasis on coordinated research, skills-building and advocacy, particularly around issues affecting young people and key populations.
“We need more multicountry research to show the nuances of our epidemics,” Ms Herdoiza said. “Through this network our organizations’ capacities to share and analyse data will be strengthened. We will also focus on sharing experiences and planning joint programmes.”
At present, there are three other members of the regional network: the Coalition of Quebec Community Organizations against AIDS in Canada; AIDES in the French Caribbean; and the Institute for Human Development in the Plurinational State of Bolivia. Other regional organizations are invited to be part of the initiative.
Region/country
Documents
Statement by UNAIDS for the UN Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) Regional Conference on ICPD+25, Geneva, 1–2 October 2018
12 October 2018
The ICPD Programme of Action has put international human rights principles, including sexual and reproductive health and rights, autonomy, non-discrimination, equality, participation, empowerment, meaningful decision-making, and accountability at the core of the Agenda. Today, almost 25 years later, the Agenda and especially the unfinished ICPD Agenda, is still relevant for many countries.
Related
29th Ordinary General Assembly of the Organization of African First Ladies for Development
16 February 2025
55th meeting of the UNAIDS Programme Coordinating Board
10 December 2024
20th Indian Ocean Colloquium on HIV/AIDS
22 October 2024
University of Pompeu Fabra
17 October 2024
Linking UN Summit of the Future with COP29
26 September 2024
Revitalized Multilateralism
24 September 2024
Plenary debate of the Summit of the Future
23 September 2024
African Union Year of Education
23 September 2024
AIDS2024 opening session
22 July 2024
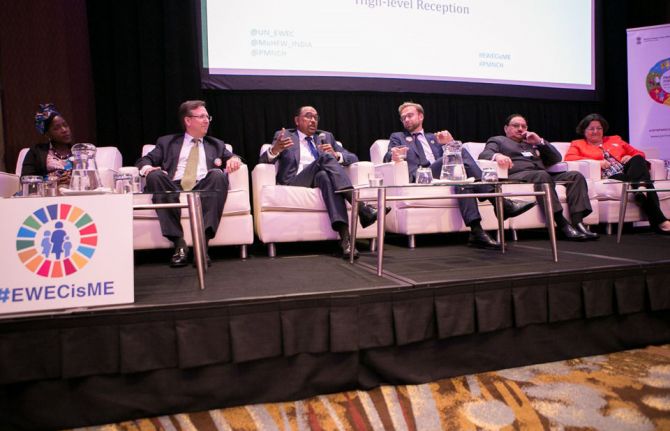
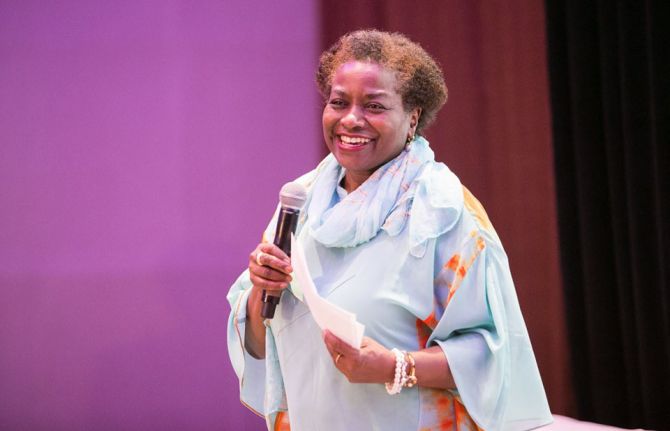
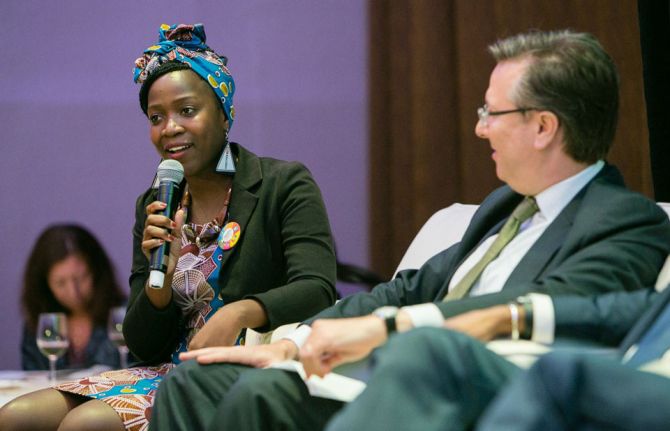





Feature Story
Uniting for every woman and every child
26 September 2018
26 September 2018 26 September 2018The health of women, children and adolescents is the cornerstone of public health. Healthy women and children create healthy societies and if adolescents are helped to realize their rights to health, well-being and education they become equipped to attain their full potential as adults. However, each year approximately 5.9 million children die before the age of five years and 289 000 women die in pregnancy and childbirth.
As part of the United Nations response to this crisis, the former United Nations Secretary-General, Ban Ki-moon, launched an initiative during the 2010 United Nations Millennium Development Goals summit to save and improve the lives of millions of women, children and adolescents around the world.
The initiative, Every Woman Every Child, was an unprecedented global movement that mobilized action by governments, the private sector, academia and civil society to address the major health challenges facing women, children and adolescents. As part of its work, the movement put into action a Global Strategy for Women’s and Children’s Health, a road map to galvanize political leadership and resources and to create a powerful multistakeholder movement for health.
The technical work of the movement is done by the H6 partnership, currently chaired by UNAIDS, which puts to work the collective strengths of UNAIDS, the United Nations Population Fund, the United Nations Children’s Fund, UN Women, the World Health Organization and the World Bank Group to operationalize the Global Strategy for Women’s and Children’s Health.
Today, spearheaded by the current United Nations Secretary-General, António Guterres, Every Woman Every Child is a multistakeholder platform that is saving millions of lives by placing women, children and adolescents at the centre of universal health coverage and the Sustainable Development Goals.
To highlight the need for continued political momentum around the movement, Every Woman Every Child held a high-level reception during the 73rd Session of the United Nations General Assembly in New York, United States of America, to underscore the importance of commitment, action and accountability by high-profile global leaders and influencers.
At the 2010 launch, more than US$ 40 billion was pledged, with numerous partners making additional financial, policy and service delivery commitments. However, speakers at the event highlighted that more help is urgently needed.
They stressed that the international community must pledge additional commitments to take Every Woman Every Child past the tipping point, which, the organizers say, would save the lives of 16 million women and children, prevent 33 million unwanted pregnancies, end stunting in 88 million children and protect 120 million children from pneumonia.
Quotes
“Today’s challenges require a new response. Every Women Every Child and the deep commitment of its partners will be critical to this.”
“We say that it is teamwork that makes the dream work and our partnership is one of the best examples of how we can deliver together, the United Nations delivering as one.”
“We are doing a lot of work in India—from birth to adolescence, we are putting in place numerous health programmes and initiatives. We are proud that our Prime Minister has taken a bold decision to help the most deprived and the most marginalized. One hundred million families have been identified across India, all of whom will benefit from support for health care so that they are not out of pocket for taking care of their health.”
“For too long we have simply not done enough. More than 5 million children die every year. That is like the whole population of my country being wiped out. We know that 35 million lives can be saved between now and 2030, but only if the Global Financing Facility is fully funded. We will be holding a replenishment in November—there is no better reason to come to Norway.”
“It is a transformative moment. It’s about leadership and about transforming leadership in the global health arena. It’s also about innovation, about how we do things differently. Which is why the H6 is so important—it is an entry point for United Nation reform—one results framework, one vision—demonstrating what we can do differently.”
“It’s so important that young people are engaged in these programmes, involved in these programmes and leading these programmes. With young people taking the lead, you will have the greatest impact. We need to do business differently, and to do this we need to take a people-centred approach and, most importantly, work together.”


















