SRH
Documents
Summary — Let Communities Lead — UNAIDS World AIDS Day report 2023
28 November 2023
This report is not only a celebration of the critical role of communities. It is a call to action to decision-makers to fully support the life-saving work of communities and to clear away the barriers that stand in their way. Press release | Full report | Fact sheet | World AIDS Day 2023
Related
 UNAIDS calls for rights, equality and empowerment for all women and girls on International Women’s Day
UNAIDS calls for rights, equality and empowerment for all women and girls on International Women’s Day

06 March 2025
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025
Documents
Amplifying successes towards ending AIDS — Case studies from eastern and southern Africa
27 November 2023
UNAIDS has compiled this set of 10 key success case studies from 5 countries in the region (Angola, Eswatini, Kenya, Malawi, Uganda) that have shown catalytic impact in the areas of HIV, male engagement, gender-based violence, and sexual and reproductive health and rights, and domestic strategies for sustaining resources.
Related
 The impact of the US funding freeze and cuts on Namibia’s civil society: A struggle for survival
The impact of the US funding freeze and cuts on Namibia’s civil society: A struggle for survival

10 March 2025
 UNAIDS calls for rights, equality and empowerment for all women and girls on International Women’s Day
UNAIDS calls for rights, equality and empowerment for all women and girls on International Women’s Day

06 March 2025
 Zambia - an HIV response at a crossroads
Zambia - an HIV response at a crossroads

24 February 2025
 Status of HIV Programmes in Botswana
Status of HIV Programmes in Botswana

20 February 2025
 Government ensures continuity of treatment in Malawi
Government ensures continuity of treatment in Malawi

10 February 2025


Press Statement
UNAIDS welcomes Kenya’s High Court judgement in landmark case of involuntary sterilization of women living with HIV
20 December 2022 20 December 2022GENEVA, 20 December 2022—UNAIDS welcomes the judgement by the High Court of Kenya at Nairobi recognizing that coerced sterilization of women living with HIV is a violation of their human rights.
The judgement follows a case brought forward in 2014 by a Kenyan woman living with HIV who was coerced by professionals at a health facility to undergo tubal ligation thus taking away her ability to have children. The High Court found that the performance of this operation without consent amounted to a violation of her rights to non-discrimination, to dignity, to health and to family.
“This decision is an important step in protecting the sexual and reproductive health and rights of women living with HIV,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “UNAIDS stands ready to work with all governments to ensure such practices are eliminated completely and that women living with HIV are able to access health services without stigma or discrimination.”
UNAIDS intervened in this case with an amicus curiae (friend of the court) brief that informed the Kenyan High Court on the health guidelines and human rights standards that each country must follow to respect, protect and guarantee the human rights of people living with HIV, and the impact that such involuntary practices can have on the HIV response. The Kenyan Legal and Ethical Issues Network on HIV/AIDS (KELIN) and the African Gender and Media Initiatives Trust (GEM) were also petitioners in this case.
HIV-related stigma and discrimination has a significant impact on the health, lives and well-being of people living with or at risk of HIV. Stigma and discrimination hinders the HIV response by limiting access to broader sexual and reproductive health and other health services. UNAIDS continues to work daily to ensure that governments invest in preventing and responding to violations linked to the forms of intersectional discrimination to which people living with HIV have been subjected.
The plaintiff in the case stated, “This was never about the money. I wanted to fight for justice for myself and all women who have had this experience, and to ensure this does not happen to other women who are living with HIV who need access to reproductive health services.”
“This case is an important moment for reproductive justice and the feminist movement. Coercive sterilization of women living with HIV is a violation of women’s most fundamental human rights and undermines effective HIV responses,” said UNAIDS Country Director for Kenya, Medhin Tsehaiu. “It is only through a human rights approach that we will end AIDS as a public health threat.”
A rights-based approach includes the right to start a family and have children, the right to decide the number and spacing of their children, the right to reproductive autonomy and the right to access quality services to support their reproductive health choices, based on their informed, safe and voluntary consent. These are fundamental human rights that belong to all women, regardless of HIV status, and are guaranteed in global and regional treaties.
“We welcome the court’s decision and although it took a long time, we are happy that the court found the client’s rights had been violated, and particularly the finding of discrimination on the basis of sex and HIV status,” said Allan Maleche, Executive Director, KELIN.
The Global AIDS Strategy 2021–2026: End Inequalities, End AIDS includes a central role for the promotion of human rights, gender equality and dignity, free from stigma and discrimination for all people living with and affected by HIV. It is a commitment by UNAIDS to an ambitious vision to end gender inequalities and realize human rights, including the right to health, calling on all partners and stakeholders in the HIV response in all countries to transform unequal gender norms and end stigma and discrimination.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Region/country

Update
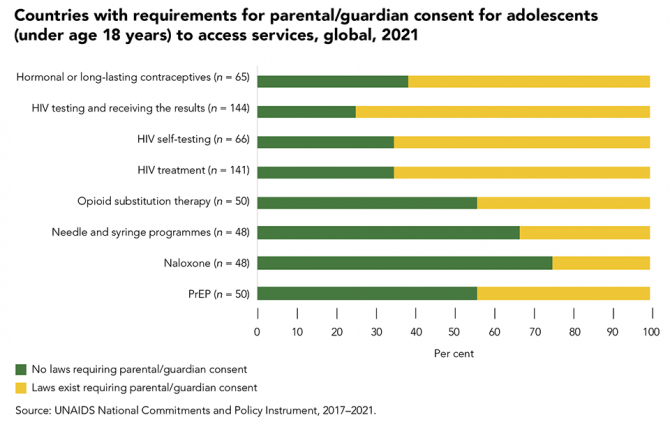
Parental consent laws leave adolescents vulnerable to HIV
14 February 2022
14 February 2022 14 February 2022Sexual activity often starts during adolescence. Many countries have age of consent laws in relation to sexual activity that are inconsistent with minimum age laws for accessing sexual and reproductive health information and services without parental permission. This means that adolescents may legally have sex before they can legally access any information or services relating to safer sex practices or contraception, leaving them at greater risk of HIV, other sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and unwanted pregnancy.
The removal of laws that require parental permission to access services for sexual and reproductive health and HIV prevention, testing and treatment has been shown to improve health-seeking behaviours. That effect is even stronger when schools can provide age-appropriate comprehensive sexuality education to young people so they can protect themselves from HIV, STIs, unwanted pregnancy and gender-based and sexual violence.
Forty countries reported to UNAIDS in 2021 that they have laws requiring parental/guardian consent for adolescents to access hormonal or long-lasting contraceptives, 108 reported that this consent is required for an HIV test, 43 for HIV self-testing, 92 for HIV treatment and 22 for PrEP. Among these countries, some provide exceptions based on demonstrated maturity: 10 for hormonal or long-lasting contraceptives, 15 for HIV testing, eight for self-testing and nine for HIV treatment. The age cut-off of parental consent laws varied by service. The majority of countries that reported having requirements for parental/guardian consent had an age cut-off of 18 years, with exceptions in a few countries where adolescents as young as 14 years could access a service without parental/guardian consent, which varied by service.
Our work


Press Statement
UNAIDS welcomes Chile’s recognition of responsibility for violating the rights of a woman living with HIV sterilized without her consent
11 August 2021 11 August 2021GENEVA, 11 August 2021—UNAIDS welcomes the announcement by Chile that it recognizes international responsibility for violating the rights of a woman living with HIV who was sterilized without her consent almost 20 years ago. The government has agreed a friendly settlement with the woman, Francisca, that includes the payment of reparations for the violation of her human rights. It has also committed to ending forced sterilization and to guaranteeing reproductive rights as human rights without discrimination.
Francisca delivered a healthy baby boy in 2002 and was then sterilized without her consent by the doctor who carried out her Caesarean section, making the decision that a woman living with HIV should not be able to have children. The friendly agreement announced this week comes after more than a decade’s litigation by the woman and her legal teams.
“This settlement is a significant moment for women around the world who have been fighting for reproductive justice for decades. Coercive sterilization of women living with HIV is a violation of women’s most fundamental human rights,” said UNAIDS Executive Director, Winnie Byanyima. “Unfortunately, this practice is still happening in many countries and efforts to stop it and bring justice to more women must be stepped up.”
This settlement comes after years of efforts before the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights (IACHR) after an earlier complaint in the Chilean justice system was unsuccessful. The case was litigated by the Chilean organization, Vivo Positivo, and the international human rights organization, Center for Reproductive Rights.
UNAIDS submitted an amicus brief to inform the IAHCR the standards that governments must uphold to address the HIV stigma and discrimination that impact women living with HIV. These include the obligation to respect, protect and fulfil women’s autonomy in decision making on matters related to their sexual and reproductive lives, their right to physical integrity and their right to be free from violence, including from violence by health personnel.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Our work
Region/country

Feature Story
The journey towards comprehensive sexuality education
28 June 2021
28 June 2021 28 June 2021School-based comprehensive sexuality education plays a vital role in promoting the health and well-being of children and adolescents, both now and in their future. It improves sexual and reproductive health outcomes, including for sexually transmitted infections and HIV, promotes safe and gender equitable learning environments and improves access to and achievement in education.
In a preview of the upcoming global report on the status of comprehensive sexuality education, more than 700 people joined an online event opened by Stefania Giannini, the Assistant Director-General, Education, for the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). While some progress has been made, she noted that there’s still a long way to go and underscored comprehensive sexuality education as one of the key priorities for action to achieve gender equality.
People attending the event heard the perspectives and recommendations of young activists for sexual and reproductive health and rights and case studies from Sweden, Tunisia and Namibia, together with engagement from policy-makers on how they are working towards ensuring quality comprehensive sexuality education for all young people.
“Like all journeys, the road towards comprehensive sexuality education is long, and sometimes winding, but it is leading us on the path to brighter, healthier futures for our young people,” Ms Giannini said.
The panel of young people collectively called for the recognition of education as a fundamental right, the need for strong implementation with proper financing and sufficient monitoring and evaluation and truly comprehensive curricula that respond to the needs of all young people.
Shannon Hader, the UNAIDS Deputy Executive Director, Programme, addressed the meeting, referring to the new Global AIDS Strategy 2021–2026 and the 2021 United Nations Political Declaration on AIDS and the importance of comprehensive sexuality education to both. “Comprehensive sexuality education is a necessary core intervention—to prevent HIV among young people and also to empower young people to recognize and address issues of violence, sexual abuse and elements of their overall sexual health and well-being. Importantly, gaps in comprehensive sexuality education knowledge are not equal. Inequalities exist based on where young people live, levels of family income or education, digital access and degrees of gender inequality in the community. The global AIDS strategy recognizes we must end inequalities to end AIDS.”
The comprehensive sexuality education global status report is a collaboration between UNESCO, UNAIDS, the United Nations Population Fund, the United Nations Children’s Fund, UN Women and the World Health Organization (WHO), with support from governments and civil society. The report provides a snapshot of the status of school-based comprehensive sexuality education around the world, which can help to inform advocacy and resourcing efforts, as governments and partners work towards the goal of ensuring that all learners receive good quality comprehensive sexuality education throughout their schooling.
“For governments and international stakeholders, we want you to stand up, speak out, change the rules and allocate resources for comprehensive sexuality education,” said Reuben Avila, the Director of Sin Control Parental and a She Decides young leader from Mexico.
The event was held in the lead-up to the Generation Equality Forum (GEF), which will be held from 30 June to 2 July and which will launch a series of concrete, ambitious and transformative actions to achieve immediate and irreversible progress towards gender equality.
”Bodily autonomy and sexual and reproductive health and rights” is one of six Action Coalitions that will be established during the GEF. Among the three actions agreed to for the Action Coalition, the first is to ”Expand comprehensive sexuality education”, with the goal of increasing the delivery of comprehensive sexuality education in and out of school to reach 50 million more children, adolescents and youth by 2026. The goal is fully supported by the Global AIDS Strategy 2021–2026, which has a target to reach 90% of all young people with comprehensive sexuality education.
“For meaningful engagement of young people, we have to make sure they have ears, eyes and teeth. The ears mean that young people are aware of their entitlements, voice means that they can advocate for these rights and entitlements to be met by duty-bearers and the teeth means that young people can hold the duty-bearers accountable for doing so,” said Marina Plesons, a technical officer on adolescent sexual and reproductive health and rights at WHO.
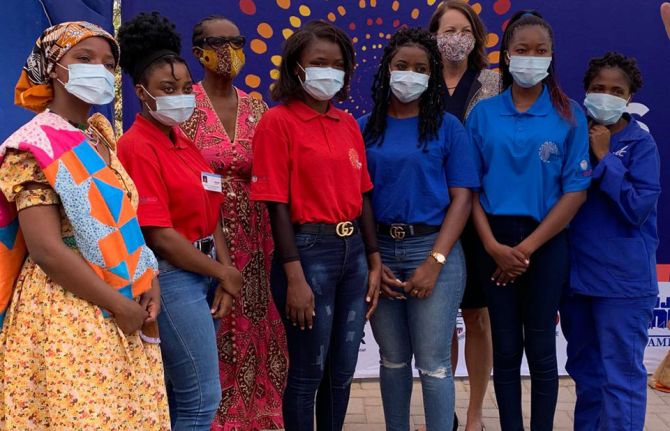


Feature Story
UNAIDS Executive Director visits projects in Namibia that empower adolescent girls and young women
05 May 2021
05 May 2021 05 May 2021Winnie Byanyima, the UNAIDS Executive Director, recently visited the Hakahana Clinic in Katutura, Windhoek, Namibia, where she saw the Determined, Resilient, Empowered, AIDS-Free, Mentored and Safe (DREAMS) project in action, a project funded by the United States of America. The clinic is a government health facility and a DREAMS participating clinic that has provided health services to 10–24-year-old adolescent girls and young women since September 2020.
Together with the United States Ambassador, Lisa Johnson, and the Executive Director of the Namibian Ministry of Health and Social Services, Ben Nangombe, Ms Byanyima met with DREAMS girls and community care workers at the facility.
“I am very impressed by the confidence and optimism the young women express as a result of the support they receive through the DREAMS programme,” said Ms Johnson.
The DREAMS project seeks to reduce new HIV infections among adolescent girls and young women in Namibia and other countries in sub-Saharan Africa. In 2019, there were 1400 new HIV infections among adolescent girls and young women aged 15–24 years in Namibia—more than double the number of HIV infections among their male peers. It is therefore critical that the HIV response continues to gain momentum.
DREAMS uses a core package of evidence-informed, multisectoral interventions that are proven to reduce new HIV infections among adolescent girls and young women. This includes empowering them with social protection, safe spaces, education and economic skills and with access to family planning and sexual and reproductive health services.
“The knowledge I learnt from DREAMS has taught me about making the right decision. I feel empowered,” said Johanna Shinana, a DREAMS Ambassador.
DREAMS is implemented in five districts in three regions of Namibia and the Hakahana Clinic provides eight safe spaces for young women mostly between the ages of 19 and 24 years.
Ms Byanyima, together with Sheila Roseau, the Country Representative of the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), Aina Heita, the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization National Programme Officer for HIV/AIDS, and Thomas Ukola, the Deputy Director at the Directorate of Special Programmes within the Ministry of Health and Social Services, also visited the Namibia Planned Parenthood Association (NAPPA) clinic, which is also in Katutura.
NAPPA is a welfare organization established in 1996 to complement the Ministry of Health and Social Services to provide sexual and reproductive health services and information to young people aged 15‒24 years and lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex people from the marginalized and underserved area around Katutura.
“I encourage young people to take advantage of the services that are offered for them and encourage others to take up these services,” said Ms Byanyima while she was at the NAPPA clinic.
Ms Byanyima was introduced to the Condomise Campaign at the clinic. The campaign, supported by UNFPA, is led by young people and provides young people with key messages on sexual and reproductive health and rights, HIV and skills on how to use condoms correctly.
Klaivert Muandingi, the President of the African Youth and Adolescents Network in Namibia, called on young people to be free in accessing condoms and other commodities. “Condomize, do not compromise. Love smart and play safe,” he said.
Related
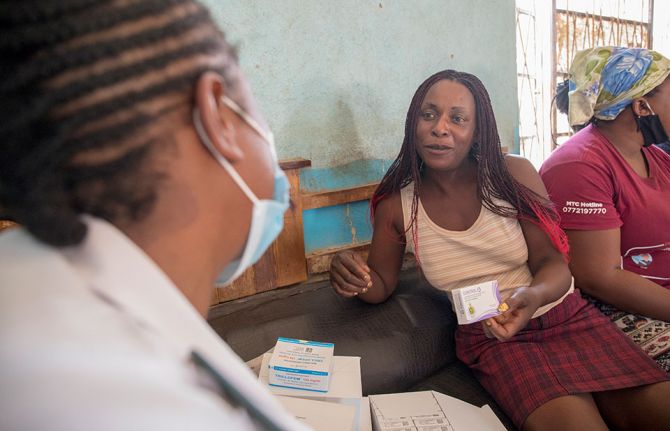


Press Statement
UNAIDS welcomes the United States of America’s decision to support women’s health, safety and rights
03 February 2021 03 February 2021GENEVA, 3 February 2021—UNAIDS warmly welcomes the announcement by the President of the United States of America, Joe Biden, that he has rescinded the Protecting Life in Global Health Assistance Policy (PLGHA, previously known as the Mexico City Policy). The policy required foreign nongovernmental organizations to certify that they would not perform or actively promote abortion using funds from any source (including non-United States funds) as a condition of receiving United States Government funding.
“Rescinding the PLGHA is a strong demonstration of the new United States Administration’s commitment to supporting women to claim their rights and to access sexual and reproductive health and rights information and services,” said Winnie Byanyima, UNAIDS Executive Director. “We look forward to working closely with the new United States Administration to ensure that all women and girls can exercise their human rights and get the sexual and reproductive health information and services they want and need.”
The former United States Administration took previous restrictions established by the Mexico City Policy to a new level by applying the policy to global health assistance provided by all executive departments and agencies. This severely limited access to critical sexual and reproductive health-care services and stifled local advocacy efforts, in turn undermining human rights in general and sexual and reproductive health and rights in particular worldwide.
UNAIDS welcomes the White House’s call to waive conditions related to the PLGHA in any current grants with immediate effect, to notify current grantees, as soon as possible, that these conditions have been waived and to cease imposing these conditions in any future assistance awards.
“Women and girls having full access to their sexual and reproductive health and rights is closely connected to their overall safety, health and well-being. We hope that this will inform the passage of the Global Health, Empowerment and Rights Act—legislation designed to permanently repeal the PLGHA,” added Ms Byanyima.
UNAIDS also warmly welcomes the announcement by the President that the United States will restore funding to the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), a key UNAIDS cosponsoring organization working around the world to provide reproductive health care for women and young people. UNAIDS appreciates the commitment by the United States Secretary of State, Anthony Blinken, to appropriate US$ 32.5 million in support for UNFPA this year.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Region/country
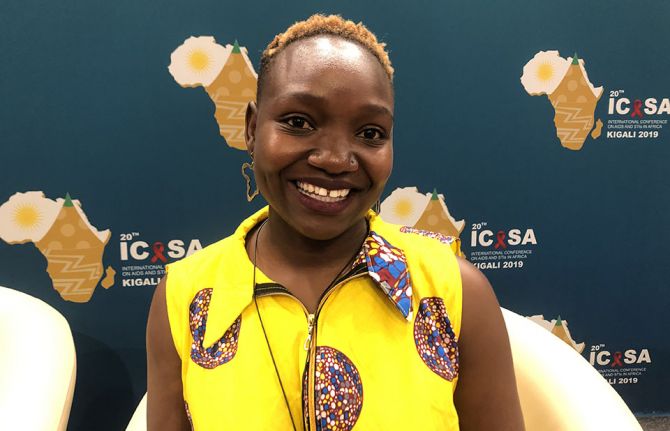


Feature Story
Challenge the stigma, pursue your right to health
20 January 2021
20 January 2021 20 January 2021Adolescent girls and young women must boldly and unapologetically seek sexual and reproductive health and rights information and services. The stigma and harmful gender norms associated with sexual and reproductive health and rights are not going anywhere, says Nyasha Phanisa Sithole, a Zimbabwean sexual and reproductive health and rights leader.
“If you are afraid of stigma, then you will not be able to access these services because we are not going to have a stigma-free environment any time soon,” she says.
Working as a sexual and reproductive health and rights advocate and a regional lead for young women’s advocacy, leadership and training at the Athena Network, Ms Sithole believes everyone has a role to play in changing the status quo and influencing decision-making.
“My story is common. It is that of a 16-year-old adolescent girl who needed access to HIV prevention commodities, but only had condoms available and, in rare cases, pre-exposure prophylaxis,” Ms Sithole says, reflecting on her experience as an adolescent.
Despite this common story, the need for comprehensive HIV, sexual and reproductive health and rights and sexual and gender-based violence services in the eastern and southern African region is critical.
Adolescent girls and young women aged 15–24 years account for 29% of new HIV infections among adults aged 15 years and older in the eastern and southern African region, when they only comprise 10% of the population. This means that there are 3600 new HIV infections per week among adolescent girls and young women in the region, which is more than double that of their male peers (1700 weekly).
The stigma and discrimination that young people face, particularly adolescent girls and young women, to access sexual and reproductive health and rights services creates barriers at various levels, including the individual, interpersonal, community and societal levels.
Furthermore, documented health rights abuses include the unauthorized disclosure of health status, being denied sexual and reproductive health and rights services and related psychological violence.
In 2014, Ms Sithole went undercover as a secret client at a youth-friendly health centre in Harare, Zimbabwe’s capital city, in a district with residential areas and schools. The first person she encountered at the centre was a nosy security guard.
“He asked me: ‘What do you need?’ A health screening, I replied. Then he asked, “Asi wakarumwa?” Meaning, “Have you been bitten?” In Shona, this is street language for someone who has a sexually transmitted infection,” she recalls.
Had she not been well-informed, Ms Sithole says she would have felt scared. “It’s something that can scare you or put you off to say, “It’s just a security guard, why are they mocking me or my situation?” Because imagine if I really had a condition that I wanted to manage, what would happen then?”
Ms Sithole said health-care workers sometimes look at adolescent girls and young women accessing sexual and reproductive health and rights services with disdain and judgement and ask, “How old are you and what do you need the condom or contraception for?”
Considering the stigma attached to accessing sexual and reproductive health and rights services, community organizations play a critical role for adolescent girls and young women. Organizations empower them with sexual and reproductive health and rights information and service referrals.
However, COVID-19 greatly impacted how these organizations work in Zimbabwe, which enforced lockdown restrictions to curb the spread of the virus.
“I think all governments weren’t fair when they clamped down restrictions on each and every organization that was working in communities,” Ms Sithole says, adding that it negatively impacted young people’s access to sexual and reproductive health and rights services.
To mitigate these risks, the Global HIV Prevention Coalition, co-convened by UNAIDS and the United Nations Population Fund, came on board to provide financial and technical support to the Athena Network in 10 countries, including Zimbabwe, to establish What Girls Want focal people in each country. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the focal people, who are adolescent girls and young women, mobilized their peers to conduct dialogues via WhatsApp to discuss the issues they face and seek peer support.
Ms Sithole says governments should invest in policy change and development to create an enabling environment where adolescent girls and young women can access sexual and reproductive health and rights and HIV information and services.
Despite the stigma and discrimination attached to seeking sexual and reproductive health and rights services, Ms Sithole says adolescent girls and young women should realize their power and use their agency to get what they need.
“Think about your life because your life is more important than anything else. So, no matter what happens, if you know there is a service you can access, go for it,” she advises.
Region/country
Related
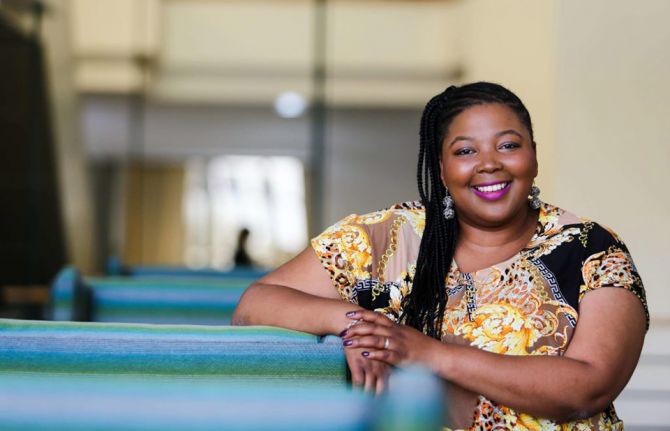


Press Statement
UNAIDS congratulates Tlaleng Mofokeng on her appointment as United Nations Special Rapporteur on the right to health
03 August 2020 03 August 2020GENEVA, 3 August 2020—Tlaleng Mofokeng, a South African medical doctor and a women's rights and sexual and reproductive health rights activist, has been appointed as the new United Nations Special Rapporteur on the right of everyone to the enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health.
"I congratulate Tlaleng Mofokeng on her appointment as the United Nations Special Rapporteur on the Right to Health—the first African women to be appointed to this important role," said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. "I know that she will fight for human rights and for everyone, everywhere to be able to get the health care they need. We both share a vision: that health care should not be just for the rich, but a right for all."
Appointed by the United Nations Human Rights Council, the Special Rapporteur on the right of everyone to the enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health monitors the right to health around the world. The post-holder studies national practices and experiences related to the right to health, identifies trends and challenges in the process and makes recommendations on how to ensure the protection of the right to health. The Special Rapporteur also receives individual complaints of alleged violations of the right to health.
The right to health is a fundamental human right enshrined in international law and countries have basic human rights obligations to respect, protect and fulfil the right to health.
"I look forward to working with Dr Mofokeng," Ms Byanyima added. "Only by ensuring that the right to health is a reality for all will AIDS be ended by 2030."
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.










