Asia Pacific
Related
What the data tell us: Projections for the HIV epidemic in western and central Europe and North America in 2030
28 March 2025
What the data tell us: Projections for the HIV epidemic in the Middle East and North Africa in 2030
28 March 2025
What the data tell us: Projections for the HIV epidemic in eastern Europe and central Asia in 2030
28 March 2025
What the data tell us: Projections for the HIV epidemic in Asia and the Pacific in 2030
28 March 2025
What the data tell us: Projections for the HIV epidemic in western and central Africa in 2030
28 March 2025
What the data tell us: Projections for the HIV epidemic in eastern and southern Africa in 2030
28 March 2025

Feature Story
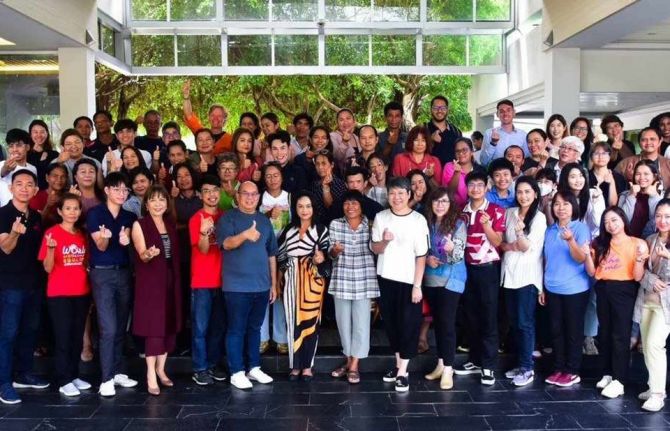
Despite progress, HIV stigma and discrimination continue to bubble beneath the surface in Thailand
24 March 2025
24 March 2025 24 March 2025A woman living with HIV shows up to her community clinic for antenatal care. The nurses ask why she got pregnant.
A man living with HIV goes to his dental appointment. He arrives first, but the staff treat him last.
A young transgender woman learns she is HIV positive. She was already scared about how she would be treated. Now she’s doubly terrified.
A man living with HIV is hopeful when he applies to a new job. He’s dismayed when they demand an HIV test.
The Thailand Stigma Index 2.0 study was launched in early March to commemorate Zero Discrimination Day. It shows that despite a strong national HIV response, challenges continue to simmer below the surface.
Sixteen percent of participants reported discrimination in healthcare settings in the past year. Among women, almost one in ten experienced prejudice while accessing health services, including coercion about contraception. Internalized stigma was common, with 39% of participants feeling ashamed of their HIV status. Self-stigma was especially high among key populations and younger people. And 3% of participants reported that they experienced a human rights violation in the past 12 months.
When compared to the 2009-2010 Stigma Index there has been progress. In that study 20% of participants were denied health services and the same proportion reported discriminatory reactions from health service providers after learning their HIV status. Shockingly, in the 2009-2010 report almost half of respondents (47%) said they experienced violations linked to their HIV status in the last year.
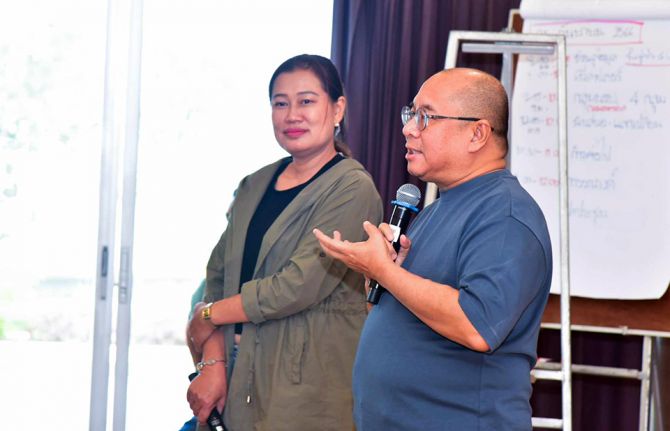
“For each individual living with HIV who has experienced stigma or discrimination the effects can be long-lasting. Therefore, even the findings that have been experienced by only a few individuals in the new study are of concern,” said UNAIDS Country Director for Thailand, Patchara Benjarattanaporn. “We are serious about the goal of zero discrimination.”
This was a Stigma Index with a difference. The Task Force ensured all groups were represented including women, young people and key populations. People living with HIV in all the provincial networks were trained to conduct the study. And they added qualitative and gender components to the methodology to deepen the analysis. The study reflects the experiences of more than 2500 respondents across 24 provinces between 2022 and 2023.
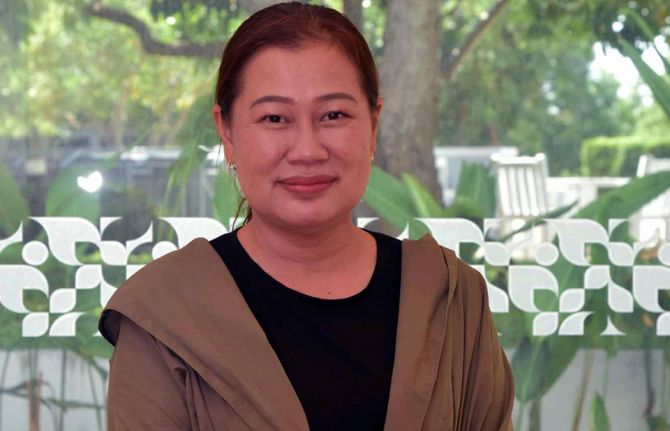
“Addressing stigma and discrimination is key to ending AIDS. At the national and local level there are still issues to be dealt with. Stigma and discrimination lead to people not getting tested, not accessing care and not adhering to treatment,” said Nipakorn Nanta, Chairman of the Thai Women Living with HIV Foundation (TWLHF).
TWLHF led the research exercise, working to ensure the experiences of women were well reflected for the first time. Ms Nanta noted that although Thailand has eliminated mother to child HIV transmission, the emphasis seems entirely on preventing infections in babies. Sometimes women’s agency and confidentiality are sacrificed.
Mr Sattayu Sithirakarn, Director of the CareMat Foundation noted that young men who have sex with men often have a difficult time handling the double stigma of HIV and their sexual orientation.
“The report lays out the issues around internalized stigma very clearly. It is important because if people living with HIV do not have hope, they don’t have the motivation to take care of themselves and have a future,” he said.
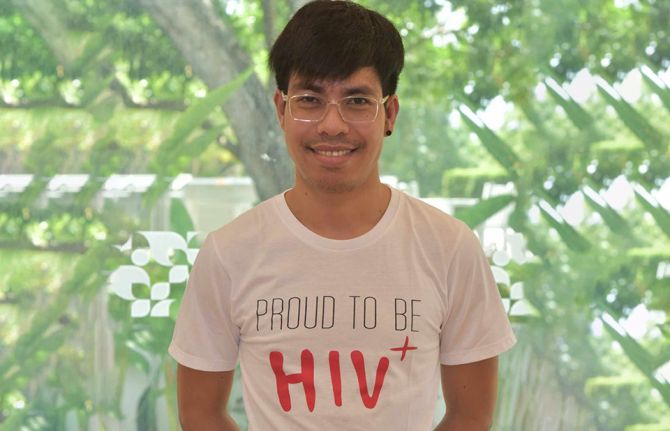
The Task Force youth focal point, Pete Thitiwatt Sirasejtakorn, shared that this was something he had to overcome.
“When I was diagnosed, my life went in a very bad direction,” he said. “At age 25 I left my two businesses. I thought I would die soon. It was unacceptable to me to die from an AIDS-related illness. I thought it was better to kill myself before I got sick. My boyfriend got tested and he was HIV-negative, but he still stayed with me. He empowered me and encouraged me to keep going. But I broke up with him because I had very high internal stigma. I felt dirty. I felt dangerous.”
The game-changer for Mr Sirasejtakorn was knowing about U=U—undetectable equals untransmittable. This refers to the scientific fact that people living with HIV who lower the virus in their blood to an undetectable level through consistent treatment have zero chance of infecting someone they have sex with.
This is one of the main strategies the report recommends for addressing both self- and social stigma. The report also calls for improved public communication, family and social engagement, enhanced healthcare workforce training, and a focus on human rights in laws and policies for key populations.
Some of this work is already underway. In December 2024, Thailand hosted a mission to review ten years of efforts to reduce HIV-related stigma and discrimination in healthcare settings. The review found that although 400 hospitals have participated in stigma reduction training, policies must be properly implemented at the provincial and district levels.
Dr Phongthorn Chanleuan, Chairman of the National Stigma Index Task Force also stressed the importance of community leadership.
“We need strong networks of not only people living with HIV but also youth, women, and LGBT people working together to address stigma and discrimination as a cross-cutting issue,” he said.
Related resources
Region/country
Related


Feature Story
Impact of US funding cuts on HIV programmes in Vietnam
19 March 2025
19 March 2025 19 March 2025Current Coverage and Services
- Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP): According to the National AIDS authority, as of January 31, 2025, there are 210 health facilities nationwide providing PrEP services, with 44,780 people using the service. Of these, 92 facilities with 31,639 clients (70.7%) are funded by PEPFAR in 11 provinces. Antiretrovirals for PrEP committed by PEPFAR in COP 2024-2025 have been delivered by one third. Current stock can cover for PEPFAR-supported PrEP clients until end of May 2025. Relevant medical facilities supported by US CDC have resumed full package service, while those supported by USAID only provide PrEP medicines from available PEPFAR stock but do not cover associated costs, which fall on patients paying out-of-pocket. The development and implementation of the AIDS Information Management System, including PrEP management system, is on hold.
- Antiretroviral Treatment (ART): ART is mainly financed by social health insurance funds and partially by the Global Fund. Technical assistance to the supply chain and treatment information system, mostly through USAID, has been affected.
- HIV Testing and Treatment: Community outreach and lay testing have been heavily affected. All treatment facilities and service points are operating at full capacity. Prevention of vertical transmission and pediatric services are also functioning without disruption.
- Supplies: ARV supplies, HIV tests, viral load tests, and condoms are available with minimal disruption. According to the Viet Nam Administration of Disease Prevention, PEPFAR committed to support about 40,000 PrEP clients in 2025. The Global Fund is supporting 23,000 PrEP clients in 2025 and 25,000 in 2026.
Immediate Risks and Disruptions
- Funding Freeze: The freeze on PEPFAR funding has significantly impacted the expansion of PrEP coverage. This has led to disruptions in access to PrEP and reduced capacity for HIV prevention services, particularly affecting men who have sex with men, and transgender people.
- Stigma and Discrimination Programs: Almost all PEPFAR supported initiatives addressing stigma and discrimination have been halted and those allowed to continue with support through US CDC are requested to not refer to transgender persons and other key populations, which could exacerbate challenges faced by key populations.
- Civil Society Organizations (CSOs): There has been a reduction or suspension of services provided by CSOs, limiting their ability to participate in essential HIV services, policy discussions, data collection and reporting, and access to government or donor support.
Politically Relevant Updates
- Government Response: The Vietnamese government, through the Viet Nam Administration of Disease Prevention, has formed an informal task team to receive feedback from organizations of people living with HIV and key populations.
- Precise numbers of the affected CBO community workers are not available. The government is not assuming the costs for the community workers affected by the PEPFAR freeze.
- International Support: The US funding cut has led to the suspension and/or termination of USAID-funded projects, including critical healthcare programs for tuberculosis and HIV prevention and strengthening of systems for health/HIV. Despite these challenges, the Vietnamese government remains committed to prioritizing resources and implementing effective measures for HIV prevention and control.
Related resources
Region/country
Related
 Impact of US funding cuts on HIV programmes in Malawi
Impact of US funding cuts on HIV programmes in Malawi

15 April 2025


Feature Story
Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia
24 February 2025
24 February 2025 24 February 2025Documented Impact on Services
Indonesia has had to pause many programmes due to the U.S. funding freeze. All community led activities funded through USAID have been paused and prevention and linkages to treatment for around 30% of men who have sex with men (MSM) in Jakarta have been affected. In addition, the expansion of PrEP programmes and a test pilot of long-acting HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) have been halted for now.
The HIV epidemic in Indonesia is mostly concentrated among key populations (MSM, sex workers, people who inject drugs and transgender people) except in Tanah Papua, where the epidemic is generalized. There are nearly 80 000 MSM in Indonesia’s capital.
There are an estimated 570,000 people living with HIV in Indonesia. Addressing the treatment gap is one of the country’s biggest challenges. Only 31% of people living with HIV are accessing treatment and 14% are virally suppressed.
First line HIV treatment is provided for free for PLHIV and is fully funded by the government as are HIV testing kits and CD4 and viral load testing kits. However, HIV self-testing kits, condoms, clean needles, PrEP and long-acting HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis are procured with the support of the Global Fund.
HIV prevention programmes depend heavily on the Global Fund and USAID, especially regarding community outreach and peer support. The Global Fund investment is focused in 178 HIV priority districts with an allocation of $102 million for three years (2024-2026). The US government made an annual investment of $11 million for the HIV response in Indonesia in 2024-25. This includes above site technical assistance for the national HIV program implemented through US-based consulting agencies such as JSI/Think Well and through multilateral agencies including UNAIDS; as well as on-site intervention for PLHIV and key populations in the city and greater Jakarta implemented by EPIC/FHI360.
Region/country
Related
 Impact of US funding cuts on HIV programmes in Malawi
Impact of US funding cuts on HIV programmes in Malawi

15 April 2025


Feature Story
Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment
21 January 2025
21 January 2025 21 January 2025Grabbing his helmet, Hadi Timotius gets in the back of his colleague’s scooter to pay a routine visit to a woman who is taking her HIV treatment again. Hadi oversees the ‘Lost and Link’ initiative at JIP, a national network of people living with HIV in Indonesia.
Region/country

Feature Story
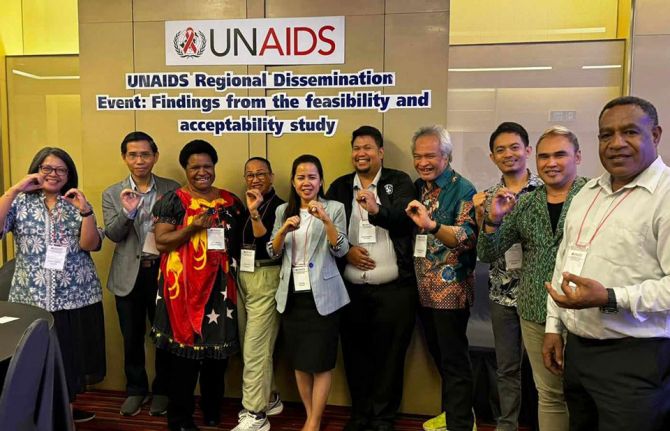
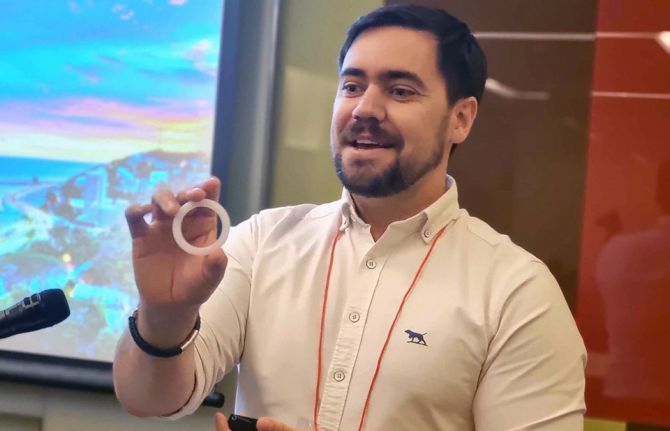
PrEP for her: Cambodia, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea and the Philippines prepare to introduce the Dapivirine ring to help prevent HIV
22 November 2024
22 November 2024 22 November 2024The only HIV prevention that Elena Felix knew of was condoms. But condoms were not something that she was able to make use of, and she contracted HIV. Thirty years after her diagnosis, she’s helped conduct research to determine whether women in the Philippines would use a more confidential tool, and one that does not need a man to agree, to lower women’s risk of HIV infection.
“We hear from women that some partners insist on not using condoms. We hear cases too of rape. Women need protection that does not depend on men” the Association of Positive Women Advocates founder explained.
The Dapivirine Vaginal Ring or DVR was given the green light by the World Health Organization for women at high risk of contracting HIV in 2021. Unlike other types of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), this one is exclusively for women. It is a silicone vaginal ring that is inserted and worn for 28 days before being replaced. It releases an antiretroviral drug locally, reducing the risk of HIV infection through vaginal sex by half.
Since its introduction, the technology was made available in several (11) African countries. And with good reason. Around two-thirds of new HIV infections in Eastern and southern Africa and Western and central Africa are among adolescent girls and women. The combination prevention strategies implemented in these two regions have super-charged progress, driving the global 39% decline in new infections since 2010.
But the Asia Pacific picture is quite different.
“This region has an HIV prevention crisis,” Eamonn Murphy, UNAIDS Regional Director for Asia Pacific and Eastern Europe Central Asia said. “And I am not speaking only of the countries where new infections have doubled, tripled or increased six times since 2010. The average regional decline in new infections is far too slow. At 13% it has virtually flatlined.”
He was speaking to a group of community, government, research and development partners from Cambodia, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea and the Philippines who met from November 11 – 12 in Bangkok. Findings were disseminated from a DVR acceptability and feasibility study conducted by ThinkPlace, and a discussion held on next steps. UNAIDS and the World Health Organization (WHO) are providing technical support for this initiative. The Australia Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade (DFAT) funded the research as part of its ongoing support for prevention work in the region.
Seven percent of new infections in Asia Pacific are among sex workers while 12 percent occur among the intimate partners of key populations. Angeli Achrekar, UNAIDS Deputy Executive Director, called for women in Asia and the Pacific to be provided more HIV prevention options.
“Choice is the way to go!” Ms Achrekar stressed. “Providing options in prevention tools and service delivery increases overall use and results. We must ensure that people have access and that they are supported with the appropriate policies and enabling environment. The ring has great potential to be empowering as an additional choice for women, including in Asia Pacific.”
A person newly acquires HIV in the Asia Pacific region every two minutes. Despite this, the overall momentum on rolling out pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) options has been sluggish. At the end of 2023 there were just 204,000 PrEP users in this region, 98% short of the 8,200,000 target by 2025. The vast majority of those on PrEP were men.
ThinkPlace Regional Director, Elliot Duffy, revealed that overall, the studies found women have high interest in this discreet, woman-controlled prevention method. Sex workers in the four countries sought the DVR given their high vulnerability to sexual violence. And in all countries the sex workers indicated that they would want to access the DVR through community-based health services or their local healthcare facilities. The research also found that healthcare providers in the four countries were enthusiastic about offering this new prevention option.
“The number one barrier is the extent to which women understand how the ring would fit. Many had questions like, “would it be lost in my body? Will I feel pain? Will I be able to have sex?’ Some women worried about a partner thinking they distrusted them,” Mr Duffy explained. “The DVR is not immune to the challenges of other HIV programs and continued effort is needed to increase awareness, generate demand and create services that are accessible.”
Already the research findings have resulted in the introduction and phased implementation of the DVR into 2024 – 2026 Global Fund grant implementation for Cambodia and Indonesia. Cambodia has begun pilot testing. At the meeting the four country teams developed plans to guide their next steps, including on further research, legal and policy reviews, regulatory approvals and community system strengthening.
DFAT Health Adviser, Joshua Metcalf-Wallach, emphasized that as stakeholders switched gears from research to rollout, they should keep communities in the driver’s seat.
“Our Indo-Pacific prevention work has shown that HIV services work best when they are key population- and community-led. As we expand prevention options for women, let us be guided by their needs and demands,” he ended.
Our work
Region/country

Feature Story
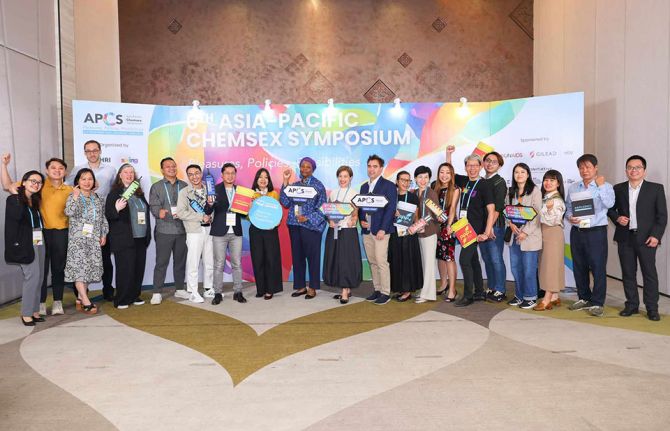
New Asia Pacific healthcare provider toolkit serves people having chemsex
13 November 2024
13 November 2024 13 November 2024Life became chaotic for Poon early. (Not his real name.)
As a gay teenager he was bullied at school by students and teachers. He moved in with his grandparents when his parents separated, but eventually left northern Thailand for Bangkok. There he survived through sex work.
Then Poon learned he was living with HIV. The weight of HIV prejudice merged with the stigma he already carried as a young gay man and sex worker. Some friends he made at a camp disclosed his HIV status online after an argument. He was diagnosed with major depressive disorder.
A partner introduced him to drug-use during sex. He went on to use multiple substances including methamphetamines and cocaine.
“Sex, drugs and alcohol are my escape,” he said.
This was one of the stories shared at the 6th Asia Pacific Chemsex Symposium (APCS). Held in Bangkok on November 6 and 7, the event brought together over 300 stakeholders from 27 countries. They shared their research and responses to a practice that remains largely hidden and not yet well understood. The event specifically explored pleasure as opposed to risk as an entry point for providing services.
Chemsex—also called High Fun in several Asian countries—refers to the use of stimulant drugs during sexual activity. It lowers inhibitions and may increase risk-taking. There are several public health implications including higher rates of HIV and sexually transmitted infections (STIs), lower adherence to treatment, overdose and the fallout linked with intoxication.
In Asia Pacific four of every five new HIV infections are among people from key population communities including men who have sex with men or MSM, people who use drugs, people in prisons or other closed settings, sex workers and transgender people. Young people make up a quarter of all new HIV infections and in some countries around half of new infections are among youth ages 15 to 24.
Several countries in the region are facing an HIV prevention crisis with new infections among MSM either increasing or decreasing far too slowly. In 2023, 43% of new infections in Asia-Pacific were among MSM. At the same time, there is evidence that the practice of chemsex in this community ranges from 3% to 31% depending on the country. But although chemsex is most visible in the MSM community, it is practiced by people from all populations.
“We are talking about sex and drugs—two topics that people call taboo,” said Brigitte Quenum, UNAIDS Regional Team Lead for Sciences, Systems and Services at the opening ceremony. “But as HIV has taught us, to reach people, we must confront the realities of their lives.”
Toolkit now available for Asia Pacific health workers
On day 2 of the symposium UNAIDS and UNODC launched the first-ever toolkit on chemsex for Asia Pacific clinical service providers. The toolkit was developed by the Australian Society for HIV, Viral Hepatitis and Sexual Health Medicine (ASHM). It is geared toward health workers in Asia and the Pacific working with men who have sex with men and transgender women.
"The increasing use of stimulant drugs in the region, including for ‘Chemsex’, poses significant health risks, including drug use disorders and various psychosocial challenges," said Masood Karimipour, Regional Representative of UNODC’s Office for Southeast Asia and the Pacific. "This UNAIDS-UNODC toolkit provides essential guidance for healthcare providers to address these challenges through evidence-based interventions. It emphasizes the importance of holistic, non-judgmental care that prioritizes the physical, psychological and social wellbeing of individuals, while ensuring access to harm reduction services and the prevention and treatment of drug use disorders within a comprehensive continuum of care."
The resource was created to support comprehensive clinical services in the region’s restrictive legal environments. Twenty-eight countries in Asia Pacific criminalise drug possession for personal use while 17 criminalise same-sex relations. Penalties for drug-related offences in the region are among the world’s harshest.
The toolkit was developed through consultation with clinicians, community representatives and government agencies. It covers chemsex basics as well as approaches to harm reduction, sexual health, and mental health services. It also covers different service delivery models including face-to-face, online and by communities. The toolkit offers guides and tools on topics such as initiating non-judgmental conversations and risk assessment.
“Stronger HIV prevention strategies tailored to chemsex are needed, along with expanded, inclusive services for sexual, physical and mental health,” said Suniya Taimour, UNAIDS’ Community-led Responses Advisor for Pakistan and Afghanistan.
Thia approach recognises that comprehensive health services can be lifesavers by using one point of contact to address multiple issues including physical, sexual and mental health as well as social issues. Poon is a living example. He has benefitted from a service package that has combined his HIV treatment with harm reduction interventions and psychiatric care. Today he is a 22-year-old university student with clear life goals who feels more empowered about his HIV status.
Our work
Region/country
- Asia and Pacific
- Australia
- Bangladesh
- Bhutan
- Brunei Darussalam
- Cambodia
- China
- Democratic People's Republic of Korea
- Federated States of Micronesia
- Fiji
- India
- Indonesia
- Islamic Republic of Iran
- Japan
- Kiribati
- Lao People's Democratic Republic
- Malaysia
- Maldives
- Marshall Islands
- Mongolia
- Myanmar
- Nauru
- Nepal
- New Zealand
- Pakistan
- Palau
- Papua New Guinea
- Philippines
- Republic of Korea
- Singapore
- Solomon Islands
- Sri Lanka
- Thailand
- Timor-Leste
- Tonga
- Tuvalu
- Vanuatu
- Viet Nam
- Samoa
Related

Feature Story
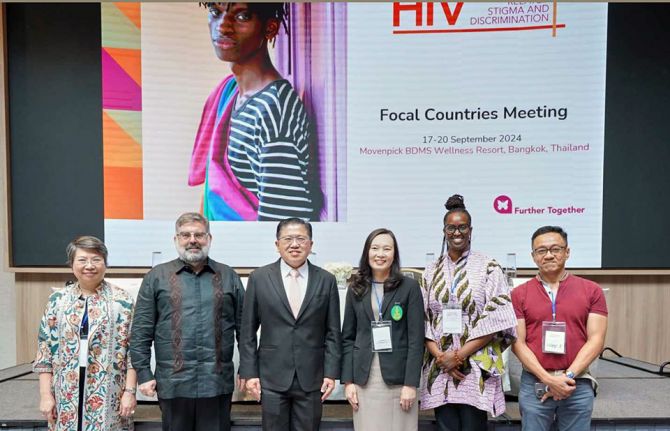
Can this innovation change the way people think about HIV?
16 October 2024
16 October 2024 16 October 2024In 2020, a gay Thai man living with HIV sparked controversy with a Facebook post. He was on antiretroviral therapy and had gotten lab tests to check the level of virus in his blood. Since his viral load was undetectable, he wrote, he was going to stop using condoms.
The public responded with a mix of contempt and disbelief. How could he? So selfish! So reckless! The resulting debate spilled from social media onto national radio and TV.
“There was a huge backlash,” remembered Dr Nittaya Phanuphak, the Executive Director of the Institute of HIV Research and Innovation (IHRI). She was telling the story from IHRI’s sunlit offices to teams from Botswana, Ghana, Ivory Coast, Jamaica, Mozambique, South Africa and Zambia. They’d come to Bangkok as part of a learning exchange coordinated by the Global Partnership for Action to Eliminate all Forms of HIV-related Stigma and Discrimination.
Dr Nittaya said that she and her father, Professor Praphan Phanuphak, thought it was their duty to contribute to the public discourse. While the man’s approach might have been unconventional, the science behind his statement was sound.
They would know. Professor Praphan diagnosed Thailand’s first HIV case in 1985 and dedicated his life to HIV research, service delivery and advocacy. He co-founded the Thai Red Cross AIDS Research Centre which in 2014 conducted cutting-edge research as part of the Opposites Attract Study. Done in Australia, Brazil and Thailand, that study tracked couples in which one person was HIV-negative and the other was living with HIV but had achieved an undetectable viral load through successful HIV treatment. It confirmed that after two years of unprotected sex, there were no cases of HIV transmission between more than 300 couples.
“It’s a scientific fact,” Dr Nittaya said. “For me, I felt like we really needed to do something. We cannot just wait 50 years for this knowledge to gradually seep into Thai society.”
The “knowledge” to which she refers is the concept of undetectable = untransmittable, or U=U for short. Last year the World Health Organization further endorsed the principle, stressing that when a person’s viral load is undetectable there is zero chance of sexual transmission.
“Before, HIV treatment just meant longevity,” said Pan (not his real name), a person living with HIV. “But with U=U, now it is love without fear.”
Within three to six months a person who takes their HIV treatment as prescribed and receives viral load monitoring can confirm that they have achieved an undetectable viral load. This removes the self-stigma associated with having an “infectious” disease. For Thai HIV response stakeholders, this concept can also transform the public’s attitudes about people living with HIV, making it easier for them to live full, happy lives.
“If social perceptions can be brought in line with the reality of HIV treatment, we can remove the stigma around getting an HIV test or diagnosis,” said Eamonn Murphy, Regional Director of UNAIDS Asia Pacific and Eastern Europe Central Asia. “The more supportive the society, the more people we successfully treat and the fewer new infections.”
But for the U=U strategy to be fully utilized, work must be done to dispel myths and bolster confidence in science.
According to UNAIDS Country Director for Thailand, Dr Patchara Benjarattanaporn, a key step in the national process was bringing decision-makers together with relevant stakeholders, including voices from communities.
“They considered both global and local evidence,” she explained. “Now there is consensus about the science. U=U also conveys the message ‘you=you’, affirming that all individuals are equal and that people are more than their HIV status. It emphasizes the importance of ensuring people are fully informed about their options and respecting their right to make choices about their sexual health depending on their realities.”
At the opening ceremony of the eight-country learning exchange, Dr Niti Haetanurak, Department of Disease Control Deputy Director, noted that the U=U concept is a key element of Thailand’s “all of society” strategy to address the prejudice and rights violations people living with HIV face. Thailand has a National Costed Action Plan to Eliminate all forms of HIV-related Stigma and Discrimination. The Ministry of Public Health and Sub-National Committee on AIDS Rights Promotion and Protection under National AIDS Committee coordinate the effort. Community organizations play a leading role.
During the exchange the country teams visited the Service Workers in Group (SWING) Foundation which serves sex workers and IHRI’s Tangerine Clinic which primarily serves transgender people. Both have come up with innovative approaches to ensure groups that usually find it challenging to receive healthcare at state-run facilities can get HIV and sexually transmitted infection (STI) testing and treatment in a friendly environment.
A key strategy is training members of those very communities to provide certain services themselves. They can even start clients on treatment for HIV and some other conditions the same day they are diagnosed. This approach makes it less likely for people to disappear into the shadows after diagnosis, with a high chance of infecting others and eventually becoming ill.
“This community-led health model can be applied to any health condition or population. But this does not really address stigma and discrimination. It just bypasses it by opening up alternative service delivery outlets for people who want to avoid negative experiences elsewhere,” Dr. Nittaya said. “We need to address the heart of the stigma as well. That is why we are working on using U=U as a tool to explore how we can shift attitudes.”
The Bangkok Metropolitan Administration (BMA) is integrating this concept into its work in healthcare settings and the workplace. A masterplan is in the works. One branch of the strategy will tackle employers requiring HIV testing in the pre-employment phase or targeting employees they find out are living with HIV. Another aspect of the approach is the integration U=U into all levels of HIV service delivery and ongoing healthcare worker sensitization. All staff in clinics and hospitals are trained, not just nurses and doctors.
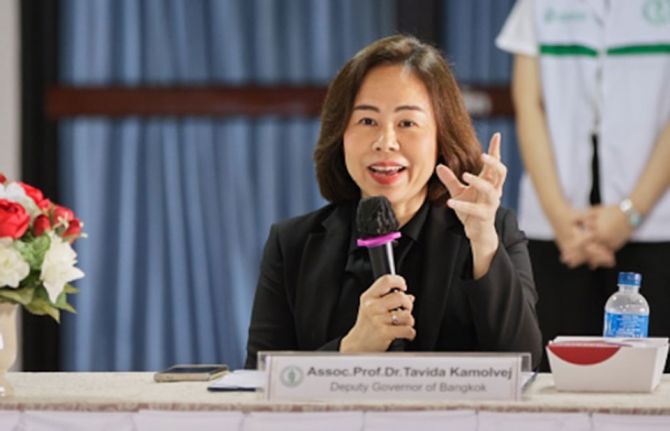
The work doesn’t stop there, though. Describing the Bangkok society as “open”, Dr Tavida Kamolvej, Deputy Governor of Bangkok, said that the whole of society was ready for deeper conversations about inclusion and HIV. But how could these approaches be applied in other countries and cities that are not quite as tolerant or accepting, she was asked.
“If you are confronted with beliefs that might not allow open conversations about HIV, sexuality and sex, you can strategically make it about health literacy, dignity and care for all people. I think this is soft enough to make people aware about health and wellbeing,” Dr Tavida advised.
Click here to learn more about the recent eight-country learning exchange to eliminate all forms of HIV-related stigma and discrimination.
Related

Feature Story
Women living with HIV in China unite to confront discrimination
14 October 2024
14 October 2024 14 October 2024There are around 1.4 million people living with HIV in China and women make up around 23.7% of them, according to the latest data from Chinese health authorities. Among those living with HIV are pregnant women who are in a particularly vulnerable position due to the stigma surrounding the disease.
In order to counter such stigma and discrimination, women living with HIV and Hepatitis B came together at The Voice of Resilience event to tell their stories and to call for additional resources for community-based organizations (CBOs) working on the frontlines providing services for women living with and affected by HIV.
In 2023 alone, more than 5,000 pregnant women were diagnosed with HIV and over 400,000 with hepatitis B, and some of them were diagnosed at very late stage to be able to receive HIV services to prevent transmission to their children, according to China’s National Health Commission. Even though services are in place to prevent the transmission of HIV to their babies, discrimination, including denial of healthcare, obstructs women from accessing such services.
“I received a call from the doctor telling me that I couldn’t receive services from their hospital because I was HIV positive,” explained Xia Jing, one of the mothers, after she went to a general hospital in Beijing for a routine maternal exam. She still cannot hold her tears when she remembers her traumatic experience. She challenged back and told the doctor r that under the law they had no right to reject her.
She was eventually referred to Beijing’s You’an Hospital, a designated hospital for infectious diseases and people living with HIV where she delivered her baby. Now she is a happy mother of a four-year-old boy. Doctor Zhu Yunxia was the doctor who helped Jing deliver her baby. Dedicated to her job for more than 30 years, she is proud of having helped so many women deliver healthy babies. She calls for empathy with people facing discrimination and unfair treatment and urges all people to look at women living with HIV without prejudice.
“Stigma undermines public health objectives by creating barriers to accessing health and social services and can reduce the quality of the services that members of affected communities receive,” said Mark Vcislo, the First Secretary at Canadian Embassy to China, which has supported the work to tackle stigma. He called for breaking down “the prejudices that can prevent and deter marginalized communities, including persons living with HIV, from accessing the health and social services they need and deserve.”
Community-based organizations (CBO) are vital support for women living with HIV. Sister Xin, for instance, who herself received help from community volunteers when she was first diagnosed with HIV, created Firefly, a community-based organization that has help more than 20,000 women living with HIV in the last 20 years. Zhang Yu whose CBO supports women living with HIV in rural areas of China’s southwestern Yunnan Province, called for more resources for CBO’s work. “CBOs are struggling with their survival due to lack of resources,” she said. “I sincerely hope the government, the charity organizations and everybody can support us to continue our work.”
China has developed a strong and ambitious plan to significantly reduce the transmission rates of HIV, syphilis, and hepatitis B by 2025 outlined in China Women’s Development Plan and Healthy China 2030. China has achieved around 99 percent national screening rates among pregnant women living with HIV over the past five years. In 2023 alone, more than 9 million pregnant women have received HIV testing services.
The Chinese government has partnered with UN agencies for the “last mile” by building a patient-centred and family-centred community service model to enable a holistic set of services and help break the barriers for both mothers and infants.
“Thanks to the combination of development of technology and social progress, women living with HIV can today give birth to healthy babies,” said Sister Xin.
Read the profile of the storytellers and more unsung community heroes committed to helping mothers and babies: http://www.unaids.org.cn/page122?_l=en&article_id=1233.
Region/country
Related
Documents
Asia and the Pacific regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
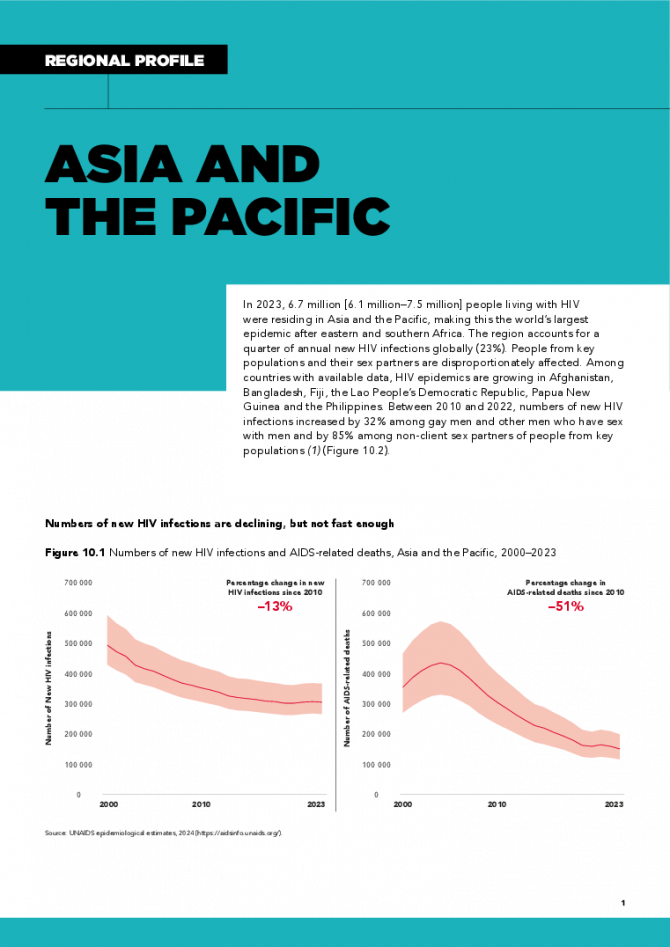
In 2023, 6.7 million [6.1 million–7.5 million] people living with HIV were residing in Asia and the Pacific, making this the world’s largest epidemic after eastern and southern Africa. The region accounts for a quarter of annual new HIV infections globally (23%). People from key populations and their sex partners are disproportionately affected. Among countries with available data, HIV epidemics are growing in Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Fiji, the Lao People’s Democratic Republic, Papua New Guinea and the Philippines. Between 2010 and 2022, numbers of new HIV infections increased by 32% among gay men and other men who have sex with men and by 85% among non-client sex partners of people from key populations. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
What the data tell us: Projections for the HIV epidemic in western and central Europe and North America in 2030
28 March 2025
What the data tell us: Projections for the HIV epidemic in the Middle East and North Africa in 2030
28 March 2025
What the data tell us: Projections for the HIV epidemic in eastern Europe and central Asia in 2030
28 March 2025
What the data tell us: Projections for the HIV epidemic in Asia and the Pacific in 2030
28 March 2025
What the data tell us: Projections for the HIV epidemic in western and central Africa in 2030
28 March 2025
What the data tell us: Projections for the HIV epidemic in eastern and southern Africa in 2030
28 March 2025