Human rights
Documents
Caribbean regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
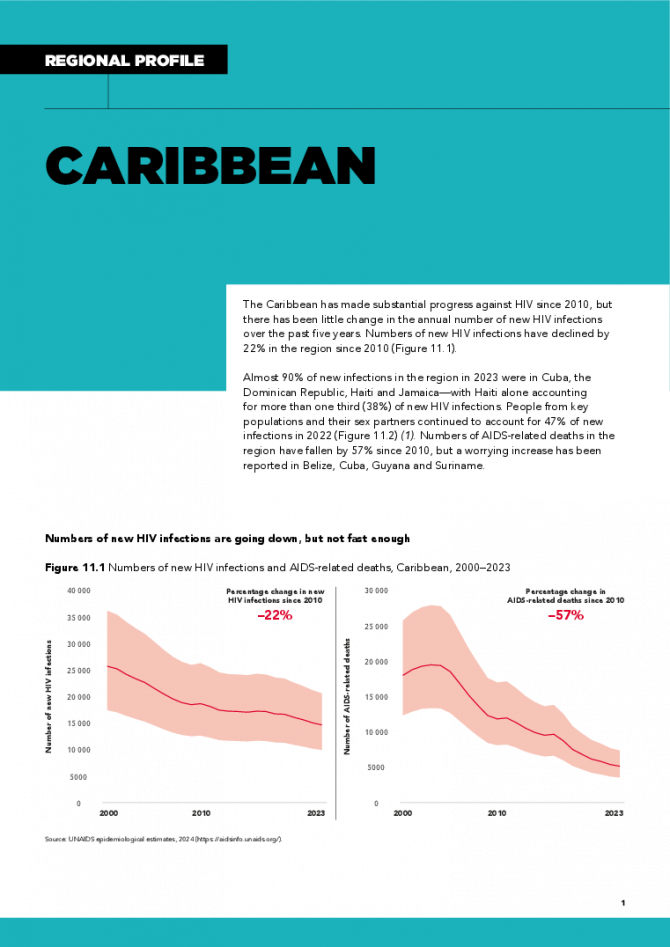
The Caribbean has made substantial progress against HIV since 2010, but there has been little change in the annual number of new HIV infections over the past five years. Numbers of new HIV infections have declined by 22% in the region since 2010. Almost 90% of new infections in the region in 2023 were in Cuba, the Dominican Republic, Haiti and Jamaica—with Haiti alone accounting for more than one third (38%) of new HIV infections. People from key populations and their sex partners continued to account for 47% of new infections in 2022. Numbers of AIDS-related deaths in the region have fallen by 57% since 2010, but a worrying increase has been reported in Belize, Cuba, Guyana and Suriname. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
 Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment
Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment

21 January 2025
Documents
Asia and the Pacific regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
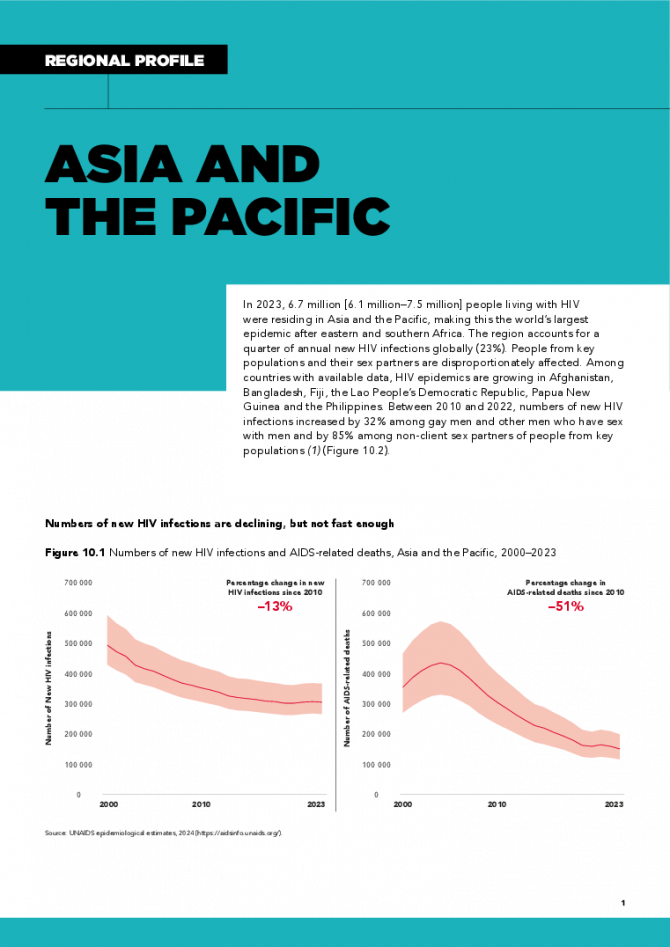
In 2023, 6.7 million [6.1 million–7.5 million] people living with HIV were residing in Asia and the Pacific, making this the world’s largest epidemic after eastern and southern Africa. The region accounts for a quarter of annual new HIV infections globally (23%). People from key populations and their sex partners are disproportionately affected. Among countries with available data, HIV epidemics are growing in Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Fiji, the Lao People’s Democratic Republic, Papua New Guinea and the Philippines. Between 2010 and 2022, numbers of new HIV infections increased by 32% among gay men and other men who have sex with men and by 85% among non-client sex partners of people from key populations. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia
Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia

24 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025


Press Statement
Decriminalization of LGBTQ+ people saves lives
19 July 2024 19 July 2024Joint Statement by UN High Commissioner for Human Rights Volker Türk and UNAIDS Executive Director Winnie Byanyima
GENEVA, 19 July 2024 — As courts and parliaments in a number of countries are in the midst of considering the legal framework around the rights of LGBTQ+ people, we highlight that punitive laws against lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer people violate human rights and undermine public health.
Such laws cost lives.
Laws criminalizing LGBTQ+ people must be consigned to history – and a growing number of countries are doing just that.
The big – and very welcome – global shift is away from criminalization. Over two-thirds of countries now do not criminalize LGBTQ+ people.
In the last 10 years alone, Angola, Antigua and Barbuda, Barbados, Belize, Bhutan, Botswana, Cook Islands, Dominica, Gabon, India, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, Nauru, Palau, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Seychelles, Singapore, and Trinidad and Tobago have all repealed laws that had criminalized LGBTQ+ people.
There is a whole host of reasons why such laws must be scrapped.
Such laws are based on prejudice.
As Namibia's High Court recently noted, "the enforcement of the private moral views of a section of the community (even if they form the majority of that community), which are based to a large extent on nothing more than prejudice, cannot qualify as such a legitimate governmental purpose."
Such laws infringe upon human rights.
The Eastern Caribbean Supreme Court put it clearly: “The criminalization of same-sex sexual expression between consenting adults is intrusive by its very nature and thereby offends the right to liberty and personal privacy.”
Many such laws are actually legacies of colonialism, imposed by colonial powers themselves.
The now scrapped punitive anti-LGBTQ+ law in Mauritius, the Supreme Court of Mauritius recently noted, “was not the expression of domestic democratic will but was a course imposed on Mauritius and other colonies.”
Such laws harm public health.
Criminalization of LGBTQ+ people generates justified fear amongst people who need access to health services, and amongst the frontline workers who provide those services.
In criminalizing countries, there is decreased provision and uptake of HIV prevention services, and decreased uptake of HIV care and treatment services. A study in sub-Saharan Africa showed that HIV-prevalence among gay men and men who have sex with men was five times higher in countries that criminalized same-sex relationships than in non-criminalized settings.
Criminalizing countries have significantly lower rates of both knowledge of HIV status and HIV viral suppression among all people living with HIV.
Such punitive laws have no “law and order” justification.
In decriminalizing homosexuality in Singapore, there was clear recognition by the Government that there was no basis for making private sexual behaviour between consenting adults a crime.
Such laws lead to harassment.
As the Supreme Court of India has stated, punitive legislation has “become an odious weapon for the harassment of the LGBT community by subjecting them to discrimination and unequal treatment.”
There is extensive evidence that such discriminatory laws increase exposure of people to brutal hate crimes, police abuse, harassment, blackmail, torture, and denial of access to healthcare, education and housing.
They also drive impunity and undermine the rule of law, harming LGBTQ+ people, their families, communities, and the whole of society.
Stigma kills. Solidarity saves lives.
The progress that has been won around the world, in legislation and attitudes, needs to continue, as does the increasing recognition that people should not be criminalized for who they are and whom they love.
Anti-rights policies, proposals and propaganda need to be challenged head on.
Together, we call on all countries to remove all punitive laws against lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer people.
Decriminalization of LGBTQ+ people is vital for protecting everyone’s human rights and everyone’s health.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.


Press Release
UNAIDS welcomes the adoption of a key HIV resolution by the Human Rights Council
12 July 2024 12 July 2024GENEVA, 12 July 2024— UNAIDS welcomes the adoption, by consensus, of a critical resolution on human rights in the context of HIV and AIDS at the 56th session of the UN Human Rights Council.
The 2024 resolution 56/20 Human Rights in the Context of HIV and AIDS, recognizes the centrality of human rights to the HIV response. The resolution reaffirms that, “the full realization of all human rights and fundamental freedoms for all is an essential element in the global response to the HIV epidemic and its sustainability.”
It also recognizes the importance of human rights and community leadership in the HIV response, ensuring access to available and affordable HIV prevention, testing and treatment services for all, without discrimination. The resolution also calls on countries to tackle discriminatory attitudes and punitive laws and policies that prevent access to health services and to support community-led organizations as well as protect civic space.
This ground-breaking text includes the first unqualified recognition of sexual and reproductive health and rights in a UN resolution and calls on countries to scale up comprehensive education on sexual and reproductive health with information on, “sexuality and comprehensive HIV prevention, gender equality and women’s and girls’ empowerment, human rights, and physical, psychological and pubertal development, to enable them to build self-esteem and risk reduction skills and to empower them in their decision-making, communication and development of respectful relationships, in order to enable them to protect themselves from HIV infection.” .
Every week, 4000 adolescent girls and young women (aged 15–24 years) became infected with HIV worldwide. 3100 of these infections occurred in sub-Saharan Africa, also where 6 out of 7 new HIV infections in adolescents (aged 10–19 years) were among girls.
UNAIDS Executive Director, Winnie Byanyima said, “We would not be where we are today in the HIV response, with 29 million people on treatment and a 56% reduction in new HIV infections, without having human rights and communities at the center of the response. However, the status quo is not enough. All stakeholders need to scale up action to respect, protect and fulfil human rights in the HIV response if we are to end inequalities and end AIDS for everyone.”
Human Rights Council members expressed concern that key populations face multiple and intersecting forms of discrimination, stigma, violence and abuse. This affects their access to clinics and/or peer-led drop-in centers and called on member states to take action to ensure access to non-stigmatizing health services free from discrimination and legal barriers.
The resolution recognizes the importance of the Global AIDS Strategy’s societal enabler targets and calls on countries to take action to remove punitive legal and policy frameworks, and end stigma. This also includes addressing gender-based violence and inequalities, as well as changing gender stereotypes and negative social norms.
The societal enabler targets, outlined in both the 2021 Political Declaration on HIV and AIDS and the Global AIDS Strategy, 2021-2026, commit countries to the following targets: that by 2025, less than 10% of people living with HIV and key populations experience stigma and discrimination, less than 10% experience gender-based inequalities and violence and less than 10% of countries have punitive laws and policies.
Progress towards the 2025 milestone has been mixed, with many countries failing to make significant progress required to be on track to meet these targets and other human rights goals.
This resolution is an important commitment by countries to re-double their efforts to ensure human rights are at the center of a sustainable HIV response.
Going forward the resolution calls on OHCHR and UNAIDS, in collaboration with other stakeholders to hold a panel at the 58th session of the Human Rights Council in 2025 to discuss the realization of human rights in sustaining and increasing the gains made in the HIV response. The session will include recommendations to countries and will be followed by a report on sustainability and human rights to be presented at the 60th HRC session.
In 2025, countries are set to develop a new Global AIDS Strategy that will take the world to the 2030 deadline to meet the Sustainable Development Goals, which includes ending AIDS as a global health threat by 2030.
UNAIDS commends the leadership of Brazil and the other members of the core group, Colombia, Portugal and Thailand, for continuing to lead the resolution on HIV at the Human Rights Council and their significant success in bringing consensus back to this relevant resolution.
More information here: OHCHR | 56th regular session of the Human Rights Council: Resolutions, decisions and President’s statements
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Documents
2024 global AIDS report — The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
This UNAIDS 2024 report brings together new data and case studies which demonstrate that the decisions and policy choices taken by world leaders this year will decide the fate of millions of lives and whether the world’s deadliest pandemic is overcome. Related links: Press release | Special web site | Executive summary | Fact sheet | Video playlist | Epidemiology slides | Data on HIV | Annex 2: Methods Regional profiles: Asia and the Pacific | Caribbean | Eastern Europe and Central Asia | Eastern and Southern Africa| Latin America | Middle East and North Africa | Western and Central Africa | Western and Central Europe and North America Thematic briefing notes: People living with HIV | Gay men and other men who have sex with men | Transgender people | Sex workers | People who inject drugs | People in prisons and other closed settings | Adolescent girls and young women | Other translations: German
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025
 UNAIDS urges that all essential HIV services must continue while U.S. pauses its funding for foreign aid
UNAIDS urges that all essential HIV services must continue while U.S. pauses its funding for foreign aid

01 February 2025
Related
55th meeting of the UNAIDS Programme Coordinating Board
10 December 2024
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
Take the rights path to end AIDS — World AIDS Day report 2024
26 November 2024
20th Indian Ocean Colloquium on HIV/AIDS
22 October 2024
 Club Eney: a safe place for those left behind
Club Eney: a safe place for those left behind

21 October 2024
 Peru approves groundbreaking law to extend health coverage for migrants with HIV and TB
Peru approves groundbreaking law to extend health coverage for migrants with HIV and TB

21 October 2024
University of Pompeu Fabra
17 October 2024
 UNAIDS statement on anti-LGBTQ+ legislation in Georgia
UNAIDS statement on anti-LGBTQ+ legislation in Georgia

01 October 2024
Linking UN Summit of the Future with COP29
26 September 2024


Press Statement
UNAIDS applauds Namibian High Court's decision to declare unconstitutional the law that had criminalised same-sex relationships
21 June 2024 21 June 2024GENEVA, 21 JUNE 2024—UNAIDS applauds the judgment by the High Court of Namibia, striking out as unconstitutional the law which had criminalised same-sex relationships. The court found the law incompatible with the constitutional rights of Namibian citizens. This decision, which is in line with a series of judgments by courts in Southern Africa in recent years, marks a significant victory for equality and human rights for all Namibians and will help protect the health of everyone.
"This decision by the High Court of Namibia is a powerful step towards a more inclusive Namibia," said Anne Githuku-Shongwe, UNAIDS Regional Director for East and Southern Africa. "The colonial-era common law that criminalized same-sex sexual relations perpetuated an environment of discrimination and fear, often hindering access to essential healthcare services for LGBTQ+ individuals. To protect everyone’s health, we need to protect everyone’s human rights.”
Originally introduced during colonial rule in Apartheid South Africa and maintained in Namibian law when the country gained independence in 1990, this law had been used to rationalize discrimination against LGBTQ+ people in Namibia. It not only violated the constitutional rights of Namibian citizens but also posed a challenge to public health. The climate created by the law discouraged LGBTQ+ individuals from seeking HIV testing and treatment, undermining efforts to control the epidemic.
"By decriminalizing same-sex relationships, Namibia creates a safer environment for LGBTQ+ communities," said Ms. Githuku-Shongwe. "This allows them to access vital healthcare services, contributing to the global goal of ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030."
UNAIDS urges all countries to follow Namibia's lead, remove punitive laws, and tackle prejudices against lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and intersex people. Since 2019, Botswana, Gabon, Angola, Bhutan, Antigua and Barbuda, Barbados, Singapore, Saint Kitts and Nevis, the Cook Islands, Mauritius, and Dominica have all repealed laws that criminalized LGBTQ+ people.
A more just, equitable and kind world is a healthier one for everyone.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Region/country




Press Statement
UNAIDS stands with LGBTQ+ communities worldwide as PRIDE celebrations get underway
29 May 2024 29 May 2024GENEVA, 29 May 2024—As LGBTQ+ communities and allies take to the streets to mark PRIDE month, UNAIDS is speaking out in solidarity, rejecting the criminalization, discrimination and stigmatization of LGBTQ+ people and insisting on respect for all.
“The PRIDE celebrations are a demonstration of the power of inclusivity,” said UNAIDS Executive Director, Winnie Byanyima. “PRIDE has brought the world a long way in the struggle to protect the human rights of LGBTQ+ people. So much has been won. But the progress that has been made is under threat. The world needs the spirit of PRIDE more than ever today: to protect everyone’s health, we need to protect everyone’s rights.”
There is much to celebrate. UNAIDS data shows that 123 countries do not penalize same-sex relations. This represents the highest number of countries rejecting criminalization ever.
More and more countries have been scrapping the harmful punitive anti-LGBTQ+ laws which are often leftovers of colonial rule. Since 2019 alone, Botswana, Gabon, Angola, Bhutan, Antigua and Barbuda, Barbados, Singapore, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Cook Islands, Mauritius and Dominica have all repealed laws that had criminalized LGBTQ+ people.
However, the human rights of the LGBTQ+ community are threatened by a globally coordinated and well-funded extremist anti-rights network who are spending millions promoting hate and social division and are proposing ever more draconian laws to punish LGBTQ+ people. Attacks on LGBTQ+ people violate human rights and undermine public health.
This perilous time calls for courage and solidarity from everyone. PRIDE has always been as much about protest and commemoration as celebration. The first marchers in New York more than 50 years ago knew that PRIDE was the antidote to stigma and discrimination – a rejection of the shame that others sought to impose on them.
Movements spearheaded by LGBTQ+ activists have driven much of the progress that has been made in protecting everyone’s human rights and protecting everyone’s health.
Today we are at a hinge moment: the end of AIDS as a public health threat is realisable in this decade, but progress is imperiled by the pushback on human rights.
At a time when support for human rights defenders is vital and urgent, funding support for civil society organizations is shrinking, as donor countries cut their budgets.
The evidence is crystal clear: stigma kills, solidarity saves lives.
This is a moment for solidarity. This is a moment for PRIDE.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.


Press Statement
UNAIDS expresses deep concern over the passing of new anti-LGBT legislation in Iraq
30 April 2024 30 April 2024GENEVA, 30 April 2024—The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) is deeply concerned about the impact of the harmful new legislation in Iraq amending the 1988 anti-sex work law to criminalize LGBTQ+ people. The legislation imposes a prison sentence of between 10 and 15 years for same-sex sexual relations. Transgender people face up to three years imprisonment for expressing their gender or receiving gender affirmation care. Individuals also face up to seven years for promoting homosexuality. And up to three years for providing gender affirmation care.
Criminalizing consensual same-sex relationships and gender expression not only violates fundamental human rights but also undermines efforts to end AIDS by driving marginalized populations underground and away from essential health services, including life-saving HIV prevention, treatment and care services.
Globally, the movement for human rights has made progress in the past 40 years. At the start of the AIDS pandemic in the early 1980s, most countries criminalized same-sex sexual activity between men, now two thirds do not. An increasing number of countries have also recognized the rights of trans and other gender diverse people. However, this new legislation in Iraq represents a significant setback and is part of a wave of punitive and restrictive laws being passed that undermine the rights of LGBTQ+ people.
The legislation passed in parliament is an amendment to an existing 1988 anti-sex work law which continues to criminalize both the selling and buying of sexual services. The amendments passed on Saturday 27 April 2024 increase the penalties in relation to sex work. These laws, which countries committed to removing under the 2021 United Nations General Assembly Political Declaration on HIV and AIDS, likewise undermine the human rights and public health of sex workers.
UNAIDS calls upon the authorities of Iraq to overturn this discriminatory legislation and fulfill its obligations under international human rights law to protect the rights of all people, regardless of sexual orientation or gender identity. UNAIDS stands in solidarity with LGBTQ+ people and communities and reaffirms its commitment to work with partners to promote equality, end stigma and discrimination, uphold human rights—including the right to health, and ensure access to comprehensive HIV services for everyone, everywhere.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Our work
Region/country
Documents
Preventing and responding to an HIV-related human rights crisis — Guidance for United Nations agencies and programmes
25 April 2024
This Guidance was developed in response to the increase in HIV-related human rights crises and the shrinking civic space for rights-related responses to HIV in recent years across the world. This document builds upon existing guidance documents, offering updated guidance for country-based United Nations staff (United Nations Country Teams) and partners to use their respective mandates to coordinate effective responses to human rights-related crises within the framework of the Resident Coordinator system, the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, global HIV and human rights strategies and frameworks.
Related
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
A shot at ending AIDS — How new long-acting medicines could revolutionize the HIV response
21 January 2025
Indicators and questions for monitoring progress on the 2021 Political Declaration on HIV and AIDS — Global AIDS Monitoring 2025
17 December 2024
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
 Global celebrities unite behind UNAIDS’ call for world leaders to “take the rights path to end AIDS”
Global celebrities unite behind UNAIDS’ call for world leaders to “take the rights path to end AIDS”

01 December 2024
Take the rights path to end AIDS — World AIDS Day report 2024
26 November 2024