Human rights




Press Statement
AIDS is at a crossroads: Take the rights path on Human Rights Day to end AIDS
10 December 2024 10 December 2024GENEVA, 10 December 2024—The world can end AIDS—if the human rights of people living with or affected by HIV are respected, protected and fulfilled, to put communities in the lead and ensure equitable access to high-quality HIV services.
The HIV response has come a long way. The progress made to date on HIV prevention and treatment services has been made possible, in large part, thanks to the advocacy of people living with HIV, communities and civil society allies, demanding treatment, demanding services, demanding dignity, demanding action – demanding their rights.
Over 30 million people are now on treatment, and annual numbers of new HIV infections have declined by 39% since 2010. However we still have a long way to go. In 2023, 1.3 million people around the world newly acquired HIV—three times higher than the global target set for 2025 of no more than 370 000 new acquisitions.
“An approach grounded in human rights is vital to enable meaningful engagement of communities and access to HIV services for all without discrimination” said Christine Stegling, UNAIDS Deputy Executive Director. “HIV services will reach the people most in need only if their human rights are upheld; if communities are in the lead, discriminatory and harmful laws are removed; HIV-related stigma, discrimination and violence are effectively tackled and if access to life-saving medicines is assured.”
Fostering resilient societies where human rights are protected and communities are enabled to lead requires long-term structural and systemic changes. If we are to have a sustainable HIV response, we must have a sustainable, well-resourced, approach to human rights.
On World AIDS Day, 1 December, UNAIDS released a report ‘The Rights Path’ to show what can be done. It shares examples from around the world of proven policies and programmes that are succeeding in protecting health and HIV services by protecting rights.
The HIV response is at a crossroads. We can end AIDS, if we take the rights path. Let us walk it together.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
On Human Rights Day, Indian community members want change and acceptance. Support them and protect them.
Hafsat Abdullahi recites a powerful poem
Documents
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
Suggested citation. UNAIDS DATA 2024. Geneva: Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS; 2024. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. Related: The 2024 global AIDS report The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads, released 22 July 2024, is available here.
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025
Documents
Take the rights path to end AIDS — World AIDS Day report 2024
26 November 2024
The world’s decades-long response to HIV is at an inflection point. Despite successes, the world is currently not on track to end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030. Press release | Download full report | Download short version
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025
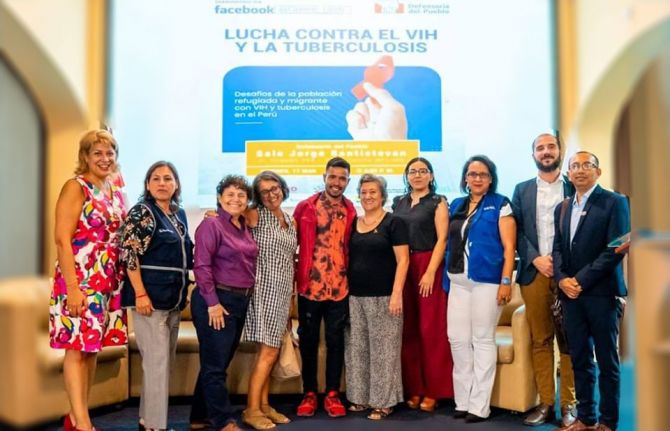




Feature Story
Peru approves groundbreaking law to extend health coverage for migrants with HIV and TB
21 October 2024
21 October 2024 21 October 2024In a milestone decision, the Peruvian Congress has passed legislation that extends temporary health insurance coverage to migrants diagnosed with HIV and tuberculosis (TB). This law allows non-resident foreigners to access healthcare services through the public health insurance system (known by the Spanish acronym SIS) while they complete their immigration processes.
This law, which incorporates proposals from Law Bills 5253, 5554, and 7260, represents a significant step in reducing barriers for migrant populations, ensuring timely medical attention without the need for official residency documentation. Now, migrants affected by HIV or TB can receive vital healthcare services, including medical consultations and diagnostic exams, regardless of their immigration status.
The legislative breakthrough follows over two years of advocacy led by the Grupo Impulsor, a coalition that includes UNAIDS, alongside partners such as USAID’s flagship initiative Local Health System Sustainability Project (LHSS), IOM, UNHCR, the Peruvian Observatory of Migration and Health of the Peruvian University Cayetano Heredia (OPEMS-UPCH), Colectivo GIVAR, VENEACTIVA, the Peruvian TB Social Observatory, and Partners in Health.
Likewise, providing timely treatment for migrants with HIV or TB not only improves their quality of life but also reduces the risk of transmission, making it a crucial public health measure benefiting everyone. It also saves money: early care is far more cost-effective, preventing advanced cases that strain the health system.
A cost-benefit analysis reveals that Peru could save around 5 million soles ($1.33 million USD) annually by preventing new infections and another 54 million soles ($14.58 million USD) through avoiding productivity losses linked to AIDS and TB-related deaths.
Migrants living with HIV in Peru remain among the most discriminated groups in the country, with 70.7% reporting stigma, according to the Ministry of Justice and Human Rights. They also face heightened vulnerability due to xenophobia, violence, and exploitation—nearly half of them have experienced physical violence or sexual exploitation. Accessing healthcare is a major challenge, with only 2% of migrants with HIV covered by public health insurance, leaving the rest to pay out-of-pocket costs that many cannot afford.
“By extending health insurance to migrants, Peru is not only addressing these barriers but also aligning with global commitments, like the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), aimed at eradicating epidemics such as AIDS and TB by 2030”, says Luisa Cabal, UNAIDS Regional Director for Latin America and the Caribbean. “This legislative victory not only marks a turning point in health policy but also sets a precedent for future reforms, ensuring a more inclusive and equitable healthcare system for all.”
Protecting everyone’s rights protects public health.
Region/country
Related


Press Statement
UNAIDS statement on anti-LGBTQ+ legislation in Georgia
01 October 2024 01 October 2024GENEVA, 1 October 2024—UNAIDS expresses deep concern over the recently adopted anti-LGBTQ+ legislation in Georgia, which poses serious risks to public health and human rights.
UNAIDS supports the UN Office for the High Commissioner of Human Rights' statement that these laws will “impose discriminatory restrictions on education, public discussion, and gatherings related to sexual orientation and gender identity.”
These discriminatory laws violate fundamental rights to autonomy, dignity, and equality, exacerbating stigma and hindering LGBTQ+ people's access to essential health services. This undermines Georgia’s efforts to end AIDS and combat other infectious diseases.
UNAIDS reiterates that laws discriminating against LGBTQ+ individuals have no place in modern society. They lead to harassment, discrimination, violence and social exclusion, jeopardizing efforts to end the HIV epidemic. We call on Georgian authorities to repeal these harmful laws, as they will further isolate marginalized communities and worsen public health outcomes.
Stigma kills, but solidarity saves lives. Upholding the rights of LGBTQ+ people is crucial to advancing public health, social cohesion, and equality for all.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.




Feature Story
Women living with HIV continue to face violations of their sexual and reproductive rights—including coercion into sterilization
24 July 2024
24 July 2024 24 July 2024Women living with HIV including women from key populations continue to suffer widespread reproductive coercion, mistreatment, and neglect when seeking reproductive health services and rights around the world, a new report by the International Community of Women Living with HIV (ICW) has revealed today. The report was launched at a joint ICW/UNAIDS event at the 25th International AIDS Conference taking place in Munich, Germany.
The report, Confronting Coercion: A global scan of coercion, mistreatment and abuse experienced by women living with HIV in reproductive and sexual health services, shows that women living with HIV face practices that undermine their bodily autonomy. Reproductive choices are monitored, and women are subjected to various coercive practices.
The report documents experiences of sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) violations and violence faced by women living with HIV and women from key populations from more than 60 countries across 3 regions and offers concrete actions for the reduction of coercive practices.
“This report offers a chilling reality of what women living with HIV experience every day in their struggle to realize their full sexual and reproductive health rights,” said Charity T. Mkona, Global Coercion Scan Committee, ICW ISC Global Chairperson. "For women living with HIV who have been subjected to coercive practices, mistreatment or abuse, the ability to heal and realize their full sexual and reproductive health and rights, demands accountability and justice."
The report reveals that reproductive coercion and mistreatment of women and gender diverse people living with HIV in SRHR services are a common, persistent, and widespread issues that require urgent action. Women living with HIV who reported engagement in sex work, drug use, or had disabilities reported experiencing coercive practices at higher rates than other women living with HIV.
Younger women living with HIV and women living with HIV who were migrants were also more likely to have experienced coercive practices than older women and women who were not migrants. Women have reported experiencing a lack of confidentiality and consensual care, as well as inappropriate medical interventions, such as unnecessary caesarean sections and forced or coerced abortions. Denial of care, stigmatizing comments or insults, and various forms of abuse - verbal, emotional, physical and sexual - were also documented.
While information about sexual and reproductive health and rights of women may be supplied to them, it is not always accurate, comprehensive, or up-to-date to empower them to claim their rights and often does not reflect the realities of women's lives.
"To end coercive practices experienced by women living with HIV, we must recognize the systemic and entrenched nature of these violations and understands that reform requires a systemic sea change and culture shift that respects women's bodily autonomy.” Sophie Brion, Director of Global Programmes at ICW.
“In a world where significant scientific advancements have been made in the treatment of HIV—including breakthroughs that allow women living with HIV whose viral load is undetectable to give birth to HIV negative babies—it’s shocking that some health care workers are not informed that women living with HIV can give birth without transmitting the virus,” said Christine Stegling, UNAIDS Deputy Executive Director for Policy, Advocacy and Knowledge. “This lack of education and coercive practices, including the forced sterilization of women living with HIV, must stop immediately.”
ICW is calling on governments worldwide, including donors and ministries of health, to eliminate these harmful practices. The organization is also calling on governments to ensure that health systems support women living with HIV to realize their full right to health, including sexual and reproductive health and rights, bodily autonomy and rights to informed consent.
"This report issues a powerful call to action to put the autonomy, desires and needs of women living with HIV at the centre of their sexual and reproductive health care programmes." said Immaculate Owomugisha Bazare, Global Coercion Scan Committee, ICW Global Steering Committee Member.
Background
The Confronting Coercion report was developed through a blend of qualitative and quantitative research, incorporating insights from a gendered analysis of recent Stigma Index 2.0 data, a desk review of literature, and a qualitative study involving women, trans and gender non-binary people living with HIV who shared experiences of reproductive coercion over the past 3 years. The qualitative part of the study looked at coercion, mistreatment and neglect related to the SRHR of women and gender diverse people living with HIV in HIV, SRH and maternity care settings.
UNAIDS has supported the development of the report to address systematic gender inequalities, in particular gender-based discrimination and violence against women living with HIV, which fuels the HIV epidemic.
Related
Documents
Western and Central Europe and North America regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
There has been a 24% drop in the annual number of new HIV infections in western and central Europe and North America since 2010, and the number of AIDS-related deaths has declined by 34%. Numbers of new HIV infections among sex workers and their clients, however, have not declined at the same rate. Despite data showing ongoing progress in HIV prevention, persistent social and economic factors, including stigma and discrimination, continue to cause health disparities, compromising the health and well-being of people from marginalized communities. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 UNAIDS urges that all essential HIV services must continue while U.S. pauses its funding for foreign aid
UNAIDS urges that all essential HIV services must continue while U.S. pauses its funding for foreign aid

01 February 2025
Documents
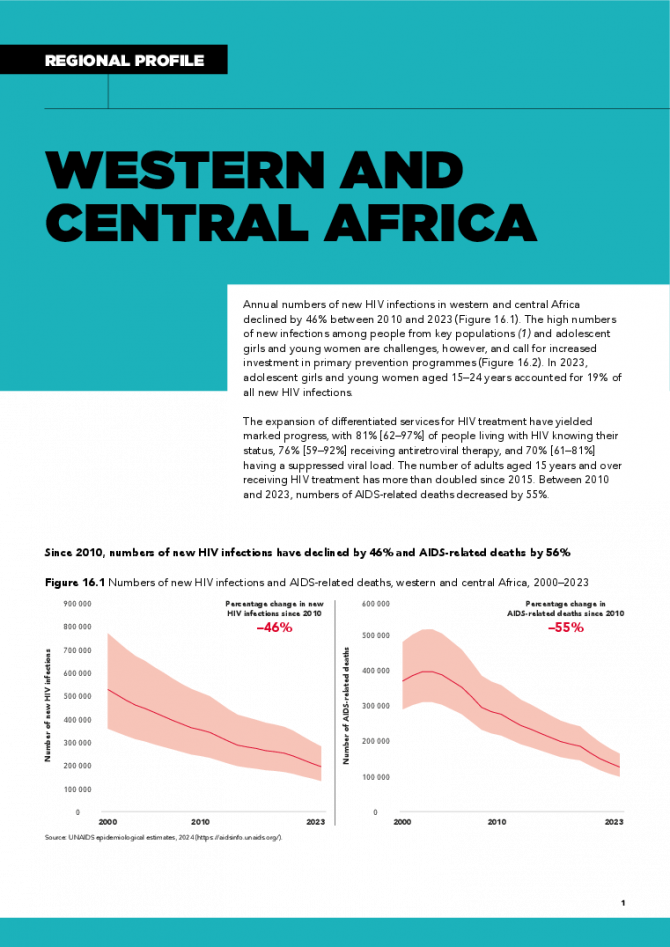
Western and Central Africa regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
Annual numbers of new HIV infections in western and central Africa declined by 46% between 2010 and 2023. The high numbers of new infections among people from key populations and adolescent girls and young women are challenges, however, and call for increased investment in primary prevention programmes. In 2023, adolescent girls and young women aged 15–24 years accounted for 19% of all new HIV infections. The expansion of differentiated services for HIV treatment have yielded marked progress, with 81% [62–97%] of people living with HIV knowing their status, 76% [59–92%] receiving antiretroviral therapy, and 70% [61–81%] having a suppressed viral load. The number of adults aged 15 years and over receiving HIV treatment has more than doubled since 2015. Between 2010 and 2023, numbers of AIDS-related deaths decreased by 55%. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
 Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment
Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment

21 January 2025
Documents
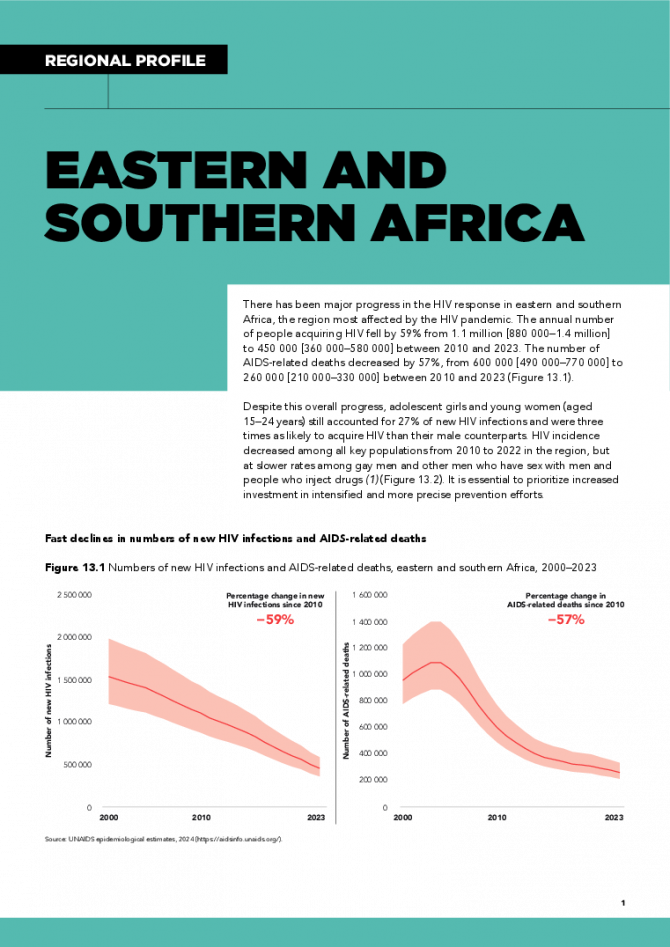
Eastern and Southern Africa regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
There has been major progress in the HIV response in eastern and southern Africa, the region most affected by the HIV pandemic. The annual number of people acquiring HIV fell by 59% from 1.1 million [880 000–1.4 million] to 450 000 [360 000–580 000] between 2010 and 2023. The number of AIDS-related deaths decreased by 57%, from 600 000 [490 000–770 000] to 260 000 [210 000–330 000] between 2010 and 2023. Despite this overall progress, adolescent girls and young women (aged 15–24 years) still accounted for 27% of new HIV infections and were three times as likely to acquire HIV than their male counterparts. HIV incidence decreased among all key populations from 2010 to 2022 in the region, but at slower rates among gay men and other men who have sex with men and people who inject drugs. It is essential to prioritize increased investment in intensified and more precise prevention efforts. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 Zambia - an HIV response at a crossroads
Zambia - an HIV response at a crossroads

24 February 2025
 Status of HIV Programmes in Botswana
Status of HIV Programmes in Botswana

20 February 2025
 Government ensures continuity of treatment in Malawi
Government ensures continuity of treatment in Malawi

10 February 2025
Documents
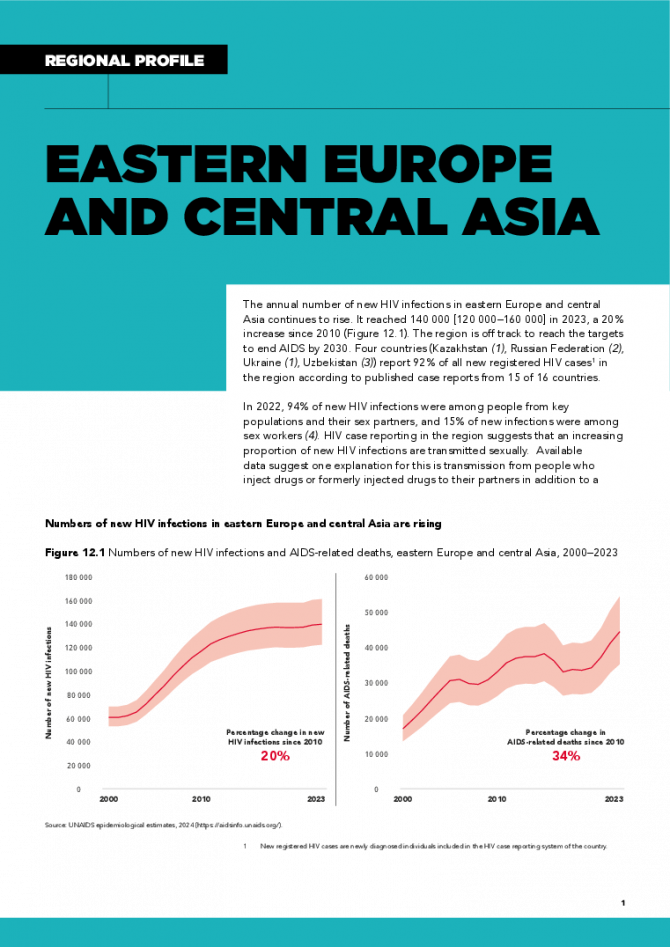
Eastern Europe and Central Asia regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
The annual number of new HIV infections in eastern Europe and central Asia continues to rise. It reached 140 000 [120 000–160 000] in 2023, a 20% increase since 2010 . The region is off track to reach the targets to end AIDS by 2030. Four countries (Kazakhstan, Russian Federation, Ukraine, Uzbekistan) report 92% of all new registered HIV cases in the region according to published case reports from 15 of 16 countries. In 2022, 94% of new HIV infections were among people from key populations and their sex partners, and 15% of new infections were among sex workers. HIV case reporting in the region suggests that an increasing proportion of new HIV infections are transmitted sexually. Available data suggest one explanation for this is transmission from people who inject drugs or formerly injected drugs to their partners in addition to a growing recognition of transmission among men who have sex with men. Unsafe drug injecting practices are a key factor in the region’s epidemic, representing 27% of new HIV infections. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery
Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery

20 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025