UNWomen The United Nations Entity for Gender Equality and the Empowerment of Women


Feature Story
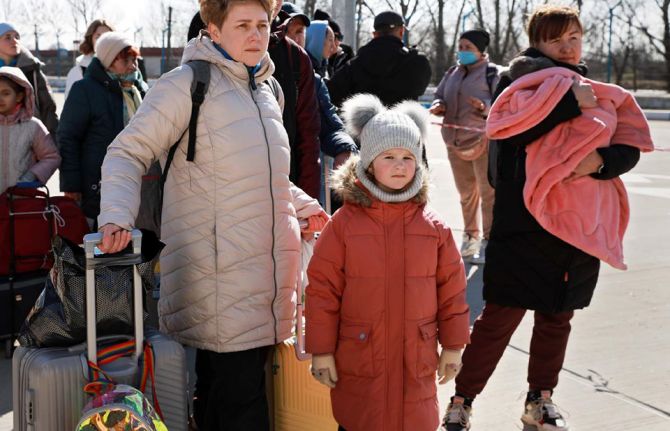
Report highlights that women and marginalized people need urgent access to health-care services in Ukraine
11 May 2022
11 May 2022 11 May 2022A new report by UN Women and CARE International highlights the urgent need to provide health-care services to women in Ukraine and sets out why the international community needs to support a gendered response to Ukraine’s humanitarian crisis.
The report also emphasizes the need for an intersectional approach to the crisis that addresses the exacerbated risks for marginalized communities—lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex (LGBTI) people, Roma people, people living with disabilities and people living with chronic diseases—who face immense hardship and have particular needs with regard to their health and safety.
“This powerful report illustrates why and how humanitarian responses need always to be gendered and need also to address the particular needs of marginalized communities,” said Winnie Byanyima, the Executive Director of UNAIDS. “The courage and commitment of women leaders who continue to serve their communities, even in the face of war, in Ukraine and across the world is an inspiration.”
The report’s analysis, which was based on surveys and interviews with people in Ukraine, was conducted in April and details some of the gender dynamics of the crisis and sets out practical and actionable recommendations for the international humanitarian response.
Women and girls interviewed for the report highlighted challenges in access to health-care services, especially for survivors of gender-based violence and pregnant women and new mothers, as well as rising fears of gender-based violence and lack of food, especially for those in conflict areas.
Many respondents referred to the health risks, including the spread of COVID-19, linked to unsanitary shelters.
The war has also impacted access to sexual and reproductive health, including family planning and maternal, newborn and child health. Many media reports have noted that conditions as a result of the war have increased the risk of premature birth.
Transgender people also require regular access to medicines, but many have had to stop hormone therapy due to supply shortages. Several LGBTI organizations are providing access to medicines to members of the transgender community, but their help does not cover all the needs.
“The Rapid Gender Analysis allows us to consult directly with affected populations in order to accurately identify what specific needs different groups of people have, and how to best meet them,” said Sofia Sprechmann Sineiro, the Secretary General of CARE International. “What we are hearing from the people of Ukraine is that certain groups—such as those with disabilities, Roma and other ethnic minorities, single mothers and unaccompanied children—are each in need of different forms of protection and assistance. To keep our response effective and relevant, such groups must be consulted and prioritized across the aid ecosystem as this truly devastating situation continues to evolve.”
The report calls for support for women-led and women’s rights organizations that provide financial resources and for their voices to be amplified at national and international platforms.
Gaps in services to respond to gender-based violence need to be filled, according to the report, while sexual and reproductive health, including the clinical care of survivors of sexual assault, and maternal, newborn and child health care, including access to contraception, should be made a priority.
“It’s critical that the humanitarian response in Ukraine takes into account and addresses the different needs of women and girls, men and boys, including those that are furthest left behind,” said Sima Bahous, the Executive Director of UN Women. “This timely analysis provides the evidence of those needs, and their urgency. Women have been playing vital roles in their communities’ humanitarian response. They must also be meaningfully involved in the planning and decision-making processes to make sure that their specific needs are met, especially those related to health, safety and access to livelihoods.”
Region/country
Related
 Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery
Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery

20 February 2025


Press Statement
UNAIDS Executive Director's message on International Women’s Day 2021
08 March 2021 08 March 20218 March 2021
Winnie Byanyima
Executive Director of UNAIDS
Under-Secretary-General of the United Nations
Women leaders have provided a guiding light for the world in responding to the COVID-19 crisis, from heads of government to coordinators of grass-roots social movements. They have reminded the world how crucial it is to have critical numbers of women, in all their diversity, in positions of leadership.
But the COVID-19 crisis has seen progress towards equality pushed back. It has widened the gap between women and men in wealth, in income, in access to services, in the burden of unpaid care, in status and in power.
Up to 20 million more secondary school-aged girls could end up out of school following the crisis. Many may never go back to school or have access to skills and economic opportunities, and will be at greater risk of violence, poor health, poverty and more.
Two and a half million more girls are now at risk of child marriage in the next five years. There has been a dramatic increase in violence against women.
Pandemics such as COVID-19 and HIV magnify the fissures in society and exacerbate vulnerabilities. Gender-based and intersecting inequalities and violence hold back the lives of women and girls all over the world.
The pandemic has brought into sharp and painful focus that even before COVID-19 an estimated 34 million girls between the ages of 12 and 14 years were out of school, one in three women globally reported having experienced physical or sexual violence and women the world over worked longer hours for less or no pay.
Women who were already stigmatized are among those who are being hardest hit by the impacts of the pandemic. The sudden loss of the livelihoods of sex workers and their lack of access to health care and social protection have intensified their vulnerabilities, especially for those living with HIV. Many female migrants and precarious workers adversely affected by the pandemic are excluded from government relief and protection programmes, as well as health services. Stigma, discrimination and criminalization put transgender women, and women who use drugs, at heightened risk of HIV and other sexually transmitted infections, and hold them back from accessing HIV prevention, treatment and care services.
Recovery strategies cannot be gender-blind or gender-neutral: they must overturn the inequalities that hold women back.
Together, UNAIDS, UN Women, the United Nations Children’s Fund, the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization and the United Nations Population Fund have convened a broad movement, Education Plus, to work with governments to secure the transformative changes that will enable all of Africa’s adolescent girls to be in school, safe and strong. That includes all the girls who have been pushed out of school during the COVID-19 crisis and those who were excluded from school even before the crisis hit.
Overcoming the COVID-19 crisis, and ending new HIV infections and AIDS-related deaths, both require that we close in on the inequalities that drive vulnerabilities. The new global AIDS strategy 2021–2026 puts the rights and multiple and diverse needs of women and girls across their life cycle at the centre of the response: from preventing vertical transmission to providing access to quality education in safe and supportive environments to ensuring comprehensive sexuality education and holistic sexual and reproductive health services.
Gender inequality is not only wrong. It is dangerous. It weakens us all. A more equal world will be better able to respond to pandemics and other shocks; it will leave us healthier and safer and more prosperous.
Progress on gender equality has never been automatic. It has never been given, it has always been won.
We are inspired by the women’s movements leading the struggle for equality. The United Nations stands alongside you to advance a world where women and girls in all their diversity will thrive and take their rightful places as equals.
This International Women’s Day let’s support and celebrate women taking the lead.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Press centre
Download the printable version (PDF)



Feature Story
Navigating Lesotho’s legal system to address gender-based violence
08 March 2021
08 March 2021 08 March 2021When Lineo Tsikoane gave birth to her daughter, she was inspired to intensify her advocacy for gender equality to give Nairasha a better life as a girl growing up in Lesotho.
“I think a big light went off in my head to say, “What if the world that I’m going to leave will not be as pure as I imagine?” I ask myself, “What kind of world do I want to leave my daughter in?”” she says.
As a result, Ms Tsikoane champions for women’s social, economic and legal empowerment at her firm, Nairasha Legal Support. It offers legal support for women in small and medium enterprises and women who are survivors of sexual and gender-based violence.
“Our main focus is gender-based violence, because this happens to be a country that has one of the highest incidences of rape and intimate partner crime in the world,” she says.
Even before the COVID-19 outbreak, violence against women and girls had reached epidemic proportions globally.
According to UN Women, 243 million women and girls worldwide were abused by an intimate partner in the past year. In Lesotho, it is one in three women and girls.
Less than 40% of women who experience violence report it or seek help.
As countries implemented lockdown measures to stop the spread of the coronavirus, violence against women, especially domestic violence, intensified—in some countries, calls to helplines increased fivefold.
In others, formal reports of domestic violence have decreased as survivors find it harder to seek help and access support through the regular channels. School closures and economic strains left women and girls poorer, out of school and out of jobs, and more vulnerable to exploitation, abuse, forced marriage and harassment.
The United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) works together with UNAIDS, the United Nations Children’s Fund and the World Health Organization on 2gether4SRHR, a joint programme funded by the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency, to address HIV and sexual and reproductive health in Lesotho.
During Lesotho’s lockdowns, UNFPA worked with Gender Links, the Lesotho Mobile Police Service and others to support efforts to prevent and respond to incidences of gender-based violence.
“We are ensuring that a helpline, where people experiencing gender-based violence can call, is in place and is working and we are also providing relevant information through various platforms for people to access all the information they need on gender-based violence,” says Manthabeleng Mabetha, the UNFPA Country Director for Lesotho.
Mantau Kolisang, a local policeman from Quthing, Lesotho’s southernmost district, characterized by rolling hills and vast landscapes, says one reason why gender-based violence is prevalent in Lesotho is because the law is not heeded in the rural areas.
“It’s difficult to implement the law since these are remote areas,” he says, adding that while he has made arrests, he has no transport to access far-flung areas in the small mountainous region.
Lesotho’s law states that a girl can marry at the age of 16 years. However, Mr Kolisang says cultural practices, coupled with contraventions of the law, has made some men believe a 13-year-old girl “can be a wife”, exposing Basotho girls to violence.
“Men don’t regard it as a crime,” he says, adding that girls have been abducted from the mountains for forced marriages.
Between 2013 and 2019, 35% of adolescent girls and young women in sub-Saharan Africa were married before the age of 18 years. Girls married before 18 years of age are more likely to experience intimate partner violence than those married after the age of 18.
Because of poverty, gender inequality, harmful practices (such as child, early or forced marriage), poor infrastructure and gender-based violence, girls are denied access to education, one of the strongest predictors of good health and well-being in women and their children.
In Lesotho’s legal system, women are regarded as perpetual minors. This categorization infantilizes women, Ms Tsikoane says. A man who abuses a woman can often walk away unscathed from the justice system if he says the woman in question is his “wife”, she adds.
“This makes women vulnerable to commodification because a child can be passed around,” she says.
Ms Tsikoane says there is a direct link between the minority status of women and HIV infection in Lesotho. In 2019, there were 190 000 women 15 years and older living with HIV in Lesotho, compared to 130 000 men.
Adolescent girls and young women between the ages of 15 and 24 years are particularly vulnerable. They accounted for a quarter of the 11 000 new HIV infections in Lesotho in 2019.
“My hypothesis is women cannot negotiate safe sex,” says Ms Tsikoane.
The dangerous reality that Basotho women live in worries Mr Kolisang. But due to a lack of institutional support and resources, he feels his actions have limited effect.
“I feel for these children. I feel for these women. I do feel for them. I can help, but the problem is how?” he laments.
Ms Tsikoane says she finds “trinkets of opportunities” for her and her colleagues to help their clients and navigate a legal system that is not favourable towards women.
“So, if you are not being well assisted at a police station, if you feel like someone is dragging your case and you are struggling to get an audience, we are there. We will support you and we will fight with you,” she says.
Our work
Region/country
Related
 Zambia - an HIV response at a crossroads
Zambia - an HIV response at a crossroads

24 February 2025
 Status of HIV Programmes in Botswana
Status of HIV Programmes in Botswana

20 February 2025

Feature Story
In South Africa, young women leading HIV and violence prevention say men’s involvement is key
01 December 2020
01 December 2020 01 December 2020This story was first published by UN Women
On World AIDS Day, UN Women spoke to survivors and community changemakers in South Africa who as part of UN Women’s HeForShe community-based initiative and a joint UNAIDS programme are engaging men and women to reject violence against women and seek HIV testing and treatment.
Until two years ago, Karabo Chabalala (28) and Sarah Baloyi (26), young women from Mamelodi — a township northeast of Pretoria in Gauteng, South Africa — were living very different lives.
“I was in a very dark place. I had multiple sexual partners and was part of a lifestyle that was not good or healthy for me,” says Baloyi. Her friend, Chabalala says, “I had many personal problems. I engaged in a transactional relationship with an abusive older man to fund my education and provide for my family.”
Their lives turned around following their involvement in UN Women’s HeforShe community-based initiative that aimed at improving attitudes and behaviours around gender-based violence (GBV) and HIV.
“Karabo introduced me to HeForShe, a community that cares for one another,” says Baloyi. “The dialogues showed me that I am not alone in my mistakes and could change my life. I have been inspired to promote safe and healthy living for young girls and to provide them with the same loving acceptance that was extended to me.”
Chabalala adds, “Many young women don’t open up at home about problems they are facing. These dialogues give us a space to express our thoughts and feelings and to ask any questions that we have about life.”
Led by UN Women’s partner, Southern Africa Catholic Bishops Conference (SACBC), and funded through the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS), the HeforShe dialogues have since 2018 engaged 115,000 men and women across seven districts (Mamelodi, Klerksdorp, Bojanela, Sedibeng, city of Johannesburg, Ehlanzeni and CapeTown) in South Africa’s five provinces.
“The dialogues are coordinated by 151 trained women and men ‘changemakers’, including young women like Baloyi and Chabalala, equipped with knowledge on HIV and violence prevention, unequal gender norms, the importance of HIV testing and adhering to treatment, responsible sexual behavior, and how socio-economic factors can drive HIV infections among men and women,” explains UN Women's South Africa Multi-Country Office Representative, Anne Githuku-Shongwe.
“Many women in Mamelodi have been victims of abuse or witnessed femicide in their homes, often at the hands of men who [are alcoholic].” says Baloyi.
“All I feel is anger,” says Chabalala. “These men don’t respect us. Women in our community are being raped and killed. Some men who perpetrate these crimes are out on bail the following day.”
“There has been a rise in GBV since the COVID-19 lockdown,” says Baloyi. “Abusive partners have been stuck at home and they are frustrated. They are no longer able to spend their time working or drinking with friends, and take it out on their partners and children. This is especially the case in informal settlements, where families live in one- or two-room shacks.”
South Africa is home to almost one-fifth of people living with HIV worldwide and has an HIV prevalence rate of 20.4 per cent among adults (15-19 years). In line with trends across Sub-Saharan Africa, in 2019, women accounted for the majority of new infections in the country. Structural gender inequalities, discrimination, violence against women and girls, and unequal gender norms continue to undermine efforts by women and girls to prevent HIV and use HIV/AIDS services.
“The stigma around HIV prevents people from seeking treatment. I have met some older patients who still fear going to the clinics because they feel judged or embarrassed,” says Chabalala.
To increase the uptake of HIV testing, the changemakers partnered with 20 local HIV counselling and testing clinics across participating districts. They also facilitated outreach for HIV testing at community and church events and developed a referral system. In two years, the HeforShe initiatives have resulted in 62 per cent of those engaged testing for HIV, and 36 per cent returning and adhering to their antiretroviral treatment. However, because of the COVID-19 pandemic, people living with HIV and people at higher risk of HIV infection are facing life-threatening disruptions to health services.
Inspired by the positive impact of UN Women initiatives in communities and empowered by the change makers, Mamelodi community members founded the national ‘Young Women for Life Movement (YWfLM)’, which has grown to 2,035 members. With support from the SACBC, the group is currently monitoring the proceeding of 30 cases of sexual and gender-based violence and 17 cases of femicide in the justice system, as well as supporting the families of survivors. They also played a crucial role in organizing food supply drives to the most vulnerable households in their communities during the COVID-19 lockdown.
“I started the Mamelodi chapter of the Young Women for Life Movement,” says Chabalala. “Being part of this community of 200 powerful young women has taught me so many things and helped me grow. It has changed my life”.
“As a YWfLM member, I work with our local clinic and visit people living with HIV in our community to confirm that they are taking their medication and to ask if they need any assistance or additional supplements,” says Baloyi. “We also have an HIV-positive support group that now mainly connects online due to the pandemic.”
Both Baloyi and Chabalala believe that men need to be more involved in initiatives to improve attitudes and behaviours to prevent GBV and HIV. “Young men need to not only be part of this conversation, they must have their own dialogues where they focus on how to change their mindset,” says Chabalala.
Baloyi adds, “Many more men need to join women in our fight. Men must join us in court and in the streets. They must fight with us.”
Related
 Comprehensive update on HIV programmes in South Africa
Comprehensive update on HIV programmes in South Africa

25 February 2025


Press Statement
UNAIDS calls for the elimination of the neglected pandemic of violence against women and girls
25 November 2020 25 November 2020GENEVA, 25 November 2020—Today, on the International Day for the Elimination of Violence against Women, UNAIDS is calling for the world to urgently scale up efforts to eliminate the neglected pandemic of violence against women and girls in all their diversity, a widespread human rights violation that affects one in three women at least once in their life.
Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, it was estimated that globally 243 million women and girls aged 15–49 years had been subjected to sexual and/or physical violence perpetrated by an intimate partner in the past 12 months. Evidence shows that the COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in significant increases in gender-based violence in nearly all countries.
“The growing evidence confirms that the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic are not gender-neutral,” said Winnie Byanyima, UNAIDS Executive Director. “The impacts of lockdowns and travel restrictions imposed in many countries to curb the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic, the failure to designate sexual and reproductive health services and services for survivors of violence as essential services, and the undermining of women’s economic security have compounded the barriers for women and girls experiencing abuse, especially those who are trapped at home with their abusers.”
Adolescent girls and young women are also increasingly being subjected to early marriage and trafficking, missing out on education because of school closures and lacking access to comprehensive sexuality education and sexual and reproductive health services, including contraception and abortion, as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
COVID-19 is increasing violence against women and amplifying existing gender inequalities, further exacerbating HIV risks and vulnerabilities for women, at the same time that access to gender-based violence services, as well as HIV and other sexual and reproductive health services, are being reduced or are unavailable during the pandemic. Violence against women is a major factor driving risks for HIV—in areas with a high HIV burden, such as sub-Saharan Africa, women subjected to intimate partner violence are 50% more likely to be living with HIV. And men who are perpetrators of violence against women tend to be at higher risk of HIV themselves and to use condoms less frequently, thus increasing the risk of HIV transmission.
Violence, or the potential for it, discourages many women and adolescent girls living with HIV from disclosing their HIV status to their partners, families and health-care providers, making it more difficult for women and girls to stay on HIV treatment.
Gender-based violence restricts women’s and girls’ decision-making and erodes their sexual and reproductive health and rights, including deciding if, how, when and with whom they have sex, their ability to protect their health and their ability to access HIV prevention services and stay on treatment.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has reflected once again just how unacceptable it is to continue with half measures and unmet commitments to ending violence against women,” added Ms Byanyima. “If we are serious about achieving gender equality, and ending AIDS, preventing gender-based violence must finally become a global, national and local priority.”
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton-Knott
tel. +41 79 514 68 96
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS Media
tel. +41 22 791 4237
communications@unaids.org




Press Release
UNAIDS calls for urgent action to strengthen social protection programmes in the face of COVID-19
26 August 2020 26 August 2020GENEVA, 26 August 2020—UNAIDS is calling on countries to adopt urgent measures to reinforce social protection programmes to shield the most vulnerable people from the health impact and socio-economic fall-out of the COVID-19 pandemic.
People living with HIV and tuberculosis (TB) are being significantly impacted by COVID-19. Modelling has estimated the potential catastrophic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic with increases of up to 10%, 20% and 36% projected deaths for HIV, TB and malaria patients, respectively, over the next five years.
Among the most vulnerable are women and girls, gay men and other men who have sex with men, sex workers, people who use drugs and transgender people. Many of them are excluded from existing social protection programmes.
“Countries must ensure that everyone is able to receive essential services including health care and they must invest adequately in social protection programmes to keep people safe and to shield them from the consequences of losing their livelihoods,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS.
The socio-economic fall-out of the COVID-19 pandemic will have the greatest impact on some of the most disadvantaged people in societies around the world. For example, COVID-19 threatens to double the number of people facing acute food insecurity to more than 265 million by the end of the year. Most of these people will be in countries already badly afflicted by conflict, economic or climate crises. Refugees are among the groups facing the greatest dangers.
Hundreds of millions of people around the world are also in line to lose their jobs in the formal and informal sectors of the economy. Around 150 million full time jobs were lost in the first quarter of the year and millions more people are set to lose their livelihoods in the months ahead.
“Today, only 29% of the world’s population has access to adequate social protection coverage,” said Guy Ryder, Director General of the International Labour Organization.” Governments must act to ensure the sustainability of livelihoods, businesses and jobs and the protection of workers’ health, rights and incomes during and after COVID-19.”
Women are particularly vulnerable to the economic crisis being disproportionately employed in the informal sectors of the economy and therefore most likely to lose their incomes. They are also often employed on the frontline of the response to COVID-19, making up 70% of the workforce in the health and social care sectors, as well as carrying out the bulk of unpaid domestic duties in the home, childcare and other caring functions.
An increase in gender-based violence during lockdown also makes it imperative for governments to invest in social protection programmes designed specifically for the protection of women and girls.
A generation of young people are also at risk from the socio-economic crash caused by the pandemic. The vulnerability of children and young people is being further amplified by school closures which have affected more than 90% of the world’s student population, interrupting their education and their access to crucial social services, such as school meals.
“Children and young people are suffering disproportionately from the socio-economic impact of the COVID-19 crisis,” said Henrietta H. Fore, Executive Director of UNICEF. “Before the outbreak, two out of three children had no or inadequate social protection fund. Countries need to live up to their commitment for social protection for everyone who needs it.”
The call for action for governments to invest adequately in social protection programmes is endorsed by UNAIDS, the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) and the International Labour Organization (ILO) and supported by the World Food Programme (WFP), the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), the United Nations Entity for Gender Equality and the Empowerment of Women (UN Women), the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) and the World Bank.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Documents
UNAIDS calls on governments to strengthen HIV-sensitive social protection responses to the COVID-19 pandemic
26 August 2020
UNAIDS calls on governments to live up to their commitment to develop nationally owned and led social protection systems for all, including floors; and scale up and progressively enhance coverage, adequacy and comprehensiveness, thereby improving the responsiveness and quality of interventions to address the needs and vulnerabilities of people living with HIV.
Related
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
A shot at ending AIDS — How new long-acting medicines could revolutionize the HIV response
21 January 2025
Indicators and questions for monitoring progress on the 2021 Political Declaration on HIV and AIDS — Global AIDS Monitoring 2025
17 December 2024
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
 Resilience amid crisis: strengthening the HIV response for displaced communities in Ethiopia
Resilience amid crisis: strengthening the HIV response for displaced communities in Ethiopia

02 December 2024
Take the rights path to end AIDS — World AIDS Day report 2024
26 November 2024
 Women living with HIV in China unite to confront discrimination
Women living with HIV in China unite to confront discrimination
14 October 2024
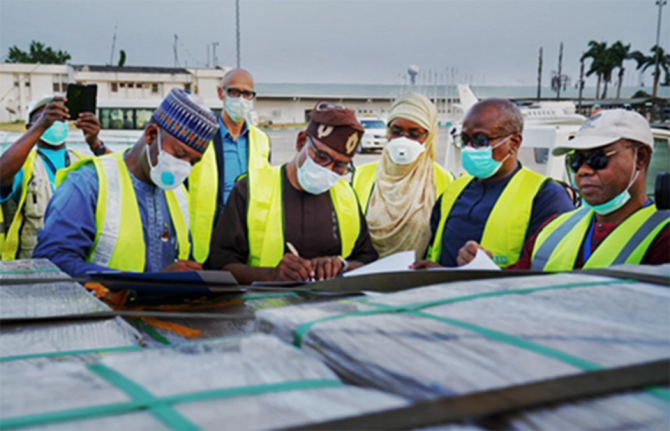


Feature Story
UNAIDS and the wider United Nations system supporting the COVID-19 response in Nigeria
10 July 2020
10 July 2020 10 July 2020The United Nations system in Nigeria joined the fight against COVID-19 shortly after the first case was detected in the country in late February 2020.
UNAIDS’ lessons learned and expertise in facilitating, linking and bringing stakeholders together have been instrumental in guiding the United Nations multi-agency response, led by the Resident Coordinator, Edward Kallon. And by proactively mobilizing its political capital and goodwill in the country, UNAIDS has helped to bring resources and better lines of communication, coordination and accountability to the national COVID-19 response.
In mid-March, the Presidential Task Force was established to develop a COVID-19 response plan for how organizations should work together. Appointed as the only development member of the task force, the Representative, a.i., of the World Health Organization (WHO), Fiona Braka, provides the overall United Nations technical leadership to the government. Lessons learned from the HIV response fed into the development of the “four ones” guiding principles for the national response to the COVID-19 pandemic—one national COVID-19 multisectoral pandemic response plan, one COVID-19 national coordinating authority, one COVID-19 monitoring and evaluation system and one COVID-19 financing and investment platform.
“The “four ones” principles will simplify and clarify roles, responsibilities and relationships, including within the government,” said the Minister of Health of Nigeria, Osagie Ehanire.
Another lesson learned from the HIV response was the importance of ensuring that marginalized and vulnerable people are given consideration at every step of the development of a response to a pandemic. The potential impact of COVID-19 on people living with HIV, key populations and the poor also had to be at the centre of decision-making.
“UNAIDS regularly coordinated with the networks since the beginning of the COVID-19 outbreak, providing technical guidance and ensuring synergy with the efforts of the government,” said Abdulkadir Ibrahim, the National Coordinator of the Network of People Living with HIV/AIDS in Nigeria.
Working with the United Nations Development Programme, UNAIDS liaised with the wider United Nations system and the government and facilitated the handover of US$ 2 million worth of emergency medical commodities to the government, ensuring that the supplies and equipment were prioritized for use in public health facilities and by health-care workers.
The One UN COVID-19 Basket Fund was launched on 6 April. Part of one of the “four ones”, the one COVID-19 financing and investment platform, the Basket Fund channels the contributions of donors to the COVID-19 response. UNAIDS played a critical role in its establishment, working with the United Nations Resident Coordinator and the United Nations Development Programme to ensure that the financing platform put people and communities at the centre. UNAIDS, UN Women, WHO and the United Nations Population Fund helped to mobilize US$ 6.5 million for civil society and community engagement, social protection for vulnerable households, community-led surveillance and monitoring of COVID-19 and HIV and the documentation of community best practices.
In announcing a €50 million contribution to the Basket Fund, the Head of the European Union delegation to Nigeria, Ketil Karlsen, said, “The COVID-19 Basket Fund gives us the opportunity to cooperate and act rapidly in the deployment of assistance that can help to enhance health-care services and cushion the most vulnerable.”
Perhaps the most important contribution by UNAIDS to the COVID-19 response in the country, however, has been advocating to harness the vast HIV infrastructure in the country for the fight against COVID-19.
“We must leverage HIV assets on the ground, including not just laboratory facilities but community health workers and volunteers. To fight COVID-19 effectively we will have no choice but to engage communities to own the response,” said Erasmus Morah, the UNAIDS Country Director for Nigeria.
In a joint effort, the United States Government, the National Agency for the Control of AIDS, the United Nations Children’s Fund, WHO, UNAIDS and the Presidential Task Force mapped and initiated the engagement of approximately 100 000 community health-care workers and volunteers to undertake risk communication, social mobilization, contact tracing and home care.
COVID-19 is far from over in the country, with cases steadily rising, and United Nations staff have not been spared. However, as Mr Kallon, said, “The United Nations must stay open for business and deliver for the people while ensuring that staff members and their dependents are provided with the necessary environment for their protection against COVID-19.” Following this, a COVID-19 isolation and treatment centre as an extension of the United Nations clinic was established for staff as frontline workers, together with their dependent family members.
Moving forwards with the COVID-19 response, in addition to the continued support for the Presidential Task Force, the United Nations Country Team, including UNAIDS, is gearing up to support Nigeria to address the major gaps in subnational preparedness. Key issues such as the loss of livelihoods, heightened vulnerabilities and food insecurity, the increased risk of gender-based violence and limited access to essential health services will also be addressed in the coming months.
Our work
Region/country
Related
 Impact of the pause of US foreign assistance in Côte d'Ivoire
Impact of the pause of US foreign assistance in Côte d'Ivoire

19 February 2025




Feature Story
Gender-based violence and COVID-19—“When we are silent, we allow these crimes to multiply”
19 May 2020
19 May 2020 19 May 2020UN Women estimates that globally in the past 12 months 243 million women and girls aged 15–49 years were subjected to sexual and/or physical violence perpetrated by an intimate partner. As a result of the lockdowns imposed to stop the spread of COVID-19, emerging data show that such violence has intensified. In France, for example, reports of domestic violence have increased by 30% since the lockdown started on 17 March, and in Argentina emergency calls about domestic violence have increased by 25% since its lockdown started on 20 March. Many other countries have reported such increases.
Recently, the Odnoklassniki social network, known as OK, hosted a broadcast for experts and others to discuss how to survive lockdown and avoid family conflict and gender-based violence. The broadcast was seen by 1.7 million OK network users across eastern Europe and central Asia.
“I live in Kyrgyzstan,” Ulzisuren Jamstran, a representative of UN Women in Kyrgyzstan, said. “Here, according to the government, the level of domestic violence increased by 65%. We see an increase in aggression against women and children in Kyrgyzstan, we see an increase in suicides among children, even young children.”
Lyudmila Petranovskaya, a Russian psychologist, explained how isolation made good relationships become better and problematic relationships become more problematic. She emphasized that people need to be aware of the options if they are locked down with an abuser. “People have to look for contacts, a hotline, call friends, try to find another place to survive isolation. Staying with the abuser is dangerous. This threat is more serious than coronavirus,” she said.
Julia Godunova, Deputy Head of the Board of the Eurasian Women’s Network on AIDS, spoke about studies in eastern Europe and central Asia that show that more than 70% of women who survived violence do not seek help because of the perceived shame.
Dina Smailova, the founder of the #DontBeSilentKZ nongovernmental organization, addressed female survivors of violence. “When we are silent, we allow these crimes to multiply. I urge women not to be silent. Our movement is expanding, we are active not only in Kazakhstan, but also in other countries of central Asia and beyond.”
The broadcast highlighted successful experiences around the world in responding to gender-based violence. The example in Spain, where women in danger can visit pharmacies and use a code word to alert staff that they need help, was praised. The role of the private sector was also shown to be important—since many shelters are not open at present, hotels are stepping in and providing shelter, either for free or at a minimal cost.
The broadcast was part of a joint initiative of the UNAIDS regional office for eastern Europe and central Asia, the UNESCO Institute for Information Technologies in Education and OK, in partnership with the regional office of UN Women for eastern Europe and central Asia.
When will men stop thinking that women’s bodies are their property?





Feature Story
Raising the voices of women at the forefront of climate change
05 March 2020
05 March 2020 05 March 2020The Pacific region has among the world’s highest rates of gender-based violence. National research show that 72% of Fijian women experience gender-based violence, compared to the global average of 35%. Women in the region also have a low representation in leadership positions—out of the 560 Pacific members of parliament, 48 are women, of whom 10 are Fijian women.
Adding to these sociocultural impacts is the climate emergency. In response, Pacific women are demanding more involvement in climate-related decision-making and to be fully engaged in climate responses.
Komal Narayan, a Fijian climate justice activist, became fascinated during her postgraduate programme in development studies about how climate change overlapped with ethics and politics. “The effects of climate change are felt most acutely by the people who are least responsible for causing the problem,” she said. This motivated her to be more active and vocal about the issue, leading to her participation, together with other young delegates from Fiji, in the twenty-third United Nations Climate Change Conference, held in Bonn, Germany, in 2017.
“My goal in life is to be part of a society that is focused on addressing the issues of climate justice and encouraging and motivating more young people to be more involved in this space, as I believe that this issue is not just yours or mine but an issue that is at heart for the entire Pacific,” Ms Narayan said.
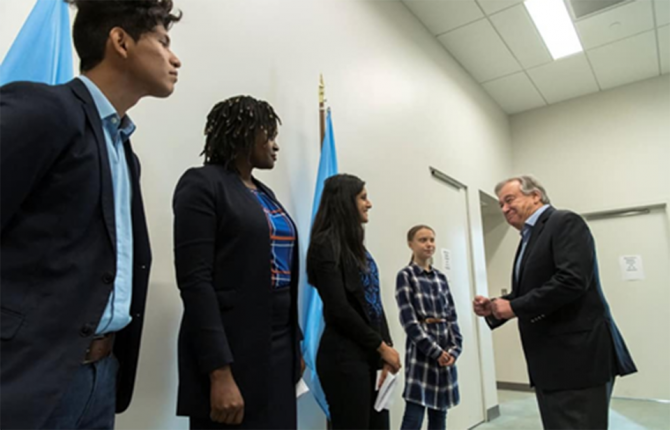
Ms Narayan was also one of the Green Ticket Recipients for the United Nations Youth Climate Action Summit in September 2019, where she was involved in a youth-led dialogue with the United Nations Secretary-General.
“As givers of life, as dedicated mothers, thoughtful sisters, domestic influencers and active contributors to socioeconomic development, we women have the power to give impetus to the global climate movement,” Ms Narayan said. “It’s about time that women and girls are given equal opportunities and equal access to resources and technology to be able to address climate justice. Countries, specifically government and civil society, should be playing a key role in this.”
AnnMary Raduva, a year 11 student at Saint Joseph’s Secondary School in Suva, Fiji, believes that climate justice must recognize the connection between humans and the environment and how vulnerable we are if we don’t do something today.
“In the Pacific region, our indigenous communities depend intimately on the ecological richness for subsistence, as well as economically, and this dependence makes our people sensitive to the effects of extreme weather events, and we cannot ignore them. We have a close relationship with our surroundings and are deeply spiritual and culturally connected to the environment, and ocean, and this relationship has positioned us to anticipate, prepare for and respond to the impacts of climate change,” Ms Raduva said.
In 2018 she wrote to the Fijian Prime Minister asking him to relook at the Fiji Litter Act 2008 to classify balloon releasing as littering in Fiji. Ms Raduva soon realized that talking about balloon releasing was not enough, however, and that she had to find eco-friendly alternatives to amplify her message. The idea of planting mangroves along the Suva foreshore soon came to her.
Since 2018, she has initiated six planting activities and has planted more than 18 000 mangrove seedlings. She was invited to New York, United States of America, in September 2019 to march for climate justice at a United for Climate Justice event organized by the Foundation for European Progressive Studies. She stood in solidarity with the indigenous communities that are on the forefront of climate change as it advances in the Pacific region.
Ms Raduva has faced discrimination as a young female activist and has been mocked as a “young, naive girl”. She was told that she must not talk about climate change because activism is reserved for boys and adults. However, she believes that ensuring the participation of women, children and lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex people and other minority groups in climate change talks is a priority for any institution or organization that aims to champion climate change issues.
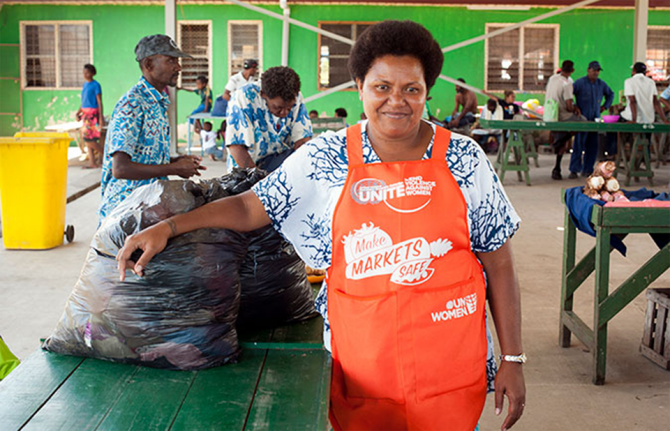
Varanisese Maisamoa is a survivor of Cyclone Winston, which in 2016 was one of Fiji’s most powerful natural disasters. In 2017, she formed the Rakiraki Market Vendors Association, working with UN Women’s Markets for Change project—“We want to empower our market vendors to be climate-resilient,” she said. Through UN Women’s leadership training, she learned to be confident when speaking out about the issues affecting market vendors and to negotiate with the market council management.
Ms Maisamoa represented her association on the design of the reconstruction of Rakiraki’s market, which now features infrastructure resilient to a category 5 cyclone, a rainwater harvesting system, flood-resistant drainage and a gender-responsive design.
Ms Narayan, Ms Raduva and Ms Maisamoa are among the Pacific women who are pushing for more of a voice in and inclusiveness for women and girls in climate action. Their activism is working to reduce discrimination against women and girls, which results in inequalities that make them more likely to be exposed to disaster-induced risks and losses to their livelihood, and to build resilience for women to adapt to changes in the climate.
Ms Maisamoa’s story has been republished with permission from UN Women’s Markets for Change project, which is a multicountry initiative towards safe, inclusive and non-discriminatory marketplaces in rural and urban areas of Fiji, Solomon Islands and Vanuatu that promotes gender equality and women’s economic empowerment. Implemented by UN Women, Markets for Change is principally funded by the Government of Australia, and since 2018 the project partnership has expanded to include funding support from the Government of Canada. The United Nations Development Programme is a project partner.
Region/country
Related
 Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia
Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia

24 February 2025





