Young people
Documents
Youth Next Level: guidance to strengthen sustainable youth-led HIV responses
19 July 2024
Youth Next Level is a suite of resources that provides concrete guidance and recommendations on how to effectively support the scale-up of youth-led HIV responses and accelerate the achievement of Result Area 7 of the Global AIDS Strategy and the 30-80-60 community leadership targets of the 2021 Political Declaration on HIV/AIDS. See also: Steps for country rollout | Definitions
Related
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
A shot at ending AIDS — How new long-acting medicines could revolutionize the HIV response
21 January 2025
Indicators and questions for monitoring progress on the 2021 Political Declaration on HIV and AIDS — Global AIDS Monitoring 2025
17 December 2024
 To end AIDS, communities mobilize to engage men and boys
To end AIDS, communities mobilize to engage men and boys

04 December 2024
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
Documents
Youth Next Level: Steps for country rollout to support youth-led HIV responses
19 July 2024
This document is designed as a summary and visual aid of the steps and recommendations for strengthening sustainable youth-led HIV responses included in Youth Next Level: guidance to strengthen sustainable youth-led HIV responses. For more details on each of the steps outlined in this document, it is recommended to consult the above-mentioned document. See also: Definitions
Related
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
A shot at ending AIDS — How new long-acting medicines could revolutionize the HIV response
21 January 2025
Indicators and questions for monitoring progress on the 2021 Political Declaration on HIV and AIDS — Global AIDS Monitoring 2025
17 December 2024
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
Take the rights path to end AIDS — World AIDS Day report 2024
26 November 2024
Documents
Youth-led responses: a definition for stakeholders supporting youth leadership in the HIV response
19 July 2024
A participatory process was convened that engaged over 100 young people in all regions to support the development of the definition. A survey, along with consultations in English, Russian and Spanish, ensured young people in all their diversity had the opportunity to feed into the process and have their say on what youth-led responses are. It was also identified in the process that for a definition of “youth-led responses” to be effective, there would need to be a definition of “youth-led organizations”, which was developed concurrently. See also: Youth Next Level: main guidance | Steps for country rollout
Related
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
A shot at ending AIDS — How new long-acting medicines could revolutionize the HIV response
21 January 2025
Indicators and questions for monitoring progress on the 2021 Political Declaration on HIV and AIDS — Global AIDS Monitoring 2025
17 December 2024
 To end AIDS, communities mobilize to engage men and boys
To end AIDS, communities mobilize to engage men and boys

04 December 2024
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
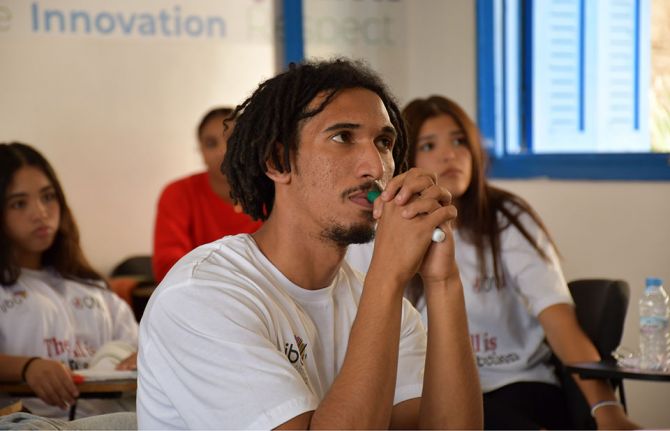
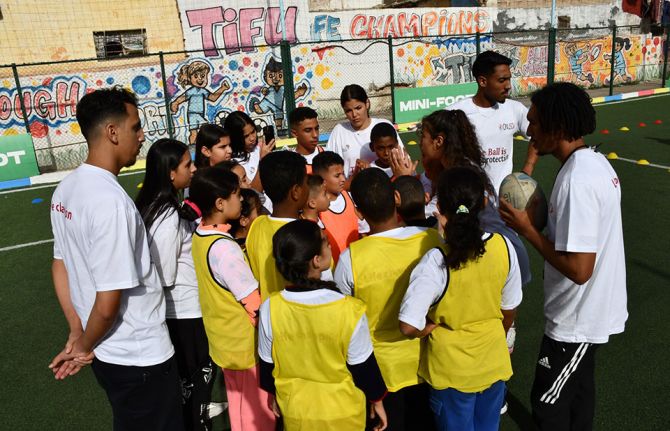




Feature Story
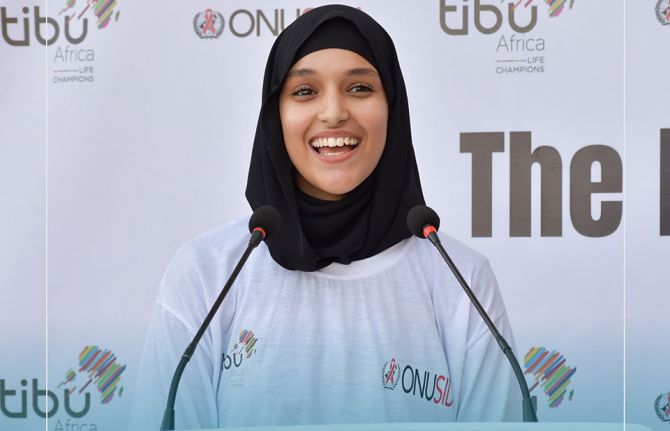
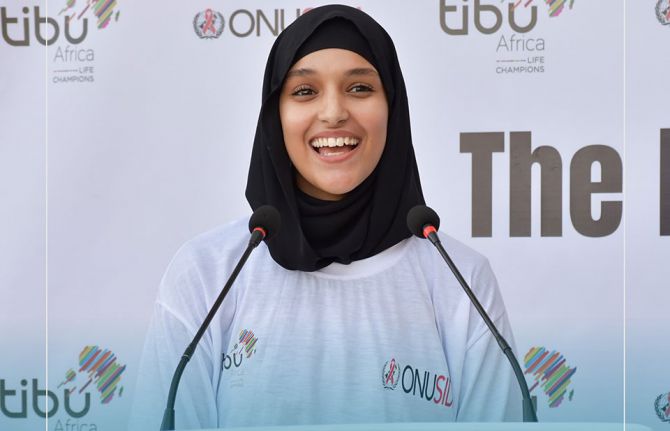
Driving change through sports and HIV awareness
20 December 2024
20 December 2024 20 December 2024Marouane Abouzid, a 25-year-old from Casablanca, grew up in an environment where social challenges and gender stereotypes were pervasive. However, his perspective changed the day he joined "The Ball is Your Protection" program, an initiative by Tibu Africa in partnership with UNAIDS, which uses sports to raise awareness about HIV, gender equality, and gender-based violence.
Before joining the program, Marouane had limited knowledge about HIV and gender equality. “The training on HIV awareness led by UNAIDS and Tibu Africa was a transformative experience,” he says. “It equipped me with essential skills like effective communication and active listening.” Thanks to the program, Marouane discovered how sports can be a powerful tool to engage young people on often-overlooked topics, such as HIV prevention and breaking gender stereotypes.
Now, trained to be a change ambassador in his community, Marouane leads sports activities and participates in educational sessions, becoming a role model for his peers. “I talk openly about what I’ve learned. I encourage my friends to get tested for HIV and respect the rights of others,” he shares.
For Marouane, this program was more than just training. “Today, I feel ready to take action and share what I’ve learned with my community,” he says.
During the closing ceremony of the "The Ball is Your Protection” project, Marouane facilitated workshops and sports activities with other young participants. “I saw how sports could become a tool for awareness and social mobilization,” he explains. These activities created a safe space for young people to discuss issues related to HIV and gender equality, free from societal judgment.
In Morocco, approximately 23,000 people live with HIV, nearly 50% of whom are women. Although the prevalence rate is relatively low, vulnerable groups such as sex workers, men who have sex with men, and people who inject drugs are particularly at risk. “Before, I thought HIV didn’t have a real impact on those around me. Now, I understand that we all have a role to play,” Marouane adds.
Marouane is not alone on this journey. Assia Ezzahraoui, 25, a participant in Tibu Africa’s Sports Vocational School program, reflects: “HIV awareness was a profoundly enriching experience. It gave me new insights into symptoms, prevention methods, and available treatments.” For Assia, taking part in the educational event deepened her understanding of HIV and reinforced the importance of protecting her health and that of those around her.
“I want to thank everyone who contributed to this initiative. Their commitment to young athletes in Morocco is truly inspiring,” says Assia, emphasizing the value of such events in educating youth about HIV.
Thanks to initiatives like "The Ball is Your Protection," young people like Marouane and Assia are playing an active role in addressing gender inequalities and HIV-related stigma. These young leaders are helping to build a healthier and more equitable future, proving that change can start with something as simple as a ball.
Partner
Region/country
Related
 Government ensures continuity of treatment in Malawi
Government ensures continuity of treatment in Malawi

10 February 2025
Documents
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
Suggested citation. UNAIDS DATA 2024. Geneva: Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS; 2024. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. Related: The 2024 global AIDS report The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads, released 22 July 2024, is available here.
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025
Documents
Take the rights path to end AIDS — World AIDS Day report 2024
26 November 2024
The world’s decades-long response to HIV is at an inflection point. Despite successes, the world is currently not on track to end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030. Press release | Download full report | Download short version
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025
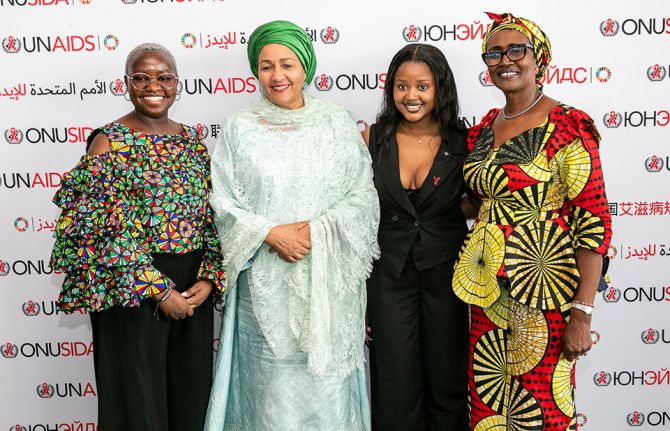




Press Release
The AIDS response is recognized as a beacon of hope and guide for revitalizing multilateralism at the 79th UN General Assembly
27 September 2024 27 September 2024NEW YORK/GENEVA, 27 September 2024—At the 79th United Nations General Assembly (UNGA79) and the Summit of the Future in New York, global leaders called for the revitalization of multilateralism to address pressing global crises, drawing on the success of the global AIDS response as a model of hope and global solidarity.
"Multilateralism is not a theory – it is the way we save lives and keep the world secure,” Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS, told the General Assembly. “When leaders work together for a common mission – anything is possible.”
At a special event convened by UNAIDS, the U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR), and the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria on 24 September 2024, leaders from governments, communities, business, and international organizations all testified to how multilateralism had driven the extraordinary gains made in the fight against AIDS, and how the path to addressing other global challenges had been illuminated by the global HIV response.
“The AIDS response shows what is achievable when leaders unite, when communities are empowered, when inequalities are tackled, when human rights are protected and when science-based policy is backed by political will,” said United Nations Deputy General-Secretary, Amina Mohammed.
UNAIDS data shows that at the end of 2023, more than 30 million people were accessing life-saving HIV treatment, compared to just 7.7 million in 2010. The data also show that since 2010, AIDS-related deaths have been halved, and new HIV infections among children have been reduced by 62%.
Across the week of the UN General Assembly, leaders set out concrete commitments to ending AIDS by 2030. These include closing gaps in access to HIV prevention, treatment and care, ending stigma and discrimination, accelerating innovation and access to new HIV technologies, and mobilizing domestic and donor resources for the HIV response.
UNAIDS set out how ensuring the end of AIDS as a public health threat, and enabling the success of the Sustainable Development Goals, require bold action to tackle global inequalities. Ms Byanyima shone a light on the financing crisis which is choking sub-Saharan Africa, leaving health and HIV services chronically underfunded. "Public debt needs to be urgently reduced and domestic resource mobilization strengthened to fully fund the global HIV response and end AIDS by 2030," said Ms. Byanyima.
Two young HIV activists, Ibanomonde Ngema from South Africa and Jerop Limo from Kenya, supported by UNAIDS to meet leaders at the UN General Assembly, called on governments to work with young people as partners. "Young people are key to ending AIDS. Leaders need to listen to us and include us in policy-making to ensure the progress made is sustained," said Jerop Limo.
Watch Special Event: Revitalized Multilateralism: Recommitting to Ending AIDS Together
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.




Press Release
Young people living with HIV urge world leaders to partner with them in the AIDS response
19 September 2024 19 September 2024NEW YORK/GENEVA, 19 September 2024—With support from UNAIDS, two young social media influencers living with HIV are on their way to the United Nations General Assembly and the Summit of the Future in New York to urge world leaders to partner with them in the response to HIV. Ibanomonde Ngema from South Africa and Jerop Limo from Kenya will call on leaders to invest in youth-friendly health systems, provide holistic services for young people living with HIV, and to partner with young people and communities, allowing them to lead in the response to HIV.
“Young people’s powerful and vibrant activism has driven so much of the progress made in the HIV response,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “They know what works for them. It is essential for leaders to listen to them to understand the specific challenges that young people face and how those challenges can be overcome. Leaders can only successfully plan how to end AIDS and sustain the advances made by partnering with young people living with HIV.”
“I am representing not only the voices of 1.5 million Kenyans living with HIV but all people living with HIV,” said Jerop Limo, a young Kenyan HIV activist. “I want leaders to leave New York knowing that we are not beneficiaries, we are equal rights holders. We have a voice, we have skills and expertise and we need an equal playing field where our data is valued, where our input is valued and where our voices are heard. We want meaningful and ethical engagement of adolescents and young people in all spaces of the AIDS response.”
Young people, especially adolescent girls and young women, are disproportionately affected by HIV. Globally, 44% of all new HIV infections were among women and girls (all ages) in 2023 and every week 4000 young women and girls around the world are infected with HIV—3100 are in sub-Saharan Africa. In 2023, some 3.1 million adolescents and young people (15-24 yrs) were living with HIV—1.9 million were adolescent girls and young women.
“Governments meeting here in New York cannot end AIDS alone. They need to involve us to find solutions. We have lived experiences of HIV, from treatment to mental health, because we navigate life with HIV every day. We need to be included in policymaking so that we can take full ownership of ending end AIDS as a public threat,” said Ibanomonde Ngema, a young South African AIDS activist. “The world can only benefit when young people are included in the global HIV response. No conversation about HIV should take place without us, from policy to practice in communities.”
Too often young people report facing stigma and discrimination, including from doctors and healthcare workers, when they access sexual and reproductive health and HIV services. This discourages them from seeking support and crucial information about their health, putting them at risk of HIV infection or of defaulting on treatment for those who are living with HIV.
Involvement of young people in the HIV response
Young people living with HIV play a critical role in the fight against AIDS in communities. They offer support and share important information about HIV that schools or parents might not talk about. They also challenge stigma and discrimination through social media, helping to save lives and encourage young people to stay on treatment.
They drive innovation in communities, for example, a self-funded project by the Youth Empowerment Group uses e-bikes to deliver antiretroviral medicines, food and adherence support to young people who often cannot attend clinics because their schooling hours conflict with clinic opening times in Namibia.
However, their transformational work is being held back because it is not being sufficiently supported. Youth-led HIV responses often operate with little or no financial and political support. At the UNGA the two young people will call on world leaders to fully support and fund their work. They will also urge leaders to uphold the human rights of young people as key to ending AIDS as a public health threat—they will call on them to protect young people’s right to healthcare, education, freedom of speech, and to provide social support to young people living with HIV.
“Providing treatment is not enough, young people living with HIV need an education and they need a job to survive,” added Jerop Limo. “We need to be seen as equal contributors and partners, and we need investment to allow us drive change. We are the leaders of the future and we need to be included now to help shape a better future for us all.”
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.




Feature Story
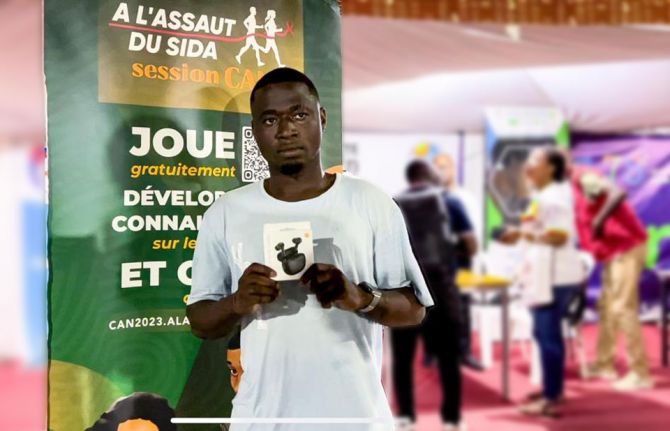
Interactive health and HIV game app reaches more than 300 000 young people in Côte d’Ivoire
09 September 2024
09 September 2024 09 September 2024Four weeks before the African Cup of Nations football tournament kicked off it was down to the wire. José Fardon, a Côte d’Ivoire web designer and digital developer, had his whole team frantically working on a special edition of an interactive health and HIV game app, called "A l'Assaut du Sida", ‘Tackling AIDS’ (AADS) to coincide with the tournament.
The UNAIDS team had secured funds for the latest rendition of the online game and had rallied UNICEF and the Global Fund to chip in.
“We had launched various versions of the game in the past, but this required a different look and feel to gel with the sporting event,” said Mr Fardon, founder of SYL.
They also needed a final approval from the National AIDS Programme (PNLS).
"Out of the many initiatives put forward ahead of the CAN, the online app really appealed to us because we knew it would not only reach the target audience, it would also make an impact,” said Eboi Ehui, PNLS Coordinating Director. “This is a generation that has never seen the ravages of AIDS so they have felt like it isn’t a problem but it is.”
The success was beyond anyone’s expectations.
The 20,000 tournament volunteers recruited by the Ministry of Youth not only played the online game themselves but they fanned out around the stadiums promoting the game by sharing the QR code with the hundreds of thousands of supporters. And with various prize giveaways during the tournament and afterwards, more and more people downloaded the app to play. Since mid-January 2024, AADS has reached nearly 200,000 adolescents and young people with the latest version reaching a lot of young boys and men (cumulatively, the three versions have reached almost 300 000 people.)
“When I think back, this idea germinated in 2016 as a tool for schools then was launched at the Francophonie Games a year later but now, we really brought it to the general public,” Mr Fardon said. “I am so proud we never gave up.”
His determination impressed more than one person.
In eight years, he convinced UNAIDS staff, the country’s Ministry of Health in close collaboration with PNLS, the Ministry of Education, the Ministry of Youth and countless partners on the ground.
UNAIDS Country Director Henk Van Renterghem, like his predecessors before him, saw the value and potential of using digital technology to reach adolescents and young people. “General knowledge about HIV and overall comprehensive sexual education has decreased and young people are struggling with so many choices that this easy to download game is without a doubt relevant,” he said.
In July 2023, he explained, the National AIDS Council was alerted by the results of a survey and beseeched HIV partners to step up communication and education efforts.
“Despite the fact that young people have more access to information through the internet and social media than ever before, many young people are struggling to make informed decisions about their sexual relations,” said Mr Van Renterghem. For example, the survey revealed that only 40% knew that medicine (anti-retroviral treatment) existed for HIV and 39% of girls (29% of boys) did not know that condoms prevented HIV transmission. Last year, 20% of new HIV infections in the country were among 15–24-year-olds, according to government data.
As a result, UNAIDS staff along with SYL, vetted and increased the number of questions expanding prevention info.
He and his staff were particularly happy because they also succeeded in expanding the scope of the content.
In went the fact that people with HIV on effective treatment can achieve an undetectable viral load and cannot transmit the virus (U=U) plus stuff about stigma & discrimination, human rights, gender equality and gender-based violence – all structural drivers of HIV.
The full game of 400 questions is like a quiz with additional information popping up. Players score points by advancing through 40 sets of ten questions. At least seven correct answers are needed to advance to the next level. It can take up to an hour to get to the last round and when the updated pilot was tested in October and November of 2023, young people responded well.
Two of the young players who scored in the best percentile agreed.
“The game really taught me a lot. There are a lot of facts about HIV and sexually transmitted diseases,” said Marie Koffi. For Wilfried Touré he said, “I learned a lot of things that I had no idea about from tuberculosis to HIV and even on a personal level I picked things up.”
Going forward national partners now want to distribute a scholastic version of the game to all Côte d’Ivoire schools.
During the final awards ceremony at the end of March, Côte d’Ivoire’s Minister of Health, Pierre Dimba, was clear. “This fun and educational online game is a response to young people's need for true and accurate information via social media,” he said. “The popularity of this game among teenagers is a real testimony that adapting our communication strategies to the habits and needs of young people pays off.”
In Mr Van Renterghem’s mind, Côte d’Ivoire should be proud.
“This home-grown low-cost tool will help us sustain our HIV prevention efforts as international funding will inevitably dwindle.”
That is in part why Mr Fardon and UN partners are dreaming even bigger.
“We would like to launch the app-based game in neighboring countries and eventually roll this out throughout western and central Africa,” he said.
“The sky is the limit.”
More information
Demographic and Health Survey
Region/country
Related
 Impact of the pause of US foreign assistance in Côte d'Ivoire
Impact of the pause of US foreign assistance in Côte d'Ivoire

19 February 2025
Documents
HIV and adolescent girls and young women — Thematic briefing note — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
In 2023, there were an estimated 1.9 million [1.1 million–2.5 million] adolescent girls and young women aged 15–24 years living with HIV, compared with 1.2 million [840 000–1.6 million] adolescent boys and young men aged 15–24 years. Globally, 44% of all new HIV infections were among women and girls (all ages) in 2023. Between 2000 and 2023, new HIV infections among adolescent girls and young women fell by 63% worldwide, and the rate of that decline has accelerated over the past decade. The estimated number of adolescent girls and young women aged 15–24 years who acquired HIV in 2023 was 210 000 [130 000–280 000]—four times higher than the 2025 target of 50 000. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
Take the rights path to end AIDS — World AIDS Day report 2024
26 November 2024
 PrEP for her: Cambodia, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea and the Philippines prepare to introduce the Dapivirine ring to help prevent HIV
PrEP for her: Cambodia, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea and the Philippines prepare to introduce the Dapivirine ring to help prevent HIV

22 November 2024
 The AIDS response is recognized as a beacon of hope and guide for revitalizing multilateralism at the 79th UN General Assembly
The AIDS response is recognized as a beacon of hope and guide for revitalizing multilateralism at the 79th UN General Assembly

27 September 2024
 Young people living with HIV urge world leaders to partner with them in the AIDS response
Young people living with HIV urge world leaders to partner with them in the AIDS response

19 September 2024