Update
Parental consent undermines the right to health of adolescents
16 March 2020
16 March 2020 16 March 2020Many countries have laws or policies that prevent adolescents from accessing essential health services without the consent of a parent or guardian. The original intention may have been to protect minors, but these stipulations often have the opposite effect and increase the risk of HIV and other health problems among adolescents.
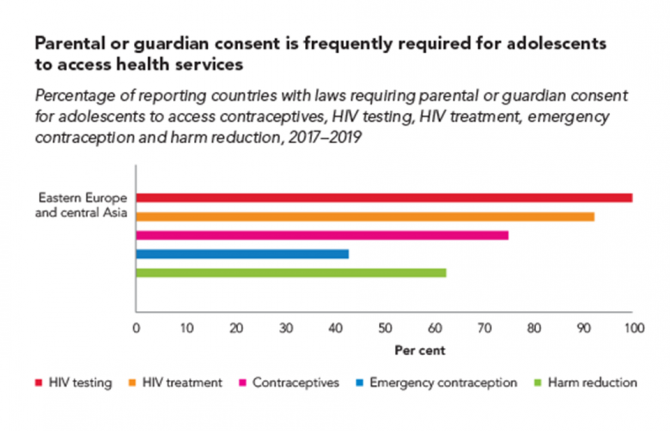
A large proportion of countries across all regions restrict access to HIV testing and treatment for adolescents. In 2019, for instance, adolescents younger than 18 years needed explicit parental consent in 105 of 142 countries in order to take an HIV test. In 86 of 138 reporting countries, they needed such consent to access HIV treatment and care. These kinds of laws and policies also may complicate or hinder adolescent access to pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), a highly effective prevention tool.
Research in sub-Saharan Africa shows that in countries where the age of consent is 15 years or lower, adolescents are 74% more likely to have been tested for HIV in the past 12 months compared with countries where the age of consent is 16 years or higher—with girls especially benefiting from the easier access.
Country-level details on which countries have consent laws can be viewed on the UNAIDS Laws and Policies Analytics web page.



