Injecting drug use IDU
Documents
Summary — Let Communities Lead — UNAIDS World AIDS Day report 2023
28 November 2023
This report is not only a celebration of the critical role of communities. It is a call to action to decision-makers to fully support the life-saving work of communities and to clear away the barriers that stand in their way. Press release | Full report | Fact sheet | World AIDS Day 2023
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
Documents
Let Communities Lead — UNAIDS World AIDS Day report 2023
28 November 2023
This report is not only a celebration of the critical role of communities. It is a call to action to decision-makers to fully support the life-saving work of communities and to clear away the barriers that stand in their way. Press release | Report summary | Fact sheet | World AIDS Day 2023
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025


Press Release
Ahead of World AIDS Day UNAIDS is calling for urgent support to Let Communities Lead in the fight to end AIDS
30 November 2023 30 November 2023A new report by UNAIDS demonstrates the critical role communities play, and how underfunding and harmful barriers are holding back their lifesaving work and obstructing the end of AIDS.
LONDON/GENEVA, 28 November 2023—As World AIDS Day (1 December) approaches, UNAIDS is urging governments across the world to unleash the power of grassroots communities across the world to lead the fight to end AIDS. A new report launched today by UNAIDS, Let Communities Lead, shows that AIDS can be ended as a public health threat by 2030, but only if communities on the frontlines get the full support they need from governments and donors.
“Communities across the world have shown that they are ready, willing and able to lead the way. But they need the barriers obstructing their work to be pulled down, and they need to be properly resourced,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “Too often, communities are treated by decision-makers as problems to be managed, instead of being recognised and supported as leaders. Communities are not in the way, they light the way to the end of AIDS.”
The report, launched in London during a World AIDS Day event organized by the civil society organization STOPAIDS, shows how communities have been the driving force for progress.
Community advocacy from the streets to the courtrooms to parliaments has secured groundbreaking changes in policy. Communities’ campaigning helped open up access to generic HIV medicines, leading to sharp, sustained reductions in the cost of treatment from US$ 25 000 per person per year in 1995 to less than US$ 70 in many countries most affected by HIV today.
Let Communities Lead shows that investing in community-led HIV programmes delivers transformational benefits. It sets out how programmes delivered by community-based organizations in Nigeria were associated with a 64% increase in access to HIV treatment, a doubling of the likelihood of HIV prevention service utilization, and a four-fold increase in consistent condom use among people at risk of HIV. It also notes how, among sex workers reached by a package of peer-based services in the United Republic of Tanzania, the HIV incidence rate was reduced to below half (5% vs 10.4%).
“We are the vehicle for change that can end systematic injustices that continue to fuel HIV transmission. We have seen groundbreaking developments with U=U, improved access to medicines, and have made great strides in decriminalisation," said Robbie Lawlor, Co-Founder of Access to Medicines Ireland. “Yet, we are expected to move mountains without being financially supported. We are supposed to fight for a more equitable world and are tasked with dismantling stigma yet are side-lined in crucial discussions. We are at a tipping point. Communities can no longer be relegated to the periphery. The time for leadership is now.”
The report highlights how communities are at the forefront of innovation. In Windhoek, Namibia, a self-funded project by the youth Empowerment Group is using e-bikes to deliver HIV medicines, food and adherence support to young people who often cannot attend clinics due to their schooling hours. In China, community organizations developed smartphone apps that link people to self-testing which contributed to a more than four-fold increase in HIV tests across the country from 2009 to 2020.
The report reveals how communities are also holding service providers to account. In South Africa five community networks of people living with HIV inspected 400 sites across 29 districts and conducted more than 33 000 interviews with people living with HIV. In the Free State province, these findings led provincial health officials to implement new appointment protocols to reduce clinic wait times and three- and six-month dispensing of antiretroviral medicines.
“I am extremely concerned about the exclusion from health services of key populations like the LGBT+ community,” said Andrew Mitchell, Minister of State for Development and Africa. “The UK champions the rights of such communities, and we will continue to protect them, working closely with our partners in civil society. I thank UNAIDS for keeping us focused on the inequities driving the pandemic and I look forward to working with our partners to champion the voice of people living with HIV and end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030.”
Despite the clear evidence of community-led impact, community-led responses are unrecognized, under-resourced and in some places even under attack. Crackdowns on civil society and on the human rights of marginalized communities are obstructing communities from providing HIV prevention and treatment services. Underfunding of community-led initiatives is leaving them struggling to continue operating and holding them back from expansion. If these obstacles are removed, community-led organizations can add even greater impetus to end AIDS.
In the 2021 Political Declaration on ending AIDS, United Nations member states recognized the critical role communities play in HIV service delivery, particularly to people most at risk of HIV. However, whereas in 2012, when over 31% of HIV funding was channelled through civil society organizations, ten years later, in 2021, only 20% of funding for HIV was available—an unprecedented backsliding in commitments which has cost and is continuing to cost lives.
“At this time, community-led action is the most important countermeasure in the AIDS response,” said Solange Baptiste, Executive Director of the International Treatment Preparedness Coalition. “Yet, shockingly, it isn’t a cornerstone of global plans, agendas, strategies, or financing mechanisms for improving pandemic preparedness and health for all. It is time to change that.”
Every minute, a life is lost to AIDS. Every week, 4000 girls and young women become infected with HIV, and out of the 39 million people living with HIV, 9.2 million do not have access to lifesaving treatment. There is a Path that Ends AIDS and AIDS can be ended by 2030, but only if communities lead.
UNAIDS is calling for: Communities’ leadership roles to be made core in all HIV plans and programmes; Communities’ leadership roles to be fully and reliably funded; And for barriers to communities’ leadership roles to be removed.
The report features nine guest essays from community leaders, in which they share their experience on the achievements they have secured, the barriers they face, and what the world needs to end AIDS as a public health threat.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton Knott
tel. +41 79 514 6896
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS Media
communications@unaids.org
UNAIDS Geneva
Michael Hollingdale
tel. +41 79 500 2119
hollingdalem@unaids.org
World AIDS Day message
World AIDS Day 2023
Watch the launch
World AIDS Day report
World AIDS Day videos




Feature Story
Demanding more options for young people who use drugs in Nepal
26 June 2023
26 June 2023 26 June 2023“Drugs were a way to escape from reality. But because of it, I have faced a lot of discrimination,” said Yukusna Kurumbang. “After a while I had no one around me. No friends I could contact. I have my family but they do not trust me. I am trying to improve.”
There aren’t many resources at Ms. Kurumbang’s disposal. She’s fashioned her own path to recovery including volunteering with YKP Lead Nepal—a youth-led organisation.
“I’m investing in myself and others to escape drugs,” she explained. “I’m trying to control my mind.”
The organisation’s President, Rojal Maharajan, recalls the feeling of isolation he too faced while using: “It’s very humiliating—the gossiping and negative comments. My family also got sick and tired of me. Eventually I had no one to tell about my problems and my mental health status.”
He started his advocacy eight years ago after a successful rehabilitation stint.
“I wanted to do this work to make sure young people who use drugs are treated as human beings. They deserve to have a good life and better opportunities,” he said.
These deeply personal perspectives help YKP Lead Nepal respond to the addiction challenge facing Nepal’s youth. And it’s a complex challenge.
There was a 2021 review of the human rights situation of people who use drugs in Nepal by the International Drug Policy Consortium, Recovering Nepal, YKP LEAD Nepal and Youth Rise International. It notes that the Narcotic Drugs Act criminalises not only drug possession, but addiction itself. According to a 2019 survey of people who use drugs, almost half had been arrested for drug use or a related offence. Among people who injected drugs the arrest rate shot up to 63%.
Treatment for drug dependence is privatised and inaccessible to most, including residents of border towns where services are most scarce. Among those who have had access to drug treatment, one in ten reports having experienced ill-treatment, violence and even torture.
The Government of Nepal has made progress around the provision of harm reduction services including needle and syringe programmes and opiate agonist therapy (OAT). However there are allegations that police frequently harass and detain people visiting these facilities.
“Punitive drug policies across the region have created a culture of violence and impunity by law enforcement,” said Ikka Noviyanti, Regional Coordinator of Youth LEAD, the Asia and the Pacific young key population network. “This makes it more difficult for people to reach the range of prevention and treatment services they need to stay safe. The situation is even more dire for youths.”
A 2019 Ministry of Home Affairs survey determined that over three-quarters of people who use drugs in Nepal are under age 30. Another study found that one-third of young people who use drugs started before age 15, with almost half commencing drug use between 15 and 19. The advocates say that in lieu of heroin which is expensive, there’s a growing trend of young people mixing and injecting tranquilizers like Diagepam, Nitrazepam and Dormin.
Injecting drug use increases the risk of abscesses as well as illnesses including HIV, Hepatitis B and C. HIV prevalence for injecting drug users is 3% for males and 2% for females. By comparison, Nepal’s adult general population HIV prevalence is 0.1%. YKP Lead Nepal is advocating for disaggregated data so they can better grasp the scale of the HIV burden carried by young people.
The organisation shares safety information with clients along with clean needles and syringes. During the Covid-19 lockdowns, for example, they home delivered both food and harm reduction packages. Their outreach includes homeless young people.
But the advocates say that even when clients are aware of the risks, there are barriers to staying safe.
“Most of them don’t want to go to the service sites,” Mr Maharajan explained. “Many of the young women have told us they are harassed at the OAT clinics. Others have a concern that the people running the needle exchange programmes are from rehabs. They don’t want to be forced to go (to rehab) because they are fearful of torture.”
UNAIDS Country Director for Nepal, Masauso Nzima, says that the Government of Nepal has made a move in the right direction with its investment in harm reduction services. However, more needs to be done to ensure a people-centred approach to drug policies “if we are to make a sustained difference in the lives of young people”.
“A critical step is the adoption of laws that treat drug dependence as a health condition rather than a crime. Action is also needed to outlaw torture and ill treatment, holding violators accountable and providing increased oversight for rehabilitation centres. Finally, we are advocating for expanded access to drug treatment and harm reduction programmes, without discrimination,” Mr Nzima said. “That means young people, women and people living in all parts of the country should have equitable access.”
YKP Lead Nepal goes a step further, calling for designated days for young women to access harm reduction services and for young people to be among the service providers.
With support from UNAIDS Asia Pacific, Youth LEAD is now piloting a “Regional Healthcare Worker Training Manual: Friendly HIV and SRHR services for young key populations in Asia Pacific”. The approach is meant to address the multiple barriers to young key populations accessing services including concerns about privacy and confidentiality, stigma and discrimination among healthcare providers, inconvenient opening hours and service packages that do not speak to their specific needs.
“Young people account for one of four new HIV infections in Asia and the Pacific,” Ms. Noviyanti said. “We are failing young people. But with targeted investments for youth-led responses and action we can turn the tide.”
Region/country
Related
 Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia
Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia

24 February 2025
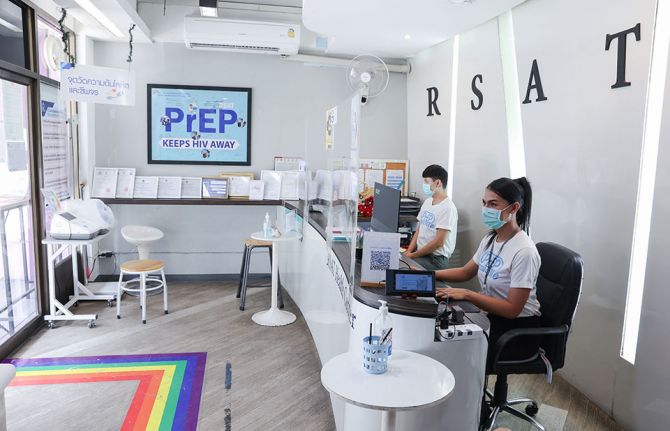




Feature Story
How to build stigma-free key population services
23 June 2023
23 June 2023 23 June 2023At his previous factory job, Tom Wang (not his real name) says coworkers gossiped about his sexuality and made fun of him. When he visited a public health facility for an HIV test, the nurse peppered him with questions like “Why do you need it? Have you been sleeping with many partners?”
Thailand is a country famed for its tolerance. It is among the world’s top locations for gender affirming care. Same-sex sexual activity hasn’t been criminalised since 1956. And the policy tide is turning on other key population issues. A 2021 Drug Law allows for harm reduction as opposed to automatic imprisonment, while a bill is in the pipeline to affirm the rights of sex workers. Yet stigma and discrimination persist. In homes, communities, schools, workplaces and—critically—healthcare settings, discriminatory attitudes can take their toll.
“Microaggressions—intentional or unconscious verbal or behavioural slights toward stigmatised groups—can drive people away from HIV prevention and treatment,” noted UNAIDS Regional Human Rights and Law Adviser, Quinten Lataire. “There are evidence-based approaches for measuring and lowering both overt and subtle stigma and discrimination in healthcare settings.”
It was this need for stigma-free services that led to the establishment of the Rainbow Sky Association of Thailand (RSAT). RSAT offers sexual healthcare for men who have sex with men, migrants, people who use drugs, sex workers and transgender people. It also advocates for the full rights and equity of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) communities. Tom Wang is amongst the clients who have benefited from their support.
This work is critical if HIV programmes are to reach and retain key population communities. In Thailand, as in the rest of Asia, these groups carry the heaviest HIV burden. Nationally HIV prevalence is 1% for sex workers, 8% for people who use drugs, 11% for transgender women and 12% for men who have sex with men.
A one stop shop for sexual health services
RSAT’s approach demonstrates how programmes can improve outcomes by implementing strategies to affirm and empower clients. They are jointly supported by PEPFAR, USAID, EpiC, the National Health Security Office (NHSO) and Thailand’s Institute of HIV Research and Innovation (IHRI).
There are no depressing charts or drab walls at their five key population clinics. At the Bangkok site the rainbow motif appears on the floors and walls. There are swarms of cut-out butterflies. Signs are either upbeat and multi-coloured or a soothing blue.
Most of the staff are themselves members of key population groups. All staff receive anti-stigma and discrimination training which even addresses the fine point of body language. Nothing about staff’s interactions should make a client feel judged or uncomfortable. The entire team is retrained annually. There is an internal complaint mechanism that allows clients to confidentially flag issues, as well quality assurance staff to ensure Standard Operating Procedures are followed. Every team member signs a confidentiality agreement.
RSAT’s service package includes on-site testing for HIV and other sexually transmitted infections, Hepatitis C, Tuberculosis and Covid-19. For transgender clients they offer hormone level monitoring. Mental health screenings which evaluate for depression, anxiety and stress have been integrated into the HIV service package. Where required, clients are referred for additional mental healthcare.
“Many of our clients engage in chem sex (recreational drug-use during intercourse). Some clients inject meth so we need to provide more than condoms. They also need clean syringes and needles which are part of our harm reduction package,” said Deputy Director, Kao Kierati Panpet.
Pre- and post-test counselling are critical. All counsellors are certified and accredited by the Ministry of Public Health according to Counsellor Supervisor, Sasiprapha Khamthi. Even before receiving HIV test results, clients know that treatment is available. Following a positive test, the counsellors reassure clients that with treatment they can live a normal life, explained Niphon Raina, Care and Counselling Supervisor.
“We also ask what their concerns are and give basic information about how HIV is and is not transmitted, using a picture book so they are clear on the facts,” Care and Counseling Officer, Bussarin Poonvisitkun added.
RSAT keeps a stock of antiretroviral therapy drugs onsite and can initiate new clients’ treatment on the day of diagnosis by giving them one month’s supply. Although HIV care is provided at the Ratchaphiphat Hospital, RSAT is able to dispense right away in accordance with instructions from a hospital doctor, delivered via telemedicine. Clients living with HIV receive help from the care and support team to navigate their next steps, including attending hospital visits.
RSAT also provides pre-exposure prophylaxis or PrEP services with hospital supervision. Mr. Tom Wang explains how this has protected his health: “I decided to get on PrEP because I am changing partners. To me PrEP is another means of protection in case you are intoxicated or the condom breaks. It’s a way to ensure I stay HIV-free.”
A redress mechanism for rights violations
The organisation advocates for structural changes to eliminate stigma and discrimination. For example, they are currently making recommendations for the Gender Recognition Draft Bill.
“But the reality is that policy and legal changes take a lot of time,” said RSAT Director, Tanachai Chaisalee.
While this longer-term work proceeds, a redress mechanism helps clients address current concerns. RSAT is tapped into the Crisis Response System (CRS) initiated by the Ministry of Public Health in collaboration with the Office of the Attorney General, Ministry of Justice. People with complaints about prejudice or rights violations in any sphere can scan a QR code and report their experience. Reports may also be sent via Facebook, email or LINE, Thailand’s answer to WhatsApp. A multi-disciplinary team conducts investigations and works with the client and other stakeholders to help.
The lion’s share of reports made via RSAT come from transwomen (78%) while gay men have lodged 17% of reports. The most common challenges relate to requirements for gender confirming attire, social exclusion (particularly during job application processes) and HIV status.
RSAT’s Human Rights Manger, Watcharawit Waraphattharanon, shares that they have been able to resolve some cases very quickly. For instance, if a person living with HIV is being forced to take an HIV test as a requirement for work, the Attorney General’s office does an emergency intervention.
“We can close these cases within one week,” he said.
“The work of key population-led, community-based organisations like RSAT is critical to reach those who most need HIV services,” UNAIDS Country Director, Patchara Benjarattanaporn stressed. “The Government’s progress in funding Community-led Health Services and building partnerships between these organisations and the public health system puts us on the path to end AIDS.”
A group of journalists visited the Ozone Foundation as part of the UNAIDS, UNDP, APN Plus and USAID/PEPFAR Southeast Asia Regional Workshop on HIV-related Stigma and Discrimination in Bangkok, Thailand on June 8, 2023. Learn more about this novel training
Region/country
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia
Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia

24 February 2025
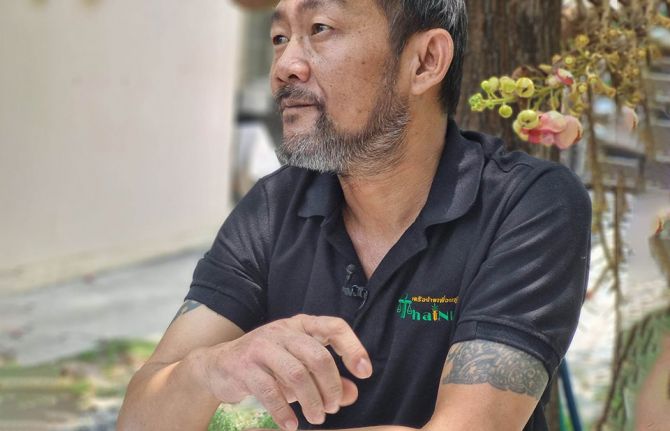
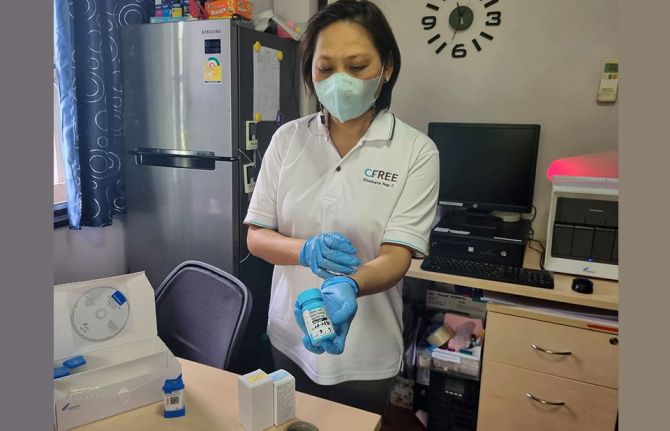





Feature Story
Compassionate care for people who use drugs in Thailand
26 June 2023
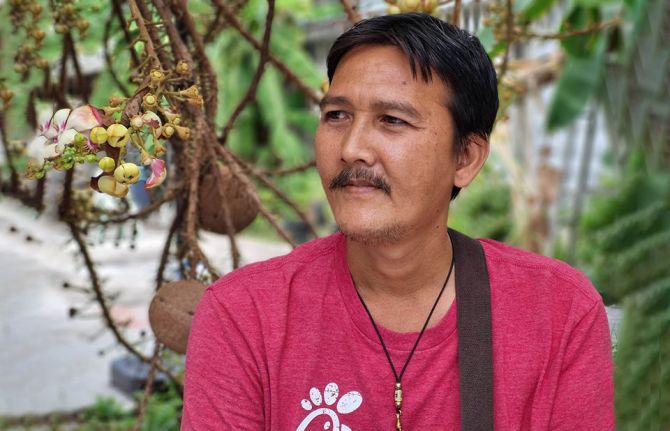
26 June 2023 26 June 2023At the Ozone Foundation clients talk about their drug use with as much openness as they discuss their jobs or families. In the yard of their Bangkok drop-in centre we sit under the cannon ball tree. Prapat Sukkeang shares his story first.
He is the Chair of the Thai Network of People who use Drugs (ThaiNPUD). He’s used substances of some kind for more than three decades. He says he started because of “small problems”. Once his family found out, he was immediately alienated: “the community and society around me became distant,” he remembers. Mr Prapat still uses. He might have yaba—a mixture of methamphetamine and caffeine—once a month.
“Ozone is the place I get knowledge about my health and about drug use. They give you information for your safety. I think without Ozone I might have overdosed,” he says plainly. “I feel very good to come here with service providers who see us as friends and provide healthcare services according to our needs. I feel respected. When we go to other places we always feel like criminals. If we go to a hospital they serve us last or reject us to get treatment. The service that we get is not equal to others.”
Jamon Aupama, a motorcycle taxi driver, lives with his wife in Bangkok. He goes to a state-run methadone clinic to avoid heroin withdrawal. He wishes he could take the methadone home and didn’t have to go there every day.
The experience at Ozone is different. Here the service delivery more closely matches his needs. He relies on Ozone for tests, clean equipment and “to hang out with friends”. He also goes for information.
“They give me detailed advice on how to protect myself from illness,” he says. “Some Ozone staff know personally about drug use, some do not. The trust comes from knowing them and the way they are trained,” Mr Jamon says.
From the ‘war on drugs’ to a more humane drug law
This people-centred service—and even these honestly told stories—were unimaginable just two decades ago. During the first three months of Thailand’s 2003 “war on drugs”, police killed almost three thousand people. Human rights groups reported widespread arbitrary arrests, beatings, forced confessions and compulsory detentions for “rehabilitation”. Use of HIV services by people who use drugs declined sharply. Terrified, people shrank into the shadows.
This chaotic context was the spark for Ozone’s formation. Back then they set up their first drop-in centres as safe spaces where clients could take a shower, have a meal and share their experiences.
Today the political and social climate is far different. A new Narcotics Law introduced in December 2021 provides for differentiated sentencing on drug crimes and alternatives to imprisonment for some offences. For the first time, the health and wellbeing of people who use drugs are being considered. There are provisions for harm reduction although it isn’t precisely defined. The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) notes the continued existence in Thailand of compulsory treatment centres, deemed by the United Nations to be ineffective and a violation of human rights. Still, this more humane drug law is a first in Southeast Asia.
“Community-based treatment should be the way to provide care. Through community literacy we can understand the patient and the situation they face to get them to have a good outcome,” says Dr Phattarapol Jungsomjatepaisal, Director of the Department of Health Service Support at the Public Health Ministry.
Ozone’s holistic service package
Ozone Foundation’s Director, Verapun “Noy” Ngammee, explains that the organisation’s raison d'être is to respond to clients’ unique situations.
“They have bad experiences with stigma and discrimination,” he starts. “It’s difficult to trust people. Many of them have been suffering for a long time. We need to have peer organisations that are community-led and driven or you would not get clients coming to services. We respect the human dignity of all people. And we believe that safety is available to people before, during or after drug-use.”
Their model identifies each person’s specific risks and needs. They’ve found that much of the harm clients experience is not directly due to drug use, but rather to the environment—anything from the inability to access healthcare to harassment by police. Ozone employs a holistic approach that puts the client at the centre. One person might only require harm reduction counselling and tools while another is ready for support to quit.
The organisation collaborated with C-FREE, a laboratory service, for screening and monitoring of Hepatitis B and C, HIV and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). They also offer the Hepatitis B vaccine. Research nurse Kewalin Kulprayong says her team has a welcoming approach.
“Clients know it is not a hospital,” she says. “It is safe. They can speak about everything here, drugs also.”
A doctor is available once a week. Some conditions can be treated at Ozone. In other cases, clients are referred to government facilities but with the benefit of peer support. These services are critical. An estimated eight per cent of people who inject drugs in Thailand are living with HIV while Hepatitis C prevalence is 42%.
"Universal Health Coverage in Thailand paves the way for comprehensive care, including essential services like HIV testing, pre-exposure prophylaxis or PrEP, treatment referrals, and screening and treatment for STIs and Hepatitis C. However, despite their inclusion in benefit packages, individuals who inject drugs face significant barriers due to pervasive stigma and discrimination, including self-stigma," says Patchara Benjarattanaporn, UNAIDS Country Director. “In this landscape, key population-led health services like Ozone’s emerge as invaluable one-stop shops, providing stigma-free care and ensuring that no one is left behind, especially those who use and inject drugs.”
Looking toward the future
Each Ozone client has their own dreams. One wants to run for political office. Another hopes to get his gender affirming surgery soon. A third imagines a life in the countryside with a small farm: “Not too many people,” he says with a chuckle. “Then I get in more trouble”.
He came to Ozone because he was depressed, anxious and dealing with a sexually transmitted infection.
“I did not have the confidence to go to a hospital and say, ‘I want treatment’. But I knew if I did nothing it would get worse. At Ozone they understand. They give me guidance. They’ve advised me to use social security to get mental healthcare. They tell me ‘people make mistakes sometimes’. I am one of those guys who makes many mistakes,” he confesses with another uneasy laugh. “But now the mistakes are getting less.”
A group of journalists visited the Ozone Foundation as part of the UNAIDS, UNDP, APN Plus and USAID/PEPFAR Southeast Asia Regional Workshop on HIV-related Stigma and Discrimination in Bangkok, Thailand on June 8, 2023. Learn more about this novel training.
Region/country
Related
 Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia
Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia

24 February 2025




Feature Story
Moldova expands harm reduction services to all prisons
05 May 2023
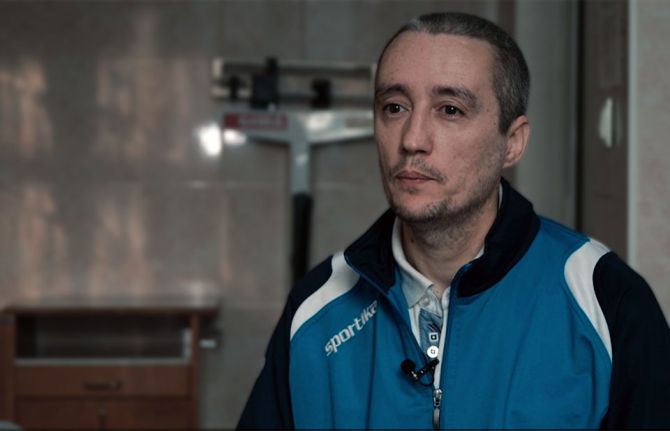
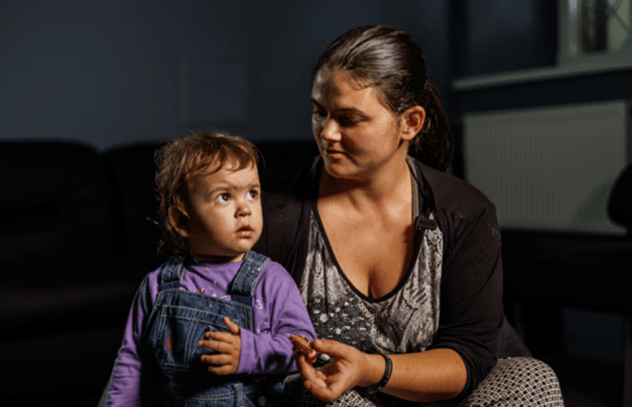
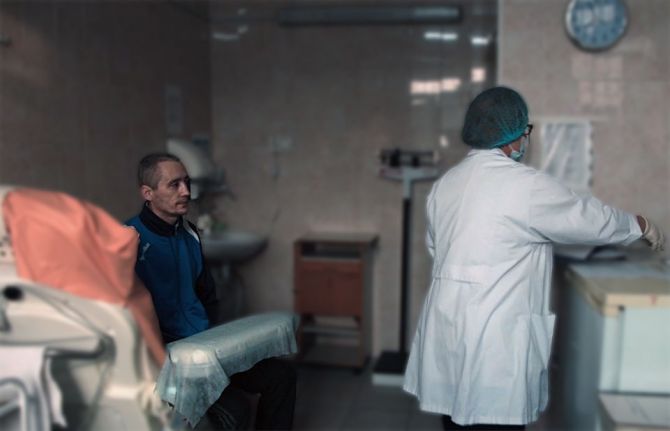
05 May 2023 05 May 2023Alexander Godin moves through a number of locked doors escorted by a guard to prison 16’s pharmacy. This is part of his daily routine. He comes to get his medicine – a syrup-like dose of methadone. Methadone is an opioid agonist therapy (OAT) to help people overcome withdrawal symptoms, decrease heroin dependence and prevent HIV infection from infected needles.
Since 2000, a few prisons in Moldova offered such harm reduction services.
Now all do.
“I have been on methadone substitution treatment for 10 years,” said Mr Godin. His family urged him to take advantage of such services so he could get healthy again.
“For years I used drugs and opioids and for this, money was needed so problems began among my family,” he said. Since he has been on the programme, he feels much better.
Any new prisoner to the country’s 17 penitentiaries sees a psychiatrist, a doctor and if needed is offered to join a treatment programme. Comprehensive harm reduction services not only include drug dependence treatment but also needle syringe exchange and HIV testing and treatment. HIV prevalence is 11% among people who inject drugs in Moldova vs 0.36% among the general population.
They are one of the most affected groups in the country.
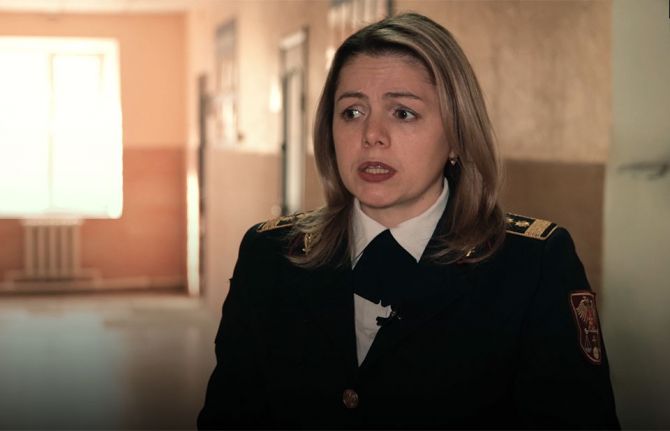
For Maria Potrîmba Head of Infectious Diseases at prison 16 (Pruncul) helping prisoners stave off drugs has positive knock-on effects.
“If a patient is on this substitution treatment the person is more aware of consequences and will more likely adhere to their other treatment,” she said.
The prisons also make sure to provide clean syringes with a regular pick-up every two days carried out by volunteer prisoners.
The head of medical unit at prison 13 (Chisinau) believes harm reduction services are important for both inmates and prison employees.
“The volunteers are all prisoners and the vast majority of them are also people who have been treated for communicable diseases like HIV or hepatitis or tuberculosis,” Oleg Costru said.
Moldova has committed more resources to the prison programme over the years. “In the beginning, when these services were developed, they were actually financed from external sources,” said Irina Barbîroș, head of the medical department at the national prison administration. “Over the years, the state assumed its commitment and took over the financing of these services from the state budget.”
UNAIDS, UNODC and WHO have been long-time supporters of expanding these services to all prisons. Currently, according to Harm Reduction International, only 59 countries globally provide OAT in prisons.
This, even though harm reduction has been proven to not increase the number of people with drug dependency but rather provide personal and public health benefits.
Svetlana Plamadeala, UNAIDS Moldova country director, has seen the pilot projects gain traction in the country and is quite proud of the success of the nationwide coverage.
“It is really about putting people in front and people at center as well as taking on a solid public health approach,” she said. For her, to end AIDS, protecting the health and human rights of people who use drugs is key. “It is about equalizing.”
Watch video
Region/country
Related
 Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery
Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery

20 February 2025



Press Release
UNAIDS calls for access to HIV prevention, treatment and care in prisons, including access to life saving harm reduction services
07 May 2023 07 May 2023Harm reduction policies and practices help people who are using drugs to stay alive and protect them from HIV and Hepatitis C
Released ahead of International Harm Reduction Day - 7 May 2023
GENEVA, 5 May 2023—Many prison systems are struggling to cope, with overcrowding, inadequate resources, limited access to healthcare and other support services, violence and drug use. In 2021, the estimated numbers of people in prisons increased by 24% since the previous year to an estimated 10.8 million people, increasing the strain on already overstretched prison systems.
Drug use is prevalent in prisons. UNAIDS Cosponsor, the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), estimates that in some countries up to 50% of people in prisons use or inject drugs. Unsafe drug injecting practices are a major risk factor for the transmission of HIV and hepatitis C due to limited access to harm reduction services, including condoms, clean needles and syringes, and a lack of comprehensive drug treatment programs, particularly opioid agonist therapy.
People in prison are 7.2 times more likely to be living with HIV than adults in the general population. UNAIDS reports that HIV prevalence among people in prisons increased by 13% since 2017, reaching 4.3% in 2021. Although data are limited, it is thought that around one in four of the total prison population has hepatitis C.
“Access to healthcare, including harm reduction services, is a fundamental human right, and no one should be denied that right because they are incarcerated,” said Eamonn Murphy, UNAIDS Regional Director for Asia Pacific and Eastern Europe and Central Asia. “Prisons are too often ignored in countries' efforts to respond to HIV. A multisectoral, multifaceted approach is urgently needed to save lives, which includes access to clean needles and syringes, effective treatment for dependence on opioid drugs and reducing stigma and discrimination.”
Both drug use and HIV infection are more prevalent among women in prison than among imprisoned men. In particular, women who use drugs and sex workers are overrepresented in prisons. Highlighting the urgent need to scale up the implementation of community-led harm reduction services for women who use drugs and women in prison.
Ms Ghada Waly, Executive Director of UNODC, said, “It is time to put compassion at the heart of our responses. To take a more serious look at de-penalization and alternatives to incarceration for minor drug offenses, focusing instead on treating and rehabilitating. To use a gender-sensitive lens when looking at women and girls who use drugs, and to ensure that they have equal access to treatment. To reach out to young people, who are using drugs more than ever before, understand their vulnerabilities to substance abuse, and help them be part of the solution. To stand with marginalized and vulnerable people, including people in prisons who are underserved by treatment programmes, and people who inject drugs, who are far more likely to be living with HIV, yet far less likely to access life-saving services”.
Among the countries reporting on prisons to UNAIDS in 2019, just 6 of 104 countries had needle and syringe programmes in at least one prison; only 20 of 102 countries had opioid substitution therapy programmes in at least one prison, 37 of 99 countries had condoms and lubricants in some prisons.
UNAIDS, UNODC, and WHO have long supported expanding harm reduction services to all prisons. However, according to Harm Reduction International, only 59 countries globally provide opioid agonist therapy in prisons.
Some countries have made huge progress in recent years. Despite the challenges faced by the influx of refugees and the repercussions of the war in Ukraine, Moldova, (which has an HIV prevalence of 3.2% in its prisons, compared to 0.4% among the general population) has committed significantly more resources into its prison systems.
In the early 2000’s few of its prisons provided harm reduction services. Today all of the country’s 17 penitentiaries provide harm reduction services including, methadone (an opioid agonist therapy), access to psychiatrists, doctors and treatment programmes, needle and syringe exchange and HIV prevention, testing, treatment and care.
Svetlana Plamadeala, UNAIDS Country Director in Moldova said, “It’s about putting people front and center, treating them as equals and taking on a solid, public health approach, grounded in human rights and evidence.”
UNAIDS, UNODC, UNFPA, WHO, ILO and UNDP recommend 15 comprehensive and essential interventions to save lives and ensure effective HIV programming in prisons. These include HIV prevention, testing and treatment, condoms, lubricant, opioid agonist therapy and post-exposure prophylaxis. However, this is only part of the solution. UNAIDS also recommends that countries amend their laws to decriminalize the possession of drugs for personal use.
UNAIDS has set ambitious targets for 2025 which include: 95% of people in prisons and other closed settings who know their HIV status, 95% who know their status are on treatment; and 95% on treatment are virally suppressed; 90% of prisoners used condoms at last sexual activity with a non-regular partner; 90% of prisoners who inject drugs used sterile needles and syringes at last injection; and that 100% of prisoners have regular access to appropriate health system or community-led services.
UNAIDS advocates that communities take an active role in planning, providing and monitoring HIV services. However, this is not always facilitated in prison settings. Without community engagement it will be impossible to reach the global AIDS targets.
For more information on Moldova’s work on HIV in prisons please read Moldova expands harm reduction services to all prisons and watch https://youtu.be/JQYtnsiJKs0
Fact sheet: UNAIDS Human rights fact sheet on HIV in prisons
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaCharlotte Sector
tel. +41 79 500 8617
sectorc@unaids.org
UNAIDS Eastern Europe and Central Asia
Snizhana Kolomiiets
kolomiietss@unaids.org
UNAIDS Geneva
Sophie Barton Knott
tel. +41 79 514 6896
bartonknotts@unaids.org
Watch: Moldova expands Harm Reduction services to all prisons
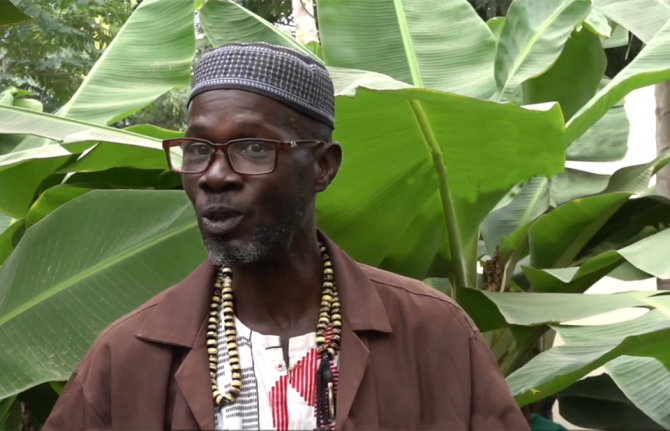
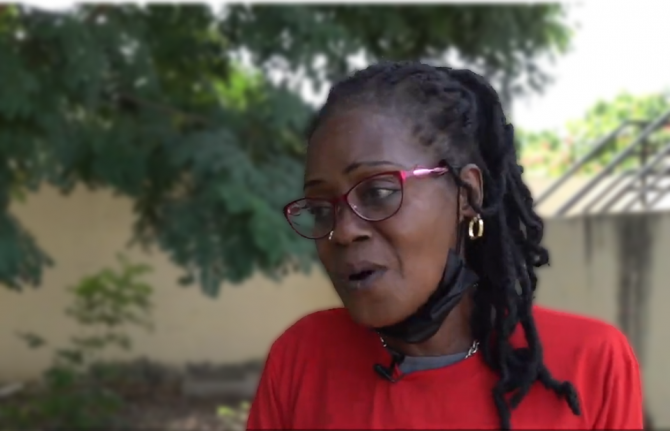
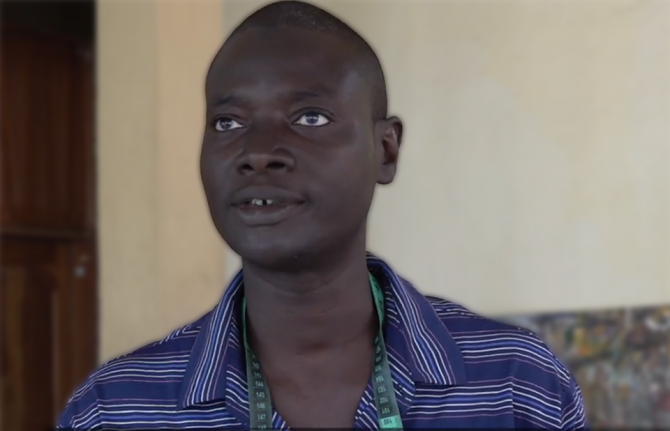




Feature Story
Leave no one behind and that includes people who use drugs
04 May 2023
04 May 2023 04 May 2023Daouda Diouf comes daily to the Fann Hospital compound daily. He is one of 250 people enrolled in CEPIAD*’s opioid substitution therapy programme (OST). OST is a globally recognized intervention to reduce injecting behaviours that put people who inject drugs at risk of contracting HIV and other blood-borne diseases, such as viral hepatitis.
“I am here to take my treatment and I am also a tailor, so I teach a few other users of drugs how to sew,” Mr Diouf said, cutting fabric in his makeshift outdoor workshop. Keeping occupied and selling his wares has helped him stay healthy for the last seven years.
Another enrollee agrees. He has found a passion for gardening and now oversees other patients at the centre’s green area.
For El Hadj Diallo, planting seeds, pruning trees is like a type of therapy. “When we are here, we forget our problems, I am happy doing it and it’s therapeutic for me,” he said.
Their other therapy consists of a daily dose of methadone. Mangane Boutha, the centre’s pharmacist carefully measures and distributes each dose in his office.
“Methadone is a medicine that acts as a heroin substitute, in our case it’s a syrup that is dosed in 10mg/ml portions with doses varying from patient to patient,” he explained.
Founded in 2014, CEPIAD has cared for more than one thousand people and is one of the first harm reduction centres in West Africa. Aside from opioid substitution, clean needle exchange and psychosocial support, they also offer health care.
“CEPIAD has become a testing and diagnostics center for HIV, and also tuberculosis as well as hepatitis and we distribute condoms,” said Dr Idrissa Ba, who coordinates the centre.
In Senegal, HIV prevalence among people who inject drugs is 9%, well above the 0.5% among the general population. Globally, due to stigma and criminalization, people who inject drugs face a 35 times higher risk of acquiring HIV than people who do not inject drugs.
Three-quarters of patients here are men but CEPIAD has been working hard to reach more women. Among people who use drugs, women are more likely to live with HIV, according to Dr Ba.
Mariama Ba Thiam, who formerly used drugs, lived for years on the streets. She is now a peer educator in Dakar. “I go out into the community and visit colleagues to raise awareness about getting off drugs and also how to reduce health risks so I refer them to CEPIAD and they can do like me, stop drugs,” she said.
Her plea: Get more funds to get more women and young people to come to the centre.
In Senegal, whilst drug use is a criminal offense, CEPIAD’s work has the support of the government, the United Nations as well as other partners.
On international Harm Reduction day, UNAIDS firmly believes that if we are to end AIDS by 2030, we can’t leave anyone behind. And that includes people who use drugs.
*The Centre de Prise en Charge Intégrée des Addictions de Dakar (CEPIAD)
Watch video
Region/country
Related
Related
55th meeting of the UNAIDS Programme Coordinating Board
10 December 2024
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
Take the rights path to end AIDS — World AIDS Day report 2024
26 November 2024
20th Indian Ocean Colloquium on HIV/AIDS
22 October 2024
 Club Eney: a safe place for those left behind
Club Eney: a safe place for those left behind

21 October 2024
University of Pompeu Fabra
17 October 2024
Linking UN Summit of the Future with COP29
26 September 2024
Revitalized Multilateralism
24 September 2024
Plenary debate of the Summit of the Future
23 September 2024
African Union Year of Education
23 September 2024












