Topics




Press Release
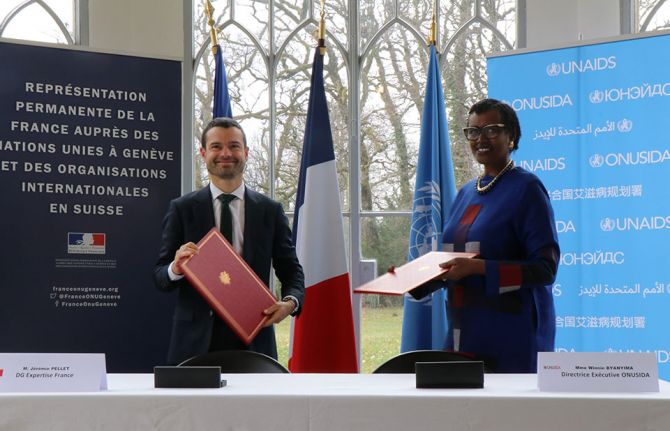
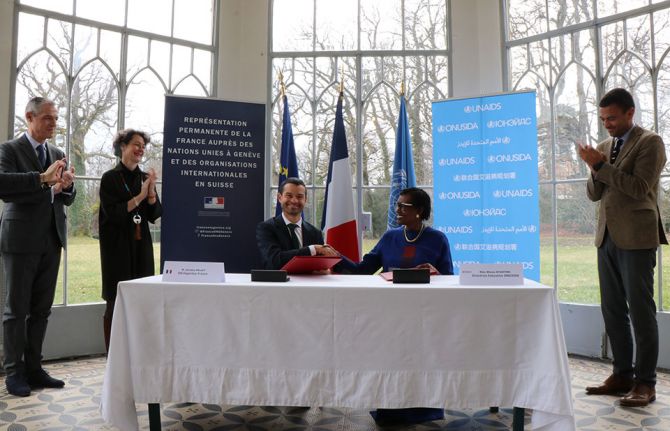
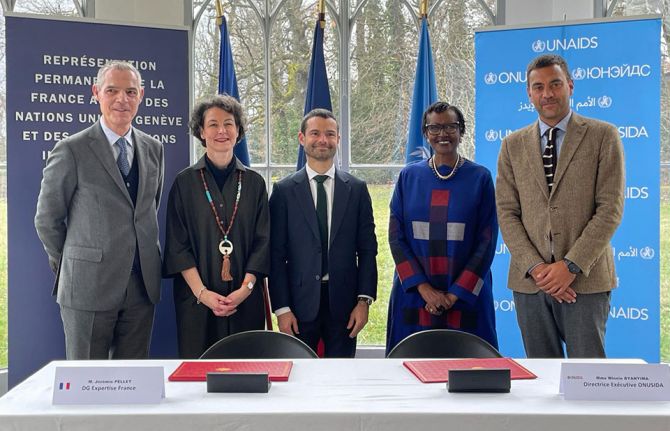
Expertise France partners with UNAIDS to fight HIV stigma and discrimination in western and central Africa
28 February 2024 28 February 2024GENEVA, 28 February 2024—The French public international cooperation agency ‘Expertise France’ and UNAIDS have signed a new partnership agreement to fight stigma and discrimination in six western and central African countries.
The aim of the €1.92 million partnership called, "Community response to stigma and discrimination and legislative reform," is to promote access to inclusive HIV services that respect human rights for key populations, including men who have sex with men, people who inject drugs, sex workers, transgender people and young women and adolescent girls in Benin, Cameroon, Côte d'Ivoire, Central African Republic, Senegal and Togo.
"Stigma and discrimination obstruct HIV prevention, testing, treatment and care, and hold back progress towards ending AIDS by 2030,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS and Under-Secretary-General of the United Nations. “It is only by protecting everyone’s rights that we can protect everyone’s health, so by joining forces with Expertise France we can uphold rights for those in need in the region.”
In the six countries, key populations are disproportionately affected by HIV. In Benin, for example, HIV prevalence in 2022 was 7.2% among sex workers, 8.3% among men who have sex with men and 21.9% among transgender people—while the rate is 0.8% among the general population. In Cameroon, HIV prevalence was 24.3% among sex workers, 20.6% among men who have sex with men and 4% among prisoners—while the rate is 2.6% among the general population.
Anne-Claire Amprou, Global Health Ambassador for France, Ms Byanyima, Jérôme Bonnafont, Permanent Representative of France to the United Nations and Jérémie Pellet, Director General of Expertise France, attended the signing ceremony at the Permanent Mission of France to the United Nations in Geneva, Switzerland.
"This agreement aims to reduce inequalities in access to care and treatment for populations most vulnerable to HIV in western and central Africa. France is thus making a commitment to global health alongside UNAIDS, in an approach based on equity, solidarity and development," said Mr Bonnafont.
Ms Amprou added, "Through this partnership, France is pleased to be able to reaffirm its commitment to strengthening healthcare systems, as well as combatting stigmatization, discrimination and gender inequalities in access to healthcare for the most vulnerable populations, by supporting for community-led efforts.”
As part of the Global AIDS strategy both France and UNAIDS are striving to improve legal and social responses to HIV with a particular focus on reducing gender inequalities and gender-based violence. This new initiative will also aim to reduce systemic barriers by promoting a more favorable legal framework that respects human rights and facilitates better access to legal services.
Jérémie Pellet, Director General of Expertise France said, "This partnership with UNAIDS embodies our commitment to supporting the most vulnerable communities and promoting a more just and inclusive society."
Expertise France via ‘L'Initiative’, an organization which helps national partners prepare and implement projects using funds from the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria, is funding the project. The funds complement efforts under the Global Fund's 7th round of funding, underlining the importance of coordinated action to remove human rights barriers to accessing health services.
Led by the UNAIDS western and central Africa regional office, based in Dakar, the project will be implemented with the support of the Civil Society Institute for HIV and Health, Alliance Côte d'Ivoire and Coalition PLUS.
Expertise France
Expertise France is the French public international cooperation agency. It designs and implements projects which aim to contribute to the balanced development of partner countries, in line with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of the 2030 Agenda and long-term development.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
L’Initiative
France created L’Initiative in 2011 in response to the difficulties that certain countries, particularly French-speaking ones, were having in accessing Global Fund grants. The French Ministry for Europe and Foreign Affairs and Expertise France, the government agency for international technical cooperation, oversee L’Initiative.
Contact
Expertise FranceEric Fleutelot
eric.fleutelot@expertisefrance.fr
UNAIDS Geneva
Charlotte Sector
sectorc@unaids.org
Region/country


Press Statement
On the 10th anniversary of Zero Discrimination Day UNAIDS calls for the protection of human rights as a path to protecting health for all
27 February 2024 27 February 2024GENEVA, 27 February 2024—Zero Discrimination Day was established by UNAIDS ten years ago to advance equality and fairness for everyone regardless of gender, age, sexuality, ethnicity or HIV status. However, progress is in peril.
Attacks on the rights of women and girls, of LGBTQ+ people, and of other marginalized communities are on the rise. And when laws, policies, practices or norms enshrine punishment, discrimination or stigma for people because they are women, or are LGBTQ+, or are migrants, or sex workers, or use drugs, the results lead to failing public health as these communities are pushed away from vital health and social services.
“The attacks on rights are a threat to freedom and democracy and are harmful to health. Stigma and discrimination obstruct HIV prevention, testing, treatment and care, and hold back progress towards ending AIDS by 2030,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “It is only by protecting everyone’s rights that we can protect everyone’s health.”
There has been progress. At the start of the AIDS pandemic 40 years ago, two thirds of countries in the world criminalized LGBTQ+ people, today two-thirds of countries do not.
38 countries around the world have pledged to end HIV-related stigma and discrimination and today 50 million more girls are in school than in 2015.
To continue this progress UNAIDS urges support for women’s movements and movements for the rights of LGBTQ+ people, for racial justice, for economic justice, for climate justice, and for peace. As communities across the world stand up for rights, the United Nations is not only on their side but by their side.
On this Zero Discrimination Day (1 March), and across the whole month of March, events and activities will remind the world of this vital lesson and call to action: by protecting everyone’s rights, we can protect everyone’s health.
“Through upholding rights for all, we will be able to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals, and to secure a safer, fairer, kinder, and happier world – for everyone,” added Ms Byanyima.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Watch: By protecting everyone’s rights, we can protect everyone’s health
Winnie Byanyima on Zero Discrimination Day
Watch: Rights for All means Health for All


Update
Statement from UNAIDS on the decision of the High Court of St. Vincent and the Grenadines to uphold discriminatory and harmful laws
25 February 2024
25 February 2024 25 February 2024UNAIDS is concerned about the impact on peoples’ health and rights following the decision of the High Court of St. Vincent and the Grenadines regarding sections 146 and 148 of the Criminal Code, which upholds discriminatory and harmful laws against LGBTQ people.
On Friday, February 16, 2024, the High Court, in an oral delivery, denied the claim by two Vincentian nationals, who reside outside of the country, that sections 146 and 148 of the Criminal Code criminalising buggery between any two persons with a penalty of up to 10 years imprisonment, violate the fundamental rights to privacy, personal liberty, freedom of conscience, freedom of expression and protection from discrimination. The Court dismissed in their entirety all claims by the two Claimants and awarded the sum of EC$7,500 prescribed costs to the Attorney General to be paid by each of the Claimants.
In the written decision published February 22, 2024, the Court in dismissing the consolidated claims of Javin Johnson and Sean MacLeish held that the Claimants had failed to establish on the evidence, a present or existing breach of any alleged rights due to lack of locus standi (the requisite standing to invoke a review by the Court) as the Claimants do not reside in the State and had not for years prior to the filing of the claims.
UNAIDS is particularly concerned that the judgment referred to protecting public health and tackling the HIV epidemic as justifying punitive anti-LGTBQ laws, because the evidence shows that such laws hinder efforts to protect public health and tackle the HIV epidemic. At paragraph 267 of the judgment the court asserted:
“to my mind the thought of a public health crisis occasioned by an unstemmed deluge of new HIV cases is a real and serious concern which reasonably justifies a public health response of the kind embedded in the challenged provisions”.
In fact, studies show that these laws have negative health outcomes. A punitive legal environment, including criminalisation of same sex relationships, drives people underground and away from vital health services, including HIV prevention, testing, treatment, and care. To achieve the goal of ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030, it is vital to ensure that everyone has equal access to essential services without fear, stigma or discrimination.
UNAIDS has estimated that not achieving decriminalization of key populations in all countries would result in about 750 000 cumulative new HIV infections from 2020 to 2030.
The decision made in the High Court of St. Vincent and the Grenadines stands in stark contrast to the rulings in Belize, Guyana, Trinidad and Tobago, Antigua and Barbuda, St. Kitts and Nevis and Barbados where the courts ruled that laws which criminalise persons based on sexual orientation and gender identity violate the protected rights to dignity, privacy, personal liberty, freedom of conscience, freedom of expression and protection from discrimination.
Regardless of the outcome of this court decision, UNAIDS holds hope that the courts will serve as a vital last resort for social justice, the protection of human rights and the advancement of public health for improved health and wellbeing for all. UNAIDS work to end AIDS and to leave no one behind will continue in partnership with communities and with all branches of government, including the courts.
Punitive laws obstruct the end of AIDS and ultimately hurt everyone’s health. As we prepare for observance of the tenth anniversary of Zero Discrimination Day on March 1st, 2024, we pay tribute to the courage of communities, and call on all duty bearers to protect the health of all by protecting the human rights for all.
NOTE FOR THE EDITORS:
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals.
ZERO DISCRIMINATION DAY
March 1st this year is the tenth anniversary of Zero Discrimination Day. Upholding everyone’s rights is the responsibility of us all. Everyone can play a part in ending discrimination. On 1 March, and across the whole month of March, events, activities and messages will remind the world of this vital lesson and call to action: to protect everyone’s health, protect everyone’s rights. #ZeroDiscrimination
Contact
UNAIDS Multi-country Office for the CaribbeanRichard Amenyah, Multi-country Director
amenyahr@unaids.org
UNAIDS Latin America and Caribbean
Daniel de Castro, Regional Communications and Advocacy Adviser
tel. +507 6998 3175
decastrod@unaids.org
Our work
Related
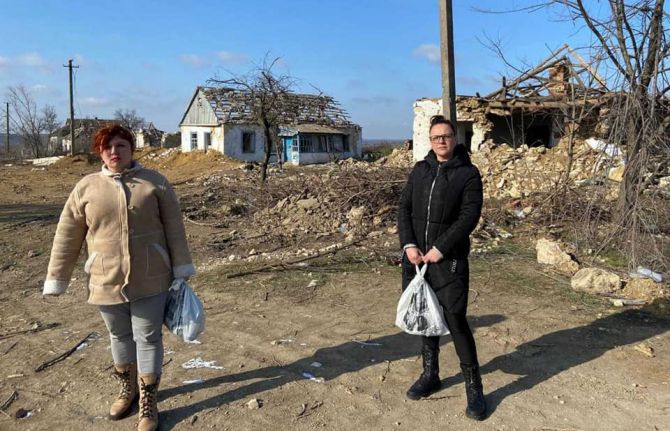





Feature Story
Two years on: UNAIDS supports Ukraine’s commitment to the HIV response
23 February 2024
23 February 2024 23 February 2024Two years of war in Ukraine have resulted in significant humanitarian consequences. Forty percent of the current population of Ukraine,14.6 million people, are in need of humanitarian assistance, 6.4 million refugees have fled the country, and more than 3 million people are internally displaced. People living with and affected by HIV continue to be vulnerable to the effects of the war, even as HIV services have been restored and are functional in most parts of the country.
Russian strikes have continued to wreak havoc on Ukrainian cities, causing death and destruction, impacting access to water, electricity, heating, and health services for millions of civilians.
In addition, there have been 1,570 attacks on health facilities and 630 health facilities damaged.
According to the latest data from The Ukrainian Public Health Center, prior to the war, Ukraine had made significant progress in reducing HIV incidence (-47%) and AIDS-related mortality (-81%) since 2010. Despite the initial disruption to the national AIDS response at the onset of the war, the national AIDS program has gradually resumed routine operations.
As of the end of 2023, the number of patients on antiretroviral therapy (ART) was only slightly below the pre-war figure, standing at 118,348 (130,724 as of February 2022). Additionally, approximately seven thousand patients are known to receive ART abroad. In the last two years, the number of patients on opioid agonist therapy (OAT) increased by 38%, reaching 27,511 people. Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) more than doubled, reaching 12,354 people.
However, in eastern and southern occupied territories data is incomplete or not available. This is true of Donetsk, Luhansk, Zaporizhzhia, Kherson regions, AR Crimea, and the city of Sevastopol. The same occurred in 2023. Despite these challenges, the surveillance system in the government-controlled areas remains operational, ensuring the completeness and quality of data on HIV prevention, testing and treatment services.
In addition, 9.6 million people in Ukraine are estimated to be at risk of or living with a mental health condition, and 3.9 million people are estimated to suffer from moderate to severe symptoms. And there has been an increase in gender-based violence.
Ukraine remains committed to the HIV response through a strong coalition of government, civil society, international organizations, and donors, first and foremost The United States President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) and The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria. This collaboration has secured vital supplies of antiretroviral therapy (ARV), tuberculosis medicines, and opioid agonist therapy (OAT), ensuring uninterrupted HIV treatment and services.
UNAIDS Secretariat, Co-sponsors and UN agencies have joined forces to provide a unified response, ensuring that vulnerable populations, including those on the frontline and in the most severely affected areas, receive comprehensive support. This collaborative effort aims to bridge gaps and address the unique challenges faced by women, people living with HIV and key populations, including the delivery of crucial humanitarian aid and HIV services.
The past two years have been very challenging. Even though the country has managed to maintain HIV services, the unpredictability of what lies ahead has many fearing the worst. Support is needed to ensure sustainability of the AIDS response and to protect key populations affected by the enduring hardships of war.
For more information and more in-depth analysis, read the Situation Report (February 2024)
Watch
Situation Report
War in Ukraine and the HIV response
Region/country
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery
Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery

20 February 2025


Press Release
Member States negotiating the pandemic instrument have an opportunity to save lives and keep the world safe, says UNAIDS
18 February 2024 18 February 2024As Member States enter the next stage of drafting and negotiating a new Pandemics Prevention, Preparedness and Response Accord, and the targeted revision of the International Health Regulations (IHR), UNAIDS underscores the importance of protecting the gains made in the AIDS response and encourages Member States to use that experience to help prevent and respond to future pandemics and health emergencies.
As part of the Sustainable Development Goals and the 2021 UN Political Declaration on HIV/AIDS, world leaders have committed to ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030. COVID-19 increased HIV vulnerability and disrupted HIV service access for millions of people around the world. The colliding pandemics of HIV and COVID-19 also led to significant setbacks in the TB response. This experience illustrated powerfully how the impact of other pandemics has the potential to halt and reverse gains achieved in the fight against AIDS.
HIV remains an ongoing pandemic which would be affected by the impact of future pandemics. The actions necessary to make the world safer from future pandemics are vital for ensuring the end of AIDS as a public health threat and for protecting people living with and affected by HIV. Equally, doing what is needed to end AIDS will help keep the world safer from other pandemics.
At UNAIDS, efforts to support Member States in the pandemic treaty negotiations are rooted in evidence. At UNAIDS, we adhere always and only to facts, science, data and the lived experience of the people in the communities and countries where we work to support and guide the HIV response. We resolutely urge that all who are engaging in the negotiations do the same, standing for evidence, and categorically rejecting any misinformation, mischaracterization, or misattribution. The systematic use of facts and data in the HIV response has built public trust, and hugely contributed to advances in HIV prevention, testing, treatment and care.
Important lessons from the HIV response that can strengthen broader pandemic prevention, preparedness and response include:
- The infrastructure built up and strengthened to respond to the HIV pandemic – from lab systems, surveillance and health information systems, procurement and supply chain management through to community infrastructure and governance approaches – is vital for addressing other pandemics. For example, this infrastructure was widely deployed and played an essential role in helping countries to respond to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Enabling equitable and timely access to scientific solutions, health technologies and medical countermeasures to all those in need is critical for saving lives and ending a pandemic. The role of regulation in ensuring the sharing of technology and know-how for generating local capacities in addressing pandemics is key.
- Tackling the inequalities which drive HIV and other pandemics is key to overcoming them. Closing social and economic gaps within and between countries will help the world to avoid the millions of preventable deaths the AIDS pandemic has seen from being repeated in future pandemics.
- Pandemic prevention, preparedness and response cannot succeed without mobilizing and enabling communities to lead themselves. Investing in community-led mechanisms is critical for successful prevention and response to pandemics.
- Human rights must be at the centre of all actions to prevent and respond to HIV and all other pandemics. The 2021 United Nations Political Declaration on HIV and AIDS, notes the need to “respect, promote, protect, and fulfil all human rights, which are universal, indivisible, interdependent and interrelated.”
- HIV has shown us that beyond being a health issue, a pandemic is a gender, social, economic, security, legal and human rights issue. Whole-of-government, whole-of-society approaches have driven progress in the HIV response. They should be employed at all levels of governance in pandemic preparedness and response.
The gains made and the lesson learnt in the global response to AIDS can help the world to be better prepared for the pandemics to come.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.


Press Statement
UNAIDS Executive Director Winnie Byanyima responds to the passage of the Human Sexual Rights and Ghanaian Family Values Bill in Ghana’s parliament
28 February 2024 28 February 2024Responding to the passage of the Human Sexual Rights and Ghanaian Family Values Bill in Ghana’s parliament, UNAIDS Executive Director Winnie Byanyima said:
“The Human Sexual rights and Ghanaian Family Values Bill, a private member’s bill passed by parliament, has not yet become a law in Ghana.
If the bill does become a law, it will affect everyone.
Ghana is respected as a stable country where the rule of law prevails, a member of the Human Rights Council, and a global leader in fighting inequality. African values and principles of Ubuntu, dignity, non-discrimination, equality, empathy, protection from violence and care for each other shaped Ghana’s independence struggles, and have continued to be at the heart of Ghana’s society and constitutional democracy. Approaches rooted in inclusion of all people have been crucial to Ghana’s progress in the HIV response. To achieve the goal of ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030, it is vital to ensure that everyone has equal access to essential services without fear, stigma or discrimination, and that providers of life-saving HIV prevention, testing, treatment and care services are supported in their work.
If Human Sexual rights and Ghanaian Family Values Bill becomes a law, it will exacerbate fear and hatred, could incite violence against fellow Ghanaian citizens, and will negatively impact on free speech, freedom of movement and freedom of association.
If it becomes law, it will obstruct access to life-saving services, undercut social protection, and jeopardize Ghana’s development success.
Evidence shows that punitive laws like this Bill are a barrier to ending AIDS, and ultimately undermine everyone’s health.”
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.




Feature Story
Countries take practical steps forward towards eliminating discrimination
09 February 2024
09 February 2024 09 February 2024Countries from across the world who have taken practical steps forward towards eliminating discrimination are showing what is possible, UNAIDS has said.
The countries are members of the Global Partnership for Action to Eliminate all Forms of HIV-Related Stigma and Discrimination, which have prioritized and pledged to accelerate the removal of stigmatizing and discriminatory practices, policies and laws across six settings: community, health, justice, education, workplace, and emergency/humanitarian. Recent progress that was made by members of the Global Partnership included:
- In the Central African Republic, the law on the rights of people living with HIV/AIDS was revised with a focus on social protection, opening new opportunities for people living with HIV to access enhanced support.
- In Argentina, the National Law for Comprehensive Response to HIV, STIs and Tuberculosis committed that care and treatment be provided without discrimination.
- In Kazakhstan, the government increased domestic funding to sustain a successful community-led programme for shelter and support for women living with HIV who had been subjected to violence.
- In Ghana, a strong partnership between the government and the community enabled mothers living with HIV and caregivers of HIV-exposed infants and children to benefit from targeted interventions that foster their and their children’s well-being, leading to improved adherence to treatment and linkage to care.
- In Thailand, a national Code of Conduct on HIV prevention and management in the workplace was adopted, and both government and the private sector committed to review HIV policies in line with the new Code of Conduct.
- In Iran, the Ministry of Health issued a bylaw to tackle the stigma and discrimination faced by people living with and affected by HIV. As a result, a protocol on elimination of stigma and discrimination in health care settings was developed to advance access to HIV services without discrimination, including strengthening the referral system.
“The practical steps forward which have been taken by members of the Global Partnership provide hope through action,” said UNAIDS Executive Director Winnie Byanyima. “They show what is possible. They show how it is through protecting the rights of every person that we can protect the health of every person. Progress on rights can power progress towards the end of AIDS.”
38 countries have joined the Global Partnership for Action to Eliminate all Forms of HIV-Related Stigma and Discrimination, and more have expressed interest in joining. More information on the Global Partnership can be found here: https://www.unaids.org/en/topic/global-partnership-discrimination
On March 1st the world will mark the tenth anniversary of Zero Discrimination Day. More information on Zero Discrimination Day can be found here: https://www.unaids.org/en/2024-zero-discrimination-day
Related


Press Statement
UNAIDS mourns the passing of Hage Geingob, President of Namibia
05 February 2024 05 February 2024GENEVA, 5 February 2024—It is with profound sadness that UNAIDS learns of the passing of Dr Hage G. Geingob, President of the Republic of Namibia. President Geingob was a distinguished leader, a tireless advocate for social justice, and a steadfast supporter of efforts to end AIDS.
The Executive Director of UNAIDS, Winnie Byanyima, expressed her deep condolences, stating, "I am deeply saddened by the news of the passing of President Geingob. He was a true people’s leader, a leader I admired and whose guidance I benefitted from. My heart goes out to his family, especially his wife Monica Geingos, the First Lady of Namibia. Africa has lost a giant son. May he rest in peace.”
President Geingob was not only a statesman who was instrumental in the anti-apartheid movement, he was also a compassionate leader who was dedicated to improving the health and wellbeing of the people of Namibia and around the world. Most recently he proposed doubling the value of the cash transfers the Government of Namibia gives monthly to poor and vulnerable Namibians. He was a pan-Africanist leader who was committed to peace, democracy and a united Africa.
President Geingob's dedication to addressing the challenges posed by HIV and to fight inequality were evident throughout his tenure. Under his leadership, Namibia made significant strides in the fight against the HIV epidemic, creating a supportive legal and policy environment.
He positioned the Government of Namibia among the global AIDS leaders, funding more than 70% of the country’s HIV care and treatment from domestic resources. He helped lead global efforts to accelerate actions on Sustainable Development Goal 10 – Reducing Inequalities. Locally, he engaged communities and implemented effective strategies to prevent new infections and provide care and support to people affected by the virus.
UNAIDS acknowledges President Geingob's pivotal role in advancing the global AIDS response, both through his leadership within Namibia and his contributions to international collaborations. His efforts have left an indelible mark on the fight against AIDS, and his vision of ending AIDS in Namibia and across the world will continue to inspire the work of UNAIDS and its partners.
The entire UNAIDS family extends its deepest sympathies to his family, friends, and the people of Namibia during this difficult time. We honour President Geingob's memory and remain steadfast in our commitment to ensure that the progress achieved in the AIDS response continues to benefit people most in need.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Region/country
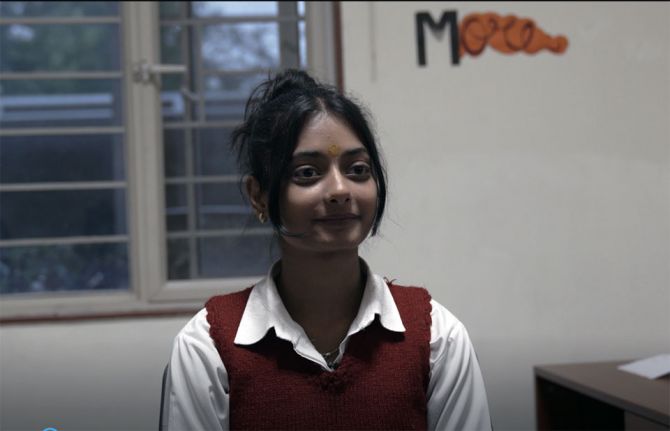

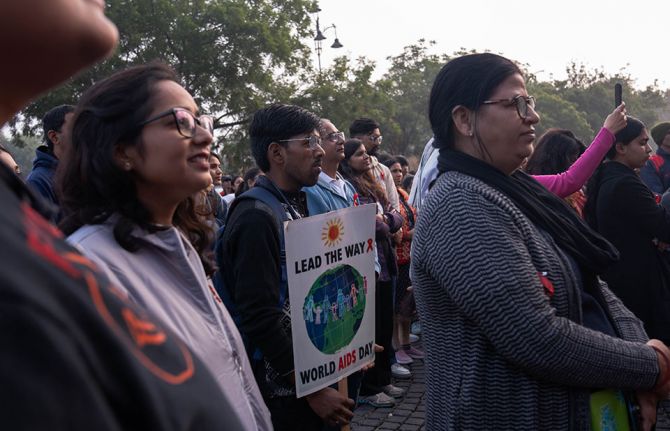


Feature Story
Young people’s inspirational leadership role in India’s HIV response
06 February 2024
06 February 2024 06 February 2024Divyanshi is an enthusiastic 18-year-old Indian girl with an inspiring personal story of courage and resilience. She was diagnosed with HIV at a very young age. She has never given up on her dreams.
“I became aware of my status around 2013-14 but it wasn’t until I moved to a care home that I understood the challenges of living with this virus,” said Divyanshi. “As a person living with HIV, I face stigma and discrimination when a friend or someone else gets to know about my positive status. But I take it as an opportunity to educate people about HIV and break their myths. I want to show the world that I can live a normal, healthy, and happy life as a person living with HIV.”
Divyanshi joined the Positive YUVA Network (PYN)—an innovative community-based organisation striving to uplift young people living with HIV—where she found support and guidance from her peers.
As a network of young people living with HIV, Positive YUVA Network is a community-based organization committed to support young people living with HIV and LGBTQI+ people in India. The organization focuses its efforts on supporting the mental health of the young people living with HIV through its “Buddy System”. This initiative acknowledges the psychological challenges experienced by young people living with HIV and supports them with professional counsellors who provide tailored assistance.
The organization provides skills development opportunities, recognizing that empowering young people living with HIV with practical skills enhances their socio-economic prospects. Through mentorship programs, the Positive YUVA Network aims to instil confidence and self-reliance among the youth, helping young people to redefine their narrative.
At the Positive YUVA Network, Divyanshi discovered her passion for photography and with the help of her mentor, is now interning at a startup, capturing moments of joy and hope. Divyanshi is an inspiration to many in how she shows that no obstacle can deter her from chasing her aspirations.
The Positive YUVA Network also works to reduce stigma and discrimination associated with HIV by raising awareness in schools. For instance, the organization used the most recent World AIDS Day as an opportunity to initiate open discussions and correct myths about HIV and AIDS among school going children with a goal to create a supportive and inclusive environment that fosters understanding and empathy for all people. By fostering empathy and a respect for the rights of everyone, the initiative helps to advance the health of everyone.
Global HIV statistics reveal that 1 out of every 4 new HIV infections globally in 2022 were among young people (15–24 years). Recognizing this demographic vulnerability, a focus on youth-specific interventions is imperative for an effective HIV response.
This community-driven initiative, and many others like this one, is playing a critical role in removing barriers for young people to meaningfully engage in the HIV-response in India. It is a powerful example of how community-led organisations are transforming the AIDS response at grassroots level.
“In India's HIV response, youth-led organizations infuse hope and resilience. These groups, driven by the energy and innovation of young minds, are building a more inclusive and informed society. Rights, recognition and respect are essential for public health efforts to succeed. The impact of organisations like the Positive YUVA Network is not limited to young people living with HIV and LGBTQ+ youth, it benefits everyone,” said David Bridger, UNAIDS Country Director in India. “We all need to recognize the indomitable spirit of these organizations—pillars of strength in our collective journey. Together, let us do all we can to support the vital role of youth-led initiatives as they lead us along the path that ends AIDS,” he added.
Our work
Region/country
Related
 Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia
Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia

24 February 2025
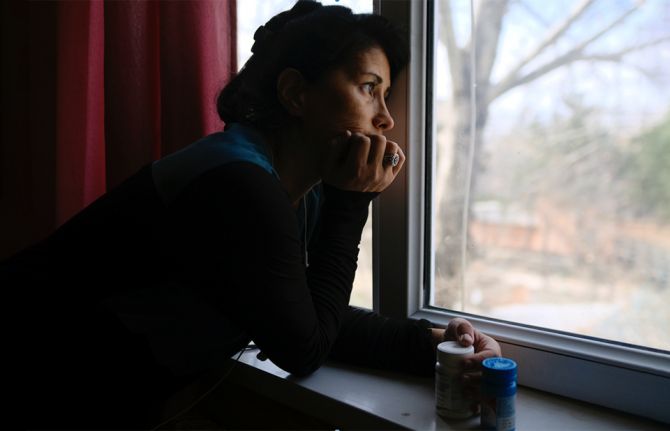


Feature Story
Tajikistan takes a positive step towards decriminalization of HIV exposure and transmission
30 January 2024
30 January 2024 30 January 2024In an important decision of the Plenum of the Supreme Court on December 26, 2023, Tajikistan has marked a significant step towards decriminalization of HIV exposure and transmission in its pursuit of justice for people living with or affected by HIV.
Through a new resolution, the courts are asked to examine more objectively issues related to criminal liability for HIV exposure and transmission under Article 125 of the Criminal Code. The resolution obliges judicial practice to be based on new norms that take into account international standards and recommendations including the Undetectable = Untransmittable concept endorsed by UNAIDS and WHO which asserts that people who are living with HIV who are on antiretroviral treatment and have an undetectable viral load cannot transmit HIV.
Article 125 of the Criminal Code currently criminalizes HIV transmission and exposure with a penalty of up to two years’ imprisonment (Part 1), while transmission by someone aware of their status is penalized with two to five years’ imprisonment (Part 2), increased to five to ten years’ when committed against multiple people or a minor (Part 3).
In some cases, decisions were made solely based on a person’s HIV-positive status, criminalizing people living with HIV rather than ensuring access to HIV services, treatment and support.
More than 70% of people convicted under Article 125 have been women living with HIV. Women living with HIV may be subjected to domestic violence, stigma, and discrimination and do not seek justice in courts, due to the fear of accidental disclose of their HIV status and further criminal prosecution.
“This new resolution is encouraging because it allows for more fair interpretation of existing laws (which is very important) but it does not establish new laws or change the Criminal Code which still criminalizes HIV exposure and transmission. Therefore, it is important to continue advocacy to change the Criminal Code and decriminalize HIV transmission and exposure.” said Tahmina Haidarova, Head of the Network of Women Living with HIV in Tajikistan.
The new move towards a more just legal framework has been the result of collaborative efforts of the Supreme Court and civil society organizations, as well as long-term advocacy of UNAIDS, UNDP, and the Global Fund to fight AIDS, TB and Malaria that reflects a holistic and inclusive approach to addressing the complexities of HIV-related legal matters.
The consequences of a punitive approach, where law enforcement takes precedence over medical professionals, has contributed to the growth of the HIV epidemic in Tajikistan - the number of new HIV infections has increased by 20% over the past 10 years. The percentage of new HIV cases among women has also grown - from 31% in 2011 to 36% in 2022.
International partners, including UNAIDS, UNDP, and the Global Fund, echo the call to repeal laws criminalizing HIV. The negative impact of such legislation on HIV testing rates and adherence to treatment cannot be overstated. An evidence-based approach is crucial for fostering a healthier society.
“Tajikistan's move towards HIV decriminalization marks a positive step towards commitment to justice, inclusivity, and public health,” said Eamonn Murphy, UNAIDS Regional Director for Asia-Pacific and Eastern Europe and Central Asia. “This journey is guided by the principles of compassion, cooperation, and evidence-based policymaking. UNAIDS, together with partners, welcomes the efforts of the Supreme Court to reduce prosecution and humanize the judicial system. UNAIDS will continue to support the country in its journey to fulfil the human rights of all people living with HIV.”
Resources
Region/country
Related
 Status of HIV programmes in Tajikistan
Status of HIV programmes in Tajikistan

05 March 2025
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery
Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery

20 February 2025


