HIV Treatment




Feature Story
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
27 February 2025
27 February 2025 27 February 2025Adrian Lindayag, a Philippines actor, learned he was living with HIV in 2017. But even before then, he’d felt the weight of the disease.
“I’ve lost friends to AIDS, and that is because of the shame and stigma surrounding the virus… the lack of education because they were afraid to get tested. Or, if they did get tested, they just gave up on their dreams, gave up on their lives.”
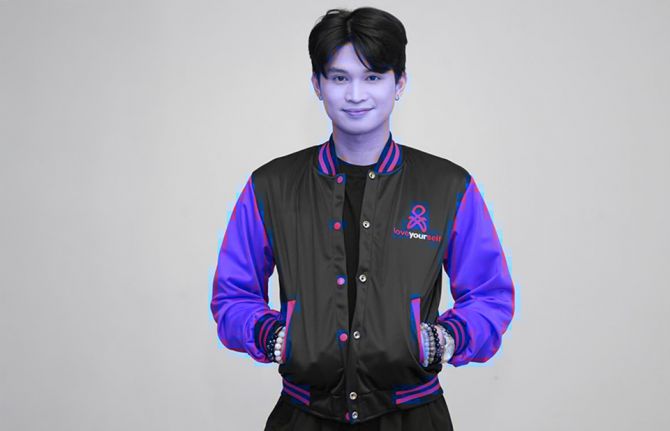
At first, he only discussed his diagnosis with his family and medical team. But last year he made the decision to go public, becoming a LoveYourself U=U Ambassador.
U=U is short for Undetectable = Untransmittable. It means that when a person living with HIV, adheres to effective antiretroviral treatment, the virus in their blood reduces to a level that is undectable, bringing the chance of passing the virus on to zero.
“I honestly didn't know about the concept of U=U before learning about my HIV status. It was my doctor who told me about it, and it changed my life radically. It gave me hope that I'll be able to still live a normal and healthy life,” Mr. Lindayag explained.
Dr. Jakkrapatara Fair Boonruang is a research physician at the Institute of HIV Research and Innovation (IHRI) in Bangkok, Thailand. He reflects that U=U has transformed the way he counsels newly diagnosed patients.
“U=U changed my clients’ lives,” he said. “Before, providers would advise them that antiretroviral treatment will keep them alive and healthy. But there was no sense of returning to who they were before the infections. U=U actually changes that. It means they can fully enjoy sexual intimacy, and mothers can deliver their babies without the fear of transmitting the virus. It has been a mantle of hope and empowerment.”
In 2014, Thai researchers joined peers in Australia and Brazil for the Opposites Attract Study. That research tracked couples in which one person was HIV-negative and the other was living with HIV but had achieved an undetectable viral load through successful treatment. It confirmed that after two years of unprotected sex, there were no cases of HIV transmission between more than 300 couples.
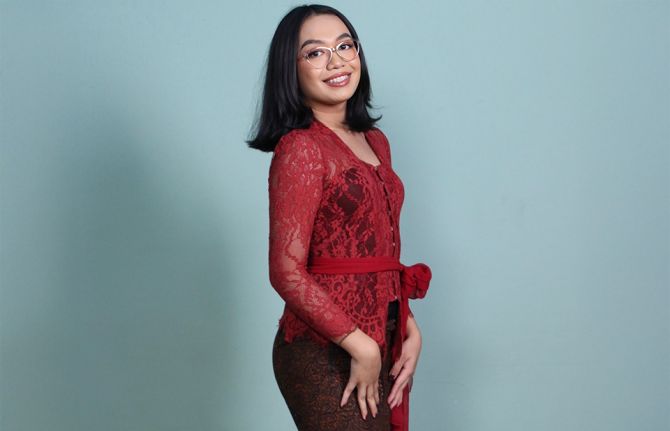
Although the U=U concept has been established as scientific fact for over a decade, the word has not gotten out to the wider world. Even some people living with HIV weren’t informed during counselling. Bella Aubree, an Indonesian activist, is one of them. When she learned her HIV status at age 16, she wondered whether she would die soon. She learned about U=U online and the message gave her hope.
“At the time I felt bored with taking ARVs (antiretroviral therapy) every day. But my motivation came from knowing at some point I will be undetectable, which means untransmittable,” she explained.
For Shan Ali, a Dostana Society peer counsellor from Pakistan, while the U=U concept has transformed his health and outlook, the knowledge hasn’t shifted attitudes among his family members.
“In Pakistan right now there are only two sets of people who know about U=U. One is the service providers and the other is people living with HIV. The general public has no idea,” Mr Ali explained. “I have tried bringing my family in for counseling, but they still discriminate towards me. They even make me eat with separate utensils. I feel very isolated and stigmatized. But in my work with community, I feel a sense of purpose.”
Karun Lama, a communications specialist for the Seven Alliance, is HIV-negative but lost both her parents to AIDS. For her, U=U holds the promise of a regular life and family with her boyfriend who is living with HIV.
“In India, where family and relatives' consent is very important, it was very difficult for us at first to make them understand because my partner's family and relatives were scared and concerned for me. They thought that my partner is putting my life at risk and he should get married to a person living with HIV only. But we've sensitized them about U=U and they have begun to understand that we can also live a life together happily and he won't transmit HIV if his viral load is undetectable,” Ms Lama said.
Eamonn Murphy, Regional Director of UNAIDS Asia Pacific and Eastern Europe Central Asia, saluted the courage of these and other community leaders working to raise awareness about the power of the U=U concept.
“Treatment saves lives. But it can also prevent new infections and transform the way we think about people living with HIV and how they see themselves,” said Mr Murphy. “This Zero Discrimination Day, we recognize the critical role of communities in spreading awareness, supporting adherence and challenging stigma and discrimination. We must ensure this essential work is facilitated and financed.”
With support from communities, researchers and UNAIDS Goodwill Ambassador for Asia and the Pacific, Miss Universe 2015, Pia Alonzo Wurtzbach, UNAIDS is leveraging the U=U message to help end HIV stigma and discrimination. On Zero Discrimination Day (1 March). UNAIDS welcomes everyone to join by sharing these messages and joining the U=U song and dance challenge on social media. #UequalsUDance #EndHIVstigma
UNAIDS RST-AP Goodwill Ambassador Pia Wurtzbach Explain U=U
A fun demo of how U=U impacts HIV transmissions
U=U. What is it and how can it help us end HIV stigma?




Press Release
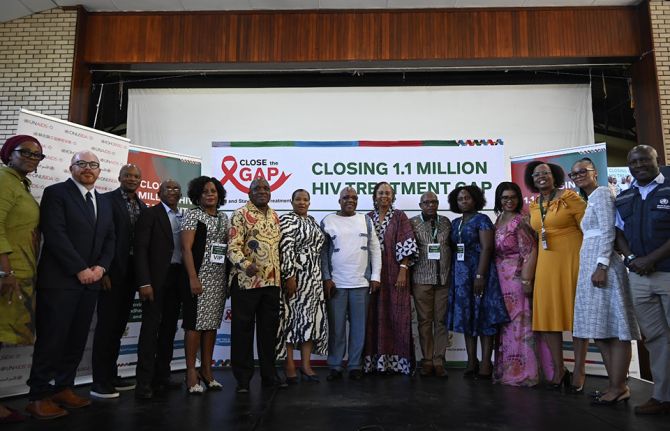
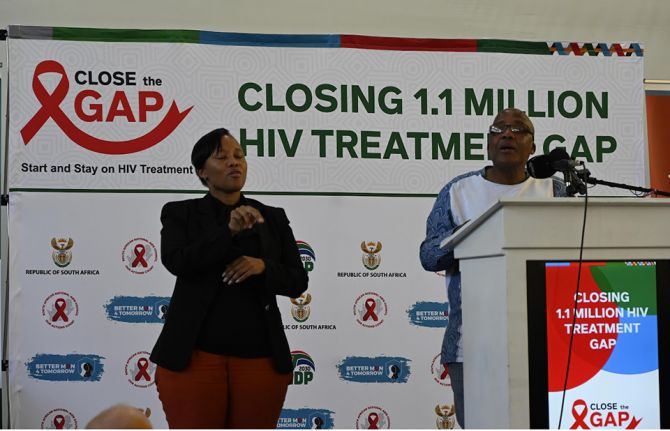
Bold new initiative to put an additional 1.1 million people living with HIV on treatment puts South Africa on the path to end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030
25 February 2025 25 February 2025JOHANNESBURG/GENEVA, 25 February 2025—UNAIDS welcomes South Africa’s plan to put an additional 1.1 million people living with HIV on life-saving treatment by the end of 2025 as a significant step towards ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030.
At the launch of the Close The Gap campaign in Soweto South Africa’s Minister of Health, Aaron Motsoaledi, said, “We should not accept that AIDS is here forever. It is not. We want to end it. It’s all in our hands and it depends on our will. We can stop it so that in future we can work on other diseases. We are taking the last mile.”
UNAIDS described the plan as inspiring.
“This plan protects the human rights of people living with HIV, offering them hope and an opportunity to live healthy and fulfilling lives by getting them onto life-saving medication,” said UNAIDS regional director for East and Southern Africa, Anne Githuku-Shongwe. “As South Africa embarks on this inspiring journey, be assured that UNAIDS will continue its strong partnership with the government of South Africa to ensure that everyone living with and affected by HIV is protected through proven scientific and evidence-based interventions.”
In South Africa, there were 7.7 million people living with HIV in 2023, with 5.9 million people already accessing lifesaving antiretroviral treatment which enables them to live healthy and productive lives. Without treatment, people living with HIV are at risk of contracting opportunistic life-threatening infections because of their weakened immune system.
At the launch, Gordon Didiza, a young man living with HIV urged other men to test for HIV and to start treatment if necessary. “I am grateful for treatment because it has kept me alive and healthy since I was diagnosed with HIV,” Mr Didiza has also survived tuberculosis.
While South Africa has the highest number of people living with HIV in the world, it has already made enormous progress in expanding the number of people accessing treatment for HIV, resulting in a 66% decrease in AIDS-related deaths since 2010. New HIV infections have also fallen by 58%. When people are taking effective HIV medication they no longer transmit the virus, meaning that treatment rollout alongside other HIV combination prevention measures, contributes to lower rates of infection and future cost savings.
Domestic resources account for around 74% of South Africa’s HIV response, which demonstrates the political will and commitment of the country’s leadership to end the AIDS pandemic. However, many services still rely on funding from the US government which accounts for around 17% of the country’s financing for the AIDS response. The sudden 90-day pause to US foreign assistance is putting some services at risk, especially HIV prevention services for young women and adolescent girls and other marginalized communities. More than 800 young women and adolescent girls aged 15—24 become infected with HIV every week in South Africa.
UNAIDS is working closely with the South African government and other partners to mitigate the impact and ensure the continuity of HIV services.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Region/country

Feature Story
A crisis unfolding: hard-won progress in Ethiopia’s HIV response at risk
13 February 2025
13 February 2025 13 February 2025Ethiopia has made significant progress in its HIV response in recent years and is on track to reach the UNAIDS 95-95-95 targets with 90% of people living with HIV in the country being aware of their HIV status; 94% of those diagnosed with HIV receiving antiretroviral (ARV) therapy; and 96% of people on ARV therapy achieving viral suppression.
But now, that progress is at risk. The recent pause in United States foreign assistance poses a direct threat to the lives and well-being of thousands of people living with HIV in Ethiopia and millions globally. Critical services are grinding to a halt, leaving people who rely on them facing an uncertain and dangerous future.
Ethiopia is heavily reliant on external funding for its AIDS response. PEPFAR provides 53% of HIV funding in the country. In 2023, UNAIDS’ estimates show that there were 610 000 people living with HIV in Ethiopia, 510 000 of whom were accessing antiretroviral treatment.
For women living with HIV, uncertainty is growing. Limited and unclear communication from healthcare providers and policymakers has left them in the dark about treatment changes, medication availability, and service disruptions. With no clear answers, they are forced to rely on rumors, fueling fear and anxiety.
“We don’t know what’s happening. Are services being cut permanently? Will we still get our medication next month? No one is telling us anything,” one woman shared.
To make matters worse, case workers and counsellors—once a vital source of medical and emotional support—are disappearing. These professionals were more than healthcare providers; they were trusted confidants who ensured women received care in a stigma-free environment. Their absence is leaving many feeling abandoned.
“They understood our struggles, checked in on us, and made sure we had what we needed,” another woman explained. “Without them, we feel forgotten.”
As services become increasingly unreliable, distress and fear are taking hold.
Shortages and desperate measures
Funding cuts bring shortages, and for women living with HIV, the fear of running out of medication is overwhelming. Access to antiretroviral therapy (ART) is essential—it keeps people alive. Yet many are already facing supply disruptions, and whispers of medication shortages are spreading panic.
“If I can’t get my medicine, what happens to me?” one woman asked. Women living with HIV who have been healthy for years now fear an uncertain future where their treatment is no longer guaranteed. People living with HIV who do not access antiretroviral therapy will eventually develop AIDS and die. To cope, many have resorted to stockpiling medication, traveling long distances and spending entire days at clinics in hopes of securing extra supplies. While understandable, this survival strategy comes at a heavy cost—disrupting work, family life, and daily routines. No one should have to live in fear of their next refill. The urgent need for stable, uninterrupted HIV treatment cannot be overstated.
Adding to the crisis, shortages extend beyond medication. The dwindling supply of test kits, including viral load tests, is threatening the future of diagnosis and monitoring. These tests are crucial to ensure that people living with HIV maintain undetectable viral levels, reducing transmission risks and protecting their health.
Fears have also been expressed around the availability of medications for HIV prevention, particularly for the prevention of vertical transmission of HIV. If the current pause in the supply of medical resources continues, the availability of these vital medications could be severely compromised, putting the lives of women and children at even greater risk. For women living with HIV who are pregnant, a lack of lifesaving medications for themselves also means their children can be born with HIV even though this is entirely preventable.
Without test kits and prevention measures, undiagnosed and untreated cases could rise dangerously. “We can’t afford to go backward,” one woman said.
A Plea for Action
The voices of these women reveal a stark and urgent reality—funding cuts have left people living with HIV in a state of uncertainty, with no clear path forward.
"Urgent intervention is needed,” stressed Tina Boonto, Country Director for UNAIDS Ethiopia. “UNAIDS is gathering information and developing funding solutions to address the shortfall, with proposals for both the government and external partners to ensure continuity of critical services. We hope Ethiopia's government will step up and lead in covering these essential services. We must act now to safeguard gains that have been made and succeed in securing sustainable support to people living with HIV."
While the future remains uncertain, one thing is clear: without swift action, the hard-won progress in Ethiopia’s HIV response is at risk.
Impact of recent U.S. shifts on the global HIV response
Region/country
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Documents
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
The objectives of the research presented in this report were to identify case studies of community-led HIV-related health and social inclusion service delivery organizations in eastern and southern Africa; describe the typologies of the services provided; and identify evidence of their service delivery and contribution beyond HIV, including advancing universal health coverage.
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025


Press Statement
UNAIDS welcomes the decision by the US Secretary of State to continue life-saving HIV treatment and convenes partners to assess and mitigate impacts on HIV services
29 January 2025 29 January 2025GENEVA, 29 January 2025— The United States Secretary of State, Marco Rubio, has approved an “Emergency Humanitarian Waiver”, which will allow people to continue accessing HIV treatment funded by the US across 55 countries worldwide. More than 20 million people living with HIV, representing two-thirds of all people living with HIV receiving treatment globally, are directly supported by the United States President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) - the world’s leading HIV initiative.
“UNAIDS welcomes this waiver from the US government which ensures that millions of people living with HIV can continue to receive life-saving HIV medication during the assessment of US foreign development assistance,” said UNAIDS Executive Director, Winnie Byanyima. “This urgent decision recognizes PEPFAR’s critical role in the AIDS response and restores hope to people living with HIV.”
In recent days, the US Department of State announced an immediate 90-day funding pause for all foreign assistance, including for funding and services supported by PEPFAR. The executive order announcing a “90-day pause in United States foreign development assistance for assessment of programmatic efficiencies and consistency with United States foreign policy” was one of the first major foreign policy decisions of the new administration. This waiver approves the continuation or resumption of “life-saving humanitarian assistance” which applies to core life-saving medicine and medical services, including HIV treatment, as well as to supplies necessary to deliver such assistance.
UNAIDS will continue efforts to ensure that all people living with or affected by HIV are served and that other key components of PEPFAR’s life-saving efforts, including service delivery and services for HIV prevention, care, and support for orphans and vulnerable children are continued.
UNAIDS is serving in its essential role to mobilize and convene partners, governments, and communities across the globe at the country level to assess and mitigate the impact of the pause on the continuity of essential HIV services.
UNAIDS has encouraged President Donald J. Trump to prioritize the U.S. Government’s leadership in the global HIV response to achieve the shared goal of ending AIDS.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Region/country


Feature Story
Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment
21 January 2025
21 January 2025 21 January 2025Grabbing his helmet, Hadi Timotius gets in the back of his colleague’s scooter to pay a routine visit to a woman who is taking her HIV treatment again. Hadi oversees the ‘Lost and Link’ initiative at JIP, a national network of people living with HIV in Indonesia.
Region/country
Related
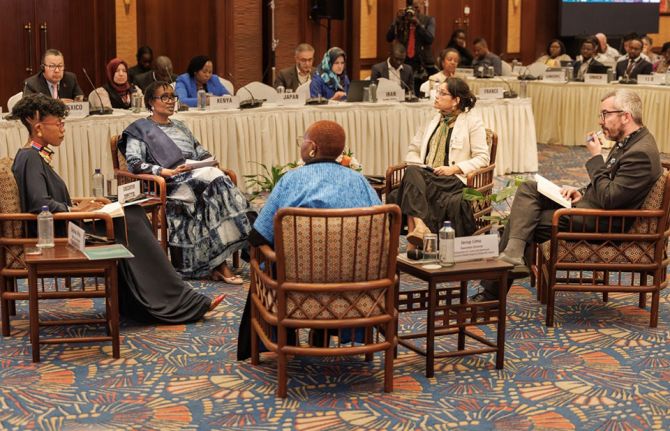



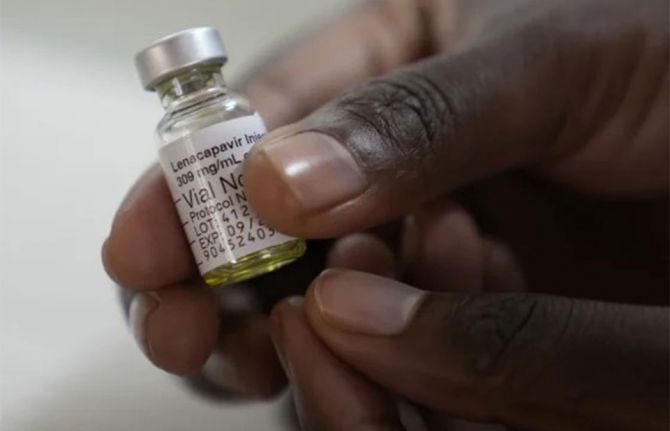

Press Statement
Global leaders in the HIV response call for access to long-acting medicines
10 December 2024 10 December 2024NAIROBI, 10 December 2024—Today, at the 55th Programme Coordinating Board for the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS), HIV leaders from across the world called for access to long-acting medicines for everyone who would benefit from them, to build toward a new era in the AIDS response.
Over the last two years, scientific breakthroughs have brought to the fore a new class of anti-HIV medicines with long-acting effects, allowing people at risk of HIV infection and those living with the virus to take medicines every few months. One is injected just twice a year. Recent studies have shown these medicines to be among the most effective ever developed. One study showed zero new infections among young African women using long-acting prevention drugs, while a study among key populations showed them more effective than oral medicines. Another study highlighted at the session showed encouraging results using long-acting HIV treatment in low- and middle-income countries.
At the “Leadership in the AIDS Response” session at the UNAIDS board, government officials, researchers, manufacturers, and civil society called for accelerating global access to use these scientific breakthroughs to interrupt the continuing AIDS pandemic. Despite existing HIV prevention tools, in 2023 an estimated 1.3 million people newly contracted HIV – two every minute. Despite HIV treatment, there is still one AIDS-related deaths every minute.
Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS, said: “We can usher in a new era by connecting technological innovation with access for all. Let us act boldly together, bring down the curve of new infections, and dramatically accelerate the HIV response.
“Let us learn from the painful lessons of the past so that we write a new story now. In the late 1990s and early 2000s, even after antiretroviral medicines were proven to be effective and rolled out in high-income countries, 12 million people on this continent still died waiting for those drugs. We can - and must – do better with long-actings. We urge the companies producing these medicines to expand their generics licenses. And we support governments making use of all their legal flexibilities to get access to affordable medicines.
“The usual trajectory is that the Global South waits years before the science reaches them. What if we do not wait for years, what if we ensure that science is treated as the public good it is? What if we disrupt the far too slow trajectory we are on and shift to a trajectory that accelerates progress, ends the pandemic, enables sustainability, and can be a model for the world?"
Secretary Ethel Maciel, Secretary of Health of Brazil, said: “Brazil has a long history of making use of technology in the HIV response. The possibility of having new long-acting medicines in the global response is a great opportunity. But we have the huge challenge of the high cost of these medicines, and the difficulty for a range of countries, including ours, to access them.
“Brazil is committed to work together in the fight to ensure that this new technology is made available to all people all over the world who are at risk of and living with HIV.”
Dr Cissy Kityo, Executive Director of the Joint Clinical Research Centre, Uganda, a leading scientist working on trials of long-acting medicines said: “We have these fantastic new tools. The technology of long-acting ARV’s antiretrovirals is remarkable. The evidence is now clear that long acting medicines will be game-changers for both prevention and treatment. The science is in, the question is how well we will use it.”
Mr Javier Padilla Bernáldez, Secretary of State for Health, Spain, said: “This new long-acting technology puts us in an exceptional situation, not an ordinary one, an opportunity that we cannot afford to miss. Long-acting medicines can change the landscape of the HIV response. But if this game-changing innovation did not reach the people it would be a nothing-changer!
“We need to remember the 2000s’ fight for universal access. We cannot repeat the same mistakes and delays of before. We need to ensure that no countries should be pressured if they choose to use the safeguards in the TRIPS agreement. The inequality gap is a global problem. We need a universal perspective, so that all countries, including middle-income countries, are included.”
Dr Sylvia Vito, Africa Head of EVA Pharma, a company in Egypt licensed to produce a generic version of lenacapavir, said: “We are a company that will not sit comfortably, but rather be in a good hurry to support the unmet HIV medical needs for our people. We intend to move fast on product development, production, and eventual registration. It is our intention that high quality long-acting generic ARV medicine will not only be available, but made accessible and affordable as well. We intend to beat the current standard of care in HIV treatment and prevention by going further to improve on the current options for patients in low and middle-income countries.”
The importance of generic production was central to the interventions of speakers. Several speakers noted the obstacle that much of Latin America, a region of rising HIV infections, has been excluded from companies’ voluntary licenses for generic versions. This is despite Brazil, Peru, Mexico and Argentina participating in clinical trials. Speakers highlighted the importance of using TRIPS flexibilities for enabling access under World Trade Organization rules, which can enable governments to supply its citizens with generic versions of patented treatments either through domestic production or imports. In the 2021 Political Declaration on HIV/AIDS, countries committed to make use of TRIPS flexibilities, specifically geared to promoting access to medicines.
Although Gilead Sciences, the producer of lenacapavir, one of the new class of long-acting medicines, has not yet announced the price of its product for use as PrEP, it costs around $40,000 per person per year in the United States where it is used for treatment. However, experts have estimated that it could be produced and sold for $40 per person per year, in line with UNAIDS estimates for sustainable pricing in low- and middle-income countries. Speakers highlighted opportunities to bring down the price of these medicines through generics, expanded local and regional production, and the use of TRIPS flexibilities by member states.
One important opportunity for progress emphasized by speakers was to build on the progress on multilateral collaboration made by Brazil, which as chair of the G20 in 2024, successfully secured worldwide support for the Global Coalition for Local and Regional Production, Innovation and Equitable Access, laying the foundations for a greatly expanded and more equitable access to medicines.
Speakers noted also the importance of choice, and of widening access to a range of new technologies, of which lenacapavir is just one. Speakers highlighted important current innovations including 2-monthly injectable cabotegravir and a three-month dapivirine vaginal ring, as well as new technologies currently in the pipeline including a once-a-month pill may move into phase 3 trials next year.
Reinforcing the importance of accelerating access to long-acting medicines, The New England Journal of Medicine has today published an article by UNAIDS Executive Director Winnie Byanyima, Linda-Gail Becker of the Desmond Tutu HIV Centre, and Matthew Kavanagh of Georgetown University’s Center for Global Health Policy and Politics, entitled “Long-Acting HIV Medicines and the Pandemic Inequality Cycle — Rethinking Access”.
The article showed that the “pandemic inequality cycle” in HIV has usually meant a decade delay between access to breakthrough HIV technologies in the global North and the global South.
In their article the authors write: “The world may look back on 2024 as a pivotal time in the fight against AIDS — the start of a revolution in the global biomedical response to HIV using long-acting antiretroviral medicines. Whether they will do so depends on whether policymakers and pharmaceutical companies avoid repeating past mistakes.”
The authors call for “a nonlinear approach to global access to ARVs that combines far more rapid sharing of technology, decentralized global production, and research and development of products that meet the needs in Africa, Asia, Latin America, and the Caribbean.”
They highlight the need for progress on long-acting treatment as well as prevention and “to break the long-standing pattern of failing to get HIV technologies to the people who need them most, to stop playing catch-up, stop accepting that innovations must reach people in the Global South years late, and use long-acting medicines to help end the pandemic.” The article is available at https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMms2412286
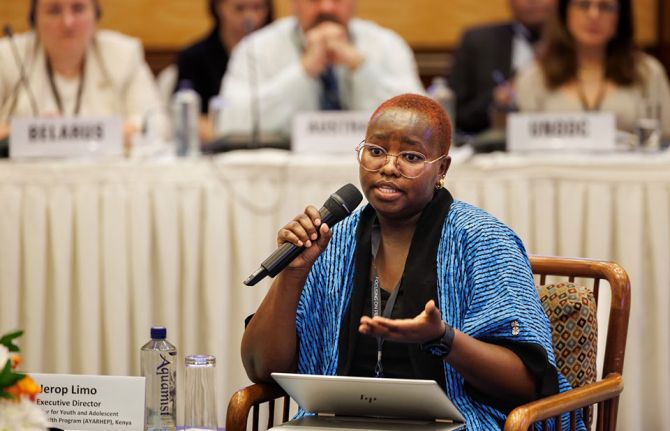
The importance of long-actings, and what is at stake in the discussions on access, was summed up by Jerop Limo, a 26 year old Kenyan activist born living with HIV who is Executive Director of the Ambassador for Youth and Adolescent Reproductive Health Program (AYARHEP):
“Taking a pill every day is not easy. It is a constant reminder of being different, and the stigmatising and shaming we experience because of it can discourage us from taking our medicines.
“This is not just about convenience. Young people living with HIV, and young people at risk of HIV, are clear: with all the pressures we face, long-acting medicines would help us stay on the medicines and help transform, and save, our lives.
“We deserve to live, and to live fully. We can’t have access on paper only. We need access for all people in all countries.
“I am inspired to see leaders coming together to centre communities and to call for access to long-acting HIV medicines. With partnership we can do this. We don’t have time to wait.”
The UNAIDS Programme Coordinating Board brings together governments, civil society and the United Nations to help guide the HIV response. UNAIDS sees the development of long-actings as a vital disruptive innovation.
“The arrival of long-acting injections is a game-changer which can help prevent millions of new HIV infections, if we ensure access to all who would benefit from them,” said Ms Byanyima. “Today, in Nairobi, leaders in the global HIV response took a bold and vital step forward on the path to access for all.”
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Documents
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
Suggested citation. UNAIDS DATA 2024. Geneva: Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS; 2024. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. Related: The 2024 global AIDS report The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads, released 22 July 2024, is available here.
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025
Documents
Take the rights path to end AIDS — World AIDS Day report 2024
26 November 2024
The world’s decades-long response to HIV is at an inflection point. Despite successes, the world is currently not on track to end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030. Press release | Download full report | Download short version
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025
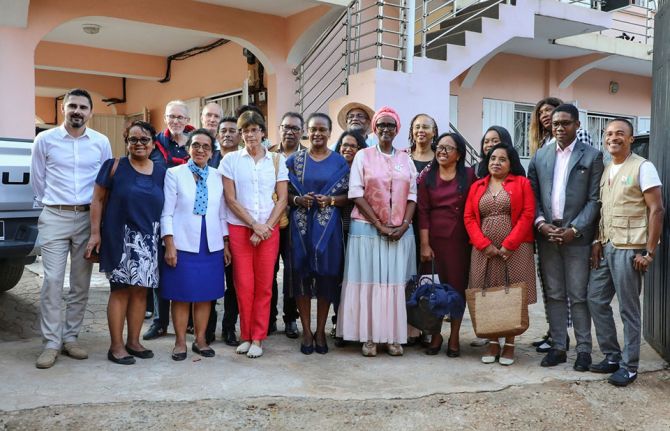
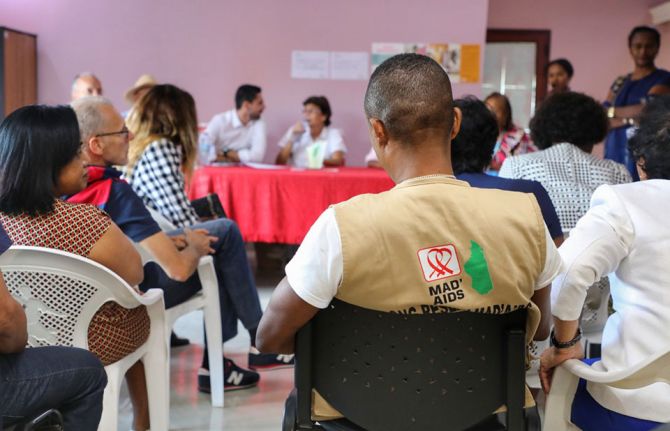
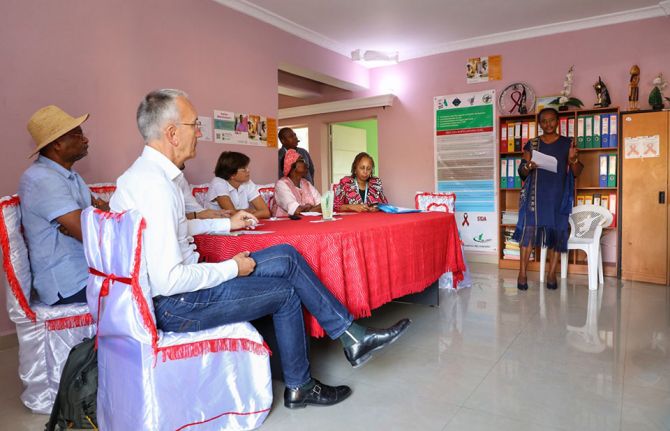




Press Release
UNAIDS calls for global solidarity to strengthen Madagascar’s HIV response to end AIDS as a public health threat
21 October 2024 21 October 2024GENEVA, 21 October 2024—The Executive Director of UNAIDS Winnie Byanyima is calling for accelerated global solidarity to strengthen Madagascar’s response to HIV, including preventing new HIV infections and expanding access to treatment, to end AIDS as a public health threat. Ms Byanyima is visiting the country between 19–24 October to support its response to the HIV epidemic. Madagascar has seen dramatic increase in new HIV infections since 2010 and a 158% increase in AIDS-related deaths over the same period. UNAIDS is concerned about what appears to be a dramatic increase in new HIV infections.
Ms Winnie Byanyima’s visit to Madagascar coincides with that of H.S.H Princess Stéphanie of Monaco, who is visiting Madagascar through the work that she does with Fight AIDS Monaco around the world, including in Madagascar, to end AIDS as a public health threat. Fight AIDS Monaco has been supporting Madagascar’s efforts to prevent new HIV infections, including ending stigma against people living with HIV and galvanising international solidarity to support efforts to end AIDS.
“Madagascar is experiencing a rapid increase in the number of new HIV infections in communities, in stark contrast to the regional trend where new HIV infections are declining,” said Ms Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “Madagascar’s pandemic is driven by gaps in HIV prevention and glaring inequalities which must be urgently addressed.”
In 2023 there were an estimated 76 000 people living with HIV in Madagascar and around 3100 people died of AIDS-related illnesses. Gaps in data gathering and weak surveillance systems make estimating the scale of the pandemic difficult. Stockouts of HIV testing kits and limited access to testing facilities further hinder accurate data collection in communities.
In addition, the majority of people living with HIV do not have access to treatment. Only 22% of the estimated 76 000 people living with HIV in Madagascar had access in 2023.
In northern Manakara HIV testing campaigns by the Ministry of Health have shown urban HIV prevalence rates ranging from 3% to 18% among the population. There is a need to strengthen comprehensive data gathering to better inform the national HIV response to effectively tackle the pandemic.
UNAIDS has been actively supporting Madagascar’s HIV response, especially in strengthening the surveillance systems to ensure more accurate and comprehensive data collection. UNAIDS has also been supporting the implementation of HIV testing and counselling services and helping to expand access to antiretroviral therapy.
Madagascar is one of the most unequal countries in the world, a factor which is driving new HIV infections. In 2023, the World Bank estimated the country’s poverty rates at 62.6%. Madagascar has been hit by cyclical natural disasters including drought in the south and cyclones, making it difficult for the country to recover and mount an effective response to HIV.
“Madagascar can scale up its response to HIV but urgently needs technical and financial support from the international community to ensure that HIV prevention commodities, including condoms, testing kits and antiretroviral treatment are available to everyone in need,” said Ms Byanyima.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.












