Latin America


Feature Story
Honduras’ HIV response at risk due to U.S. freeze of foreign assistance
26 February 2025
26 February 2025 26 February 2025Honduras' HIV response is experiencing critical disruptions due to the U.S. funding pause for many HIV services. Approximately 100 healthcare workers had stopped providing lifesaving services following the initial U.S. stop-work-order last month, reducing access to essential HIV services like testing, prevention, and treatment for people living with HIV. These interruptions in access to HIV services create great individual – and public - health risks. While some affected healthcare workers were instructed that they could resume work on 24 February, it is not clear how many of them returned to work. It is estimated that approximately 20 000 people live with HIV in Honduras. The country’s HIV response relies on external financial support for prevention among key populations. The Global Fund, PEPFAR and USAID have been supporting the country’s efforts to end AIDS as a public health threat.
Community-based organizations are struggling to fill the gap due to severe resource shortages, which compromise service quality and continuity at community level. Additionally, the disruption of prevention programs has increased the risk of new HIV infections, especially among key populations. This is compounded by the recent suspension of PrEP distribution for LGBTQ+ people, who are among the population disproportionately affected by HIV. The ongoing disruption to the country’s HIV response could reverse the progress Honduras has made in the past years in reducing new infections rates.
The funding pause has also halted multiple initiatives designed to ramp up the country’s HIV response, including the cancellation of targeted HIV prevention campaigns aimed at reducing new HIV infections especially among key populations. These programs were meant to be mainly led by local civil society organizations. UNAIDS has been working with both the government and community-led organizations in supporting the country to end AIDS through scientific and evidence-based technical interventions to end AIDS as a public health threat.
Region/country
Related
 Comprehensive update on HIV programmes in South Africa
Comprehensive update on HIV programmes in South Africa

25 February 2025
 Zambia - an HIV response at a crossroads
Zambia - an HIV response at a crossroads

24 February 2025

Feature Story
The critical impact of the PEPFAR funding freeze for HIV across Latin America and the Caribbean
19 February 2025
19 February 2025 19 February 2025The U.S. decision in January to freeze all funding for U.S. foreign assistance, including for the U.S. President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR), has had a critical impact on several countries in Latin America and the Caribbean, exacerbating existing challenges in the HIV response. More than 20 countries in the region rely on these funds to deliver HIV treatment, prevention, and care services, including community-led services focused on the most discriminated and marginalized communities.
Following the decision to freeze all U.S. funding for foreign assistance, the U.S. Government issued a waiver allowing some funding to support lifesaving services. However, confusion about which services may be supported and a lack of support for some services means the situation remains critical, posing a serious risk of setbacks in the AIDS response in the region. While some key treatment services and prevention of vertical transmission have been gradually coming back into operation, most countries have been facing disruptions in their HIV treatment programs.
The lack of funding has led to a significant decrease in community-led HIV prevention efforts, a reduction in treatment adherence, counseling, and social support and monitoring activities. Consequently, there are increased risks of new HIV infections, of higher mortality rates, and a deterioration in the quality of care for people living with HIV, directly impacting their capacity to access treatment and to achieve viral suppression – crucial steps towards the global target of eliminating AIDS as a public health challenge by 2030.
In Colombia and Peru, the freeze has severely affected migrants and refugees, who are estimated to have an HIV prevalence two times higher than the general population. Approximately 4,000 migrants and refugees are receiving antiretroviral treatment (ART) in Colombia thanks to the government efforts and cooperation funds, but the withdrawal of such resources is directly impacting this vulnerable group and the country's capacity to include them in the health system. One community-led organization supporting HIV services among migrant and LGBT communities had to end contracts for 40 out of 70 team members, significantly reducing their capacity to provide essential services to reach such populations.
In the Dominican Republic, even though the government guarantees access to antiretroviral treatment, the pause in PEPFAR funding has left thousands without access to essential HIV services. PEPFAR supports around a third of HIV care services, including PrEP services, health human resources, and laboratory networks. The reduction in community assistance has made it difficult for people to access their medications, especially those who live far from care. The quality of services offered by the Comprehensive Care Services (known by the acronym SAI in Spanish) in the Dominican Republic has been highly compromised, with many staff and services entirely dependent on PEPFAR funds.
El Salvador has also been impacted, with PEPFAR projects supporting comprehensive HIV care clinics now suspended. This has caused a slowdown in care, and the opportunity for new diagnoses and early initiations of antiretroviral treatment is likely lost.
In Guatemala, the HIV epidemic is mainly concentrated among key populations such as transgender individuals, gay men and other men who have sex with men, and sex workers. The distribution of PrEP for these groups has been severely disrupted, with many organizations that rely on U.S. Government funding suspending their work. The reduction of personnel, including medical staff as well as outreach workers that were funded through PEPFAR has resulted in people being unable to access HIV prevention and treatment services.
Haiti has seen a significant impact on its HIV response, with PEPFAR covering around 60% of the national response. The stop-to-work order has thrown the response into disarray, causing anxiety for the 127,000 Haitians living with HIV who are on treatment. In the context of the humanitarian crisis and gang violence, more than 1 million people are now internally displaced in Haiti, many of them displaced multiple times– among them women, girls and children. Escalating violence has also led to the closure of 39% of health facilities, including two of the capital’s three major hospitals. Access to healthcare has never been more limited. The quality-of-service delivery of medicines has also been affected, with approximately 5,000 health workers receiving directives to stop working.
In Jamaica, 70% of HIV resources come from external sources – with PEPFAR covering around 50% of services. The pause in funding has raised concerns about the delivery of HIV prevention services for at risk populations delivered via civil society organizations. Civil society groups have reported that their institutional stability and survival are at risk, with many unable to guarantee the continuous employment of their field staff in charge of liaising with the most discriminated and affected populations who need HIV services.
In Panama, the suspension of a study on recent HIV diagnoses and the halt in laboratory sample transportation have further limited essential diagnostic and monitoring services. The country had already been facing significant disruptions, particularly among the indigenous Ngäbe-Buglé population, who are expected to face increased obstacles to accessing HIV services. In 2023, despite representing only 5% of Panama's population, the territory, which is home to approximately 225,000 residents, accounted for 30% of the nation's AIDS-related deaths among individuals aged 29 or younger, as reported by the Panama Ministry of Health.
In Brazil, on the other hand, the Unified Health System (SUS) guarantees uninterrupted universal and free access to health services, including HIV diagnosis, treatment and prevention for all people living in Brazil. The “A hora é agora” project, carried out in five capital cities with PEPFAR resources, worked to provide specific services such as doctors, reception and delivery of antiretroviral drugs and PrEP in addition to public health services, so the national response to HIV was not impacted by the cut in resources.
Latin America is one of the three regions in the world where new HIV infections have increased since 2010, with a rise of 9%, which highlights the urgency of addressing these disruptions. The Caribbean region has made significant progress in reducing new HIV infections and increasing access to treatment. Still, the freeze on PEPFAR funds threatens to reverse these gains and the ongoing process of creating sustainability roadmaps to increase national funding for the HIV response.
UNAIDS continues to work with various partners to help mitigate the impact and find the best solutions and calls for the continuity of all essential HIV services in the region.
"United States support through PEPFAR has been a cornerstone of the HIV response in our region, including a key driver for strengthening the sustainability and resilience of national responses. The recent humanitarian waiver reflects the commitment of the American people to save lives and maintain momentum to end AIDS by 2030," says Luisa Cabal, UNAIDS Regional Director for Latin America and the Caribbean. "UNAIDS will continue to convene communities, civil society organizations, governments, and partners to advocate for continued support and critical HIV services supported by PEPFAR. It is also time for the governments of the region to play a leadership role in guaranteeing the right to health of their most marginalized populations."
Region/country
Related
 Comprehensive update on HIV programmes in South Africa
Comprehensive update on HIV programmes in South Africa

25 February 2025
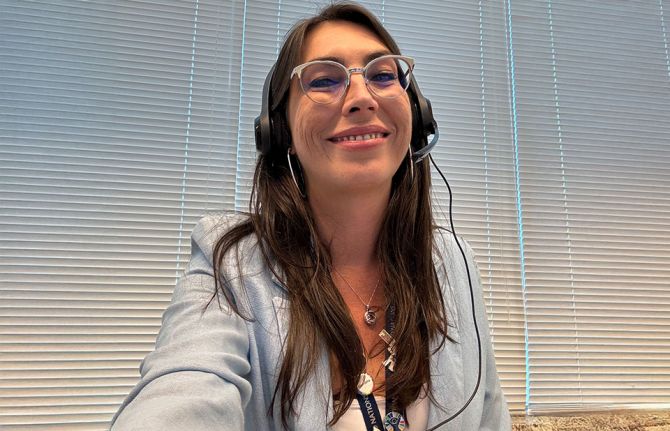




Feature Story
Upholding dignity for everyone: Ariadne Ribeiro Ferreira
21 November 2024
21 November 2024 21 November 2024Now 43 years old, Ariadne Ribeiro Ferreira, a trans woman working for UNAIDS in Brazil, advocates to leaders and speaks to media around the world. As she is an inspiration to colleagues, many are keen to learn more about Ariadne’s story.
From a young age, Ariadne sensed that she was different from those around her. “When my sister arrived, I understood, as a child, that I was like her,” Ariadne recalls.
Ariadne's situation, already challenging, became dangerous when her mother remarried. “My stepfather would beat me almost every day, berating me for my lifestyle,” she recalls.
At just 13, Ariadne was forced to flee her home. "I had no choice," she remembers. Despite these difficulties, she was fortunate to have a caring grandmother who took her in and provided support. “My grandmother was different from the rest of the family. She was like a teacher to me,” Ariadne reflects. Her grandma had a transgender friend named Zeze, an activist who also inspired her.
At the age of eighteen while living with her grandmother, Ariadne’s life took a turn when she heard on the radio that a local hospital would begin offering sex change surgeries with state support. “My grandma was overjoyed at the news and danced for me,” Ariadne recalls with a smile. Shortly after Ariadne began her transition.
However, that same year she experienced a traumatic event when she contracted HIV after being raped. Despite this devastating ordeal, she refused to give up. She began treatment and continued her life with determination and resilience.
By the age of 24, she had completed all her surgeries, and she had been legally registered a woman. Ariadne officially changed her name on all her documents.
She pursued education to open up opportunities. “I had the chance to specialize at UNIFESP, the second-best university in Brazil. Since then, I have continued my education, earning a specialization, a master’s degree, and recently a Ph.D.”
Ariadne began her healthcare career in Itanhaém, where she worked in a peer education program at a health facility and contributed to a cooperation agreement with the State Government. “I focused on HIV prevention programs, gaining visibility as one of the few transgender professionals at the time,” she explains. “This recognition opened up new opportunities for me.”
Reflecting on her proudest achievements, Ariadne highlights her work with homeless individuals in São Paulo, Brazil and her role in establishing the state’s first shelter for homeless transgender people. Following these accomplishments, she joined UNAIDS in 2019, where she continues to advocate for transgender rights and supports people living with and affected by HIV, using her voice to uplift and empower others.
Ariadne's makes use of her extensive experience to champion the rights and well-being of everyone living with HIV, including UN staff. Working with UN Plus, she is pioneering innovative strategies to uphold dignity in every workplace. Building a future free from stigma and discrimination, say Ariadne and UN Plus, is how to enable everyone to perform at their best, and to thrive.
Region/country
Related




Press Release
Experts back G20 action to tackle pandemics by addressing the inequalities which drive them and by boosting production of medicines in every region of the world
29 October 2024 29 October 2024RIO DE JANEIRO, BRAZIL, 29 October 2024—Today, at a special event organized for the G20 Joint Finance and Health Ministerial, the Brazilian government and experts from the Global Council on Inequality, AIDS and Pandemics backed calls for efforts to break the “inequality-pandemic cycle” that is fueling continued disease emergencies. Two crucial measures could enable the world to tackle current and future pandemics.
They urged leaders to recognise, for the first time in G20 history, inequality as a driver of pandemics, requiring both measurement and decisive action. They also championed boosting the development, production and supply of life-saving health products in every region of the world.
Evidence gathered by the Global Council on Inequality clearly demonstrates the inequality-pandemics cycle. Inequalities within countries and between them deepen the disruption and loss of life in current and recent pandemics, from AIDS to COVID, mpox and Ebola. Failure to address these inequalities is leaving communities across the world vulnerable and exposed to future outbreaks. This presents an important opportunity for the G20, which sets the agenda for international financing, to focus attention and action on the social determinants of pandemics.
The dependence of countries across the Global South on medicine production in the Global North has also been shown to undermine pandemic responses. They are consistently last in line to receive life-saving vaccines and medicines, despite bearing much of the world’s disease burden.
Nísia Trindade, Brazil’s Minister of Health, who is also a member of the Global Council on Inequality, AIDS and Pandemics, declared: “By building production capacity in every region, we can learn from past mistakes by ensuring that medicines for neglected and socially determined diseases are made around the world and that capacity is available to respond swiftly to future outbreaks.”
Joseph E. Stiglitz, Nobel Prize Winning Economist, Co-Chair of the Global Council on Inequality, AIDS and Pandemics, explained: “Reforms in both the developed and developing countries and in international agreements and institutions, and investments which help broaden the production of medical products and reduce prices are vital to address market failures and accelerate access to medicines for the people in greatest need.”
Sir Michael Marmot, Professor of Epidemiology and Director of the Institute of Health Equity at University College London, Co-Chair of the Global Council on Inequality, AIDS and Pandemics noted: “The evidence is clear: social determinants increase the intensity of pandemics. The greater the inequality in society, the worse is the pandemic. But we also know we can intervene against these with education, social protection measures, and making societies more fair. Re-investing in the public good and upholding of human rights will make societies less vulnerable to pandemics.”
H.E. Monica Geingos, former First Lady of Namibia and Co-Chair of the Global Council on Inequality, AIDS and Pandemics set out: “To effectively end the AIDS pandemic and prepare for future health crises, we must confront the complex web of inequalities that exacerbate these challenges. Inequality encompasses more than just income disparities; it includes social, political, and health inequities that intersect in significant ways. The geopolitical landscape further complicates these dynamics, as nations characterized by pronounced inequality are disproportionately impacted by the responses to pandemics. This systemic inequality is often reinforced by international frameworks that perpetuate and deepen existing disparities, underscoring the urgent need for comprehensive and equitable approaches to health and governance.”
The two initiatives—addressing inequality as a pandemic driver and the move to boost regional health product production— offer a unique opportunity for G20 leaders to take transformative action towards greater health equity and global health security, speakers agreed.
Winnie Byanyima, UNAIDS Executive Director and Convenor of the Inequality Council, remarked: "President Lula has put equality at the heart of Brazil’s G20 agenda. He is right. Inequalities need to be addressed urgently, and the production of medicines and vaccines expanded across the world, or the next pandemic will hit us even harder. G20 leaders here in Rio have the opportunity to transform the way the world responds to outbreaks and pandemics by tackling the inequalities which drive them. We are counting on G20 leaders to seize this moment to save lives and protect the health of everyone.”
Joe Phaahla, Deputy Minister of Health, South Africa, confirmed: “As we assume the G20 presidency in 2025, South Africa will continue to champion the agenda of universal health coverage through equity, solidarity and innovation.”
Tributes were paid to the Ministry of Health in Brazil for its leadership in advancing these critical issues at the G20, including proposing a new Global Coalition for Regional Production, Innovation and Equitable Access and including social determinants of pandemics in the work of the G20 Joint Health and Finance Ministers task force.
Notes for editors
Brazil proposes the establishment a Global Coalition for Regional Production, Innovation and Equitable Access Alliance for Regional Production and Innovation. It is bringing together a network of key actors, including countries, academia, private sector, and international organizations, for research and development and production of vaccines, medicines, diagnostics, and strategic supplies to combat diseases with strong social determinants and that mainly affect vulnerable populations. For more information on the G20 Health Working Group, see the G20 website: https://www.g20.org/en/tracks/sherpa-track/health
About the Global Council on Inequality, AIDS and Pandemics
The Council was established by UNAIDS in 2023 and is comprised of experts from academia, government, civil society and international development actors committed to implementing evidence-based solutions to address inequalities fuelling AIDS and other pandemics. It is chaired by Nobel Laureate Professor Joseph Stiglitz, Former First Lady of Namibia Monica Geingos, and Professor Sir Michael Marmot who chaired the Commission on Social Determinants of Health. Learn more at inequalitycouncil.org.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
Ben PhillipsUNAIDS Communications Director
phillipsb@unaids.org
UNAIDS Brazil Advocacy and Communication Officer
Thainá Kedzierski
KedzierskiTH@unaids.org
Watch
Region/country




Feature Story
Peru approves groundbreaking law to extend health coverage for migrants with HIV and TB
21 October 2024
21 October 2024 21 October 2024In a milestone decision, the Peruvian Congress has passed legislation that extends temporary health insurance coverage to migrants diagnosed with HIV and tuberculosis (TB). This law allows non-resident foreigners to access healthcare services through the public health insurance system (known by the Spanish acronym SIS) while they complete their immigration processes.
This law, which incorporates proposals from Law Bills 5253, 5554, and 7260, represents a significant step in reducing barriers for migrant populations, ensuring timely medical attention without the need for official residency documentation. Now, migrants affected by HIV or TB can receive vital healthcare services, including medical consultations and diagnostic exams, regardless of their immigration status.
The legislative breakthrough follows over two years of advocacy led by the Grupo Impulsor, a coalition that includes UNAIDS, alongside partners such as USAID’s flagship initiative Local Health System Sustainability Project (LHSS), IOM, UNHCR, the Peruvian Observatory of Migration and Health of the Peruvian University Cayetano Heredia (OPEMS-UPCH), Colectivo GIVAR, VENEACTIVA, the Peruvian TB Social Observatory, and Partners in Health.
Likewise, providing timely treatment for migrants with HIV or TB not only improves their quality of life but also reduces the risk of transmission, making it a crucial public health measure benefiting everyone. It also saves money: early care is far more cost-effective, preventing advanced cases that strain the health system.
A cost-benefit analysis reveals that Peru could save around 5 million soles ($1.33 million USD) annually by preventing new infections and another 54 million soles ($14.58 million USD) through avoiding productivity losses linked to AIDS and TB-related deaths.
Migrants living with HIV in Peru remain among the most discriminated groups in the country, with 70.7% reporting stigma, according to the Ministry of Justice and Human Rights. They also face heightened vulnerability due to xenophobia, violence, and exploitation—nearly half of them have experienced physical violence or sexual exploitation. Accessing healthcare is a major challenge, with only 2% of migrants with HIV covered by public health insurance, leaving the rest to pay out-of-pocket costs that many cannot afford.
“By extending health insurance to migrants, Peru is not only addressing these barriers but also aligning with global commitments, like the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), aimed at eradicating epidemics such as AIDS and TB by 2030”, says Luisa Cabal, UNAIDS Regional Director for Latin America and the Caribbean. “This legislative victory not only marks a turning point in health policy but also sets a precedent for future reforms, ensuring a more inclusive and equitable healthcare system for all.”
Protecting everyone’s rights protects public health.
Region/country
Related
Documents
Latin America — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
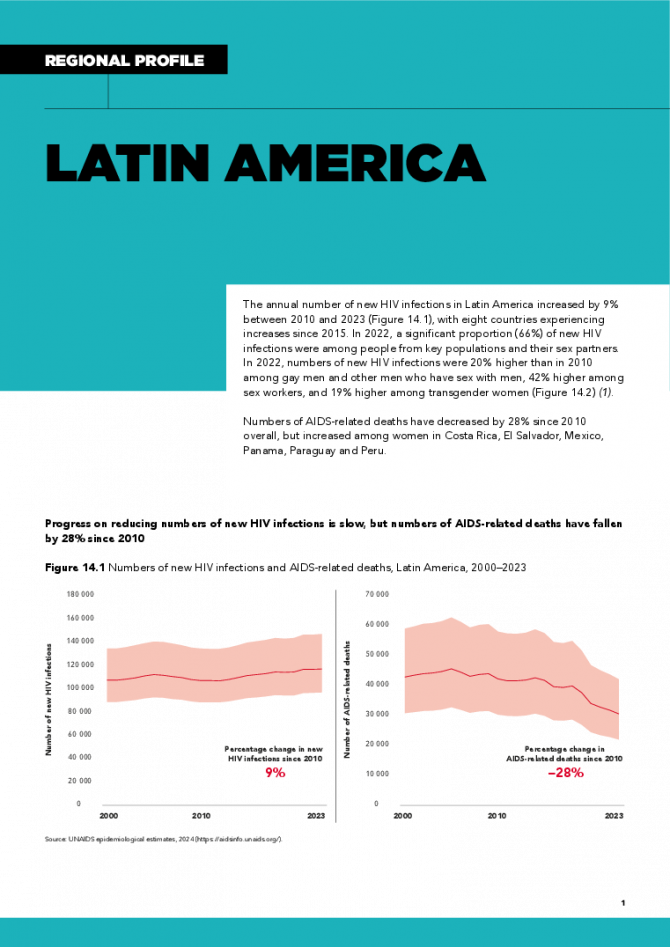
The annual number of new HIV infections in Latin America increased by 9% between 2010 and 2023, with eight countries experiencing increases since 2015. In 2022, a significant proportion (66%) of new HIV infections were among people from key populations and their sex partners. In 2022, numbers of new HIV infections were 20% higher than in 2010 among gay men and other men who have sex with men, 42% higher among sex workers, and 19% higher among transgender women. Numbers of AIDS-related deaths have decreased by 28% since 2010 overall, but increased among women in Costa Rica, El Salvador, Mexico, Panama, Paraguay and Peru. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 The critical impact of the PEPFAR funding freeze for HIV across Latin America and the Caribbean
The critical impact of the PEPFAR funding freeze for HIV across Latin America and the Caribbean
19 February 2025


Press Release
UNAIDS commends Mexico's ban on conversion therapy
12 June 2024 12 June 2024UNAIDS has applauded the decision by Mexico to ban the practice of so-called "conversion therapy".
"The stigma and discrimination that so-called ‘conversion therapy’ perpetuates have damaged public health. Mexico's move to end this harmful practice will help secure public health. All countries should follow Mexico’s example," said Luisa Cabal, UNAIDS Regional Director for Latin America and the Caribbean.
Health and human rights experts have condemned so-called “conversion therapy” for causing severe psychological distress. In 2012, the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) noted that such therapies had no medical justification and represented a severe threat to health and human rights. In 2015, the joint statement by UN agencies condemned “abuse in medical settings, including unethical and harmful so-called ‘therapies’ to change sexual orientation.” In 2016, the World Psychiatric Association found that "there is no sound scientific evidence that innate sexual orientation can be changed." In 2020, the Independent Forensic Expert Group (IFEG) declared that offering such therapy is a form of deception, false advertising, and fraud. In 2020, the report on conversion therapy by the UN Independent Expert on sexual orientation and gender identity called for "a global ban on practices of 'conversion therapy'”. So-called “conversion therapy” is false and harmful, and needs to be ended everywhere.
UNAIDS experience has shown that stigma and shame drive people away from essential health services and support systems, including from HIV prevention, testing, treatment, and care. Protecting the human rights of every person, UNAIDS research shows, is essential for protecting public health, because it enables inclusive and equitable access to health services without discrimination.
"The evidence is clear,” said Ms Cabal. “Stigmatizing practices harm public health. Ensuring inclusion, acceptance and respect for the human rights of everyone is vital to protect everyone’s health. Stigma kills, and solidarity saves lives.”
Region/country
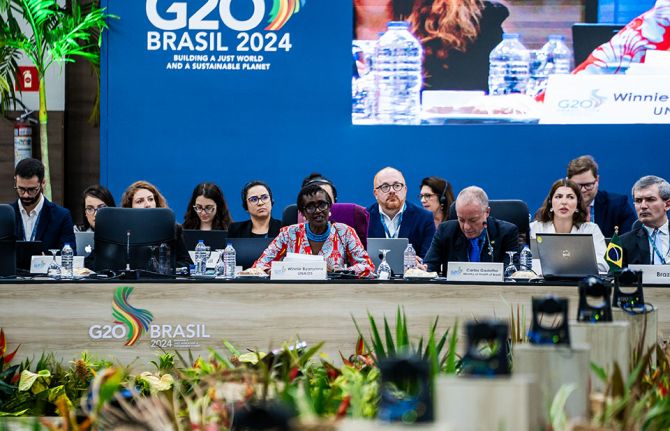
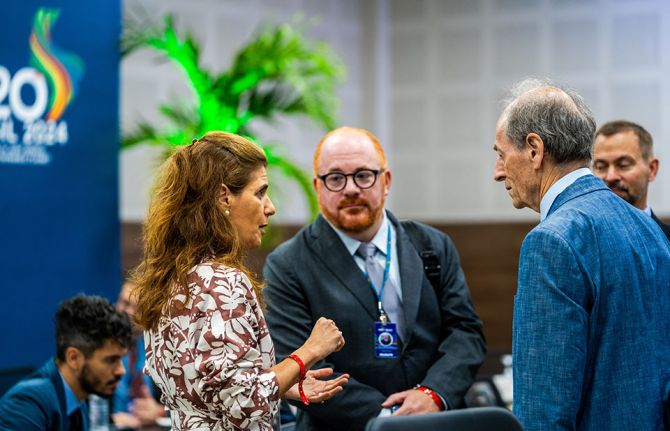





Press Release
UNAIDS Executive Director and Inequality Council urge G20 to back bold network on medicine production and address the social determinants of pandemics
06 June 2024 06 June 2024SALVADOR, BRAZIL, 6 June 2024—At the G20 preparatory meeting in Brazil, Executive Director of UNAIDS and Under-Secretary-General of the United Nations, Winnie Byanyima, today urged governments to support a new G20 Alliance, proposed by the Brazilian government, to enable life-saving medicines to be produced in every part of the world. Co-Chair of the Global Council on Inequality, AIDS, and Pandemics Sir Michael Marmot also called on G20 delegates to address the social determinants of pandemics, such as education and human rights, as a concrete part of the G20’s pandemic preparedness efforts.
The medicines initiative aims to create a global alliance of local and regional manufacturers of drugs, vaccines and other health technologies and unite a diversified network of local and regional producers to ensure an adequate supply of medicines and technologies for everyone, everywhere.
Ms Byanyima called on the G20 to ensure that the alliance takes a bold approach that strengthens efforts to fight dengue and other neglected diseases, improves global defences against future pandemics, and accelerates access to the latest technologies against HIV.
“Focusing together on neglected diseases and the major killers of vulnerable people is not only strategic, it can deliver during future pandemics,” said Ms Byanyima. “We can be thankful that, for all its devastation, COVID-19 responded to a vaccine, unlike HIV. There is no reason to believe the next pandemic will be like COVID-19. We need to build capacity for vaccines and treatment.”
The responses to many diseases that impact vulnerable populations – from Ebola to Mpox to HIV – would benefit greatly from this initiative, Ms Byanyima told governments today.
“The alliance can supercharge the HIV response. It can supercharge the production pipeline for innovations,” said Ms Byanyima. “An alliance could also build capacity where it is not. The majority of people living with HIV, who get up every day and take that pill, live in Africa. But few of those drugs are actually made in African countries.”
“Brazil’s leadership and experience in this area has inspired this global effort. And we need the support of the whole G20 to make it a success.”
The agenda of the G20 meeting on health is helping to push global health policy towards tackling the systemic inequalities that drive ill-health. UNAIDS is coordinating a Global Council on Inequality, AIDS and Pandemics that is gathering evidence on how inequalities deepen and prolong pandemics, including HIV and COVID-19. That evidence is being shared with policymakers at the G20 and other international forums.
On Monday, world-renowned expert Sir Michael Marmot gave a keynote address the G20 meeting on the potential of focusing concretely on the social determinants to strengthen pandemic preparedness, predict the severity of future pandemics, and improve the efficacy of responses.
“Improving health leads to a better economy. And the way to improve health is not just to invest in healthcare, but in the social determinants of health,” Professor Marmot said. “For example, in Botswana, there is clear evidence that the longer young people remain in education, the lower the rates of HIV.”
Addressing social determinants, building manufacturing capacity, and enabling people everywhere to access the whole range of HIV prevention and treatment options, including the latest long-acting technologies, is vital for ensuring the end of AIDS as a public health threat. The G20 initiatives would play a key role in achieving that objective in a sustainable way, while also contributing to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals and supporting efforts to quickly respond to the next pandemic.
Notes for editors
Brazil's main proposal for the G20 Health Working Group is to establish the creation of an Alliance for Regional Production and Innovation. This initiative aims to establish a network that brings together key actors, including countries, academia, private sector, and international organizations, for research and development and production of vaccines, medicines, diagnostics, and strategic supplies to combat diseases with strong social determinants and that mainly affect vulnerable populations, such as dengue, malaria, tuberculosis, Chagas disease, and leprosy. For more information on the G20 Health Working Group, see the G20 website: https://www.g20.org/en/tracks/sherpa-track/health
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Learn more
Op-ed by Winnie Byanyima
Region/country
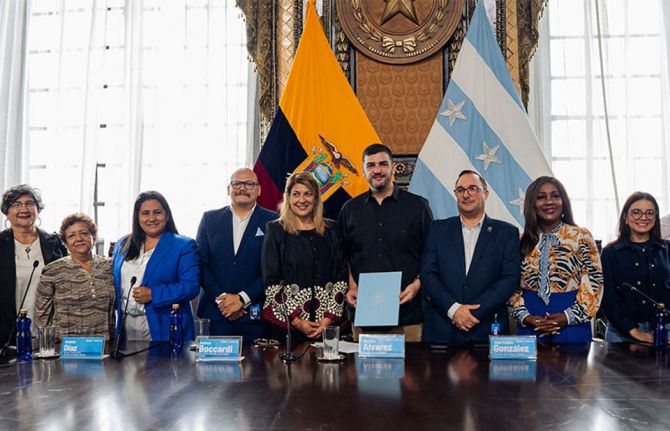


Feature Story
Guayaquil joins the worldwide group of cities committed to ending the HIV epidemic
15 March 2024
15 March 2024 15 March 2024Mayor Aquiles Alvarez Henriques of Guayaquil, Ecuador's largest city and the nation's main port, signed the Paris and Sevilla Declarations on February 28, placing the city among the almost 500 municipalities around the world that are committed to fast-tracking action at local level to improve the quality of life of people living with and affected by HIV. Through this commitment, the city pledges to contribute to the country's goal of ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030.
Guayaquil is the capital of the province of Guayas, Ecuador's most populated province and the most affected by HIV, with over a third of all new HIV infection notifications in the country, according to the Ministry of Public Health of Ecuador. It has a concentrated epidemic among key populations, with an HIV prevalence of 7.3% among gay men and other men who have sex with men (MSM), for example.
"A significant number of cases reported with HIV in 2023 live in Guayaquil", said Andrés Díaz, Technical Director of the city's Infectious Disease Prevention Unit of the Health and Hygiene Directorate. "We know that the best way to improve HIV prevention is through education and sensitization of citizens so that they can get tested."
Guayaquil has made significant efforts to intensify HIV screening and has increased the detection of HIV-positive cases by 1.6%. Diagnosed people are immediately linked to the public health system to start first-line antiretroviral treatment, which is universally available to nationals and migrants in Ecuador.
Nonetheless, the Health Department of the Guayaquil Municipality has developed a plan with key actions to be implemented as a result of the city’s commitment to the Fast-Track initiative. Some of the most strategic priorities incorporate the scale up of HIV services, including HIV prevention, early diagnosis, and timely treatment of HIV and other sexually transmitted infections; the sensitization of civil servants on issues of stigma, discrimination, and gender-based violence linked to HIV; and facilitate the engagement of communities, specially from key and vulnerable population, in the definition and implementation of HIV programmes at community level.
Representatives of community and civil society organizations such as Corporación Kimirina, the Ecuadorian Coalition of People Living with HIV, and the Silueta X LGBT+ Trans Association attended the event. These organizations play a crucial role in the city's efforts to respond to HIV. "Citizen involvement under the local authority's leadership, with emphasis on the most vulnerable and at-risk community groups, is vital to achieving the goal of ending AIDS by 2030,” emphasized the delegates of Corporacion Kimirina Maria Elena Acosta and Lily Marquez. Similarly, Joan Morales from the Ecuadorian Coalition of People Living with HIV stressed that "By signing the Paris and Sevilla Declarations, Guayaquil joins many other cities that have committed to provide accelerated and sustained health services that allow us to eradicate not only AIDS but also TB, Malaria, and other tropical diseases, with actions that contribute to reducing discrimination towards people living with HIV and other affected communities."
Created in 2014, the Paris Declaration on Fast-Track Cities Ending the HIV Epidemic is a political declaration with commitments and targets that include ending urban AIDS and tuberculosis (TB) epidemics, as well as eliminating viral hepatitis (HBV and HCV). It also articulates a mandate to place people at the center of the response. To define and facilitate that mandate, the Sevilla Declaration on the Centrality of Communities in Urban HIV Responses was created in 2022, outlining the 10 commitments that cities and municipalities are asked to make to increase the engagement of and promote leadership by affected communities in attaining the Fast-Track Cities initiative's goals, objectives, and targets.
"We congratulate the Mayor's Office of Guayaquil for its commitment to contribute to Ecuador’s efforts to reach the 2025 Global AIDS Strategy targets, reducing the number of new HIV infections and AIDS-related deaths and eliminating stigma and discrimination in all its forms,” said Andrea Boccardi Vidarte, Director of the UNAIDS Office for the Andean Countries. "This commitment is also a recognition of the leadership of communities most affected by HIV and their support to the city's goals."
Our work
Region/country
Related


Feature Story
Seeking justice for HIV-related discrimination in the workplace in Guatemala
18 December 2023
18 December 2023 18 December 2023In the heart of the bustling Guatemala City, Juan used to face the daily grind of life with an unwavering spirit. He had been diagnosed with HIV several years ago and had learned to manage his health effectively. As a dedicated employee at a marketing firm, he poured creativity into every project he touched.
Life seemed to be on an upswing for him until an unexpected turn of events unfolded at the workplace. A colleague stumbled upon Juan's medical records and, in a breach of privacy, discovered his HIV status. Soon, whispers spread through the office, and Juan began to feel the cold stares and hushed conversations whenever he walked by. Ultimately, he was dismissed from his company for "restructuring reasons."
As the discrimination became more blatant, Juan decided it was time to take action. He sought advice from Líderes Profesionales, a network of lawyers specializing in discrimination cases for people living with HIV. With UNAIDS's support, this network is committed to fighting for justice and equality for marginalized communities.
Upon hearing Juan's story, the lawyers at Líderes Profesionales were appalled by the flagrant violation of privacy and the subsequent discrimination. They quickly assembled a legal team dedicated to ensuring justice for Juan. The lawyers explained the legal protections in place for individuals with HIV, emphasizing that workplace discrimination based on health status is a clear violation of the law.
Together with Juan, the legal team initiated a lawsuit against the firm. They filed a complaint citing violations of privacy, discrimination, and failure to provide a safe and inclusive work environment and asked for payment of benefits and compensation for unjustified dismissal.
Líderes Profesionales worked tirelessly to expose Juan's unjust treatment, seeking justice for him and advocating for broader change in workplace policies. They organized workshops to sensitize companies, urging them to implement comprehensive diversity and inclusion training and policy.
As of December 2023, the case is still ongoing. The legal team's goal is to seek compensation for Juan and foster an environment where such discrimination would not be tolerated in the future.
"Juan's experience and five other discrimination-related workplace cases this year inspire us to continue our advocacy work," says Julio Rodríguez, Director of Líderes Profesionales. "We redouble our efforts to support individuals facing discrimination, using each case as an opportunity to raise awareness and push for systemic change."
In Guatemala, 31,000 people are estimated to be living with HIV. HIV-related stigma and discrimination are still pervasive. According to the latest National Stigma Index (2017), 14% of people living with HIV reported losing their job or source of income due to their positive status for HIV, and 13% of people living with HIV reported being denied employment or opportunity to work because of HIV.
"Having access to legal support really represented a turning point for Juan. Empowered by it, he is a more vocal advocate for HIV awareness and anti-discrimination efforts," says Marie Engel, UNAIDS Country Director for Guatemala, Honduras and Nicaragua. "Through his journey, Juan contributes to a more just and inclusive society for all."