Transgender and HIV risk
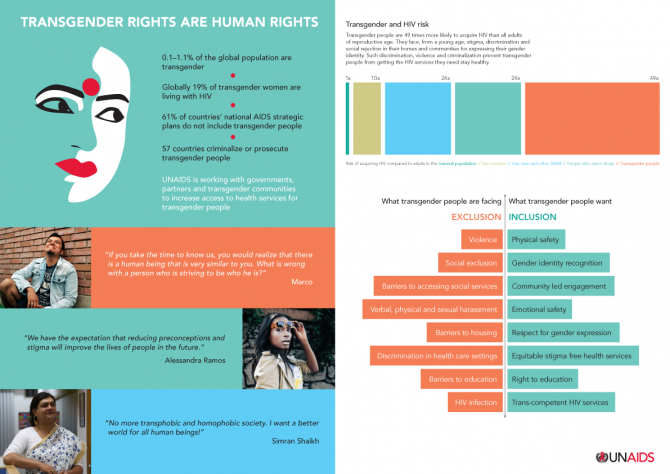
UNAIDS is working with governments, partners and transgender communities to increase access to health services for transgender people
Young people




03 May 2017
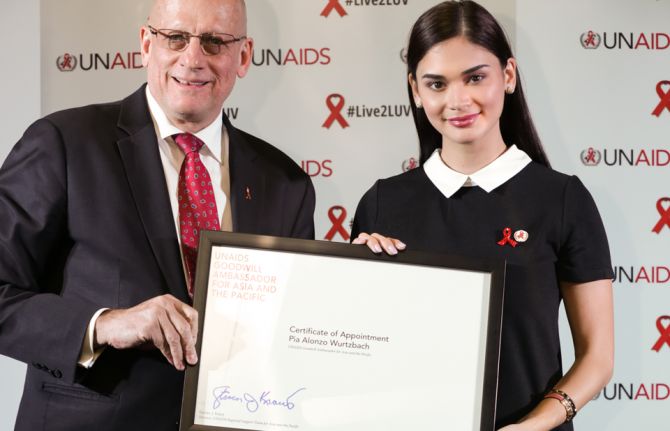
03 May 2017 03 May 2017UNAIDS has appointed Pia Wurtzbach, Miss Universe 2015, as a Goodwill Ambassador for Asia and the Pacific. The announcement was made at a special event with students at Ateneo de Manila University in Quezon City, Philippines.
“I am very happy to be a UNAIDS Goodwill Ambassador for Asia and the Pacific,” said Ms Wurtzbach. “I’m overwhelmed. It’s been a dream of mine to work with the United Nations. I will do my best. I will use my voice for this cause.”
In her new role, Ms Wurtzbach will raise HIV awareness among young people and promote zero discrimination towards people living with HIV and key populations, including men who have sex with men and transgender people.
“Many young people still do not have the skills and knowledge to protect themselves from HIV,” said Steve Kraus, Director of the UNAIDS Regional Support Team for Asia and the Pacific. “With her huge popularity among young fans and immense following on social media, Ms Wurtzbach will amplify our efforts and help end the AIDS epidemic in the region.”
Ms Wurtzbach has been actively involved in humanitarian affairs, speaking out against cyberbullying and supporting people living with HIV, as well as the lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex (LGBTI) community. During her reign as Miss Universe, she had an HIV test in front of cameras to encourage people to know their HIV status, and attended the United Nations General Assembly High-Level Meeting on Ending AIDS in New York, United States of America.
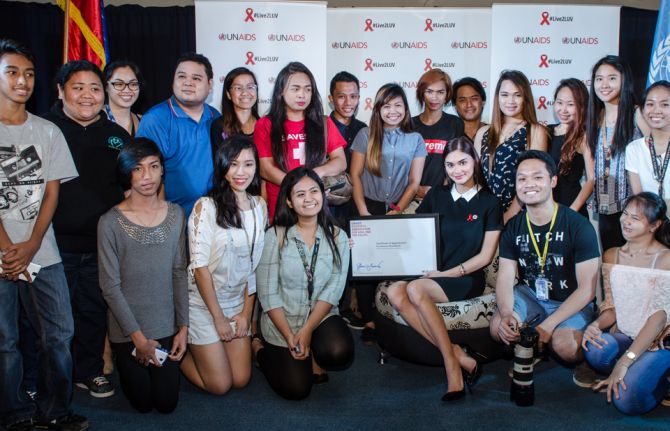
The appointment event was attended by young people from different universities in the Metro Manila area, as well as representatives of the United Nations, government officials, the media and the Act!2030 Philippines network and other community groups representing young people and key populations.
The Asia and Pacific region has made progress in its HIV response, with new infections dropping by 5% among people of all ages between 2010 and 2015. However, in 2015, young people accounted for 37% of new HIV infections and data analysis indicates that there is a significant epidemic of HIV among an increasingly younger group of gay men and other men who have sex with men in urban areas of South-East Asia and China.
Surveys conducted in eight countries in Asia found that comprehensive knowledge of HIV among young people is low, increasing their vulnerability to HIV. UNAIDS and its partners are conducting an HIV awareness campaign for youth on social media with the hashtag #Live2LUV and Ms Wurtzbach will be helping to promote this campaign as part of her new advocacy role.



11 April 2017
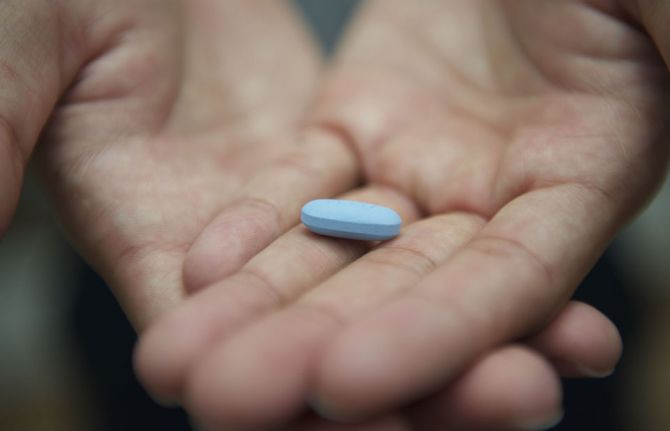
11 April 2017 11 April 2017The National Health Service (NHS) in Scotland, United Kingdom, announced on 10 April that pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) would become available in Scotland.
PrEP is taken as a daily pill to significantly reduce the chances of contracting HIV. UNAIDS recommends PrEP use by people who are HIV-negative but at higher risk of becoming infected. The people who can benefit most from PrEP include gay men and other men who have sex with men, transgender people, sex workers and serodiscordant couples before the partner living with HIV becomes virally suppressed.
Since government estimates show that a large proportion of new HIV infections in Scotland are among gay men and other men who have sex with men, the introduction of PrEP could make a significant impact on the number new HIV infections in Scotland.
PrEP has been made available in a number of countries around the world as choice for HIV prevention. It cannot currently be obtained from the NHS in the rest of the United Kingdom, but can be accessed from some private clinics.
Countries agreed in the 2016 United Nations Political Declaration on Ending AIDS to reach 3 million people with PrEP by 2020.

27 February 2025

UNAIDS is working with governments, partners and transgender communities to increase access to health services for transgender people
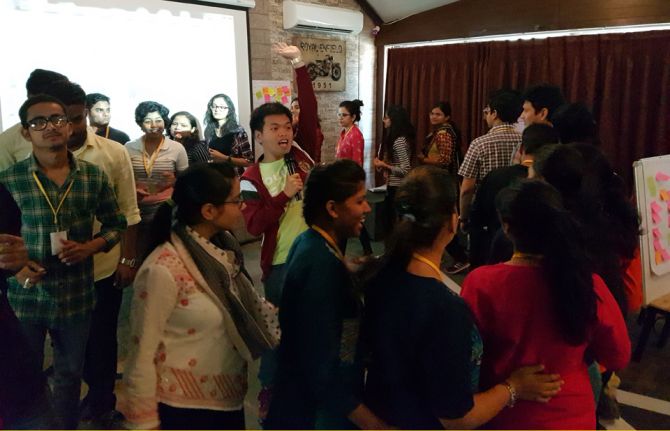






24 March 2017
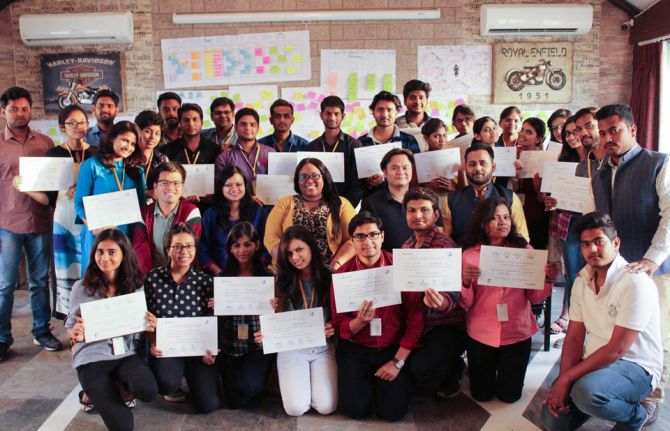
24 March 2017 24 March 2017Ayushi Tripathi is a student at Banaras Hindu University in Varanasi, a city in India’s northern state of Uttar Pradesh.
She explains that she comes from a family where talking about sex is taboo. “We never talk about it at home. Even seeing an advertisement about condoms is uncomfortable for my parents,” she said. But nonetheless, she was intent on attending a youth health workshop.
This week, she joined 27 other students for a three-day workshop to raise young people’s awareness of their sexual and reproductive health and rights. The training was led by the Dove Foundation, a youth-led organization based in Varanasi and supported by UNAIDS. The advocacy materials used were developed by the PACT, a global coalition of 25 youth networks working on HIV and sexual and reproductive health and rights.
“When I was younger, I didn’t have knowledge on where to get information and access to HIV services,” Ms Tripathi said. “Until I took this workshop, I had no idea that young people in India face challenges in accessing HIV testing and services.”
Monique Long from the Jamaica Youth Advocacy Network led the training, which provided youth and adolescents with the skills and information necessary to tackle the different barriers affecting their health.
“Working with this diverse group of intelligent and energetic young people reminds me of why we say youth are the future. This training also reaffirms that youth right here and right now have the capacity and the will to do amazing things to change the world,” Ms Long said.
Asia and the Pacific is the region with the largest number of young people in the world. In the region, people are starting sex at an increasingly younger age and having multiple sex partners, placing young people at higher risk of HIV.
During the training, the participants stressed how many countries are not tailoring their programmes to young people. For example, India requires people under 18 years old to have parental consent for HIV and other sexual and reproductive health services. Comprehensive sexuality education is often not taught in schools. The low levels of HIV knowledge and discrimination faced in health-care settings further exacerbate the situation.
The PACT and UNAIDS have been working with governments and other partners in advocating for the revision and reform of age of consent laws. The training provided young people with the techniques and skills needed for prioritizing advocacy issues, mapping different stakeholders, crafting key advocacy messages and lobbying.
“UNAIDS knows that the future of the HIV response lies in the hands of young people,” said Aries Valeriano, Youth Officer at the UNAIDS Regional Support Team for Asia and the Pacific. “We are working hand in hand with youth organizations and community groups to break down the barriers that young people face and that keep them from staying healthy and productive.”
After completing the workshop, Ms Tripathi said she plans to start a community of advocates at her university to push for ending the age of consent laws in India. As Ms Tripathi received her completion certificate, she beamed. “The workshop helped to open my eyes on social activism,” she said. “I am so inspired and hope to really influence policies in my university and beyond.”
UNAIDS is working to ensure that the target in the 2016 United Nations Political Declaration on Ending AIDS of ensuring that 90% of young people have the skills, knowledge and capacity to protect themselves from HIV and have access to sexual and reproductive health services by 2020, in order to reduce the number of new HIV infections among adolescent girls and young women to below 100 000 per year, is met.

24 February 2025
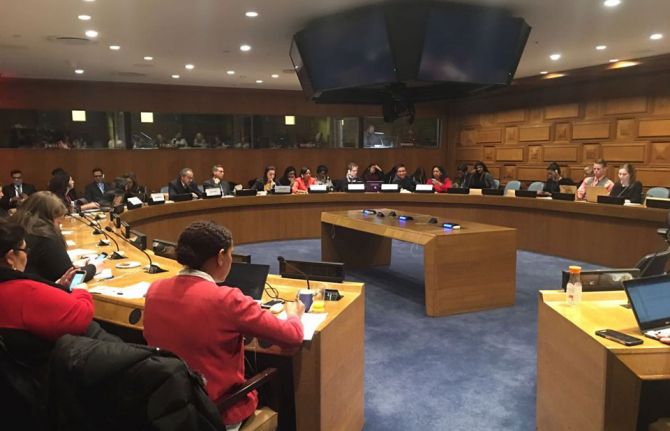


24 March 2017
24 March 2017 24 March 2017Child marriage is widespread across much of Latin America and the Caribbean, accounting for around 23% of marriages in the region, despite laws against it.
The impact of child marriage and early unions (where one of the members is aged below 18 years of age) on girls and their societies can be devastating. Evidence shows that there is a strong link between child marriage and early unions with child pregnancy, maternal and infant mortality, lower education levels for girls and lower ranking on the human development index. And child marriage and early unions make girls more vulnerable to contracting sexually transmitted infections, including HIV.
At a high-level side event co-hosted by the Permanent Missions of Panama and Guatemala to the United Nations in collaboration with UN Women, the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) and UNAIDS, lessons learned and programmatic and policy options to address child marriage in Latin America and the Caribbean were presented.
In the event, which took place on 17 March at the United Nations Headquarters in New York, United States of America, during the sixty-first session of the Commission on the Status of Women, the participants recognized that child marriage and early unions are a violation of human rights and are a grave threat to the lives, health and future development of girls.
The event focused on the importance of supporting legislative reforms to raise the legal age of marriage to 18 and promoting programmes to empower girls and young women.
The event identified successful approaches and strategies for reducing the rates of child marriage. For example, Panama—where an estimated 26% of girls are married before the age of 18 and approximately 7% before the age of 15—has reformed its national legislation on the legal age of marriage. The minimum legal age for marriage in Panama is now 18 years, as is the age of consent. Previously, with parental permission girls aged as young as 14 years and boys aged 16 years could marry. In Guatemala, thanks to advocacy actions led by UN Women, civil society and international cooperation, reforms to the civil and penal codes have been approved to increase the minimum age for marriage to 18 years.
Since 2015, UNAIDS has partnered with UN Women, UNICEF, UNFPA and PAHO/World Health Organization in a joint initiative on eliminating child marriage and early unions that supports government actions to ensure that, throughout their life cycle, the multiple needs of girls and women are recognized and guaranteed.
UNAIDS is working with countries to eliminate gender inequalities and all form of violence and discrimination against women and girls by 2020, as outlined in the 2016 United Nations Political Declaration on Ending AIDS.
“Child marriage and early unions are a violation of human rights. Full Stop.”
“Ending child marriage is a moral and legal imperative, and it requires action at many levels. Governments, civil society and other partners must work together to ensure that girls have access to education, health information and services, and empowerment.”
“I recognize efforts conducted by countries like Panama, Guatemala, Ecuador and Mexico to put an end to child marriage. This is as an example to ensure girls’ human rights.”
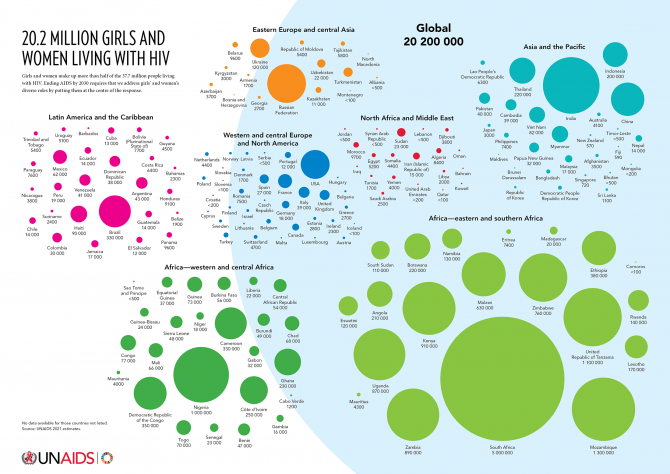
Girls and women make up more than half of the 37.7 million people living with HIV. Ending AIDS by 2030 requires that we address girls’ and women’s diverse roles by putting them at the centre of the response.
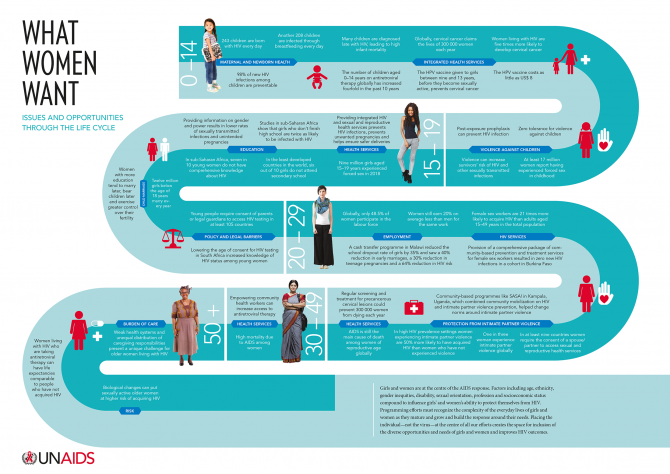
Factors including age, ethnicity, gender inequities, disability, sexual orientation, profession and socioeconomic status compound to influence girls’ and women’s ability to protect themselves from HIV.
08 March 2017
Today, we are at the cusp of eliminating new HIV infections among children—a movement led by women. More women are accessing antiretroviral therapy than men, transferring the benefits of their good health to their families and economies. When young women are empowered and have their rights fulfilled, HIV prevalence falls, there are fewer unintended pregnancies, fewer maternal deaths and fewer dropouts from school and more women join the workforce. When young women have access to education, health outcomes dramatically improve.

06 March 2025

27 February 2025
02 December 2024
26 November 2024

27 September 2024

19 September 2024